An in-situ compensation method for residual magnetic field for single-beam serf atomic magnetometers
A technology of residual magnetic field and atomic magnetic intensity, which is applied in the use of magneto-optical equipment for magnetic field measurement, magnetic field size/direction and other directions, which can solve the problems of poor anti-interference ability and low compensation accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
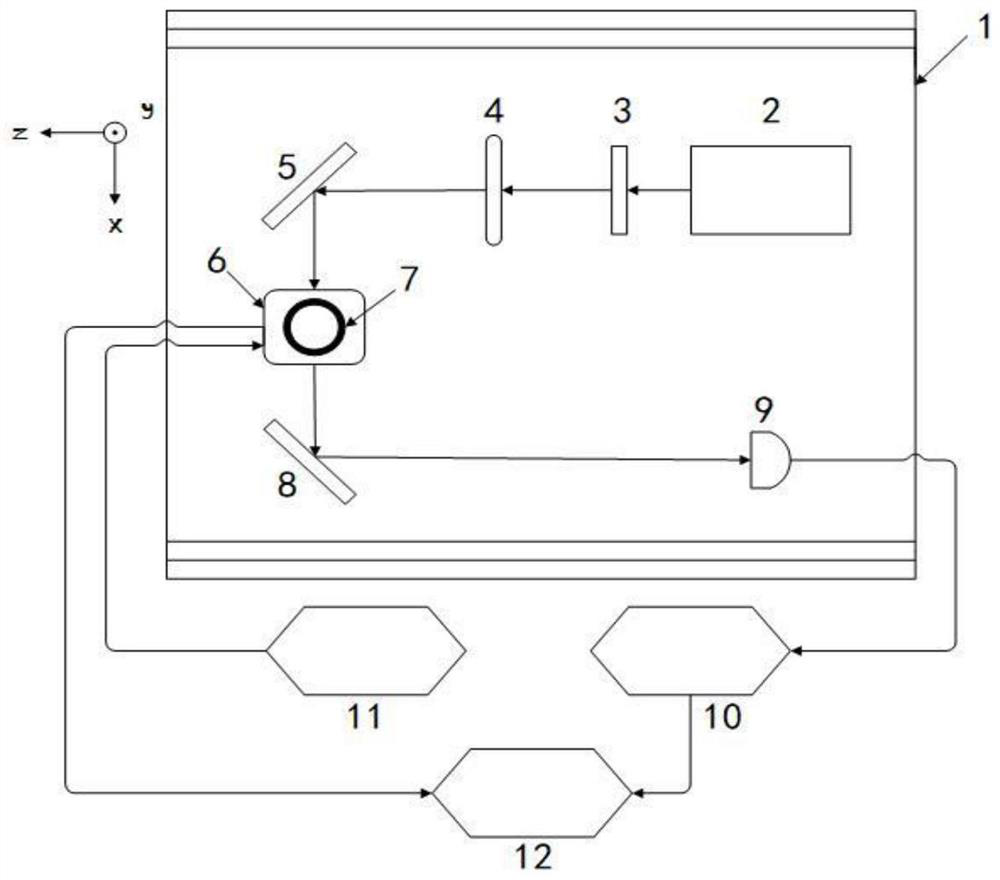
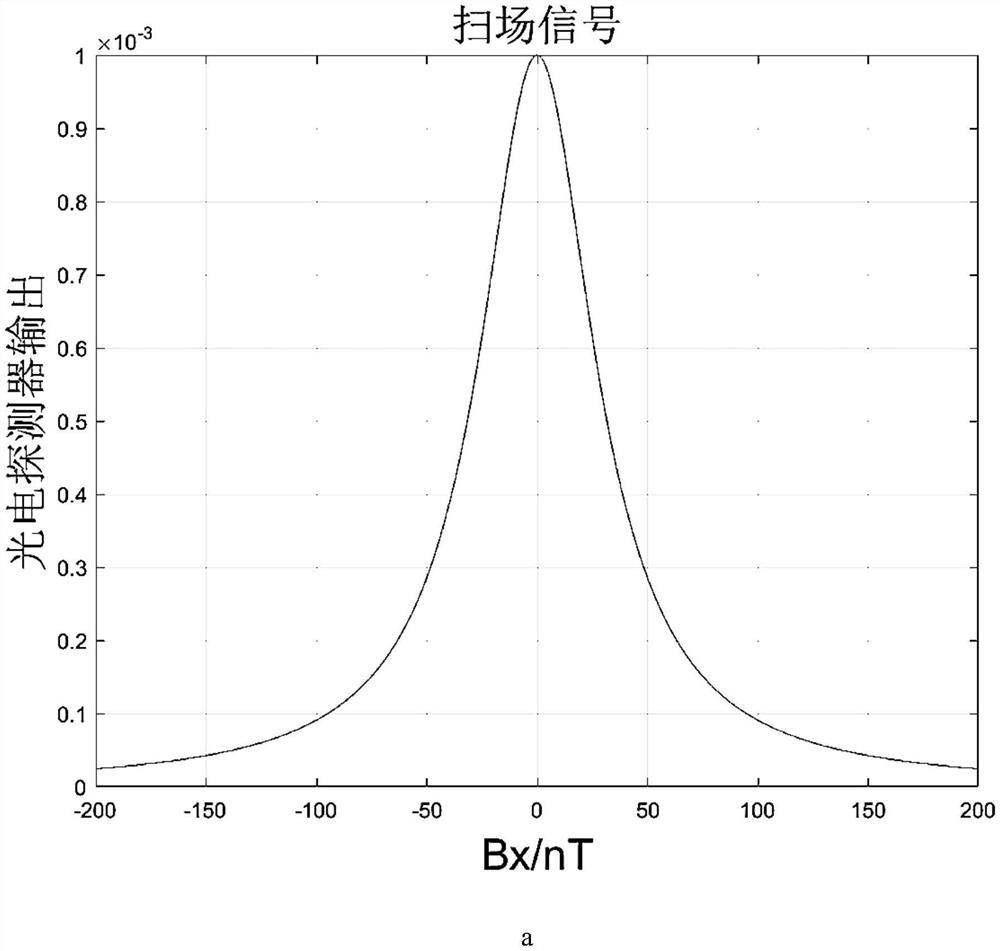
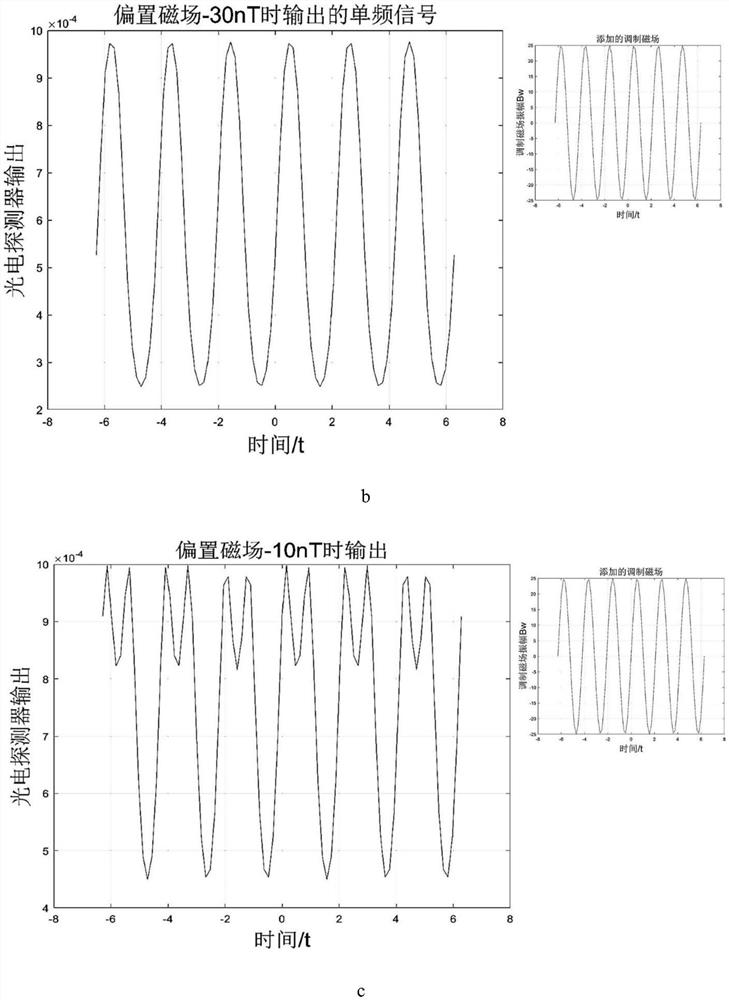
[0023] like figure 1 As shown, the device for the experimental verification of the method of the present invention includes: a magnetic shield barrel 1, a laser 2, a polarizer 3, a 1 / 4 wave plate 4, a first plane mirror 5, a three-axis magnetic compensation coil 6, and an alkali metal gas chamber 7. A second flat mirror 8 , a photodetector 9 , a preamplifier 10 , a function generator 11 , and a display interface 12 . The magnetic shielding barrel 1 is a three-layer permalloy magnetic shielding barrel. First, the laser generates a laser beam that satisfies the laser wavelength at the center of the D1 line of the alkali metal atom, and is used for pumping and detection at the same time. The polarizer generates linearly polarized light, and then the 1 / 4 wave plate converts the linearly polarized light into circularly polarized light. , and then ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com