Data processing device, data processing method, and recording medium
A data processing device and quantitative technology, which is applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, database indexing, etc., can solve problems such as uneven dispersion, excess clusters, and reduced quantization efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example >
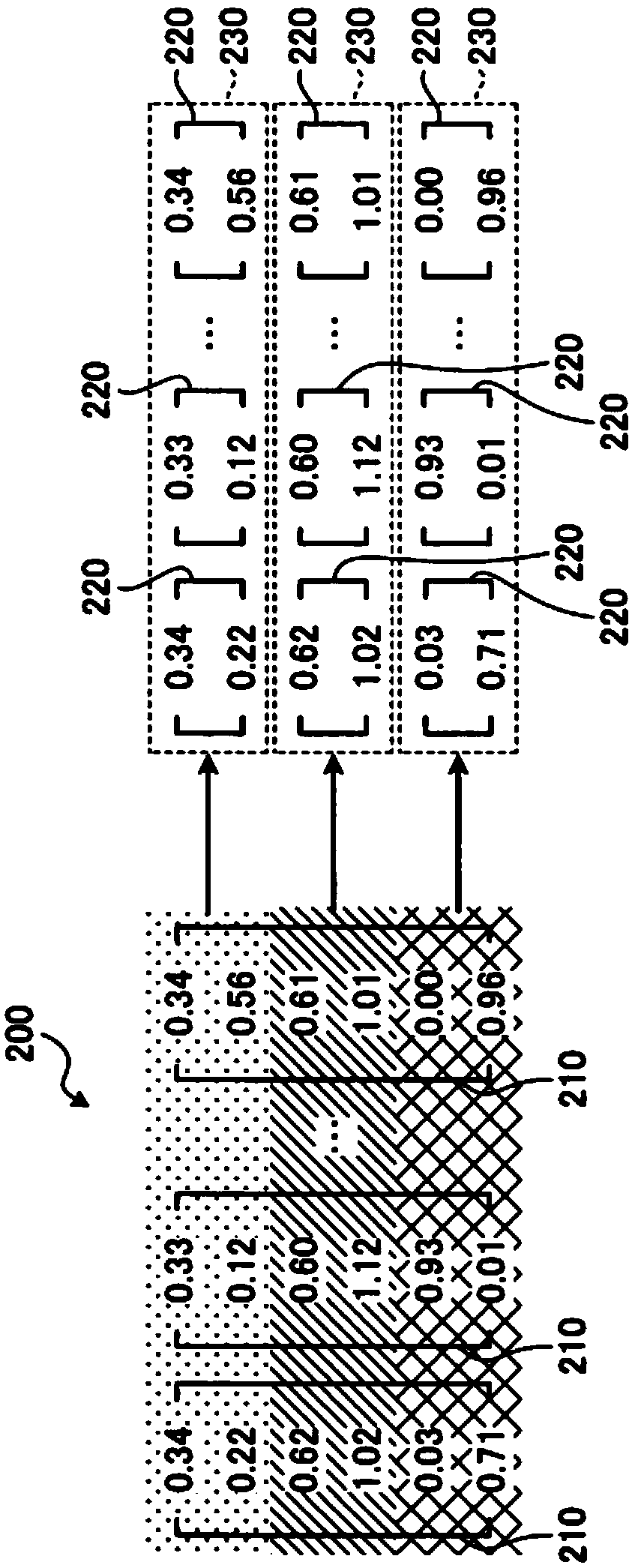
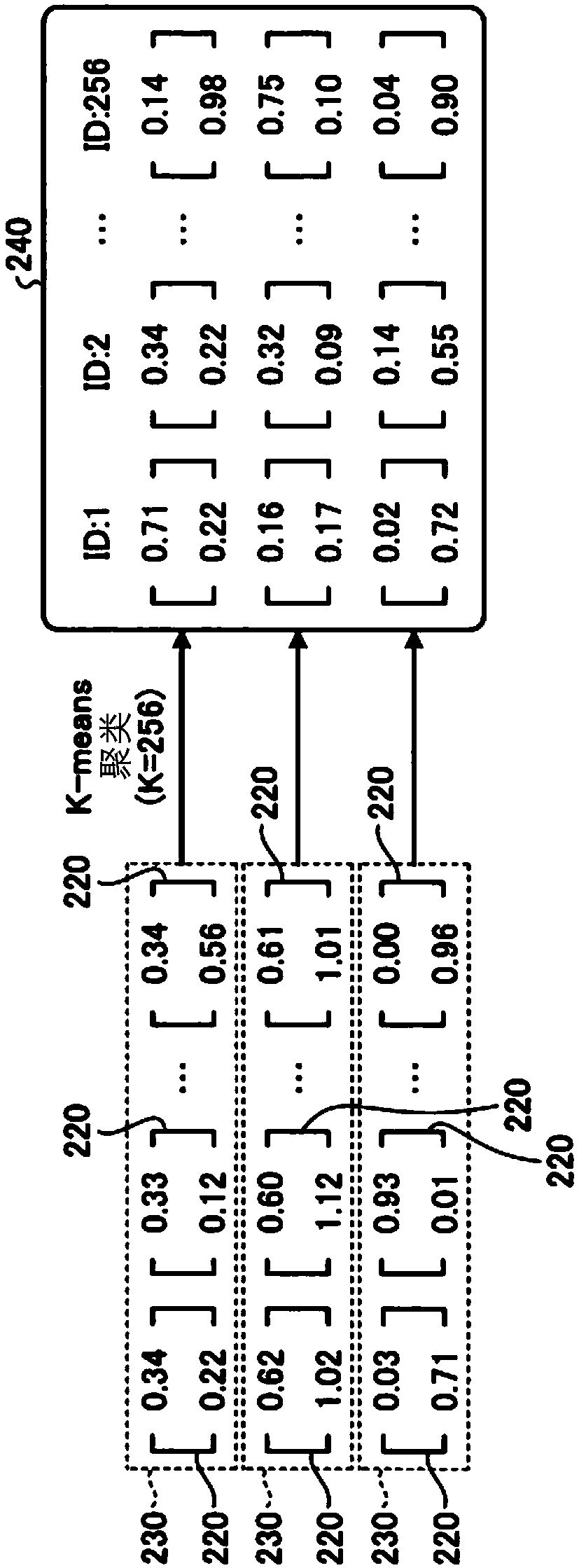
[0042] Figure 6 It is a block diagram showing a functional configuration example of the data processing device 10A of the first embodiment. Such as Figure 6 As shown, the data processing device 10A of this embodiment includes a subvector group generation unit 11 , a codebook generation unit 12 and a conversion unit 13 .
[0043] The sub-vector group generator 11 generates M sub-vector groups 230 from the feature vector set 200 composed of N feature vectors 210 . The M sub-vector groups 230 respectively include N-dimensional variable sub-vectors 220 obtained from each of the N feature vectors 210 . The N variable sub-vectors 220 each have one or more dimension values extracted from the feature vector 210 as elements. The number M of sub-vector groups 230 generated by the sub-vector group generation unit 11 is a value smaller than the dimension D of the feature vector 210, but it is not a fixed value as in the past, but a variable value determined adaptively. .
[0044]...
no. 2 example >
[0058] Next, a second embodiment will be described. Compared with the first embodiment described above, the present embodiment adds a function of adjusting the upper limit value T of the number of clusters as a parameter for determining the quantization level. Other functions are the same as those of the above-mentioned first embodiment, so only the functions specific to this embodiment will be described below.
[0059] If the actual application is considered, it is necessary to have the following goals: to what extent can the variation rate of the retrieval accuracy before and after converting the feature vector set 200 into a compressed code set 260 be allowed; or to convert the feature vector set 200 into a compressed code set 260 To what extent is the compression ratio increased. Therefore, it is required to set a target value of a rate of change or a compression rate for retrieval accuracy as a hyperparameter.
[0060]Here, where X is the number of times the feature vec...
no. 3 example >
[0072] Next, a third embodiment will be described. Compared with the above-mentioned second embodiment, this embodiment adds the following function: when a new feature vector 210 is added to the feature vector set 200, it is judged whether the codebook 240 needs to be updated, and only when it is judged that it needs to be updated The codebook 240 is updated. Other functions are the same as those of the above-mentioned first embodiment, so only the specific functions of this embodiment will be described below.
[0073] In practical applications, it is sometimes required to add new feature vectors 210 corresponding to the reserved feature vector set 200 at any time. Here, if the codebook 240 is updated every time a new feature vector 210 is added to the feature vector set 200, updating the codebook 240 will require a lot of calculation time, which is not efficient. Therefore, in this embodiment, when a new feature vector 210 is added to the feature vector set 200, it is judge...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com