Calculation method of ice lake surge height and application thereof
A calculation method and swell technology, applied in the calculation field of swell height of ice lakes, can solve problems such as defective calculation methods, inability to calculate swells, poor active disaster prevention, etc., and achieve the effect of ensuring the applicability of disaster prevention.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
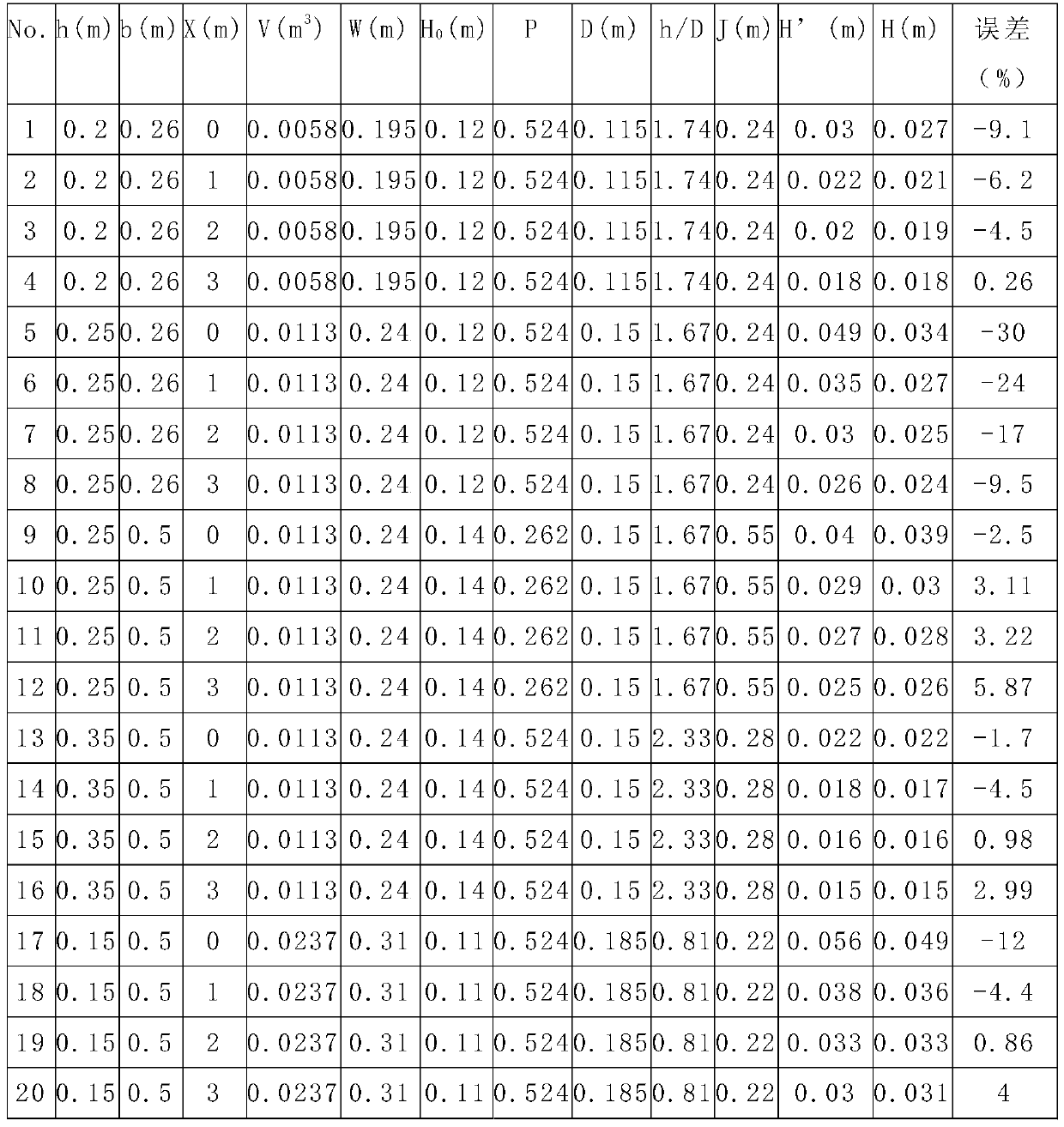
[0052] A calculation method for the swell height of a glacial lake, comprising the following steps:
[0053] a. By the location of the glacier body, the attributes of the glacier are distinguished; continental glaciers or marine glaciers have dry climate, less snowfall and low negative temperature, and high snow line, less income and less expenditure, weak activity, and short ice tongue. Glacial geomorphology is weak, which belongs to continental glaciers; on the contrary, it belongs to marine glaciers; if it hangs on the mountain slope and does not descend to the foot of the mountain, the glacier is small in scale and thin in thickness, with an area of less than 1km 2 , it is a hanging glacier; determine the basic data of the ice avalanche through surveying and mapping, including the position of the ice crack at the back end of the ice avalanche, the position of the front end of the ice avalanche, the average length L of the ice avalanche and the average width W of the ice a...
Embodiment 2
[0079] A calculation method for the swell height of a glacial lake, comprising the following steps:
[0080] a. By the location of the glacier body, the attributes of the glacier are distinguished; continental glaciers or marine glaciers have dry climate, less snowfall and low negative temperature, and high snow line, less income and less expenditure, weak activity, and short ice tongue. Glacial geomorphology is weak, which belongs to continental glaciers; on the contrary, it belongs to marine glaciers; if it hangs on the mountain slope and does not descend to the foot of the mountain, the glacier is small in scale and thin in thickness, with an area of less than 1km 2 , it is a hanging glacier; determine the basic data of the ice avalanche through surveying and mapping, including the position of the ice crack at the back end of the ice avalanche, the position of the front end of the ice avalanche, the average length L of the ice avalanche and the average width W of the ice a...
Embodiment 3
[0106] A calculation method for the swell height of a glacial lake, comprising the following steps:
[0107] a. By the location of the glacier body, the attributes of the glacier are distinguished; continental glaciers or marine glaciers have dry climate, less snowfall and low negative temperature, and high snow line, less income and less expenditure, weak activity, and short ice tongue. Glacial geomorphology is weak, which belongs to continental glaciers; on the contrary, it belongs to marine glaciers; if it hangs on the mountain slope and does not descend to the foot of the mountain, the glacier is small in scale and thin in thickness, with an area of less than 1km 2 , it is a hanging glacier; determine the basic data of the ice avalanche through surveying and mapping, including the position of the ice crack at the back end of the ice avalanche, the position of the front end of the ice avalanche, the average length L of the ice avalanche and the average width W of the ice a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com