Improved method and terminal for maximizing life cycle in wireless sensor network
A wireless sensor network and life cycle technology, applied in the field of wireless sensing, can solve the problems of long total links, inability to transmit, and reduce network life, so as to avoid power waste, avoid detour problems, and improve network life.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0084] Please refer to Figure 1 to Figure 7 , Embodiment 1 of the present invention is:
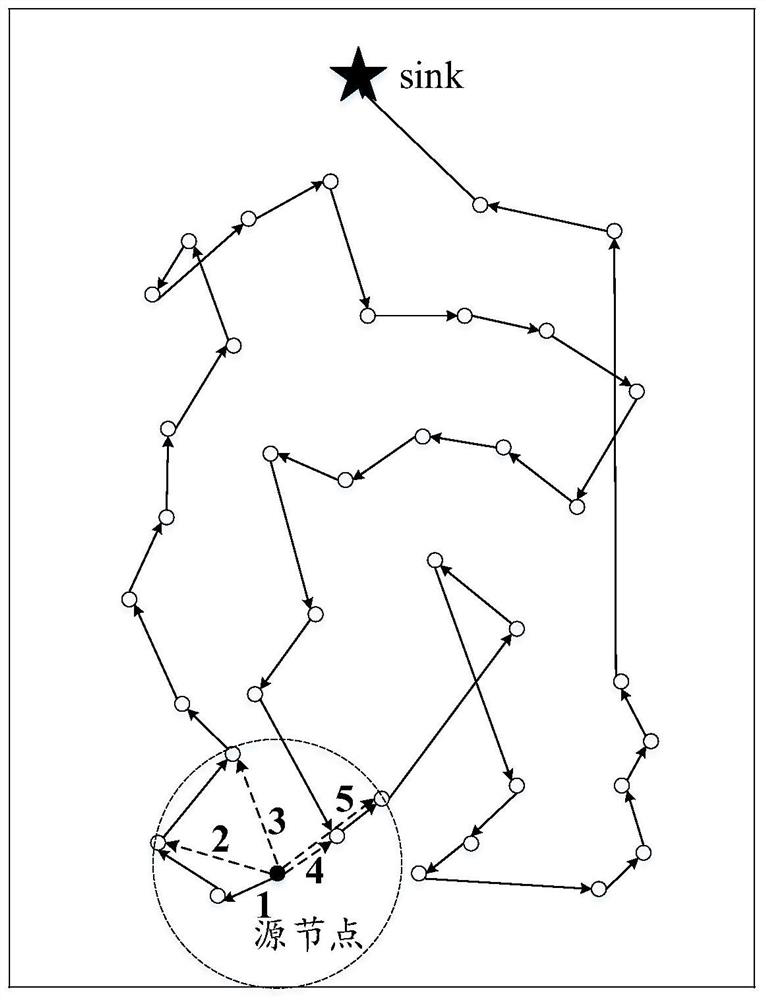
[0085] Before this example, if figure 2 As shown, the solid dot is the source node, also known as the source node. The path transmitted according to the PEGASIS protocol is shown by the solid line, and there are obviously "detours" and excessively long links. If it is transmitted according to a fixed distance, three paths 2, 3, and 5 may appear. Obviously, the path numbered 2 is the worst; if only the transmission direction is considered, there may be three paths 3, 4, and 5. Obviously, from From the perspective of maximizing energy utilization, the path numbered 3 or 5 is optimal. Therefore, only considering the transmission distance or only the transmission direction cannot effectively prolong the life of the network.
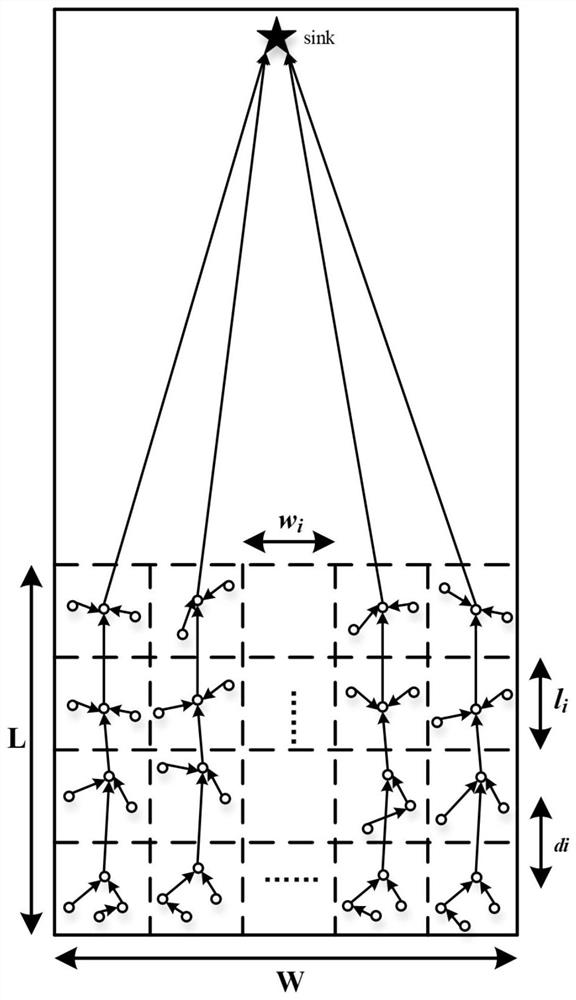
[0086] while this example image 3 The improved method for maximizing the life cycle in the shown wireless sensor network includes steps:
[0087] S1. Divide the ...
Embodiment 2
[0138] Please refer to Figure 8 , the second embodiment of the present invention is:
[0139] The improved terminal 1 that maximizes the life cycle in the wireless sensor network includes a memory 3, a processor 2, and a computer program stored on the memory 3 and operable on the processor 2, and the above-mentioned embodiments are realized when the processor 2 executes the computer program One step.
[0140] In summary, the improved method and terminal for maximizing the life cycle in wireless sensor networks provided by the present invention divide the transmission space of static sensor nodes into more than one grid space, wherein each cluster in each grid space The head node is transmitted to the cluster head node in the previous grid space close to the sink in the form of multi-hops, so that the transmission between nodes is constantly close to the sink to avoid the problem of detours; ordinary nodes in each grid space Select the cluster head node according to the PEGA...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com