Peptides for treatment and prevention of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and fibrosis
A technology of adipose tissue and peptide sequences, which is applied in the treatment of fibrosis, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, and hepatic steatosis, and can solve problems such as unsuccessful and insufficient effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
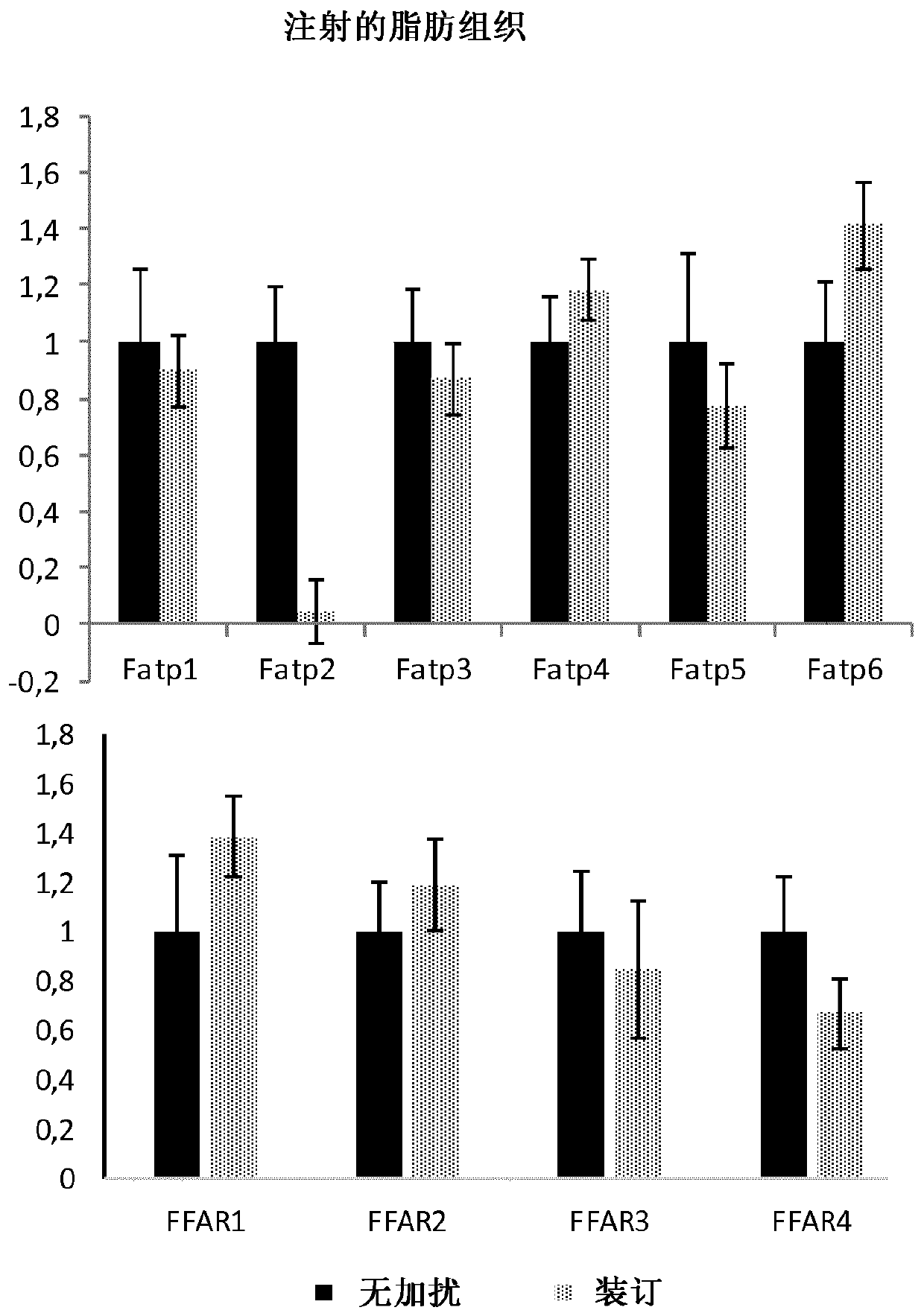
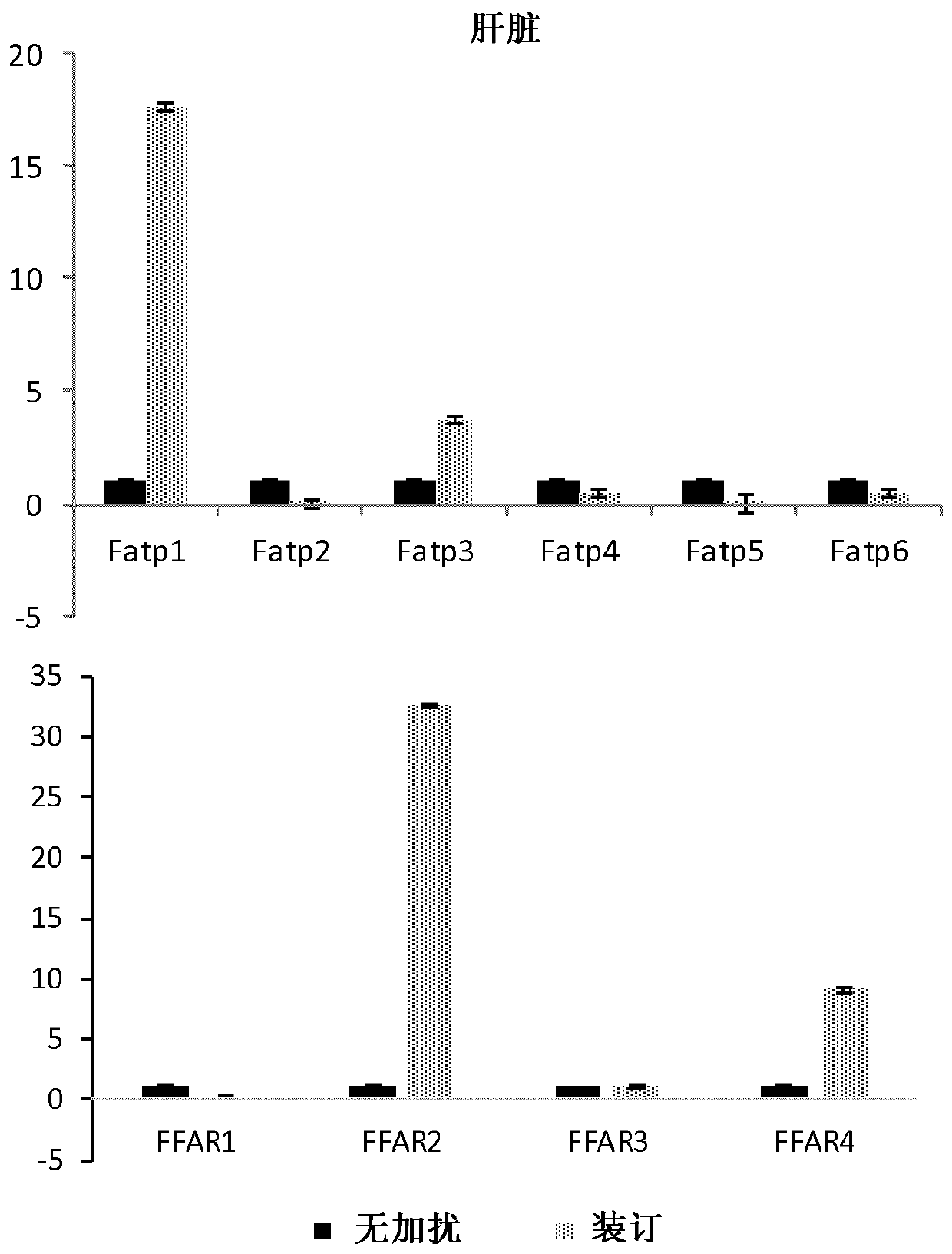
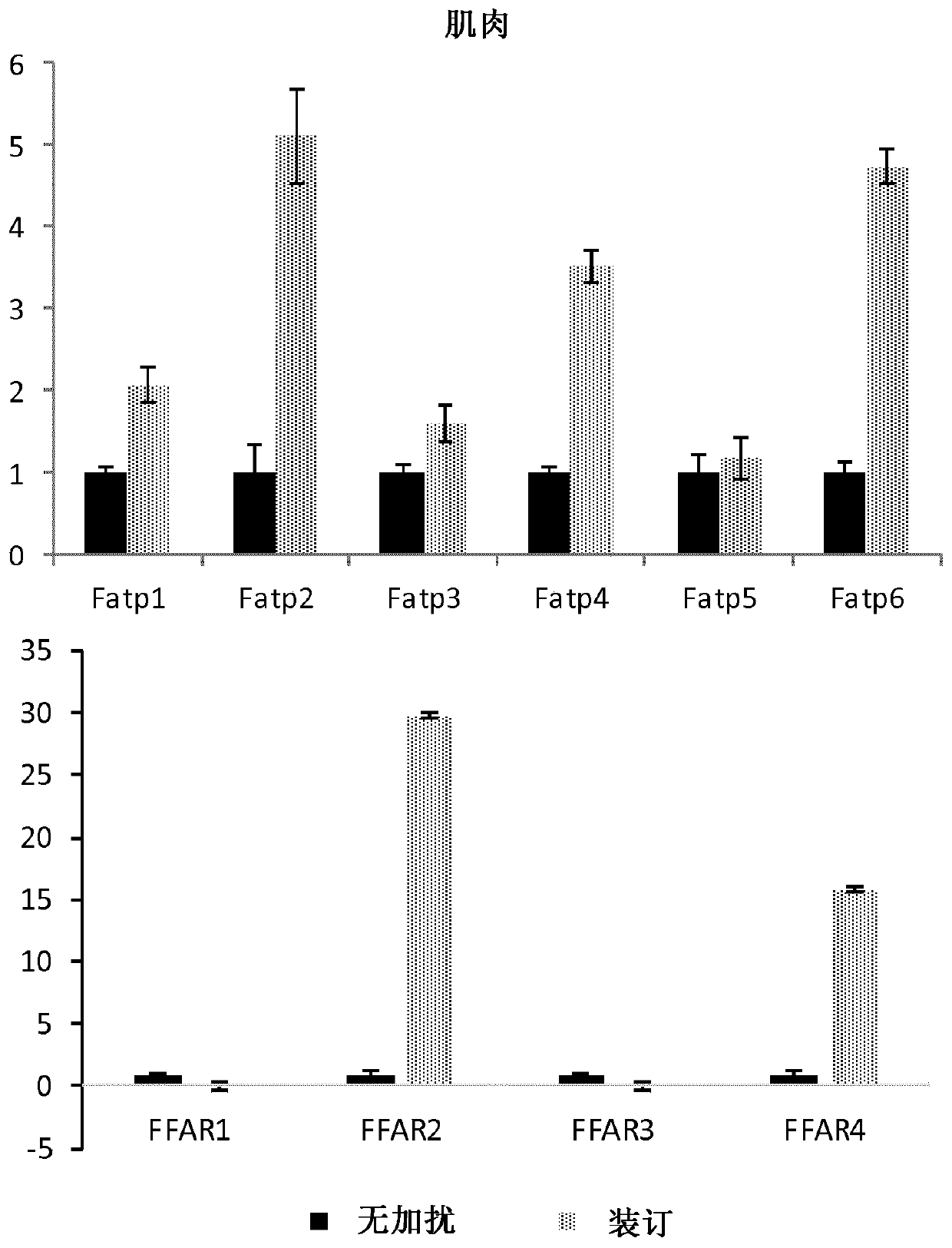
[0265] Example 1: Effect of Adipose Tissue-Targeted PATAD Treatment on Expression Levels of Key Fatty Acid Transporters and Receptors 11 Days Post-Injection
[0266] Since subcutaneous injection of PATAD is involved in restoration of glucose absorption in adipose tissue, the inventors measured all 6 isoforms of FATP(1-6) (fatty acid transporter 1-6) and 4 of FFAR (free fatty acid receptor) Expression levels of the isoforms to assess any effects on these genes.
[0267] Interestingly, PATAD injection caused an extremely specific and dramatic decrease in FAPT2 in adipose tissue, such that the effect of PATAD treatment was directly related to the decrease in FATP2 expression ( Figure 1A ). Since it was previously shown that PATAD peptides do not circulate in vivo, that their effects are limited to adipose tissue, and also based on their mechanism of action by interfering with ALMS1-PKC interactions, the new role of PATAD in adipose tissue is to reduce FATP2. The expression leve...
example 2
[0268] Example 2: ADPIF peptide is more active than PATAD peptide in reducing FATP2 expression level in adipose tissue
[0269] Mice were injected with a single dose of scrambled peptide or PATAD or ADPIF. Eleven days after injection, mice were euthanized and adipose tissue was sampled for RNA extraction followed by real-time PCR. FATP2 expression levels were similar to lean controls, while PATAD, although effective in reducing FATP2 expression levels in adipose tissue, was less effective than ADPIF ( Figure 2A ).
example 3
[0270] Example 3: ADPIF effectively increases circulating levels of GLP-1 11 days after adipose tissue injection.
[0271] Mice were injected with a single dose of scrambled peptide or PATAD or ADPIF. Eleven days after injection, mice were euthanized and plasma was obtained and used to determine circulating GLP1 in mice with the indicated treatments. Both PATAD and ADPIF restored high circulating levels of GLP1, with ADPIF causing a greater increase than PATAD ( Figure 2B ).
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap