Honeysuckle protoplast separation and culture method and special culture medium
A technology of protoplasts and culture methods, applied in the direction of plant cells, etc., to achieve the effects of increasing yield and vitality, increasing strength, and improving enzymatic hydrolysis effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] A method for separating and cultivating honeysuckle protoplasts, comprising the following steps:
[0032] (1) Disinfection of explants
[0033] Select the young leaves of robust honeysuckle test-tube plantlets as explants, wash them with detergent and rinse them in running water for 10 minutes, then disinfect them with 75% alcohol for 30 seconds, and then use 0.1% HgCl 2 The solution was sterilized for 10 minutes, and finally washed 3 times with sterile water.
[0034] (2) Pretreatment of explants
[0035] Place the sterilized leaves in a petri dish, add plasmolysis solution for pretreatment for 60 minutes; the composition of plasmolysis solution is as follows: KNO 3 190mg / L, CaCl 2 2H 2 O 75mg / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 125mg / L, KH 2 PO 4 17.5mg / L, MnSO 4 4H 2 O 2.23mg / L, H 3 BO 3 0.62mg / L, KI 0.083mg / L, Na 2 MoO 4 2H 2 O 0.025mg / L, CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O0.0025mg / L, ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.86mg / L, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 2.79mg / L, Na 2 -EDTA 3.73mg / L, vitamin B10.05mg / L, vitam...
Embodiment 2
[0045] The influence of embodiment 2 pretreatment time on honeysuckle protoplast separation
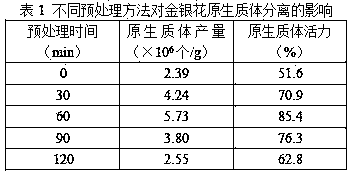
[0046] For the pretreatment of the explants in Example 1, five gradient pretreatment times were set in this experiment, namely: 0, 30 min, 60 min, 90 min, and 120 min. Protoplasts were isolated and purified from the explants pretreated for different times, and the yield and viability of the protoplasts were measured (see Table 1).
[0047]
[0048] The results in Table 1 show that with the prolongation of the pretreatment time, the yield and vigor of honeysuckle protoplasts first increased and then decreased. When the pretreatment time was 60 min, the yield and vigor of honeysuckle protoplasts reached the maximum. 5.73×10 6 individuals / g and 85.4%; with the further extension of pretreatment time, its yield and vigor decreased sharply, therefore, the most suitable pretreatment time for honeysuckle leaves was 60 minutes.
Embodiment 3
[0049] The influence of embodiment 3 different enzymolysis methods on honeysuckle protoplast separation
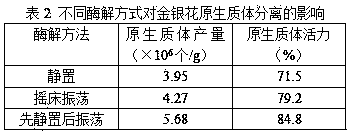
[0050]For the separation of protoplasts in Example 1, three enzymatic hydrolysis methods were set up in this experiment, which are: standing enzymolysis, that is, mixing the leaves with the enzymatic hydrolysis solution and then standing enzymatic hydrolysis at 28°C for 8 hours in the dark; shaking Bed shaking enzymolysis, that is, mixing the leaves with the enzymatic solution and placing them on a shaking table (28°C, 40rpm) for 8 hours of oscillating enzymolysis; first standing still and then oscillating enzymolysis, that is, mixing the leaves with the enzymatic solution and then standing for 4 hours , and then placed on a shaker (28°C, 40rpm) for oscillating enzymatic hydrolysis for 4 hours. The protoplasts obtained through different enzymatic hydrolysis methods were purified, and then the yield and activity of the protoplasts were measured (see Table 2).
[0051]
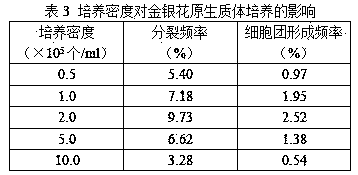
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com