Adjustment of subjective and objective refractions
A technology of refractive power and visual impairment, applied in the field of spectacle lenses or spectacle lens series, which can solve different problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0347] -ΔM -2 =ΔM +2 = 1, 0Dpt
[0348] -ΔM -1 =ΔM +1 =0,5Dpt
[0349] Akk 1 = 0 Dpt
[0350] Akk 2 =1,75Dpt
[0351]
[0352]
[0353]
[0354]
[0355]
[0356]
example 2
[0358] -ΔM -2 =ΔM +2 = 0 Dpt
[0359] -ΔM -1 =ΔM +1 = 0 Dpt
[0360] Akk 1 = 0 Dpt
[0361] Akk 2 =1,75Dpt
[0362]
[0363]
[0364]
[0365]
[0366]
[0367]
example 3
[0369] -ΔM -2 =ΔM +2 = 1,5Dpt
[0370] -ΔM -1 =ΔM +1 =0,75Dpt
[0371] Akk 1 =0,5Dpt
[0372] Akk 2 = 2,0 Dpt
[0373]
[0374]
[0375]
[0376]
[0377]
[0378]
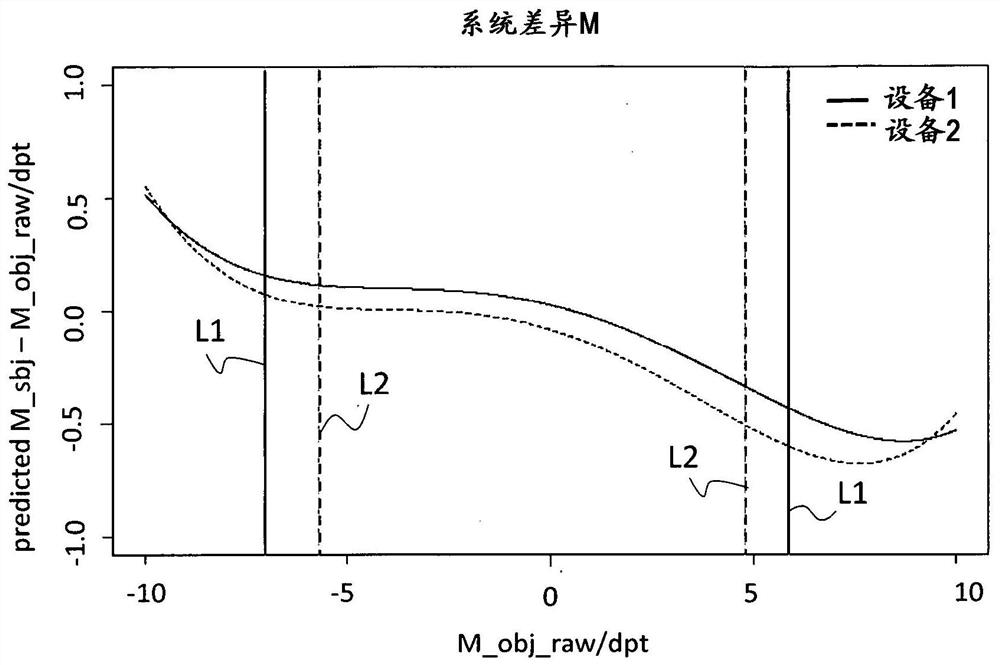
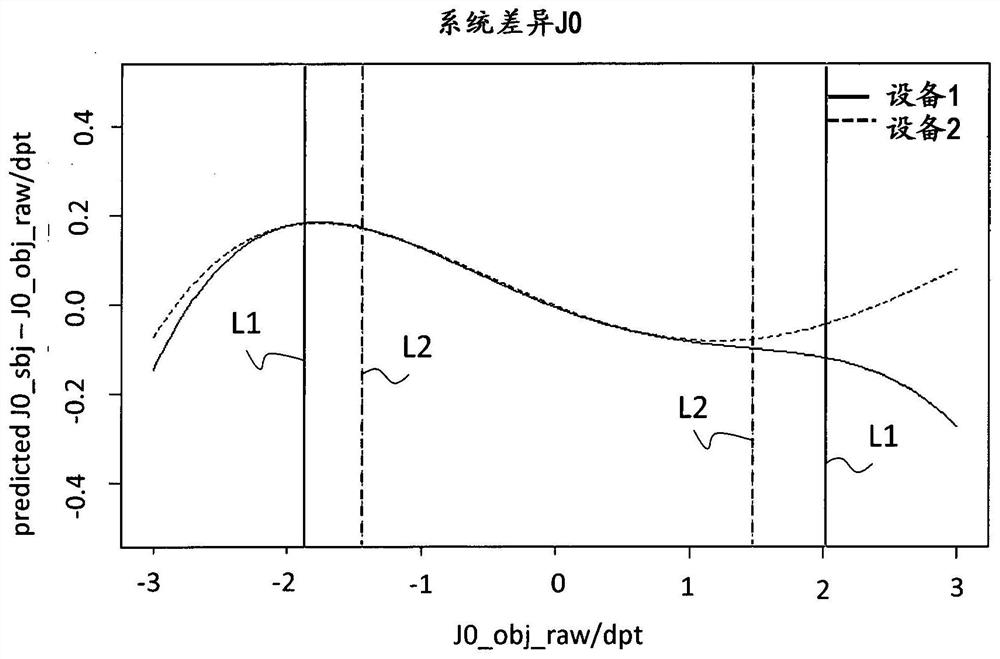
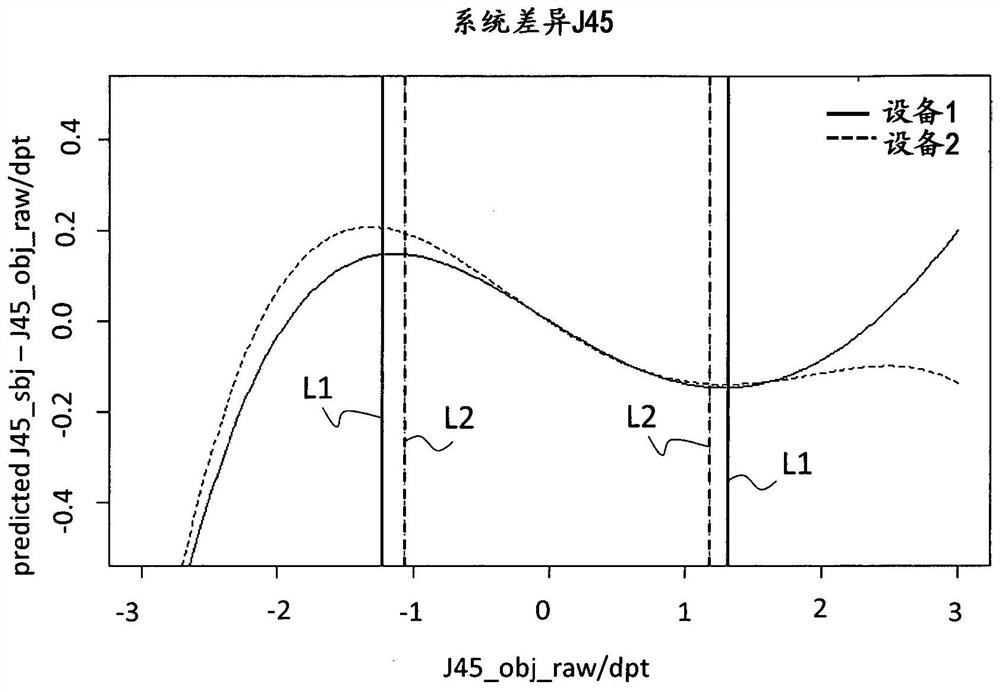
[0379] image 3 shows the weighting of the subjective spherical equivalent according to Example 1 Figure 4A shows the weighting of the subjective spherical equivalent according to Example 2 Figure 4C shows the weighting of the subjective spherical equivalent according to Example 3 In terms of reducing statistical measurement errors in subjective and / or objective measurements, image 3 The weight ratio shown Figure 4A The weights shown are more favorable.
[0380] According to example 1 ( image 3 ), Example 2 ( Figure 4A ) and Example 3 ( Figure 4B ) depends on the difference (or difference) between the downlight and the spherical equivalent corrected in step 1 ΔM=M sub -M obj . As mentioned above, the function consists of a number of plateaus of constant weight, betwee...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com