Distributed resource allocation
A resource allocation and resource technology, applied in resource allocation, multi-program device, program control design, etc., can solve problems such as consumption, excessive computing resources and time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
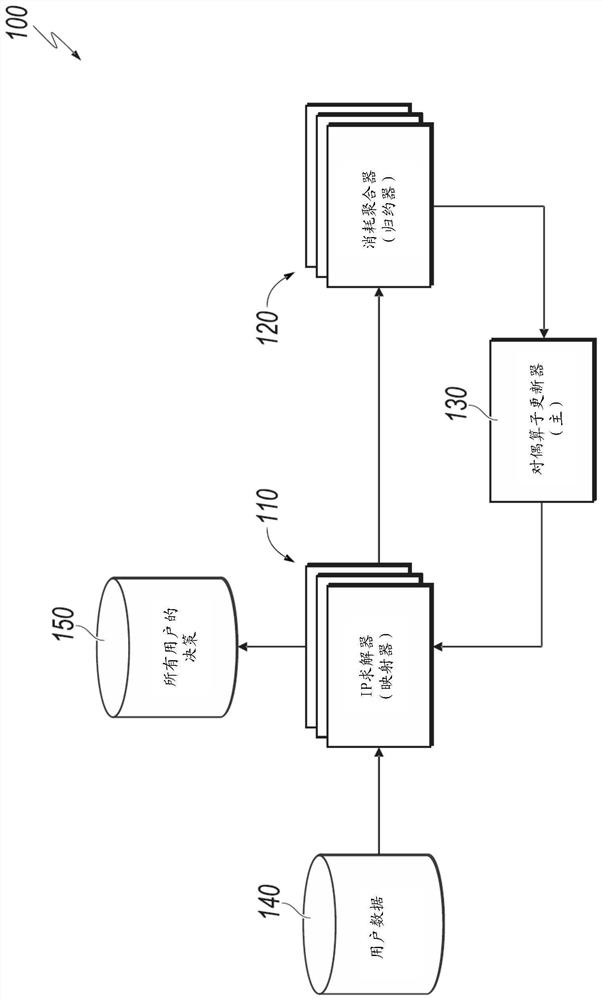
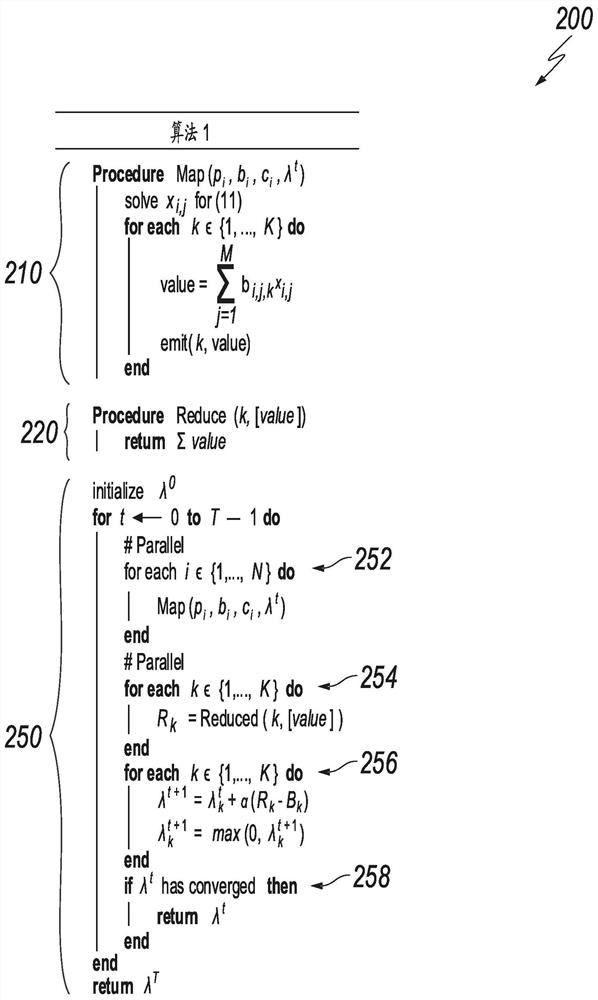
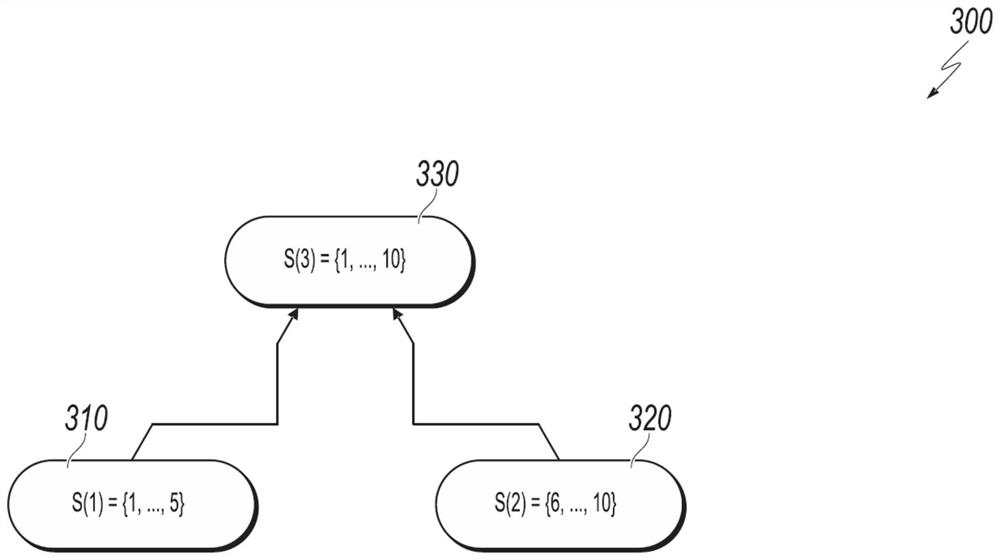
[0029] This article describes techniques for resource allocation. These techniques generally involve solving the large-scale knapsack problem (KP) in a scalable distributed paradigm via synchronized coordinate descent (SCD). In some embodiments, the described techniques can help solve the knapsack problem on a scale of billions or more with multiple global constraints. In some embodiments, the described techniques can help solve such large-scale knapsack problems without compromising the optimality of the solution or violating constraints. In some embodiments, techniques may be implemented using off-the-shelf distributed computing frameworks (eg, MPI, Hadoop, Spark). In some embodiments, these techniques can save storage space, reduce computational complexity, and improve the speed of solving the knapsack problem. In some embodiments, these techniques can solve resource allocation problems on an unprecedented scale (e.g., the knapsack problem with billions of decision and co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com