Automatic text abstracting method based on heterogeneous graph network
An automatic summarization and heterogeneous graph technology, applied in the field of text processing, can solve problems such as the inability to effectively capture long-distance text interaction information, semantic deviation, and the inability of sequence modeling to represent long-distance information.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
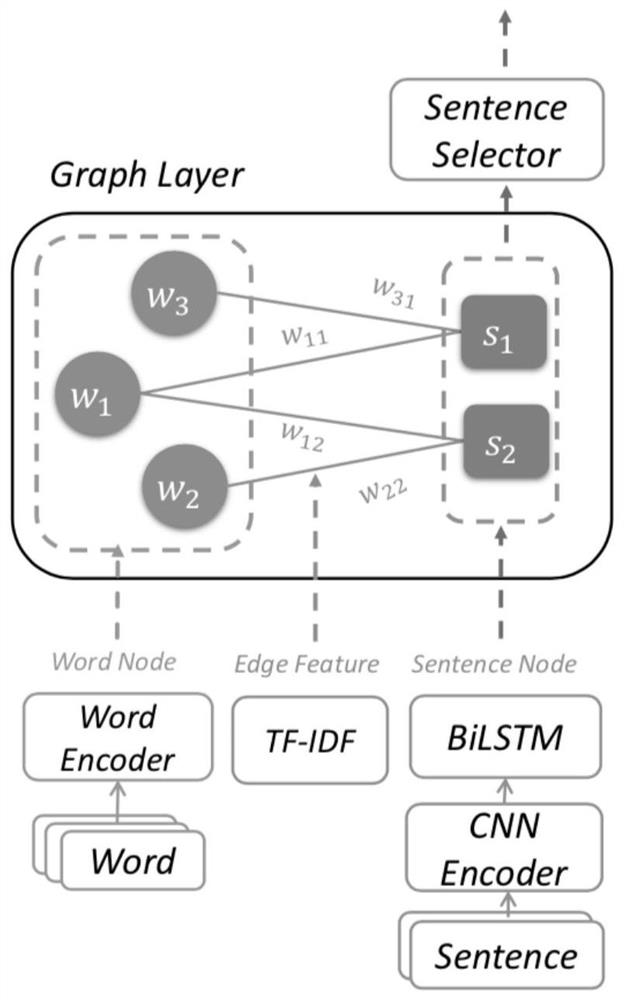
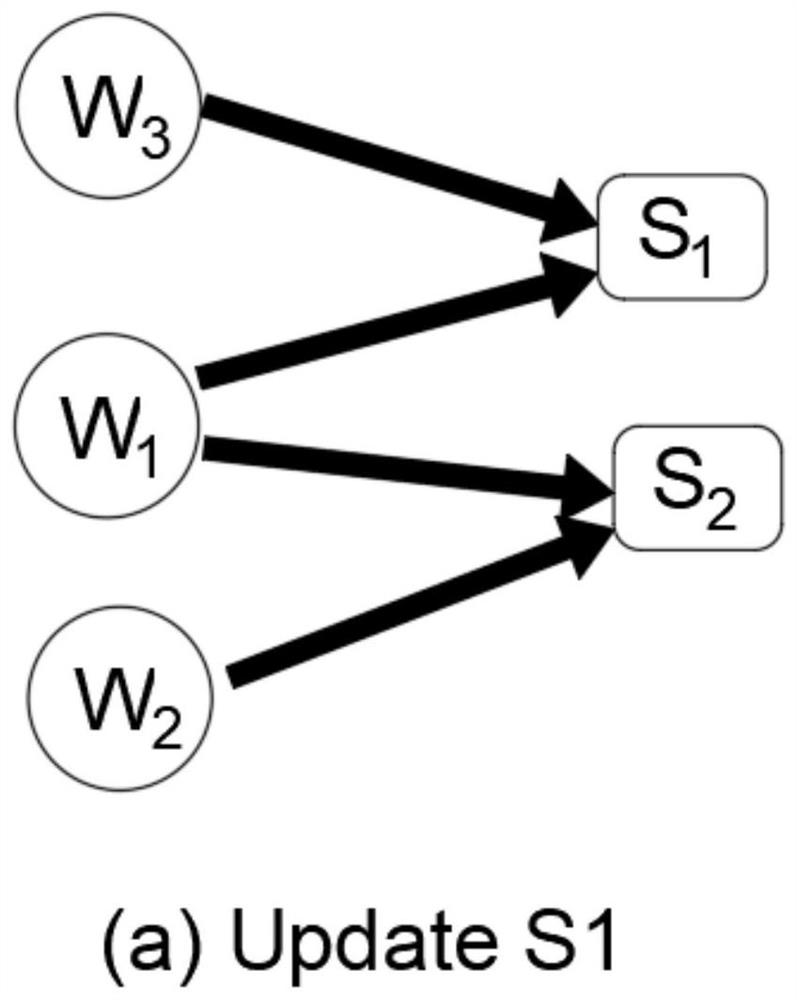
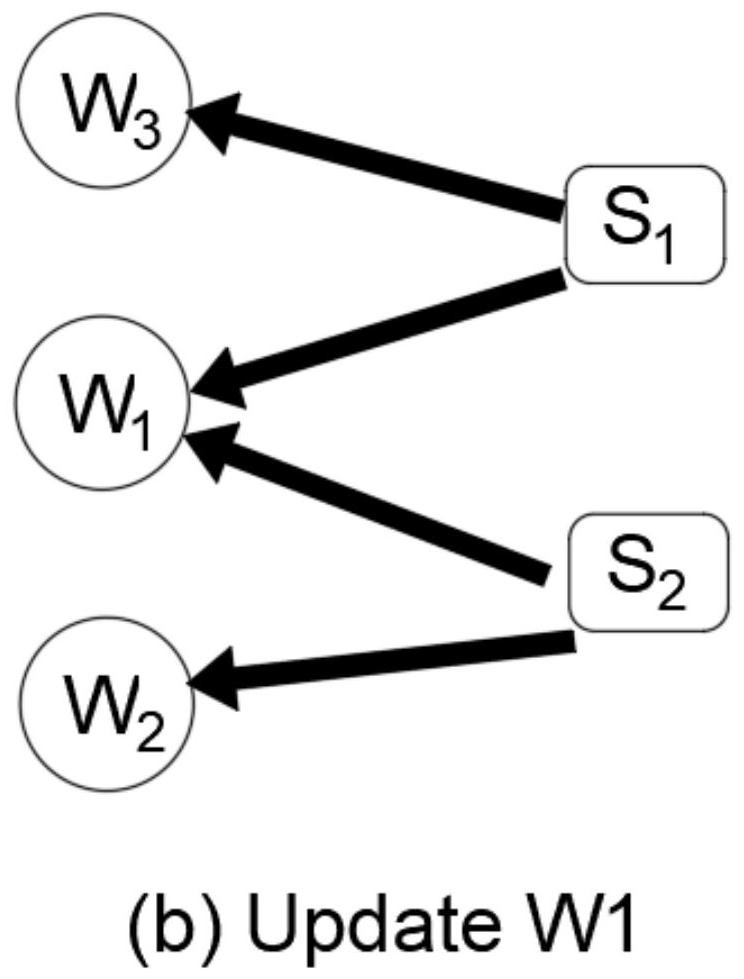
[0051] Given a document D={s 1 ,...,s n}, which means that this document has n sentences, and extractive text summarization is defined as predicting a sequence {y 1 ,...,y n}, where y i = 1 means that the i-th sentence will be extracted as part of the summary. The model has two kinds of nodes, which are word nodes and sentence nodes, so the definition of a heterogeneous graph is a graph network G={V,E}, where V represents the collection of all types of nodes, and E represents the edges between all nodes gather.
[0052] Raw documents are long pieces of text, such as news corpora. This type of data has no obvious characteristics. If a sequence model such as LSTM is used for modeling, the relationship between long-distance sentences and words cannot be well modeled. Therefore, it is necessary to model the heterogeneous graph of the text first. , respectively connect word nodes, sentence nodes, and word and sentence nodes, and initialize these nodes and connection edges. A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com