Neutralizing granzyme b for providing cardiac protection to subjects undergoing myocardial infarction
A technique for myocardial infarction and heart protection, applied in the fields of cardiology and medicine, to solve the problems of unknown mechanism of cardiac cytotoxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
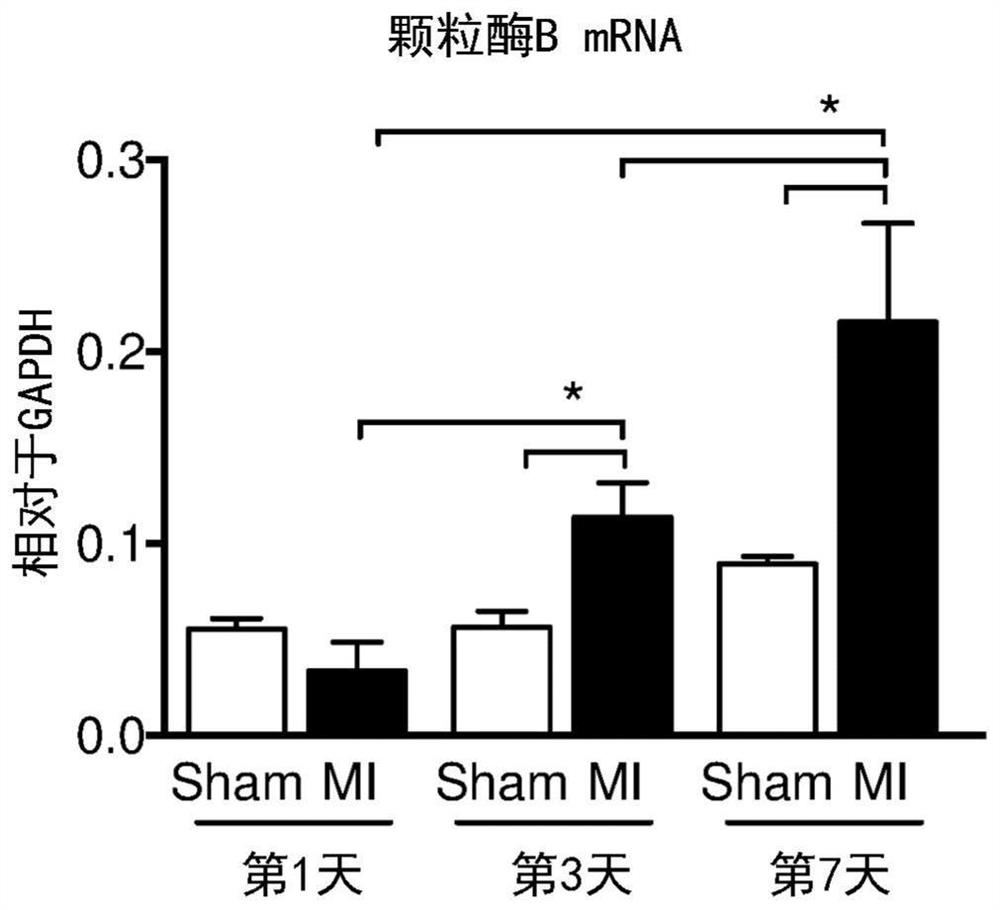
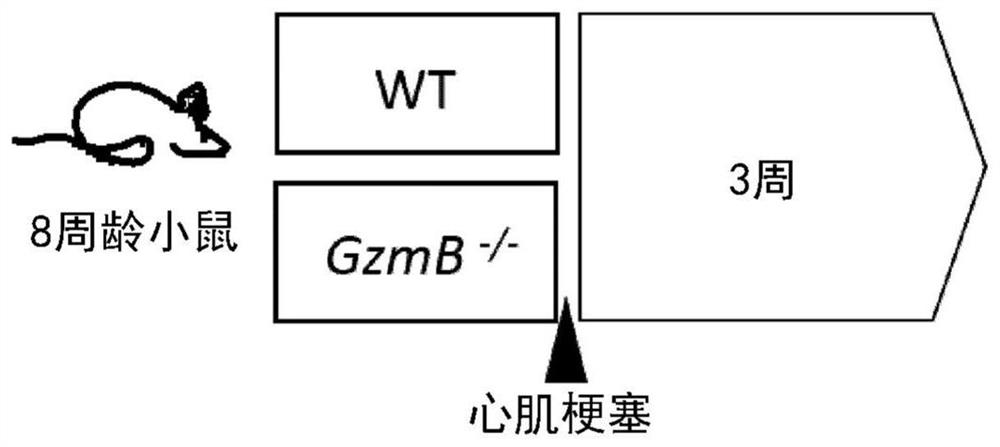
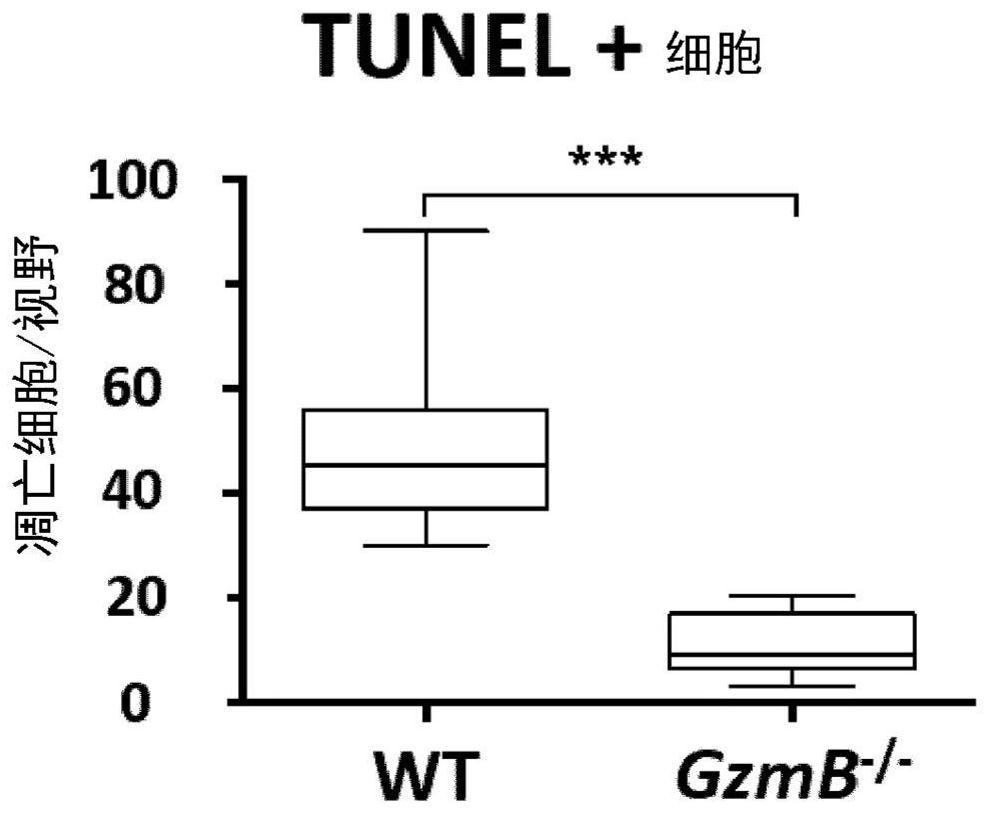
[0005] Acute myocardial infarction (MI) is a common condition leading to heart failure and sudden death. Here, the inventors demonstrate that after acute MI in mice, CD8+ T lymphocytes are rapidly recruited and activated in ischemic heart tissue, and release granzyme B, leading to cardiomyocyte apoptosis and deterioration of myocardial function. Antibody-mediated (CD8-specific antibody) depletion of CD8+ T lymphocytes reduced intramyocardial granzyme B content and apoptosis and inflammatory responses. Finally, CD8 depletion limited myocardial damage and improved cardiac function. These effects were reproduced in mice with CD8+ T cell-selective granzyme B deficiency. Granzyme B is also produced by other cell types such as NK cells. Interestingly, global loss of granzyme B (GzmB - / - mice) reduced apoptosis in the myocardium, reduced local pro-inflammatory signatures and ultimately limited infarct size after MI. The inventors also demonstrated that elevated circulating levels...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap