Cross-tie
a cross-tie and railway technology, applied in the field of railway tracks, can solve the problems of difficult control of the relative positioning between the running rails, time-consuming and expensive installation of railway tracks, and inability to take into account the effect of the relative positioning of the running rails
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
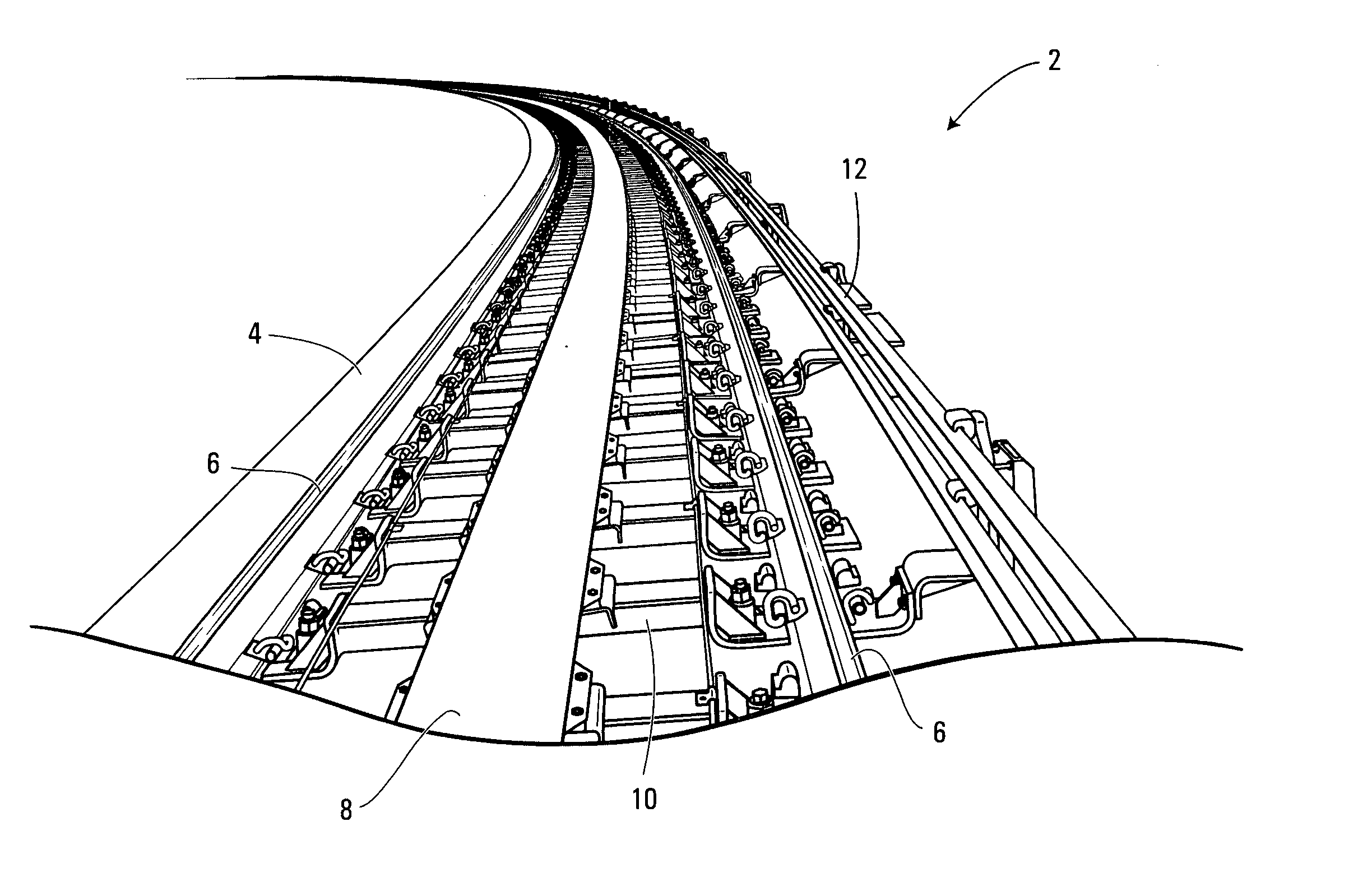
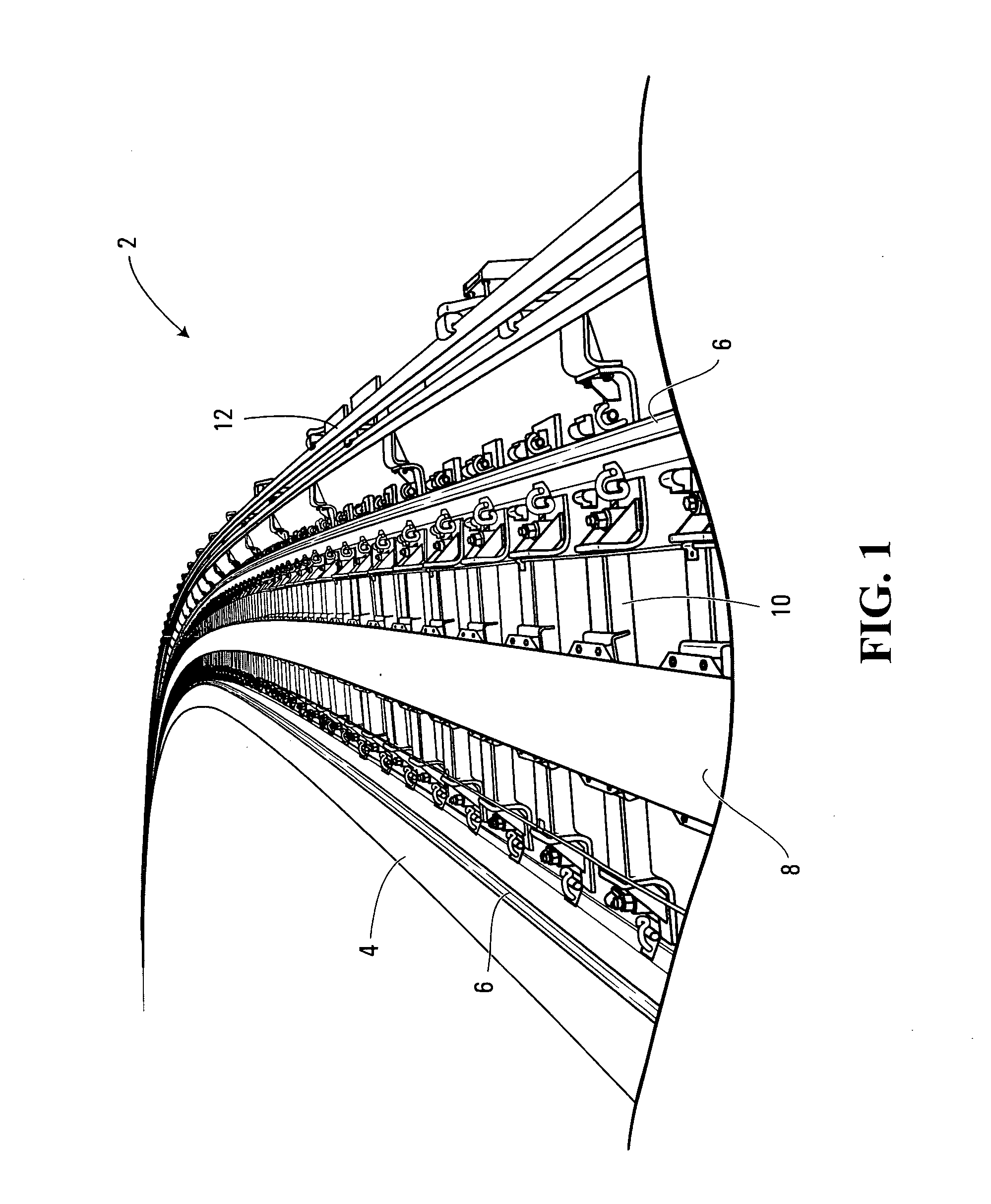
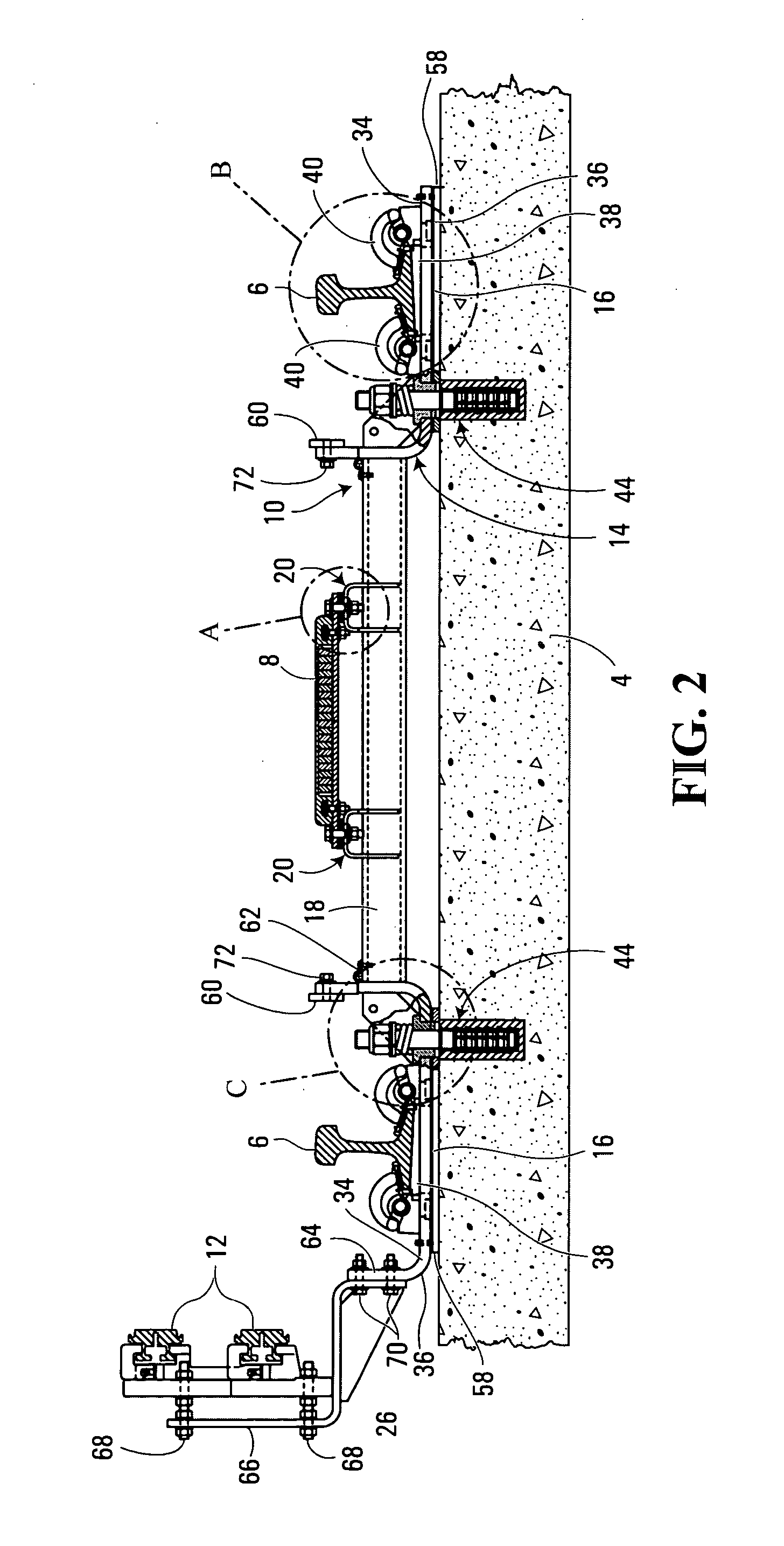
[0020] Shown in FIG. 1 is a railway track 2 for a rail vehicle (not shown) that uses a linear induction motor (LIM) as its primary source of propulsion. The railway track 2 includes a guideway 4 that is typically formed of concrete, and a plurality of cross-ties 10. The cross-ties 10 are operative to support a pair of running rails 6, a reaction rail 8 and at least one power rail 12. In the non-limiting example of implementation shown in FIG. 1, the cross-tie 10 is operative to support two power rails 12.
[0021] As shown, the running rails 6 are positioned on the cross-tie 10 in a parallel, spaced apart relationship, such that the wheels of the railway vehicle can travel therealong. The reaction rail 8 is positioned between the two running rails 6, and is operative to complete a flux path with a primary portion of the linear induction motor located on the railway vehicle, so as to propel or retard the railway vehicle along the track. The power rails 12 are positioned perpendicular t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com