System and method of virtual modeling of thin materials
a technology of virtual modeling and thin materials, applied in the field of three-dimensional computer-aided modeling and garment design, can solve the problems of complicated problems, and does not provide any disclosure directed to specific product features
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
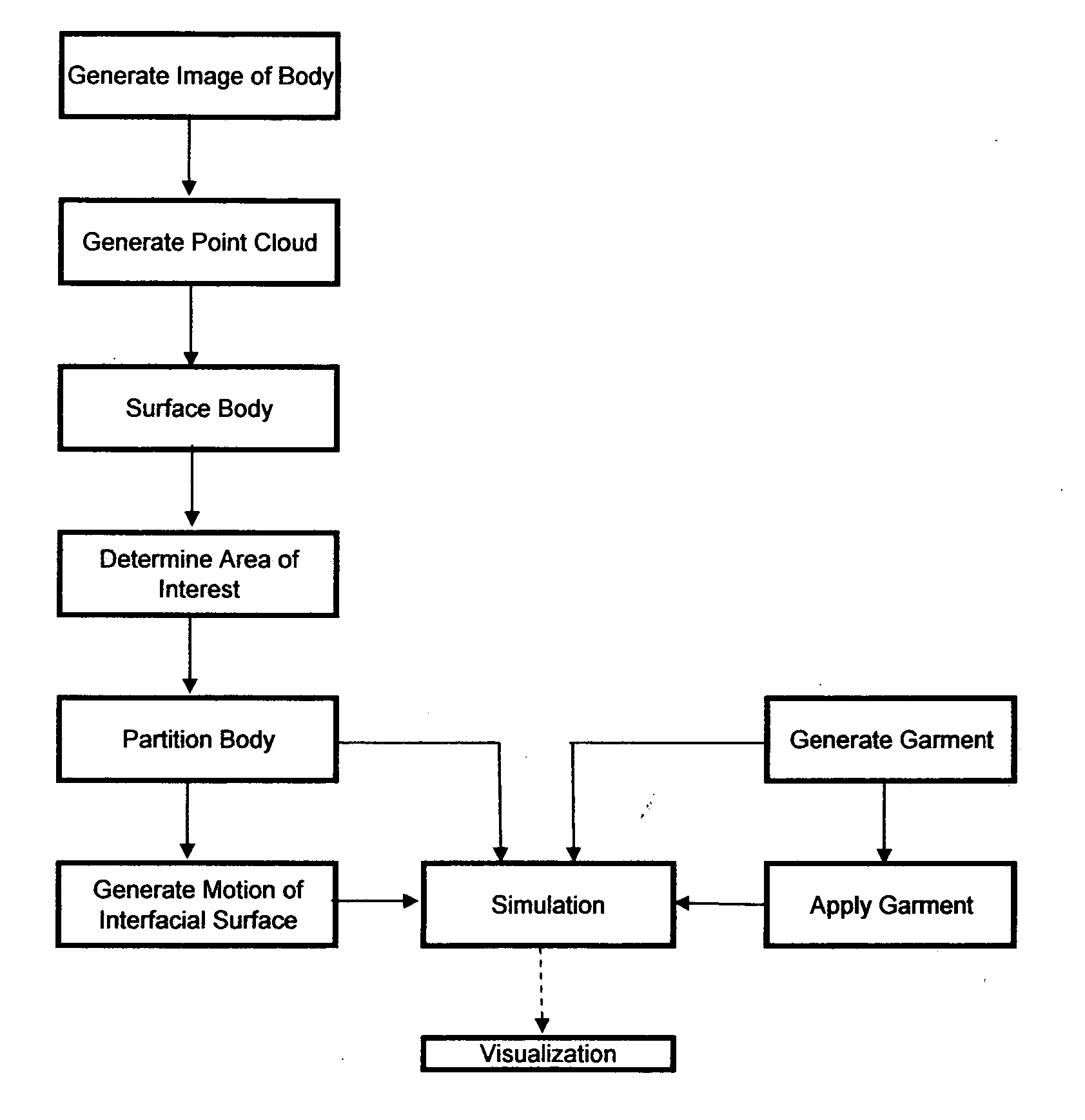
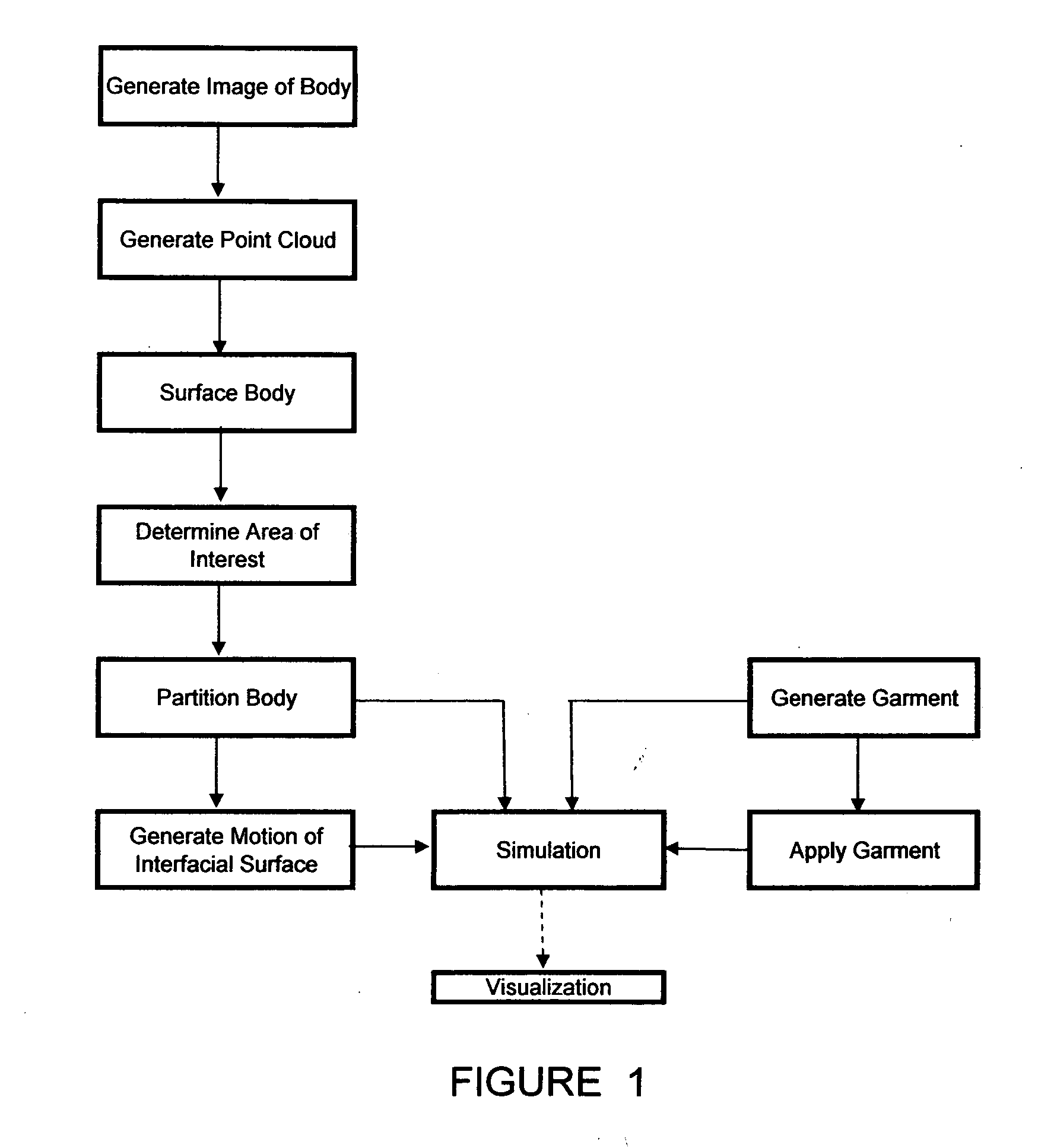
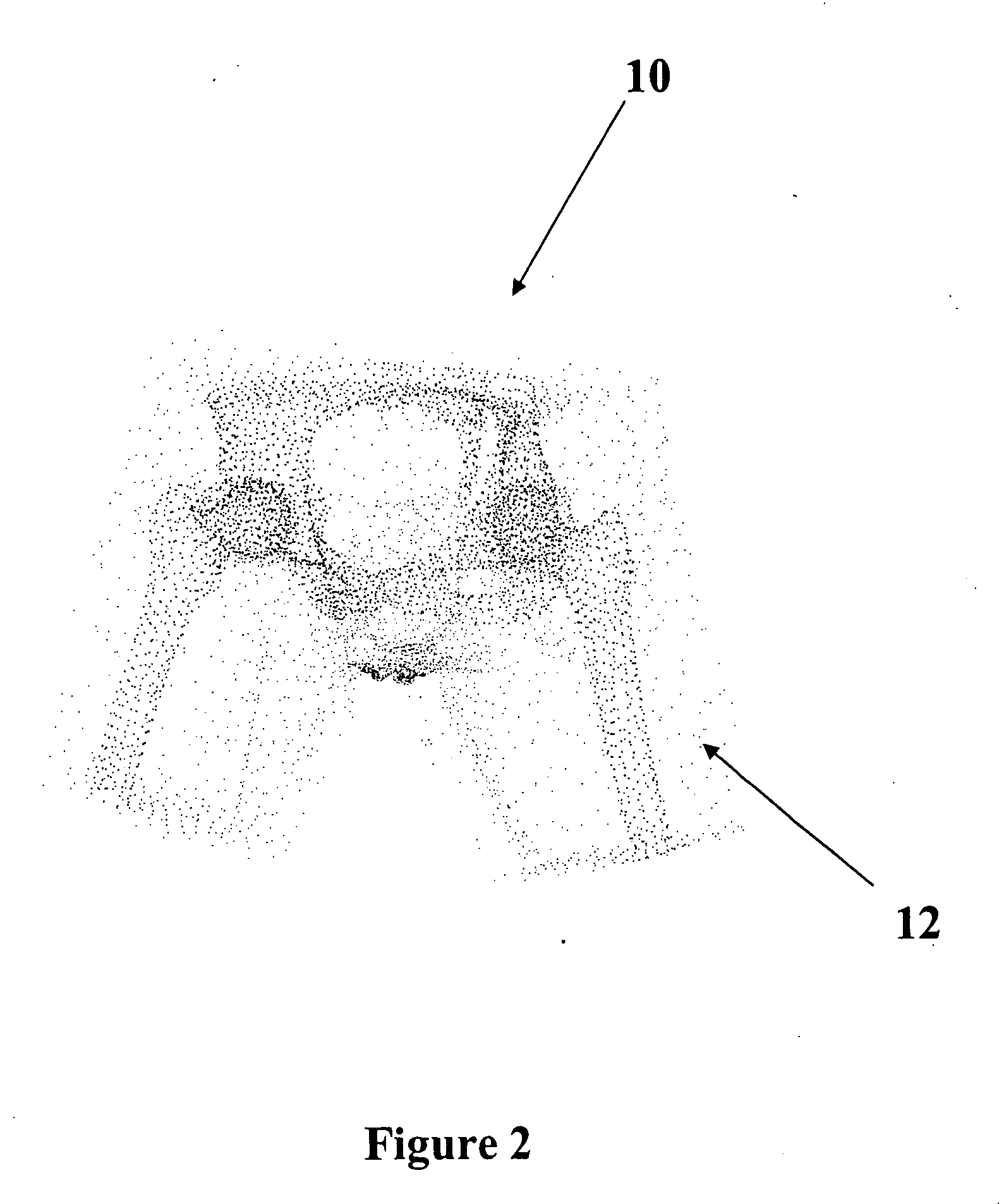
[0034] The virtual model of the present invention can be used to virtually model the dynamic behavior of a body, such as a human body, and the body's interaction with garments. As used herein, the term “garments” means any article or object intended for placement on or in the body and intended for temporary wear. Therefore, the term garments includes externally-worn articles, such as clothing including hats, gloves, belts, shirts, pants, skirts, dresses, thermal wraps (that can be worn over other clothing) and the like. The term garments also includes internally-worn articles such as earplugs, hearing aids, mouth guards, and tampons. Internally-worn articles generally have externally-disposed access means for placement and removable, such as finger extensions on earplugs and strings on tampons. Some garments can be partially external and partially internal, such as earrings in pierced ears, hearing aids having externally-disposed portions, and interlabially-placed catamenial devices...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com