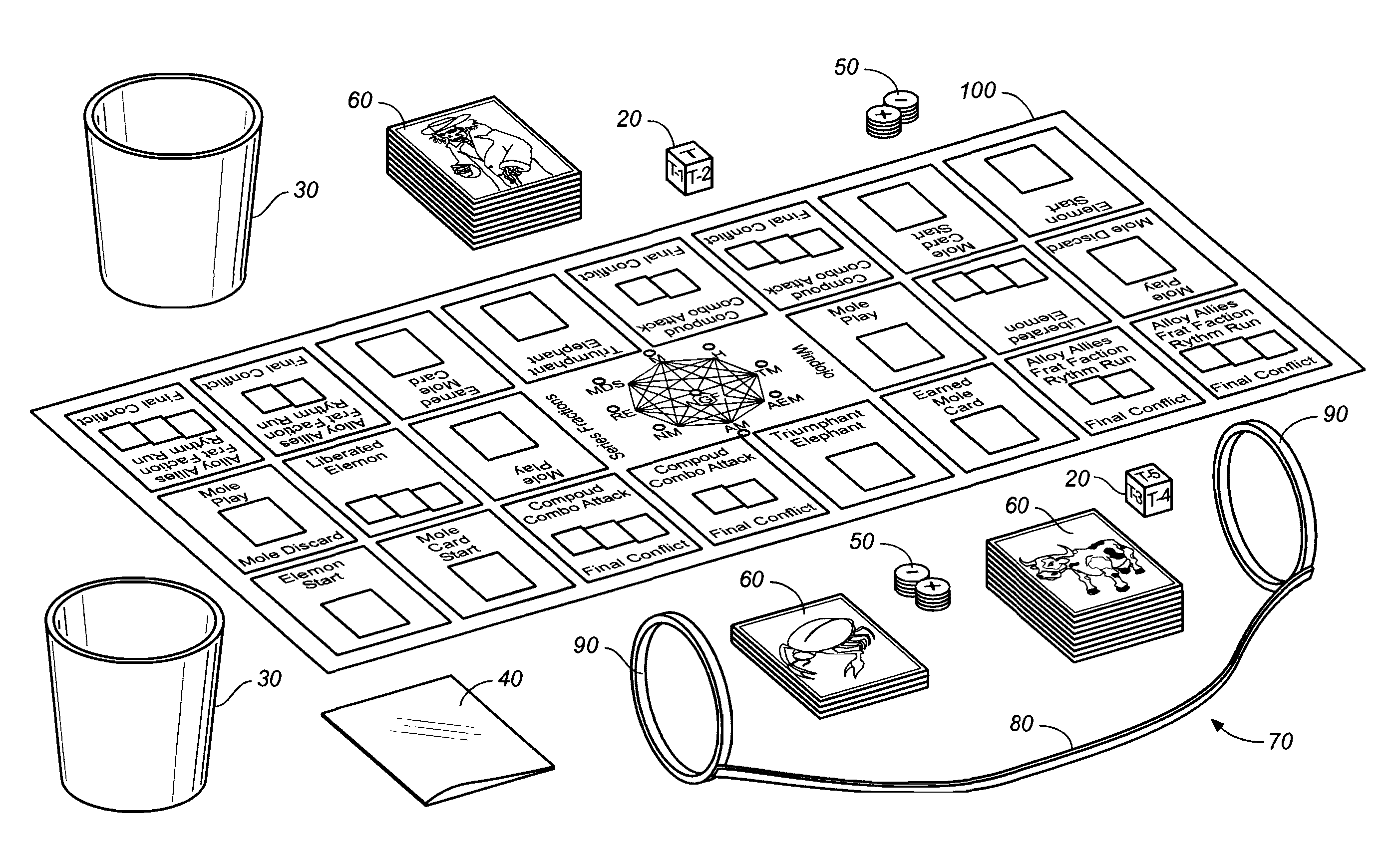
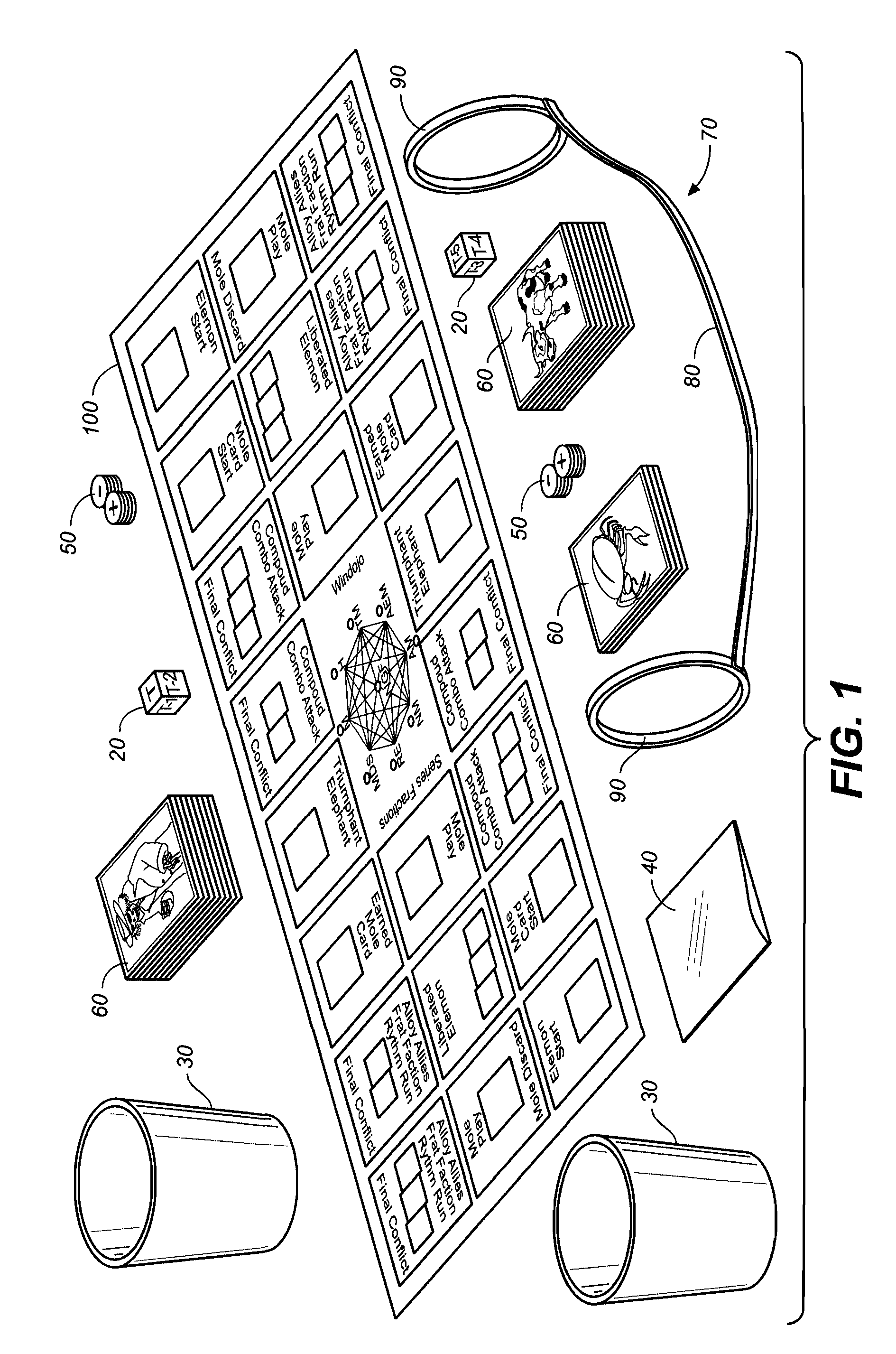
Educational Battle Game Method Of Teaching Key Theories And Facts
a battle game and key theory technology, applied in the field of educational games, can solve the problems of difficult mastery and remembering, limited pedagogic value of games, and other limitations, and achieve the effect of high pedagogic value and
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
OO
[0107] In this example one die and 3 electrocoins are rolled. The die covers the 6 to 10 range value. The die has 6 sides and for this range would read: T−Bone=10 (highest value in the range), T−1=9, T−2=8, T−3=7, T−4=6, T−5=6. The T means top range value with the minus number subtracting from that on a T−#. In this example, T−4 and T−5 have the same value because the bottom of the range is listed as 6 (one cannot go any lower than the bottom value of the listed range). In this example, if a T−3 is rolled, the calculated value is 7.
[0108] The three electrocoins are rolled at the same time as the die, and in this example only the plus + side of the coins are counted. If the electrocoin roll results in two plus (+) and one minus (−) as results, the equation requires that only the plus sides are counted, so the result is a 2 value.
[0109] Thus, in this first example, the final damage number is the 7 from the range die plus the 2 from the electrocoin flips, or Damage=7+2=9.
example 2
[0110] In this example one die and 3 electrocoins are rolled. The die covers the range value of 5 to 9. The die has six sides and for this the range would read: T=9 (for Top, highest value in the range), T−1=8, T−2=7, T−3=6, T−4=5, T−5=5. The T means top range value with the minus number subtracting from that on a T−#. In this example, T−4 and T−5 have the same value because the bottom of the range is listed as 5 (again, one cannot go any lower than the bottom value of the listed range). In this example if the roll of the dice showed a T−4, then the value would be 5. The attack equation requires that both plus (+) and minus (−) be counted on the three electrocoins flipped during or after the die are rolled. If the coins showed two plus (+) and one minus(−) for results, the one minus cancels out one plus, leaving one plus result. The final number is 5 from the range die plus 1 from the electrocoin flips, and so Damage=5+1=6.
[0111] Factions: In the inventive game the element characte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com