Multilevel speed regulation jack
a technology of multi-level speed regulation and jack, which is applied in the direction of clutches, fluid couplings, lifting devices, etc., can solve the problems of time and effort consumption, slow jacking process, etc., and achieve the effect of fewer speed ranges, different load capacities, and more speed ranges
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
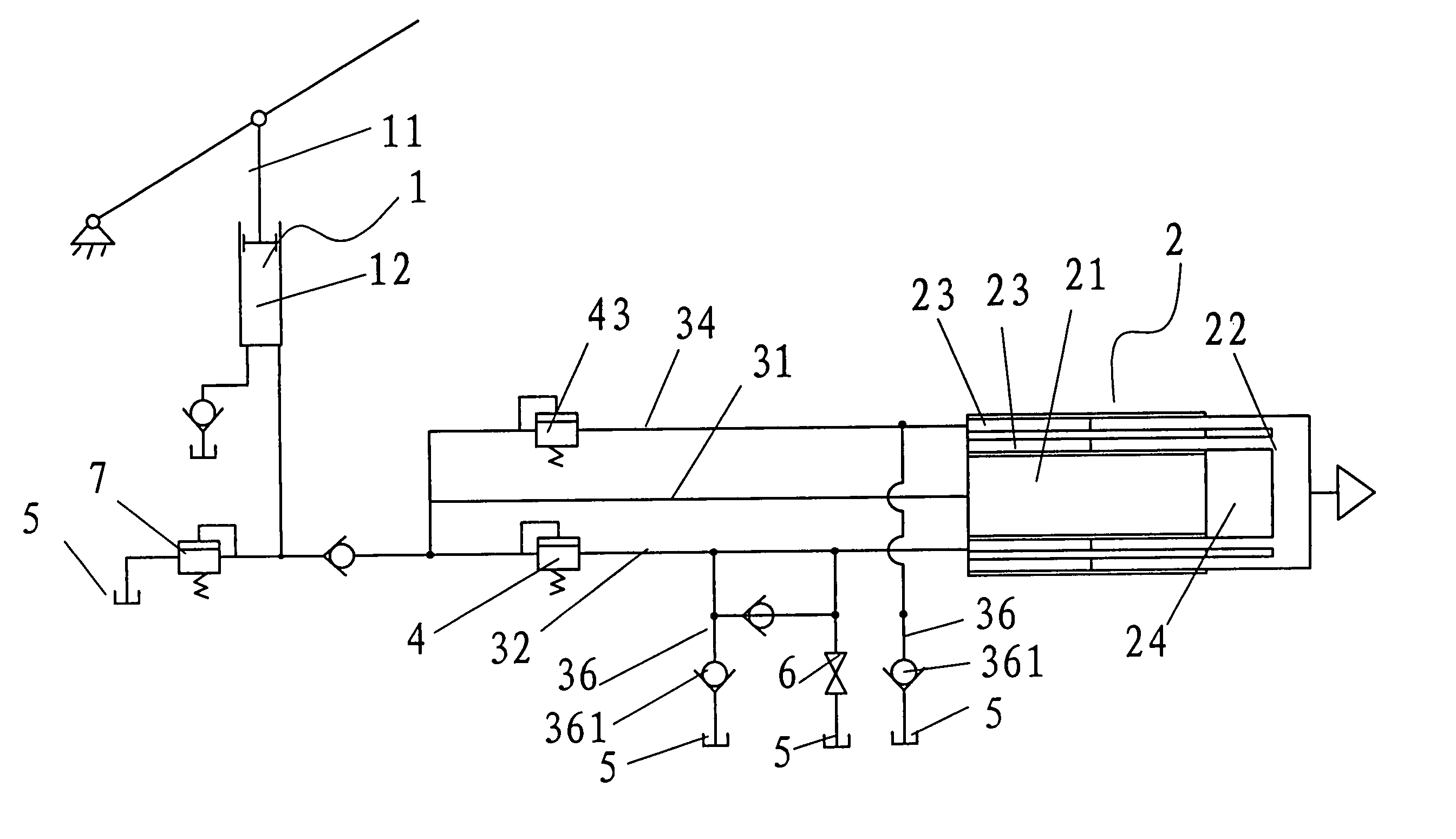
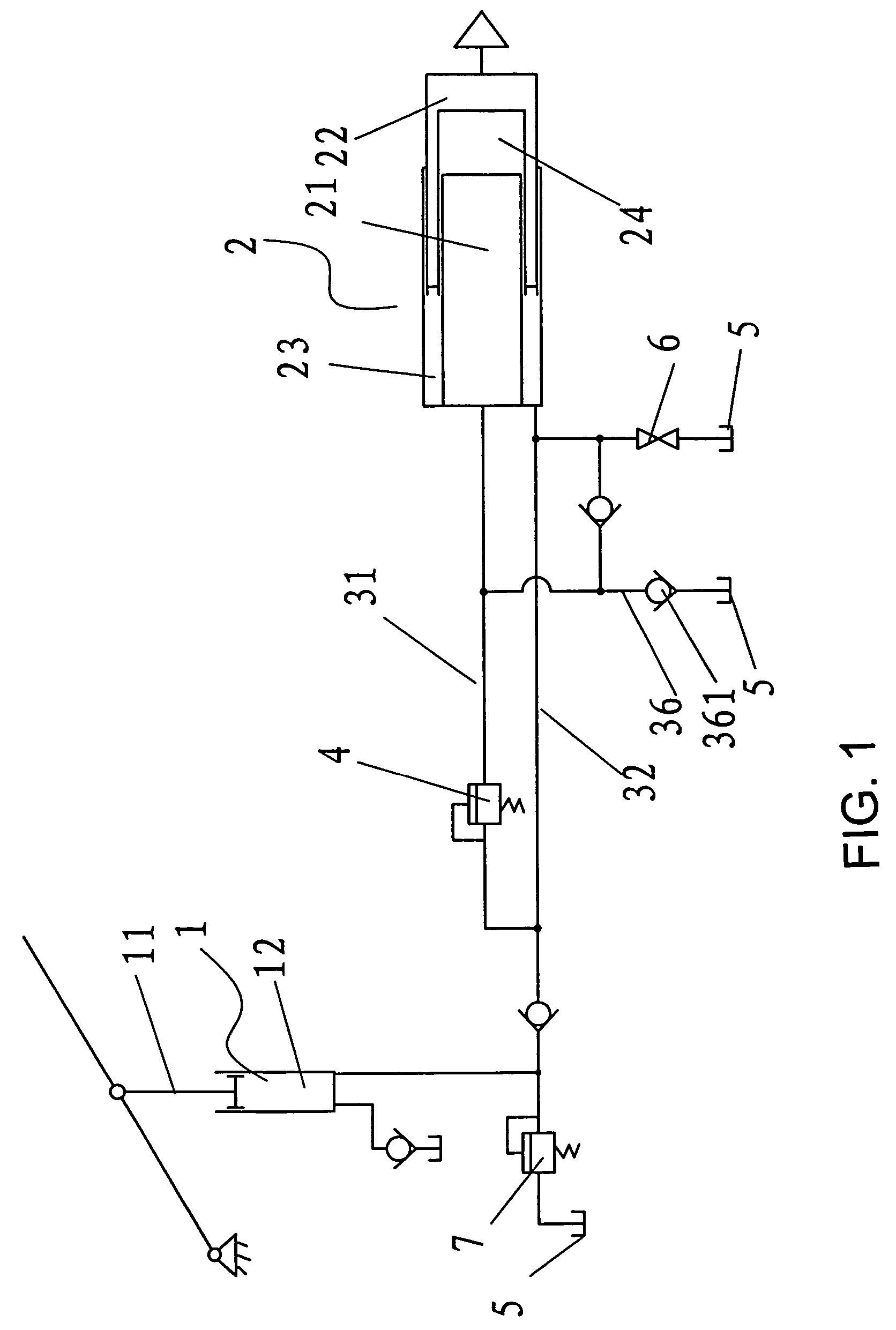
[0042]As illustrated in FIG. 1, this embodiment of the present invention has one annular in-flow oil chamber 23. Control valve 4 may be installed in fluid channel 31, which is connected to the central in-flow oil chamber. The control valve controls the connection state of fluid channel 31 based on the load signal it senses. When there is a zero or light load, pressing down piston rod 11 in input cylinder 1 forces the fluid in an out-flow chamber 12 inside input cylinder 1 to flow into annular in-flow chamber 23 via fluid channel 32. The fluid pushes piston 22 in output cylinder 2 through its annular end surface as thrust area at a speed V1. Because the thrust area of piston 22 in output cylinder 2 in this example is small, V1 is large and piston 22 moves fast, and the system has a high jacking efficiency.
[0043]As the load increases, the pressure of fluid increases accordingly and eventually it opens control valve 4 in fluid channel 31, and some of the fluid is pumped into central in...
embodiment 2
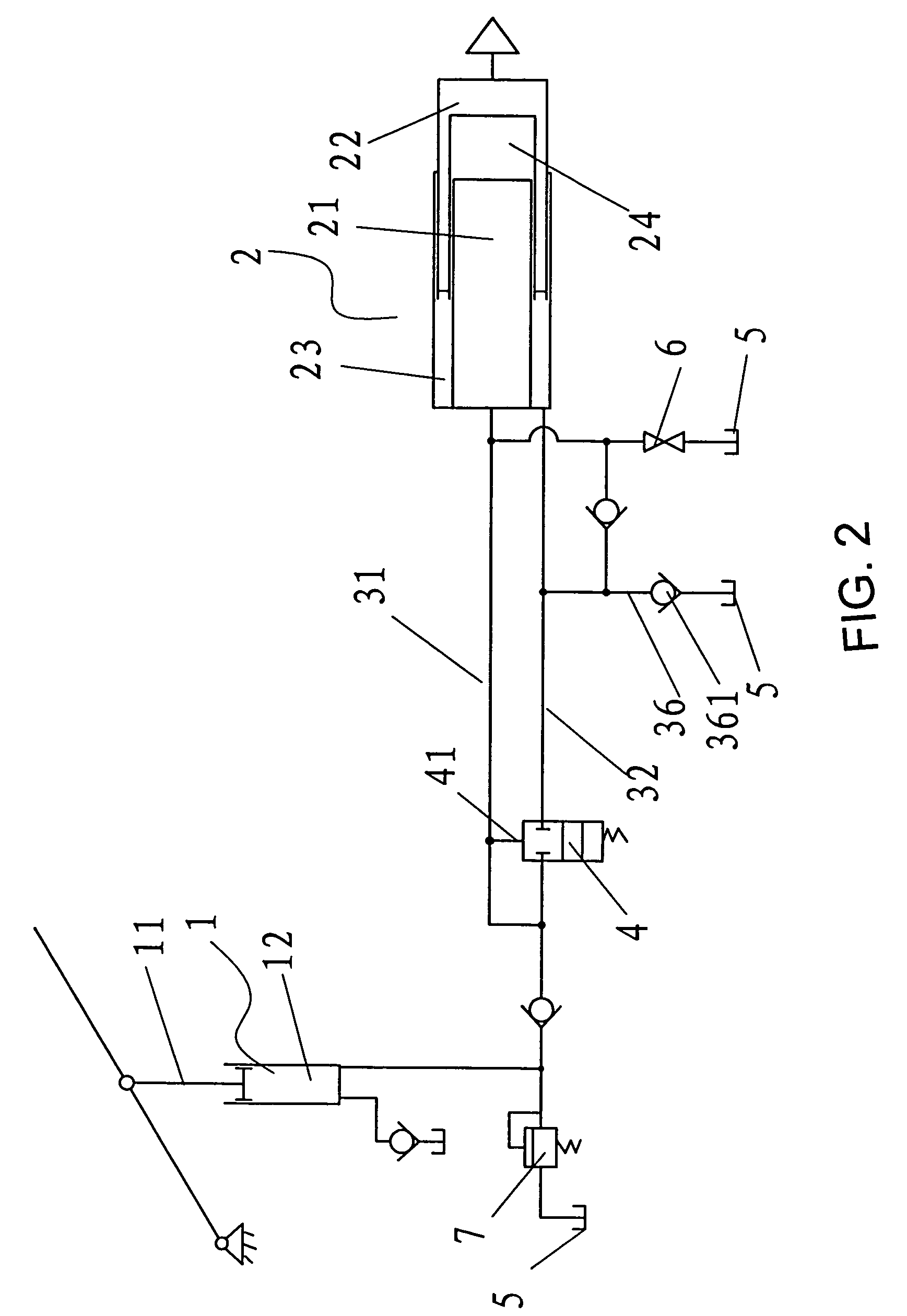
[0049]As illustrated in FIG. 3, in this embodiment of the present invention, output cylinder 2 has one annular in-flow oil chamber 23. Control valve 4 is installed in fluid channel 31 connected to central in-flow oil chamber 24. The system has at least one other input cylinder 1′ unidirectionally connected to annular in-flow oil chamber 23 through fluid channel 33. Fluid channel 33 is connected to oil reservoir 5 via control valve 42. The system may have one or more additional input cylinders 1′. Each addition of an input cylinder 1′ adds one speed range to the jack system. Using a system of only one additional input cylinder 1′ as an example, the working process and principle of speed switching is detailed in the following.
[0050]With a zero or light load, by pressing down piston rod 11 in the input cylinder 1, both input cylinders 1 and 1′ force fluid oil into annular in-flow oil chamber 23 through fluid channels 32 and 33, respectively. The pressure of the fluid pushes forward pis...
embodiment 3
[0057]The basic structure and working principle of this embodiment is similar to those of the embodiment 1, and therefore will not be repeated here.
[0058]The difference between this embodiment and the embodiment 1 is illustrated in FIG. 5. Cylinder body 21 of output cylinder 2 may have two or more annular spaces, and piston 22 has correspondingly two or more tube sleeves. Each sliding sleeve is movably positioned in its corresponding annular space to form an individual annular in-flow oil chamber 23. Each annular in-flow oil chamber 23 is connected to input cylinder 1 through a parallel fluid channel. In each fluid channel a sequence-programmed and threshold-preset control valve is installed. The control valve controls the connection state of the fluid channel based on the load signal it senses. Each addition of an annular in-flow oil chamber 23 adds at least one speed range to the system, making it a multiple speed jack system. Using a system of two annular in-flow oil chambers 23 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com