Cable tie with wide neck
a cable tie and wide neck technology, applied in the direction of hose connection, flexible container closure, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the tensile strength through the section, reducing the tensile strength, and reducing the area through the section, so as to improve flexibility and bending, improve the neck design, and reduce the strength of the loop
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
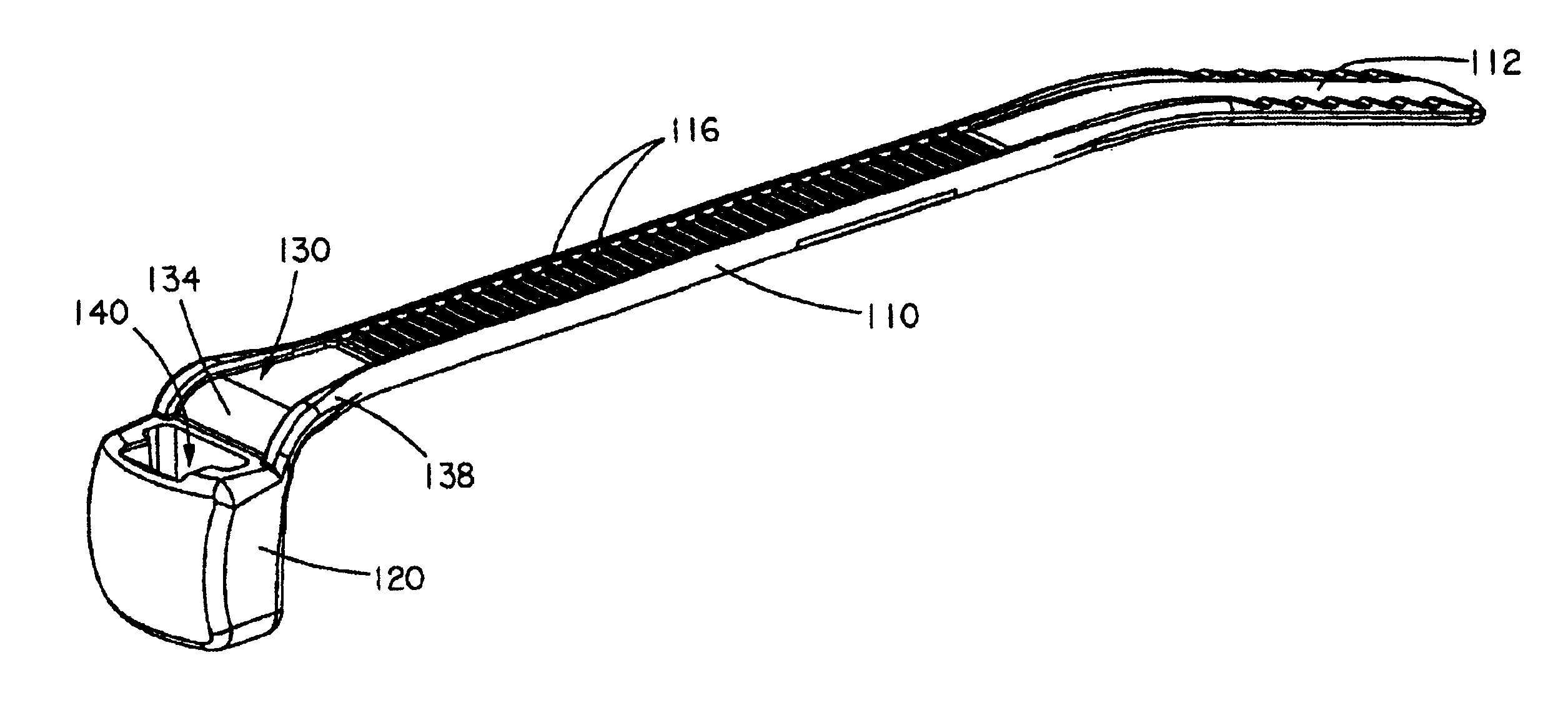
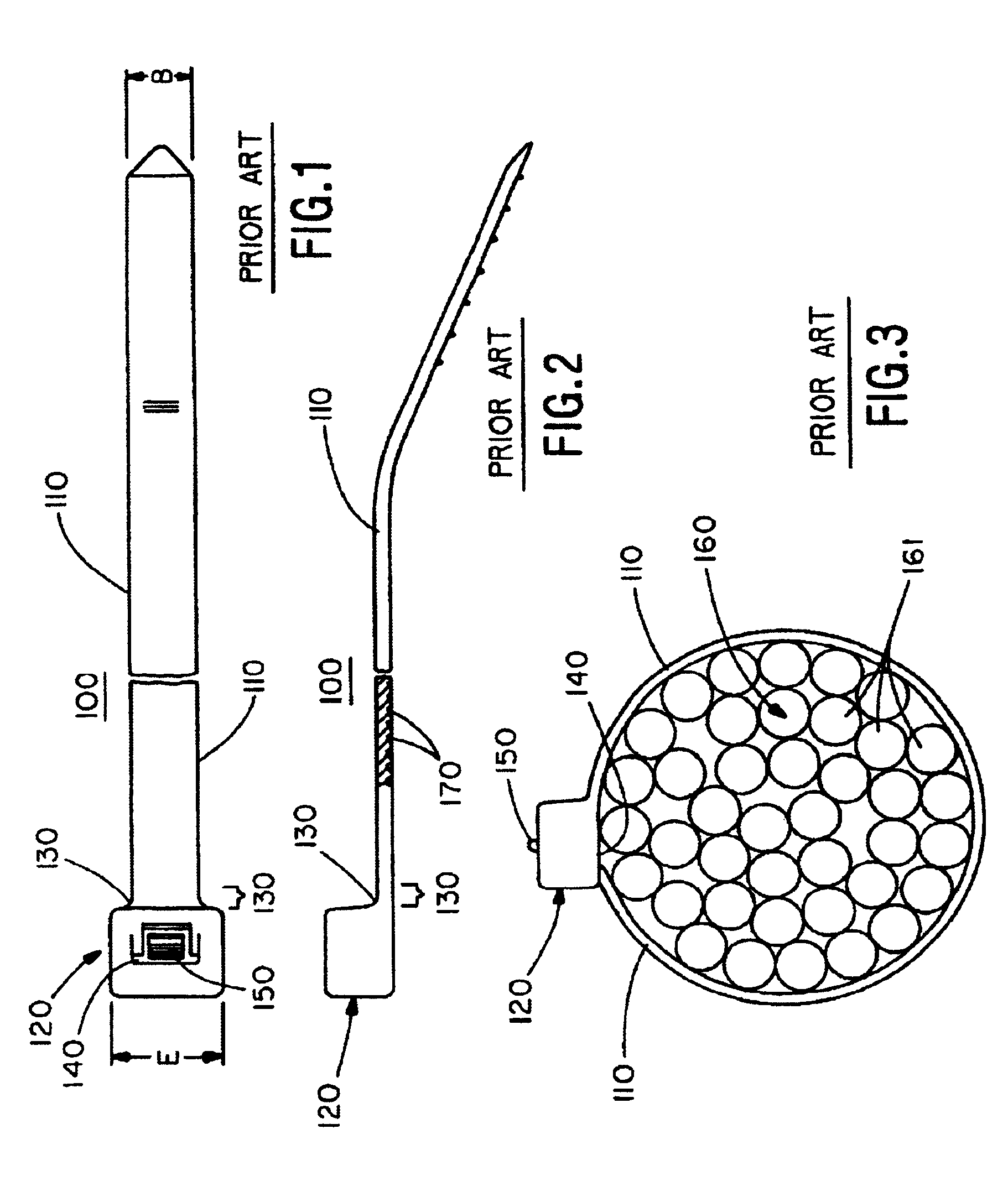
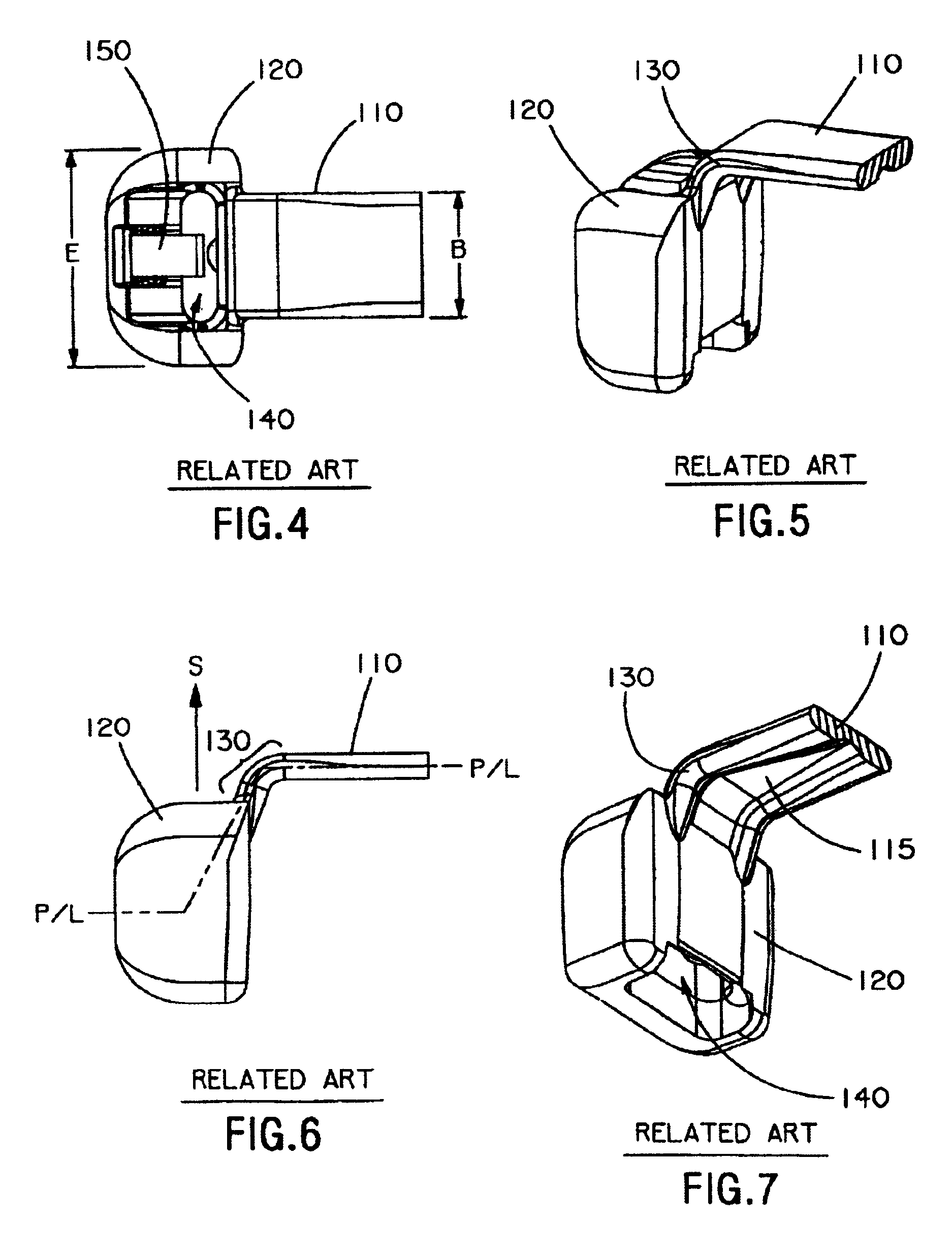
[0042]The invention relates to a cable tie having improved flexibility at a neck section of the cable tie, which is particularly important in a bent neck type cable tie. Conventional cable ties primarily use neck cross-sections that substantially correspond to the cross-section of the strap (see FIG. 10). While this results in a neck section that has a tensile strength equal to the rest of the strap, it results in the previously described problems of bent neck cable ties with a stepped parting line.
[0043]The strap thickness, parting line angle, and strap body edge radii limit the size of the radii that can transition from cable tie head to neck in a bent neck type cable tie. The general equation for the moment of inertia for a simple rectangular cross-section cable tie is I=(B×T3) / 12 where B is the width of the strap and T is the thickness of the strap. The design of FIGS. 8-9 results in a neck with limited flexibility as the neck cross-section is approximately the same as the cross...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com