High-speed digital receiver parallel adaptive blind equalizing method
A digital receiver, self-adaptive technology, applied in baseband system components, electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve problems such as inability to achieve high-speed equalization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
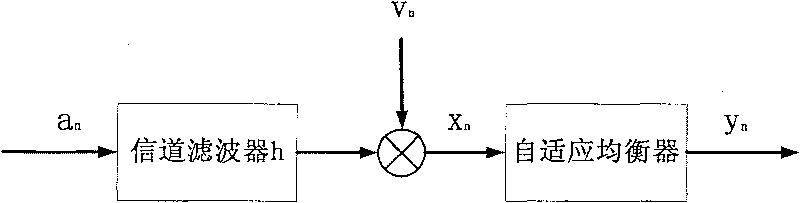
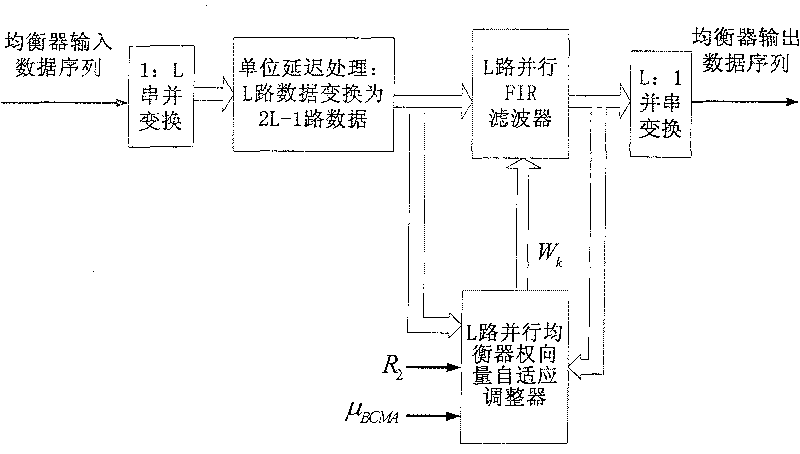
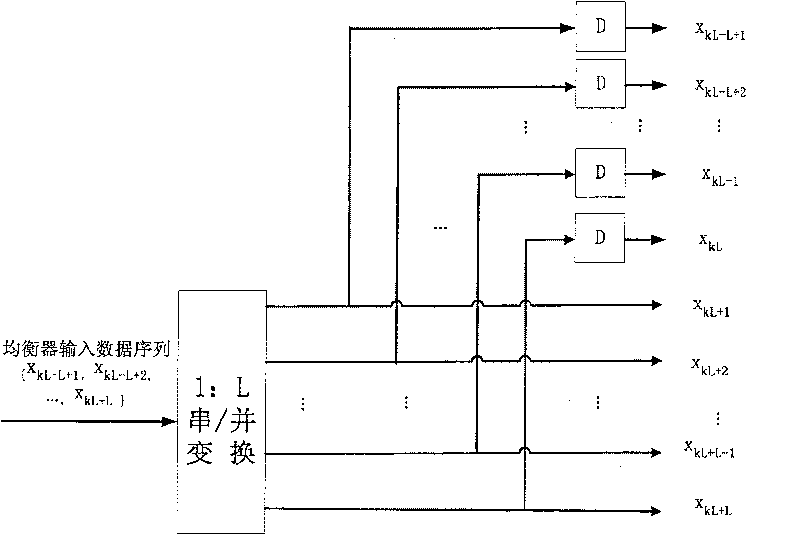
[0020]In high-speed digital communication, when the channel changes rapidly, it is difficult to track accurately, and high-speed transmission will bring large signal group delay distortion, the initial adjustment of the tap coefficient of the equalizer has nothing to do with the training sequence, that is, self-recovery or "Blind" recovery. See J.G. Proakis, Digital Communications, 4th ed., McGraw-Hill Inc. N.Y., 2001. In addition, it operates on each data symbol, and the training process is uninterrupted, so the blind algorithm will better adapt to the situation of channel time variation and large group delay distortion. The most commonly used algorithm for blind equalization is CMA, which was developed by D.N.Godard in D.N.Godard, "Self-Recovering Equalization and Carrier Tracking in Two-Dimensional Data Communication Systems", IEEE Trans.on Communications, vol.COM-28, Nov.1980: 1867 - Proposed in 1875. The CMA method mainly minimizes the defined non-convex cost function, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com