Neckdown detection control method for arc welding of consumable electrode
A melting electrode, arc welding technology, applied in arc welding equipment, welding equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as reducing sputtering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
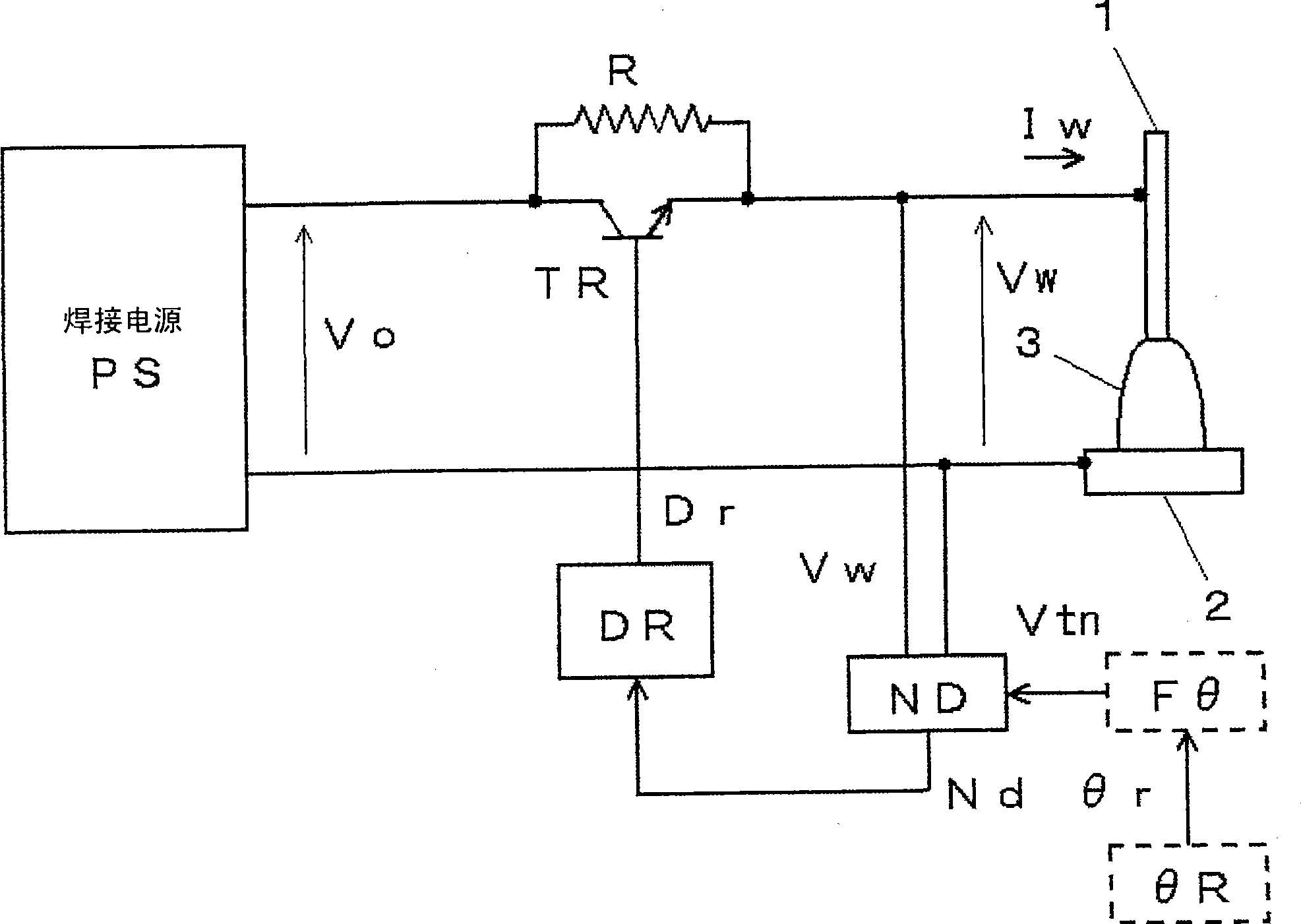
[0101] figure 1 It is a block diagram of a welding device for implementing the necking detection control method according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. This figure is similar to the above Figure 9 Correspondingly, the same symbols are assigned to the same modules and their descriptions are omitted. Below, with reference to the accompanying drawings Figure 9 The different modules indicated by dashed lines are illustrated.
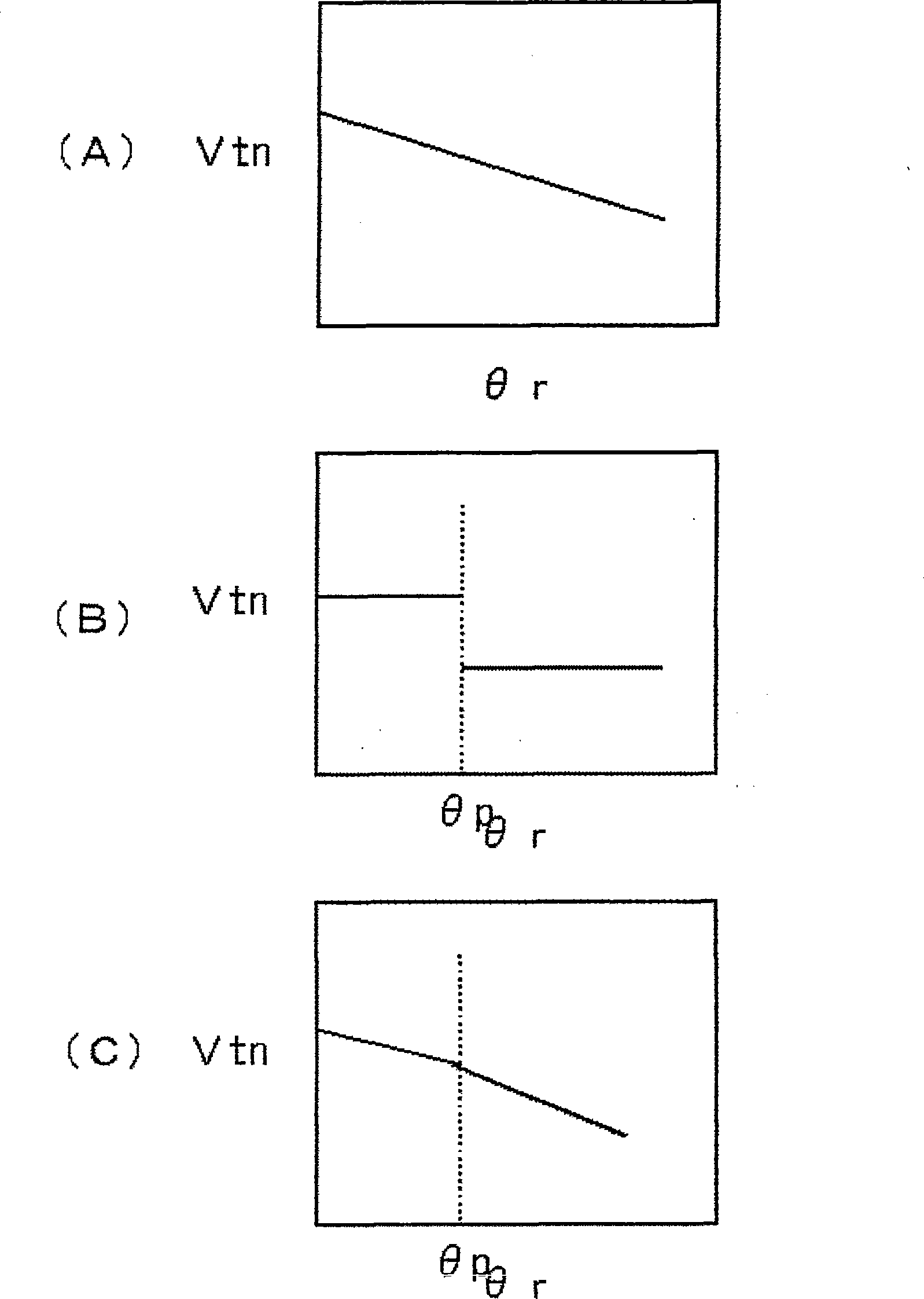
[0102] The advance angle setting circuit θR outputs a predetermined advance angle setting signal θr. The advance angle-corresponding constriction detection reference value setting circuit Fθ takes the advance angle setting signal θr as input, and calculates the constriction detection reference value signal Vtn by using a predetermined advance angle-corresponding constriction detection reference value setting function f(θr). value and output. Corresponding necking detection reference value setting function Vtn=f(θr) of this advancing angle...
Embodiment approach 2
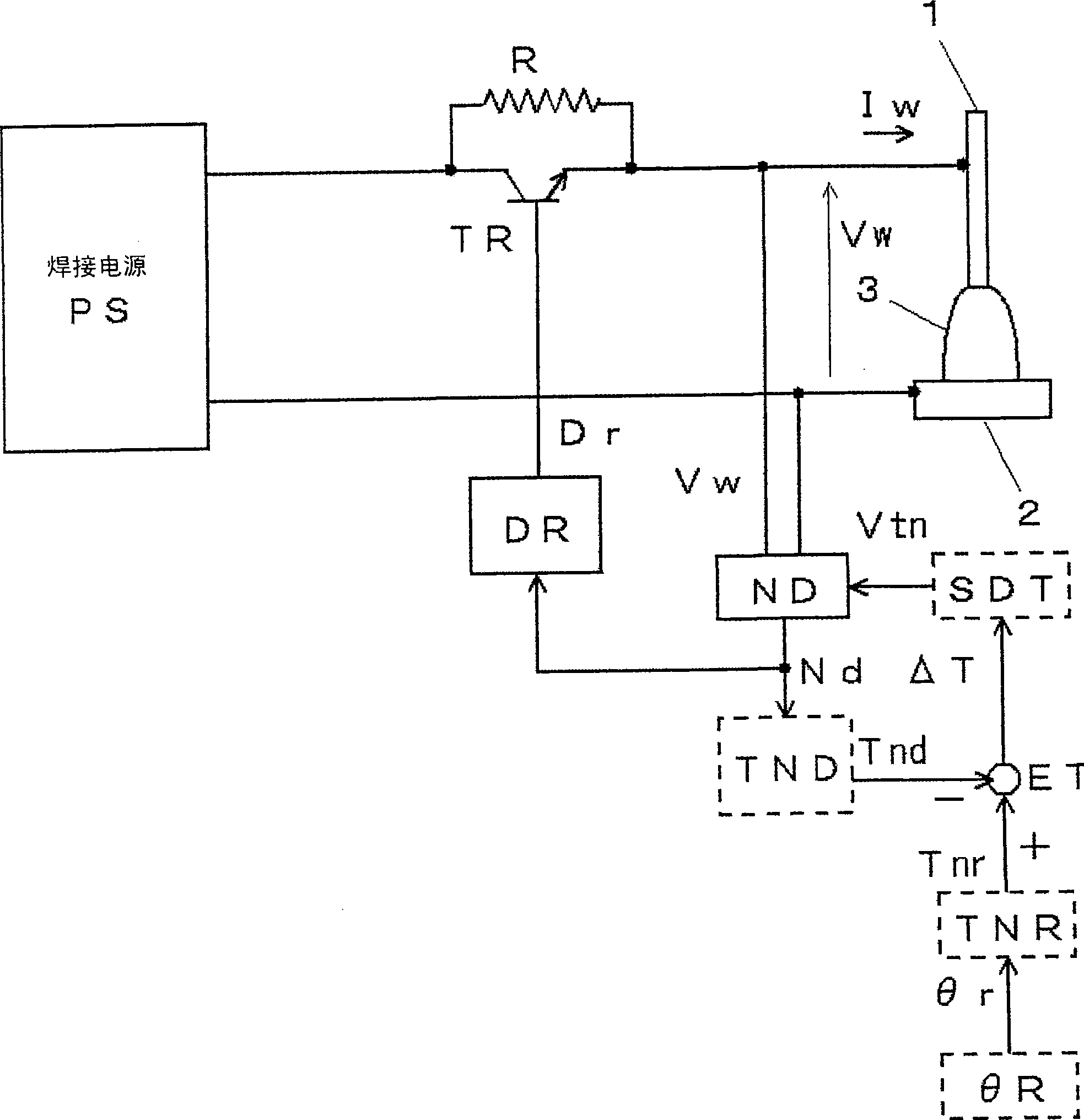
[0110] image 3 It is a block diagram of a welding device for implementing the necking detection control method according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. In this figure against the above Figure 9 The same modules are assigned the same symbols and their descriptions are omitted. Below, yes and Figure 9 The different modules indicated by dashed lines are illustrated.
[0111] The constriction detection time detection circuit TND receives the constriction detection signal Nd as input, detects the constriction detection time Tn for each short circuit, calculates their average value, and outputs the constriction detection time detection signal Tnd.
[0112] The advance angle setting circuit θR outputs a predetermined advance angle setting signal θr. The advance angle corresponding constriction detection time setting circuit TNR takes the advance angle setting signal θr as input, and outputs the constriction detection time setting signal Tnr according to a predetermi...
Embodiment approach 3
[0120] Figure 5 It is a waveform diagram of a short-circuit current showing a constriction detection control method for molten electrode arc welding according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. Figure (A) is a waveform diagram when the advancing angle of the welding torch is small, and Figure (B) is a waveform diagram when the advancing angle is large. The following description will be made with reference to this figure.
[0121] At time t1, when the droplet formed at the tip of the welding wire and the base metal are in a short-circuit state, the short-circuit current, which is the welding current energized by the short-circuit load, increases. As shown in the figure (A), when it is detected that the occurrence of necking in the droplet is detected at time t2, the short-circuit current suddenly decreases. When the arc occurs again at time t3, the welding current increases. The same applies to the case of the figure (B). However, in Embodiments 1 and 2, since the a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com