Styrenated terpene resin as well as methods of making and using the same
一种苯乙烯化萜烯、苯乙烯的技术,应用在聚合物领域,能够解决昂贵催化剂体系、有毒、经济合理性障碍等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Example 1 (Using α, β, sty - ie with 0% limonene: Inventive process fed at -10°C)
[0076] A 1.0 liter flask was charged with 140 g of a terpene resin solvent (xylene) recovered from Arizona Chemical's Panama City factory and 10.5 g of anhydrous aluminum chloride, and the suspension was stirred at ambient temperature under a nitrogen atmosphere. The suspension was then cooled to -10°C. Using the addition funnel, mix 175 g in 30 minutes Blends of α-pinene, β-pinene and styrene (weight ratio 35:35:30) was added to the flask while maintaining the polymerization temperature at -12—-8°C (external cooling using ethanol-dry ice mixture if necessary). After the blend feed was complete, the reaction was stirred at -12 to -8°C for an additional 2 hours. Subsequently, the contents were warmed to 25°C and stirred for 3 hours. At the end of 3 hours, the contents were quenched with 100 g of cold water (to neutralize the catalyst). The remaining steps of the method were as desc...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Example 2 (inventive process using α, β, limo, sty-: feed at -10°C)
[0078] Except that the catalyst charge was 6.1 g and within 60 minutes the Alpha-pinene, beta-pinene, limonene, and styrene blend of (The weight ratio is 30:37:3:30) into the flask while keeping the polymerization temperature at -12—-8°C, using the same method as in Example 1. Immediately after the blend feed was complete, the reaction was warmed to 45°C and stirred for 90 minutes. The resulting resin had the following properties: softening point = 103.1°C, yield = 89.0%, clear color = 2 Gardner.
Embodiment 3
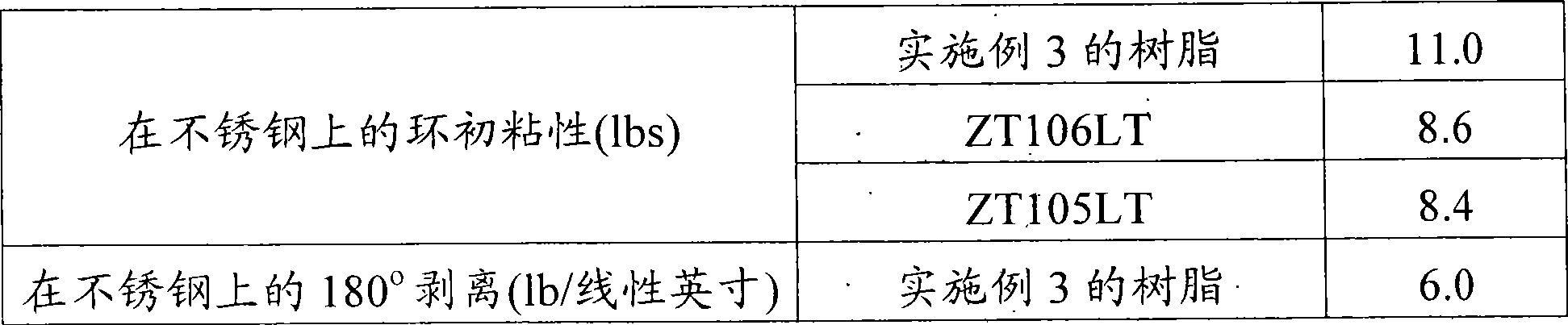
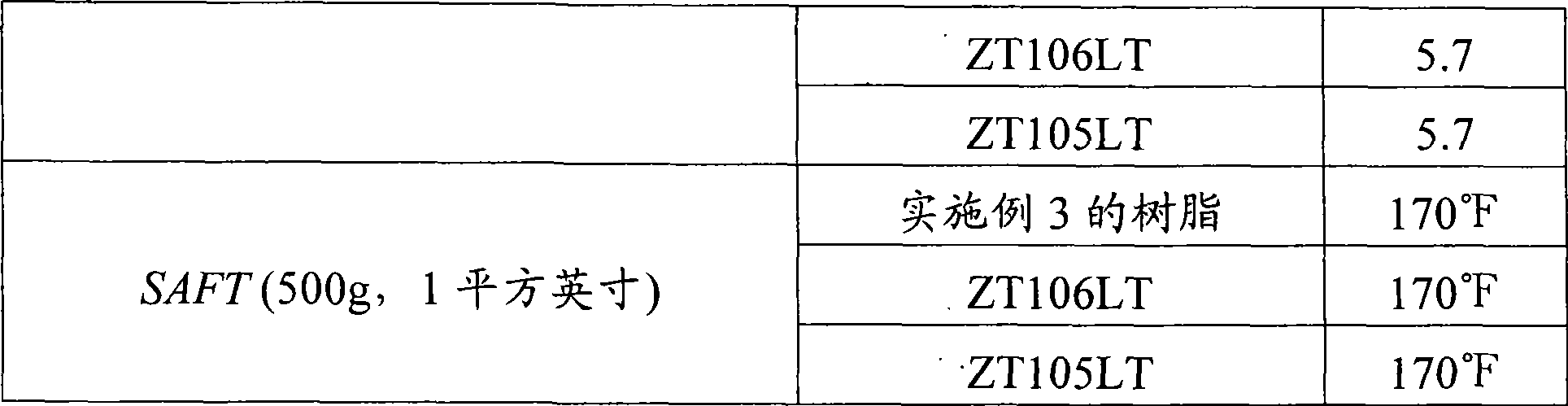
[0079] Example 3 (Inventive process using α, β, limo, sty-: feed at +5°C)
[0080] Except that the polymerization temperature is +5°C and within 60 minutes the α-pinene, β-pinene, limonene and styrene blend (The weight ratio is 30:37:3:30) into the flask, while keeping the polymerization temperature at +3—+7°C, using the same method as in Example 1. Immediately after the blend feed was complete, the reaction was warmed to 45°C and stirred for 90 minutes. The resulting resin had the following properties: softening point = 103.9°C, yield = 88.0%, clear color = 1+Gardner.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com