Uplink/downlink retransmission method based on wireless communication time division duplexing system
A time-division duplex system and wireless communication technology, which is applied in the direction of error prevention/detection using the return channel, communication between multiple stations, etc., can solve problems such as no solution for uplink data or downlink data retransmission, etc. To achieve the effect of making up for the retransmission mechanism
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
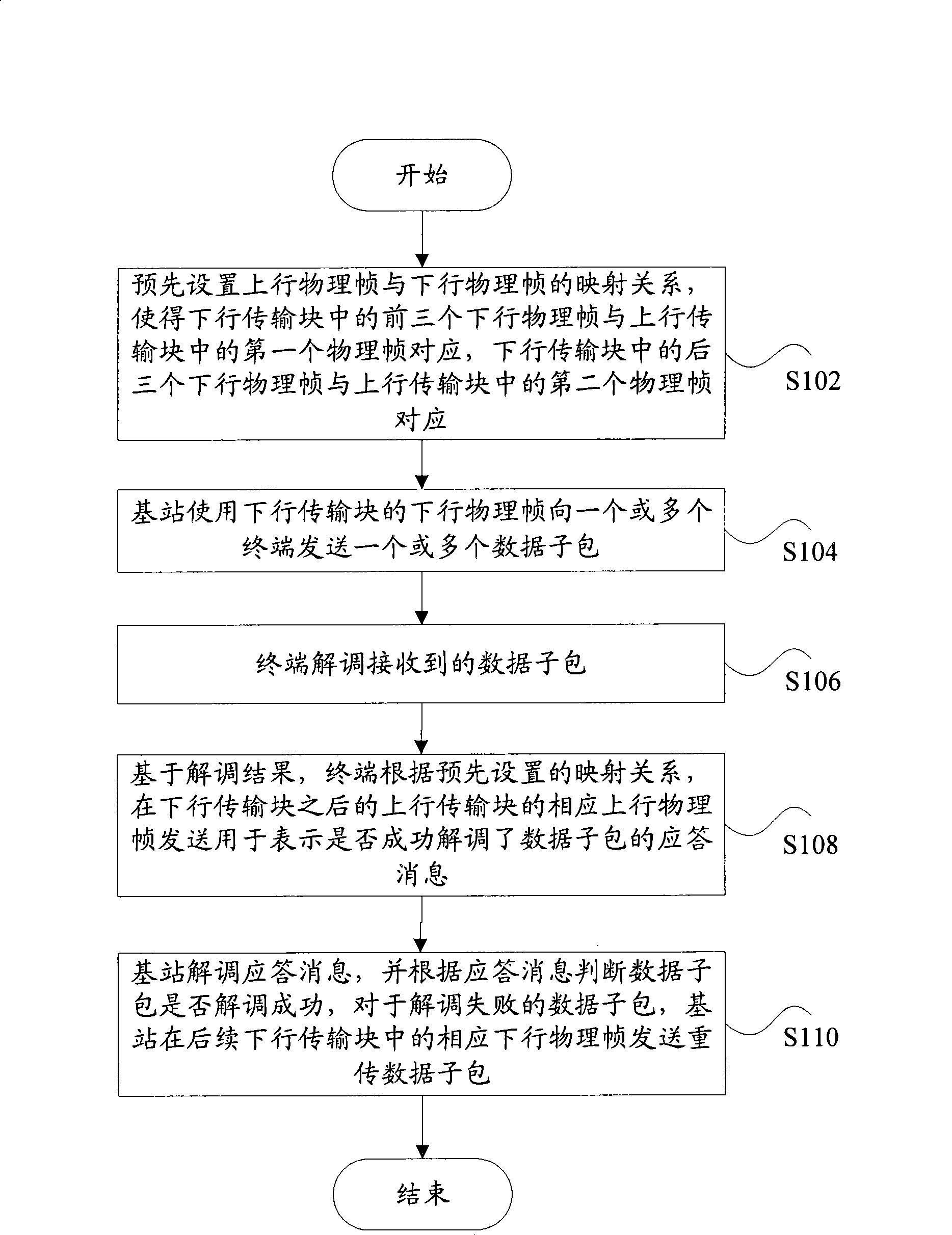
[0032] First of all, in view of the lack of a retransmission mechanism in the downlink data transmission of the TDD6:2 mode, the embodiment of the present invention provides a downlink retransmission method based on a wireless communication TDD system. The above wireless communication TDD system is based on a continuous The downlink transmission blocks of 6 downlink physical frames are used for downlink transmission, and the uplink transmission blocks including 2 consecutive uplink physical frames are used for uplink transmission in a TDD mode (ie, TDD6:2 mode).
[0033] figure 1 It is a flowchart of a downlink retransmission method based on a wireless communication TDD system according to an embodiment of the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes the following processing:
[0034] Step S102, preset the mapping relationship between the uplink physical frame and the downlink physical frame, so that the first three downlink physical frames in the down...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Embodiment 2: Delay-sensitive business processing with fast device processing capability
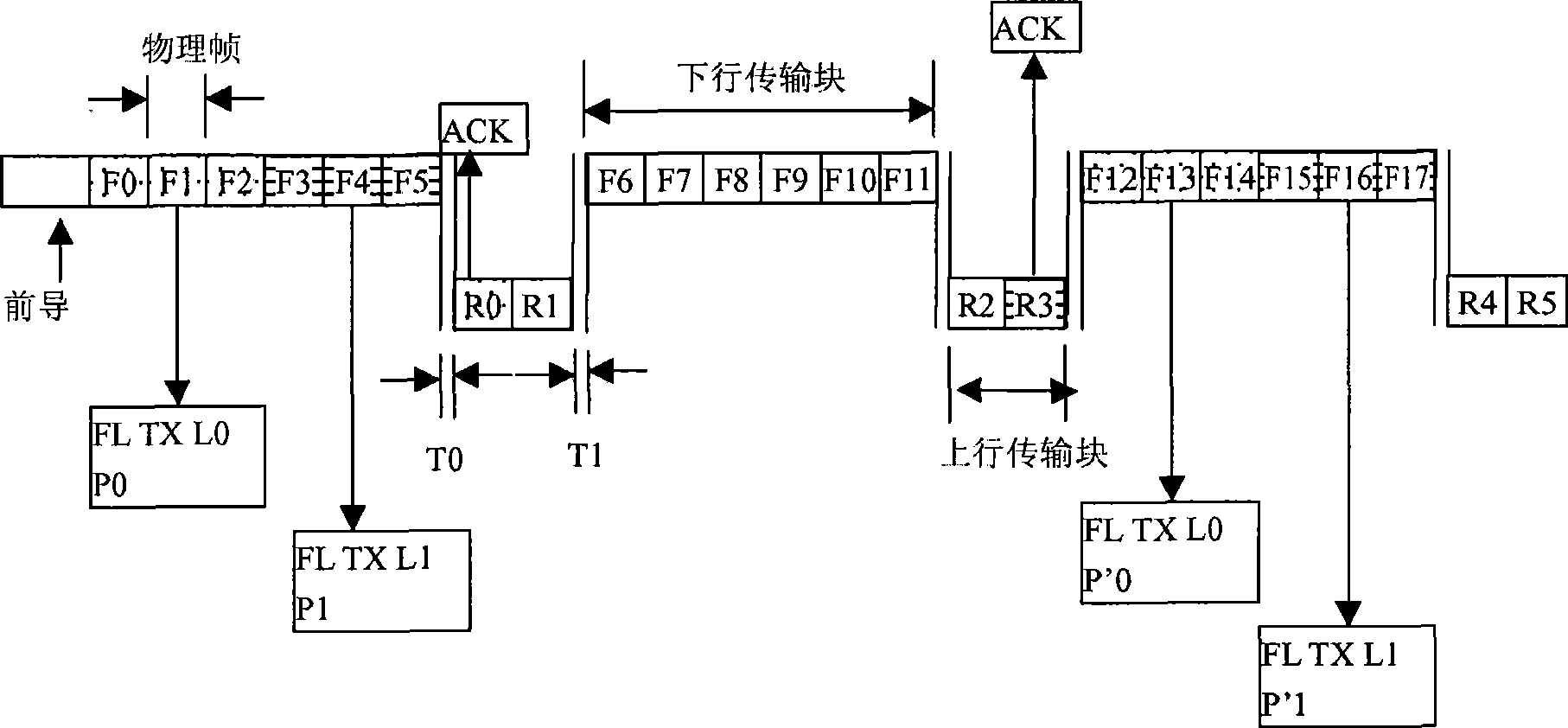
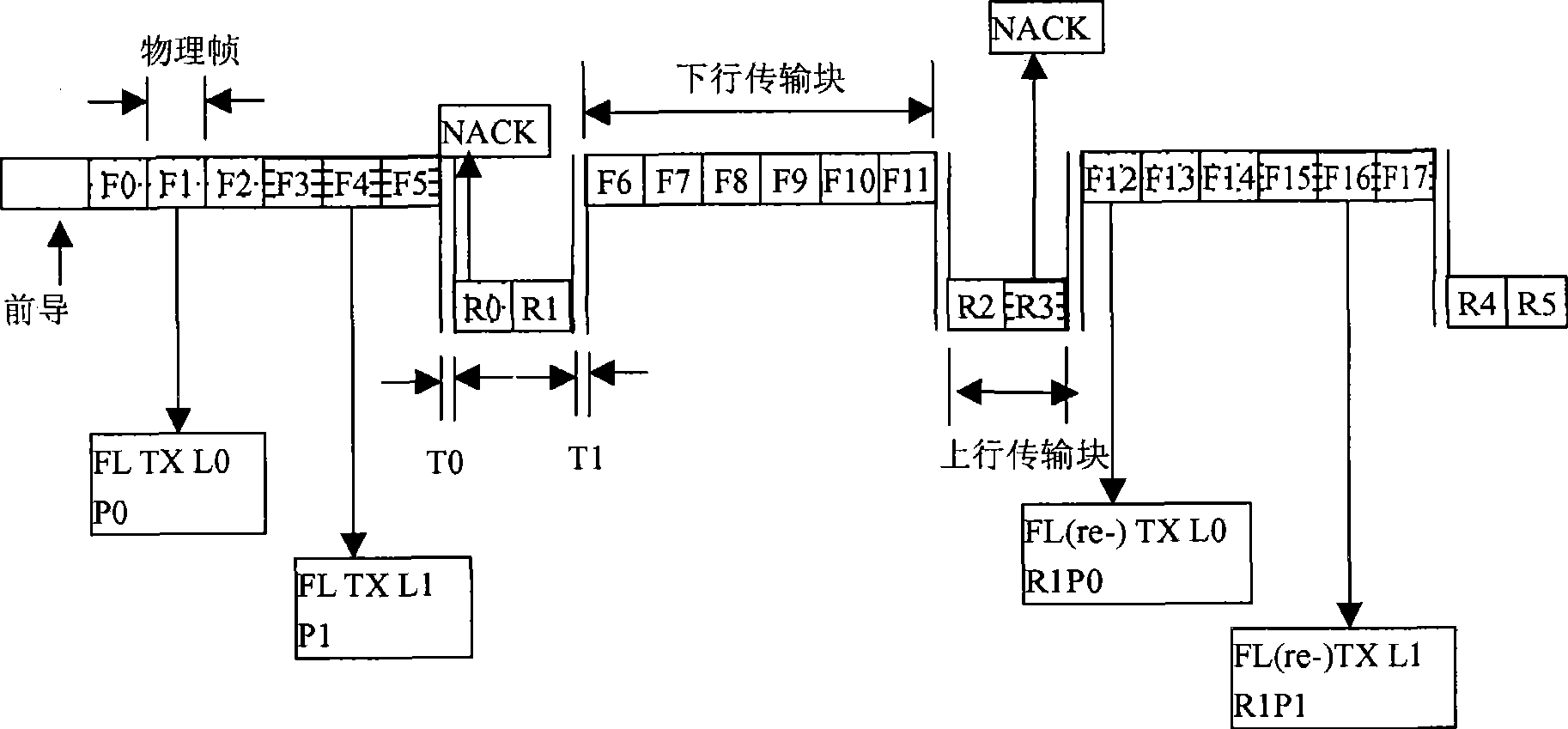
[0073] In this embodiment, after demodulating the data subpackets at L0 and L1 positions, the terminal sends ACK or NACK messages respectively on the uplink transmission block composed of the next two consecutive uplink physical frames. ACK indicates that the terminal has successfully demodulated data, and NACK indicates that the terminal has not successfully demodulated data. The ACK / NACK messages at the two different positions respectively correspond to the data subpackets P0 and P1 at the two different positions of L0 and L1 respectively.
[0074] The base station demodulates the ACK / NACK messages at these two different positions. If it is an ACK message, it means that the terminal successfully demodulates the data, and the base station will place the corresponding physical frame group position on the downlink transmission block composed of the next 6 consecutive downlink physi...
Embodiment 3
[0099] In the superframe transmission unit, a downlink transmission block consists of 6 consecutive downlink physical frames. Among the six downlink physical frames, it is assumed that the second and third physical frames are set as the first physical frame group, and the fourth and fifth physical frames are set as the second physical frame group. For the convenience of explanation, the positions of these two physical frame groups are respectively defined as L0 and L1. The terminal sends uplink data to the base station through an uplink transmission block composed of two consecutive uplink physical frames, and the data subpackets sent from these two uplink physical frames are respectively defined as P0 and P1. The data subpackets of the two different physical frames may be sent to the base station by one terminal, or may be sent to the base station by different terminals. The starting position of the data subpacket transmission can be in the first uplink transmission block of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com