High-power density permanent magnetic brushless motor with moment holding function for mechanical arm
A permanent magnet brushless motor, high power density technology, applied in the direction of electromechanical devices, electrical components, magnetic circuit static parts, etc., can solve the problems of complex motor system structure, achieve complex program reduction, large torque output, and realize structure simple effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
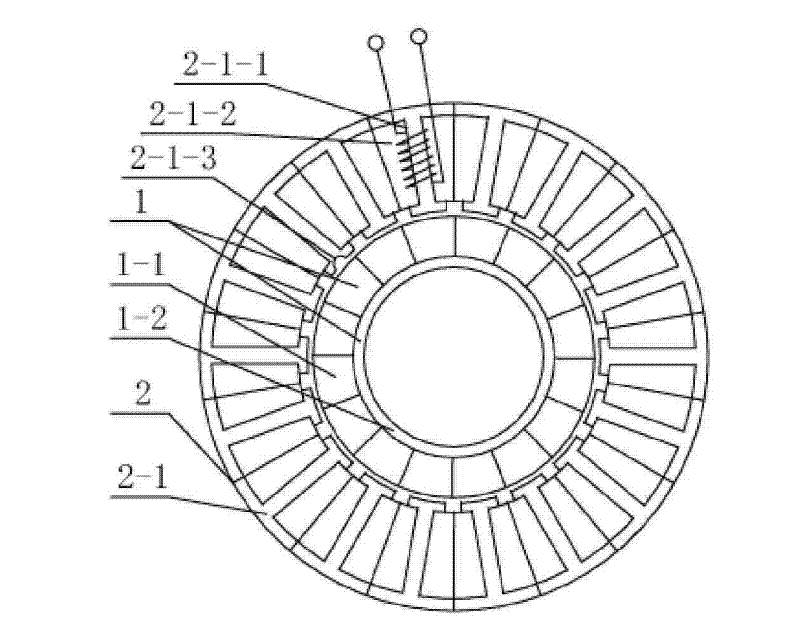
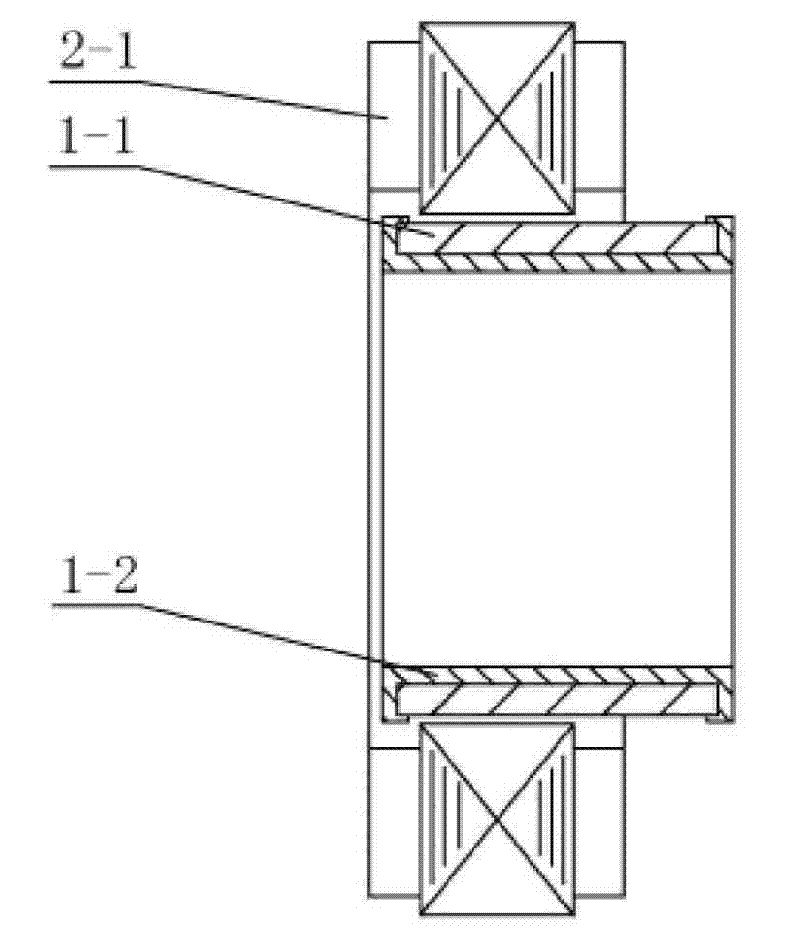
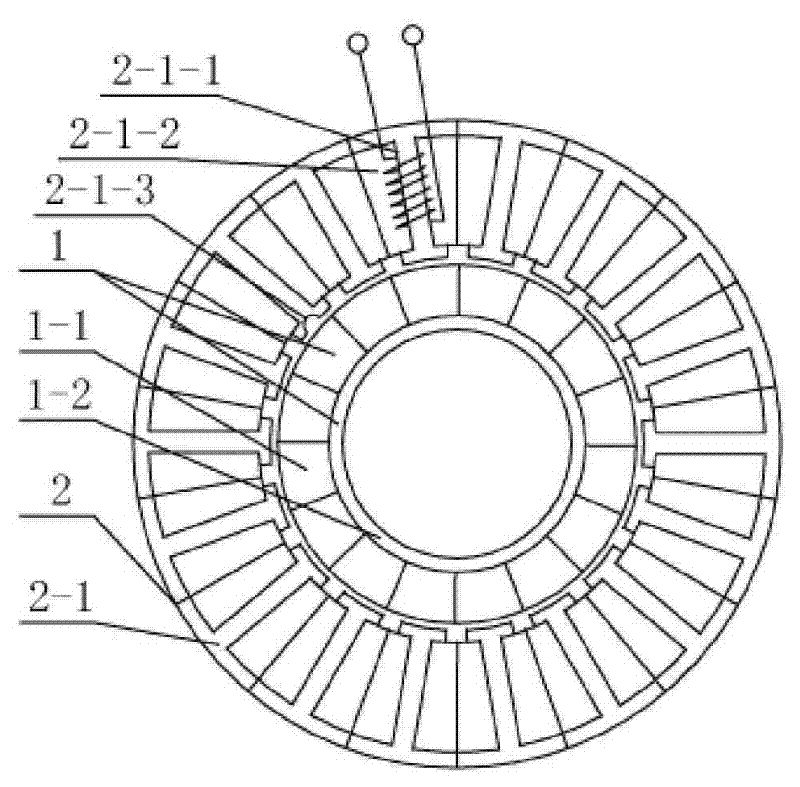
[0007] Specific implementation mode 1: the following combination Figure 1-Figure 2 To illustrate this embodiment, this embodiment includes a hollow disk permanent magnet rotor 1 and a stator 2. The hollow disk permanent magnet rotor 1 is composed of a rotor pole 1-1 and a snap ring rotor yoke 1-2, and the rotor pole 1-1 and The clasp-type rotor yoke 1-2 adopts a clearance fit; the stator 2 is composed of multiple stator cores 2-1, each stator core 2-1 has a stator tooth, and the multiple stator cores 2-1 are connected end to end to form each other The stator teeth 2-1-1 and the stator slots 2-1-2 are spaced apart. The stator teeth 2-1-1 are wound with three-phase symmetrical windings in fractional slots. The number of turns of each phase winding is equal. Each stator tooth The in-phase windings wound on 2-1-1 are connected in series with each other; there is an air gap between the inner circular surface of the stator core 2-1 and the outer circular surface of the rotor pole 1-...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0015] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the radius range of the semicircular groove 2-1-3 is 0.1 mm-0.2 mm. Other components and connection relationships are the same as in the first embodiment.
[0016] The radius of the semicircular groove 2-1-3 depends on the required positioning and holding torque. If the positioning and holding torque is required to be larger, the radius should be relatively larger, and vice versa.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0017] Specific embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and the first or second embodiment is that the air gap ranges from 0.25 mm to 0.35 mm. Other components and connection relationships are the same as those in the first or second embodiment.
[0018] The air gap is minimized on the premise of ensuring the assembly requirements, which can appropriately increase the air gap magnetic field density and improve the power density of the motor.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com