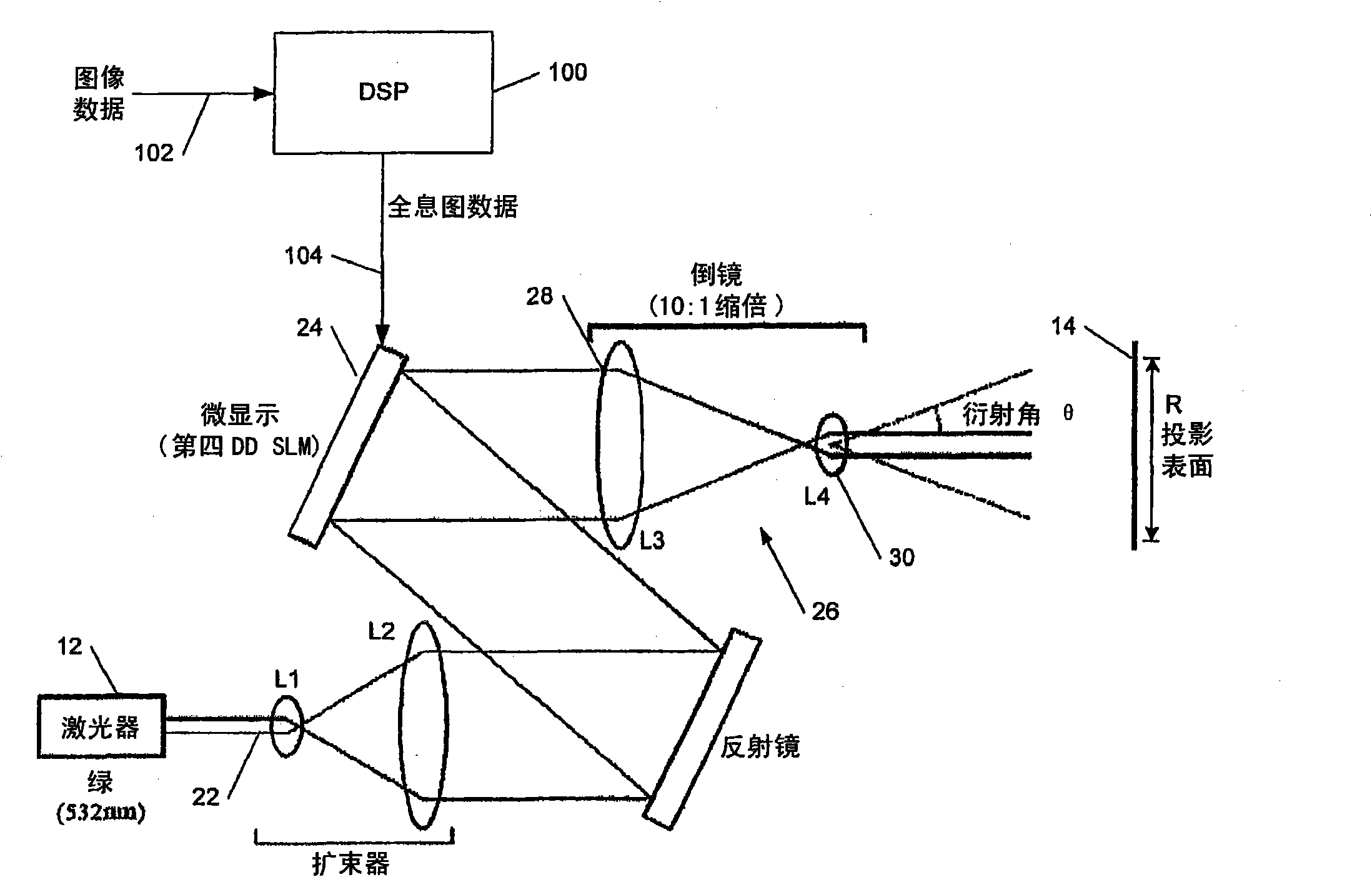
Holographic image display systems
A hologram, holographic technology, applied in the direction of hologram optical elements, characteristics of hologram objects, properties/properties of holograms, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
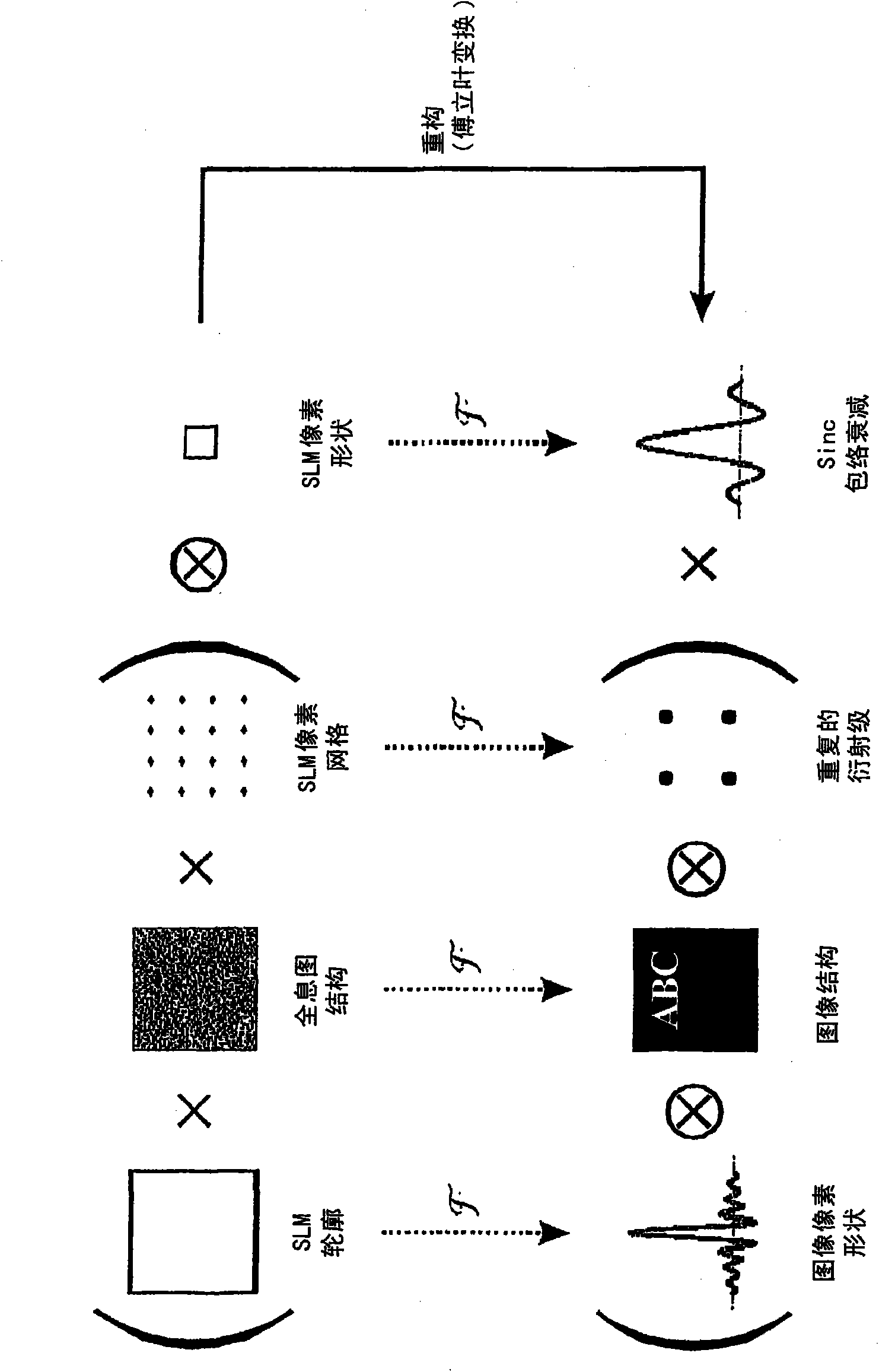
[0036] This invention describes a technique for increasing the diffraction efficiency of holographic projections by shifting the SLM pixel diffraction (sinc decay) envelope.
[0037] Holographically formed images suffer from an effect called "sinc decay" caused by square pixels on the SLM, where the SLM imposes a sinc-shaped intensity modulation centered at the zeroth order across the reconstructed field, resulting in Undesired strength reduction in the edge direction. This leads to two problems.
[0038] 1. Image intensity is no longer uniform across the field. This can be compensated by pre-multiplying the input image by modulating the inverse of the sinc envelope.
[0039] 2. The point gradually decays along the direction away from the center of the sinc envelope, resulting in a significant decrease in diffraction efficiency. Precisely, light moves from the edge of the first diffraction order (first sinc lobe) to an undesired higher diffraction order (sinc tail). So to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com