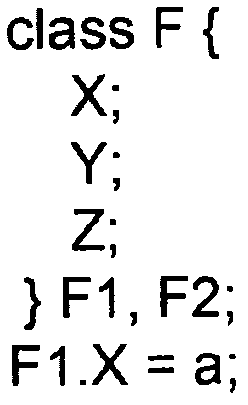Efficient automated translation of procedures in constraint-based language
A technology of automatic translation and constraint programming, applied in the field of automatic translation, can solve the inefficiency of the pure declarative programming model and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 7
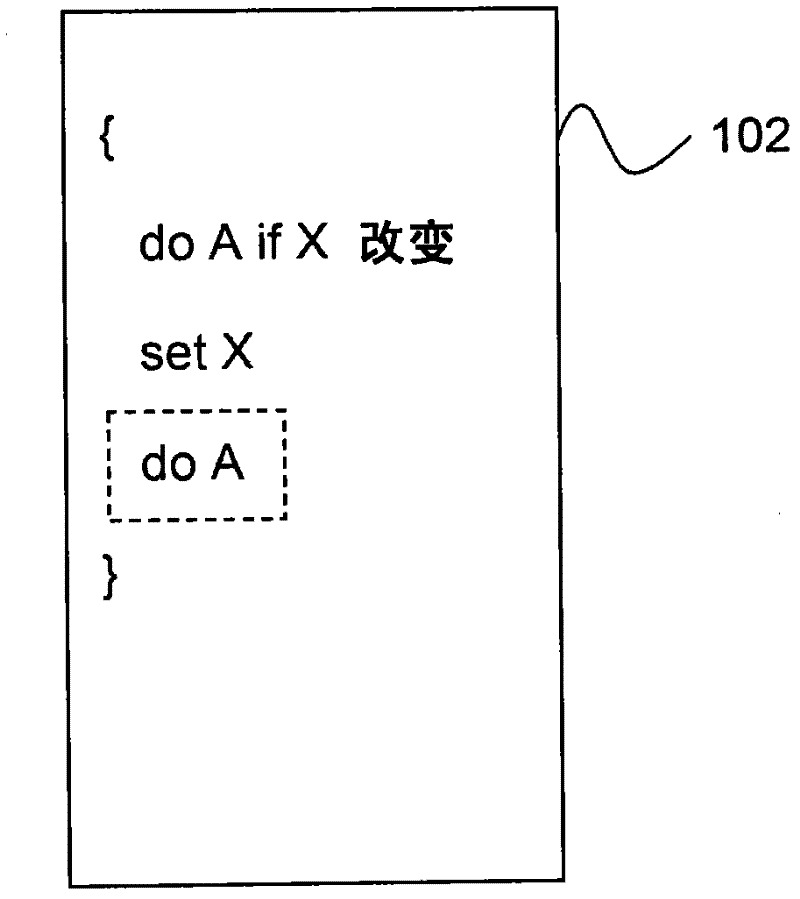
[0128] Example 7 shows how to optimize constraint implementation by providing state—in this case oldPart—in the context associated with the constraint set. In the case of other constraints, such as those specifying that the output be an approximation of the first derivative of the input, the constraint set may require additional states in order to perform the required computation.
[0129] In case of an input specified as a collection, the corresponding internal representation may use the reactor class as the entry type of the collection, including the "next" pointer and key fields required for the collection implementation. That is, reactor classes are used instead of "entry" structures used to implement non-intrusive collection data structures such as hash tables, trees, and linked lists, saving space and additional code compared to using separate entry objects.
[0130] In one embodiment, the internal representation may include a constructor procedure for a constraint set t...
example 1
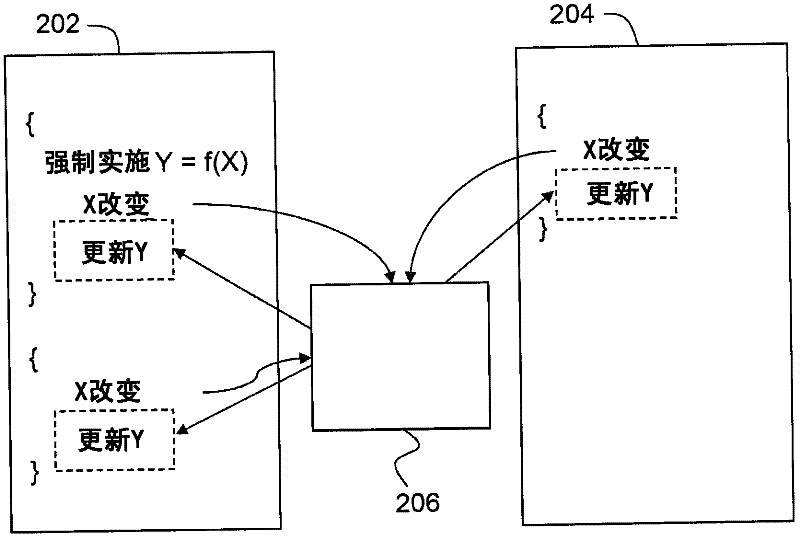
[0132] The second constraint in Example 1 will be triggered by a change in the reported total. This constraint can be implemented with a similar structure, with a reactor for the report total data member as well as the billing "avgPrice" data member. Thus, an update to the total results in a call to the reactor, which causes the "cost" data member in the report to be recalculated by the implementation of the "onTotal" function.
[0133] As an optimization, an embodiment may implement this constraint set to determine that updating report->total must also update report->cost, and report->total must not be updated by other means. Thus, implementations can dispense with a separate reactor for report->cost driven by changes to report->total, and simply update report cost, as shown in the extended version of "onPart" in Example 8 That maintains part of the function that reports totals.
[0134]
[0135] Here, the last line of the function implementation directly updates the rep...
example 10
[0162] Example 10 Imperative code triggered by an update of total
[0163] --------------------------------------------------
[0164] In one embodiment, the translator can be programmed with knowledge of recognizing and being able to generate expressions for the requirement cases of multi-way constraints, thereby generating errors on input processing when multi-way constraints that cannot be handled are specified. The programmer then needs to implement constraints using a combination of more fundamental constraints and / or imperative programming (if applicable). Since the translator can be programmed to recognize what it can handle (and thus also what it cannot handle), the translator does not produce executions that are incorrect implementations of the specified constraints. Furthermore, since the main purpose herein is to improve the simplicity of imperative programming by adding constraints rather than eliminating all expressive means except constraints, the advantages of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com