Method for improving electron label reading efficiency based on power control
An electronic tag and reading efficiency technology, which is applied in the field of improving the reading efficiency of electronic tags based on power control, can solve problems such as performance degradation, and achieve the effects of reducing the number, reducing the probability of conflict, and achieving a large degree of freedom.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
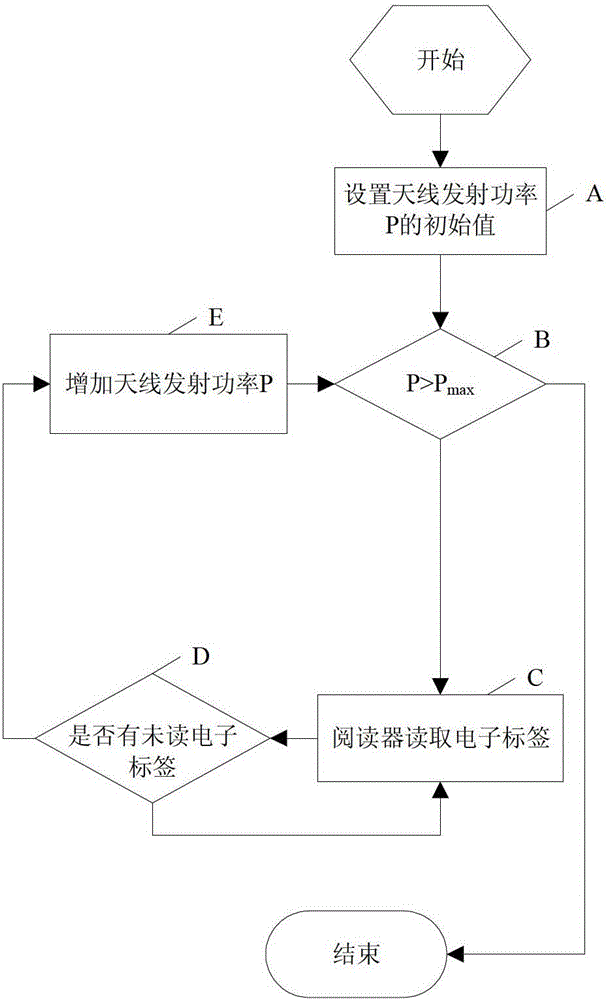
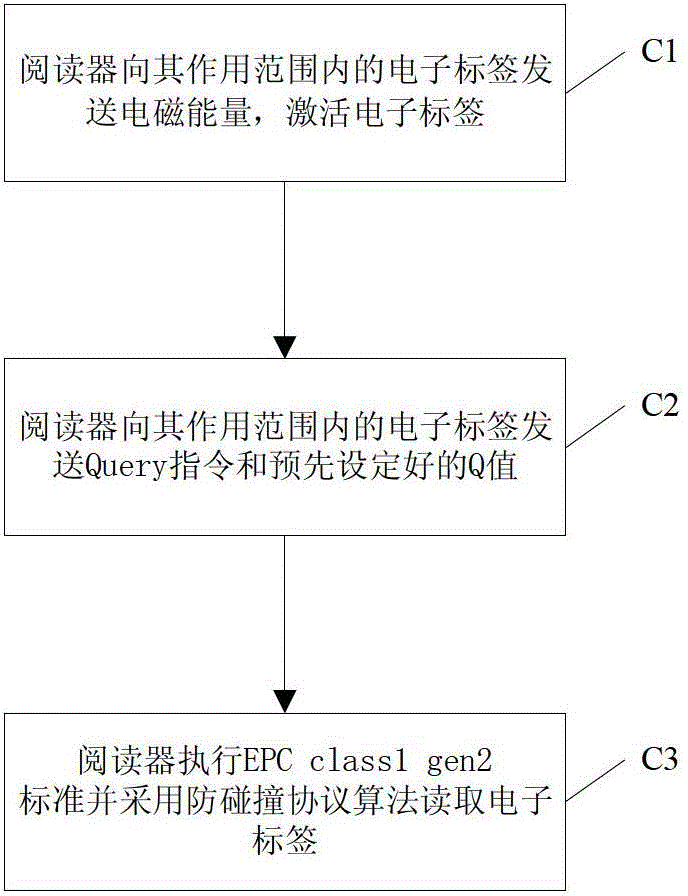
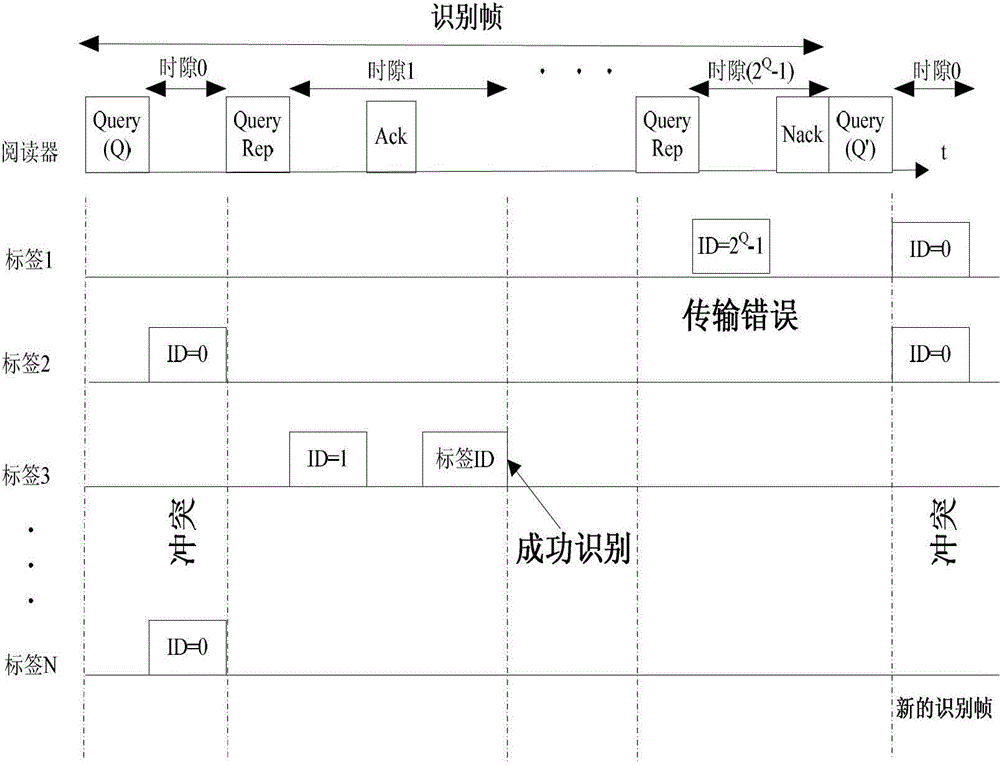
[0028] The invention provides a method for reducing the collision of radio frequency identification (RFID) electronic tags and improving the reading efficiency of the electronic tags by following the EPC class1 gen2 standard without any modification to the underlying structure or communication protocol of the electronic tag. The present invention realizes the grouping of the electronic tags within the action range of the reader through power control, and then identifies each group of electronic tags respectively, thereby avoiding the decline of the identification performance of the reader due to the increase in the number of electronic tags.
[0029] From the electromagnetic field and antenna theory, it can be known that the greater the transmitting power of the reader antenna, the smaller its range of action, and the smaller the distance of the electronic tag that the reader can read, and vice versa. In the application environment with dense electronic tags, by reducing the re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com