Modified propylene polymer
A technology for modifying propylene polymers, applied in the field of modified propylene polymers, which can solve problems such as increased fluidity, unusable modified propylene polymers, and low molecular weight, etc., and achieves an excellent balance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0040] In the preparation of the propylene polymer (A), in order to remove the residual solvent contained in the propylene polymer (A) or the ultra-low molecular weight oligomers produced during the preparation process, the propylene polymer (A) can be Drying is performed at a temperature at which the propylene polymer (A) melts. Examples of drying methods include those disclosed in JP 55-75410A and JP 2565753.
[0041] · Random copolymerization
[0042] As mentioned above, the random copolymer in the present invention includes: a random copolymer composed of a structural unit derived from propylene and a structural unit derived from ethylene; a random copolymer composed of a structural unit derived from propylene and a structural unit derived from Random copolymers composed of structural units of other α-olefins; random copolymers composed of structural units derived from propylene, structural units derived from ethylene, and structural units derived from other α-olefins oth...
Embodiment 1
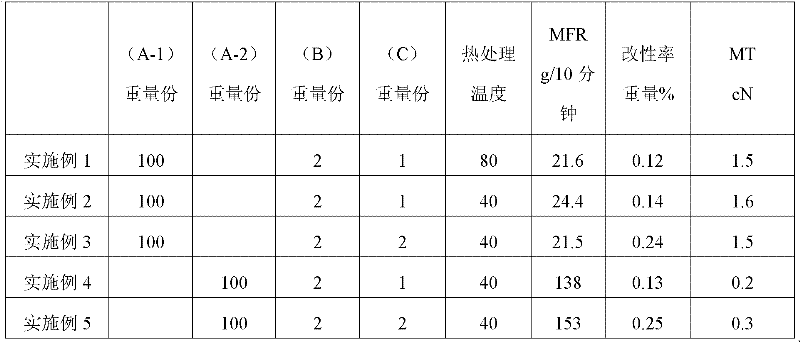
[0147] [Example 1, Comparative Example 1]
[0148] Mix the propylene polymer (A), the ethylenically unsaturated bond-containing compound (B) and the organic peroxide (C) uniformly, and then use an extruder to perform heat treatment under the conditions given in Table 1 to obtain modified propylene polymer. A single-screw extruder was used as the extruder. The preset barrel temperature is 80° C., and the preset screw speed is 75 rpm. The blending ratio of the propylene polymer (A), the ethylenically unsaturated bond-containing compound (B) and the organic peroxide (C) and the physical properties of the resulting modified propylene polymer (A) are given in Table 1. out.
Embodiment 2-5
[0149] [Example 2-5, Comparative Example 2]
[0150] A modified propylene polymer was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the preset temperature of the barrel was set to 40° C. and the screw speed was set to 65 rpm in the corresponding Example. The physical properties of the obtained modified propylene polymer are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melt flow index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melt flow index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap