Micro-electro-mechanical comb tooth mechanism capable of adjusting tooth gaps by electrostatic force
A tooth gap and electrostatic force technology, applied in the field of micro-electromechanical system structure, can solve the problems of wasting driving force, weak sensing detection signal, and increased gap, so as to increase the amplitude of sensing detection signal, increase detection sensitivity, The effect of expanding the scope of application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
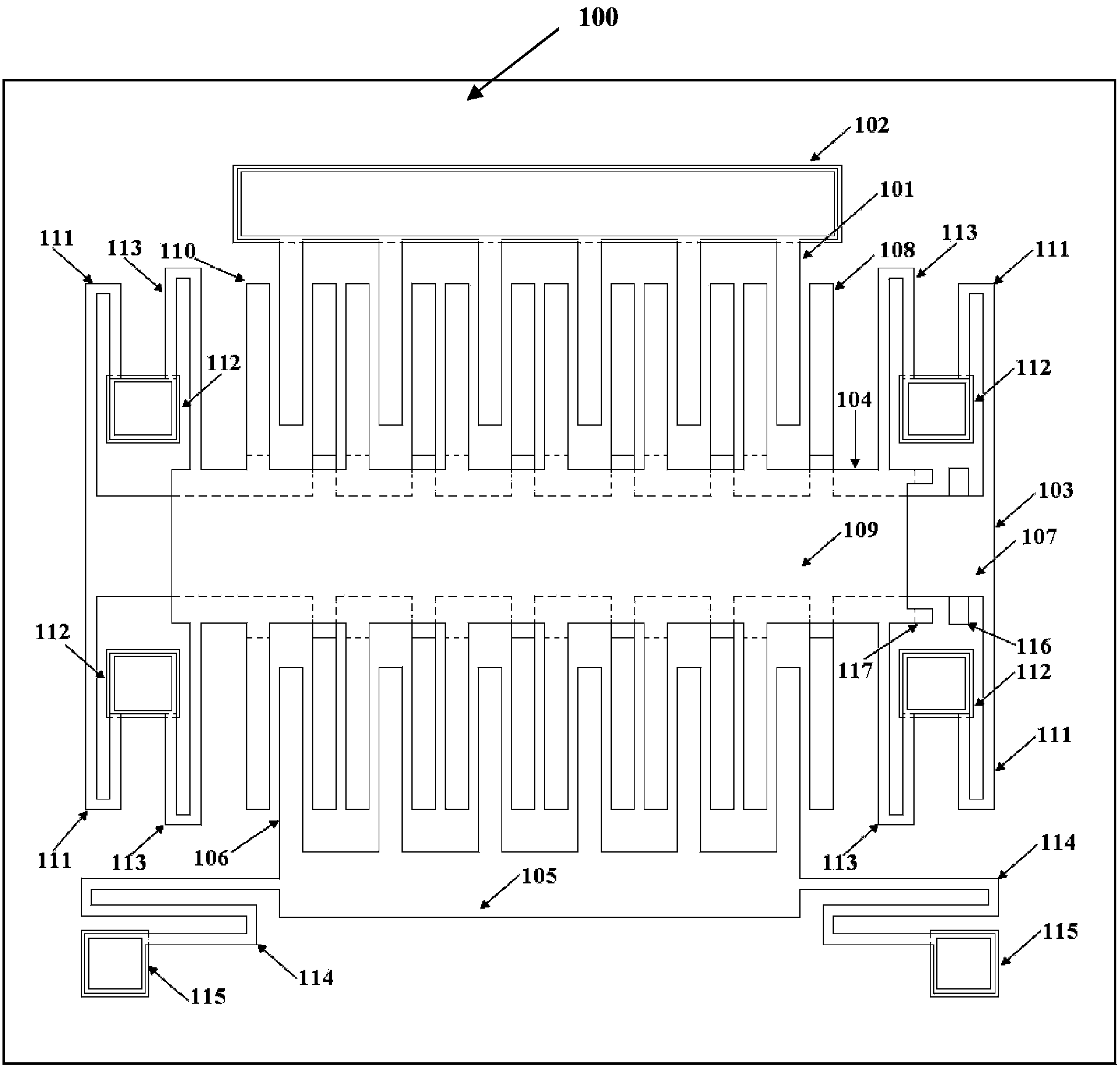
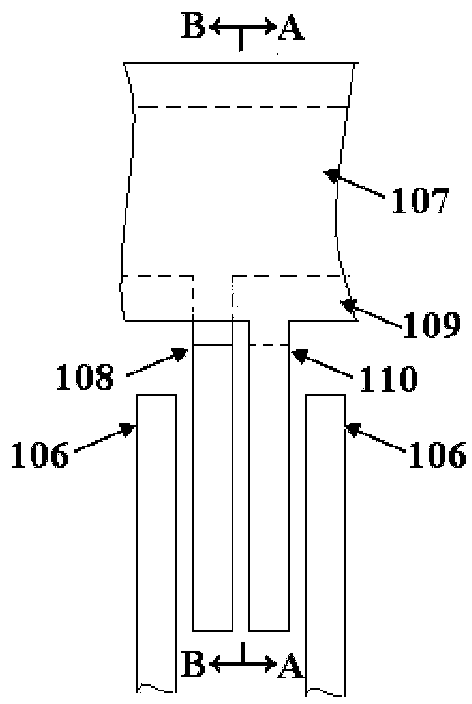
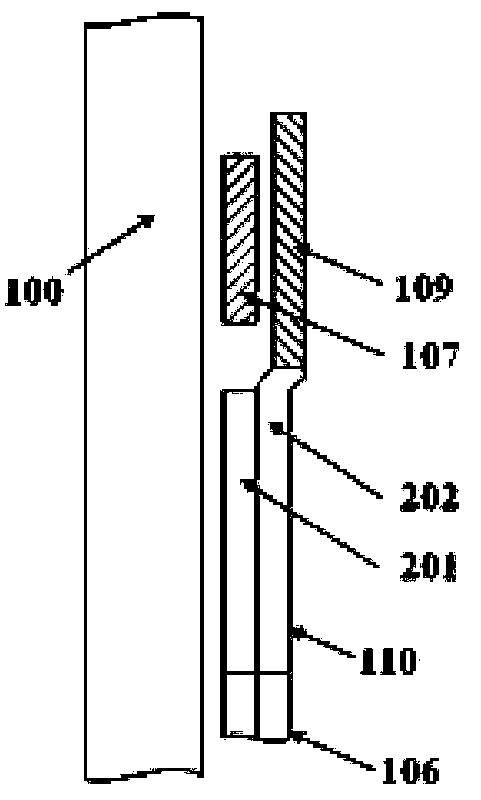
[0025] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 4 As shown, a micro-electromechanical comb tooth mechanism of the present invention that modulates the tooth gap by electrostatic force includes electrostatic driving teeth, fixed teeth consisting of left-moving fixed teeth 103 and right-moving fixed teeth 104, movable teeth, four first Anchor region 112 and insulating substrate 100 . The four first anchor regions 112 are respectively fixedly connected to the insulating substrate 100 . The left-moving fixed tooth 103 includes a first wide beam 107 , a left-moving comb tooth 108 , and four first folded beams 111 bent along the transverse direction. When the first folded beam 111 bent along the transverse direction moves, it can only move along the transverse direction. The left-moving comb teeth 108 are fixed on both sides of the first wide beam 107 . Both ends of the first wide be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com