Novel distributed optical fiber temperature and stress sensor
A distributed optical fiber and stress sensor technology, applied in the field of optical fiber sensing network, can solve the problem that the length of the sensing fiber is only tens to hundreds of meters.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
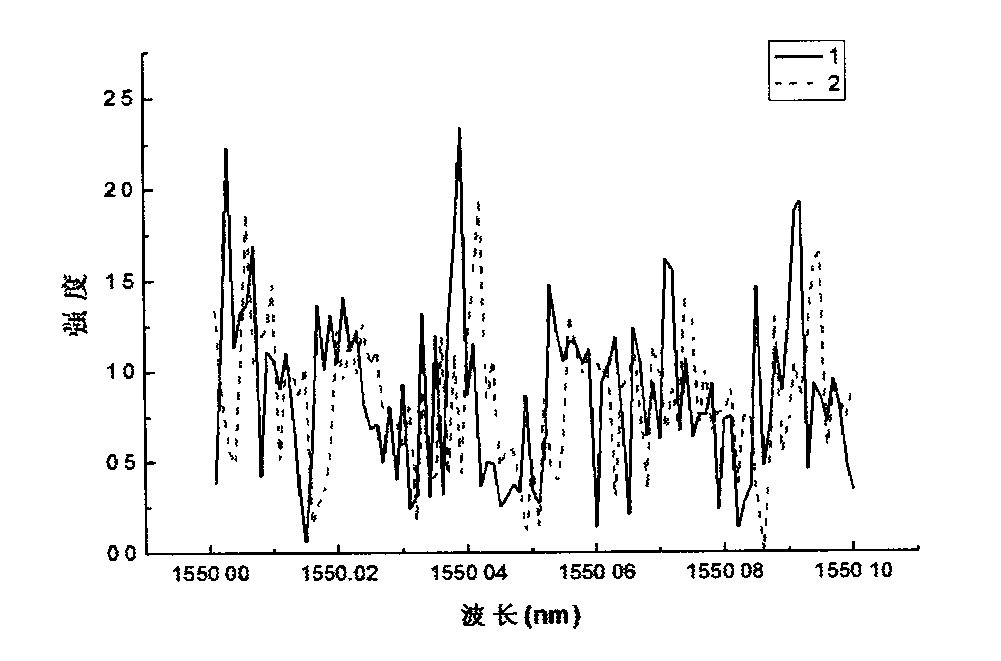
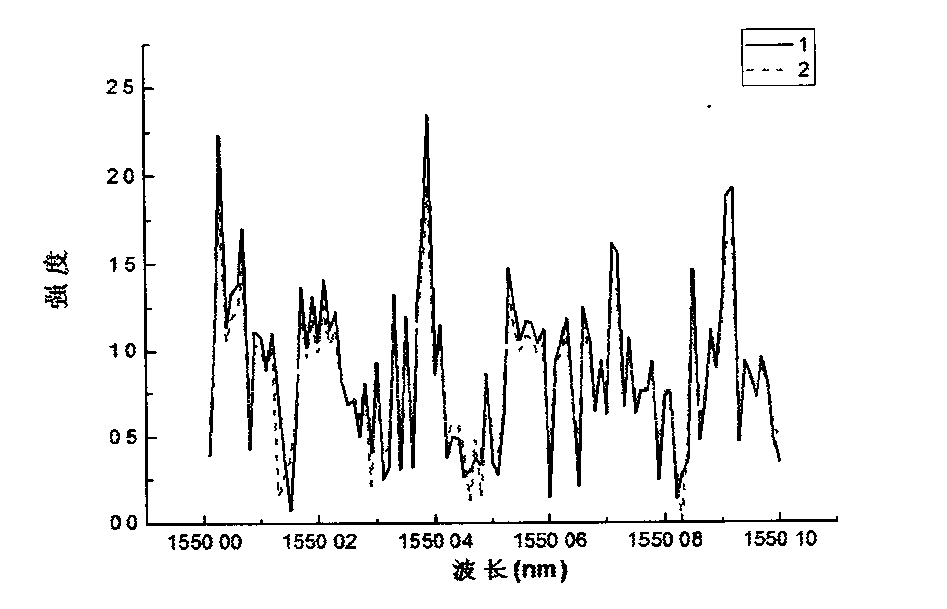
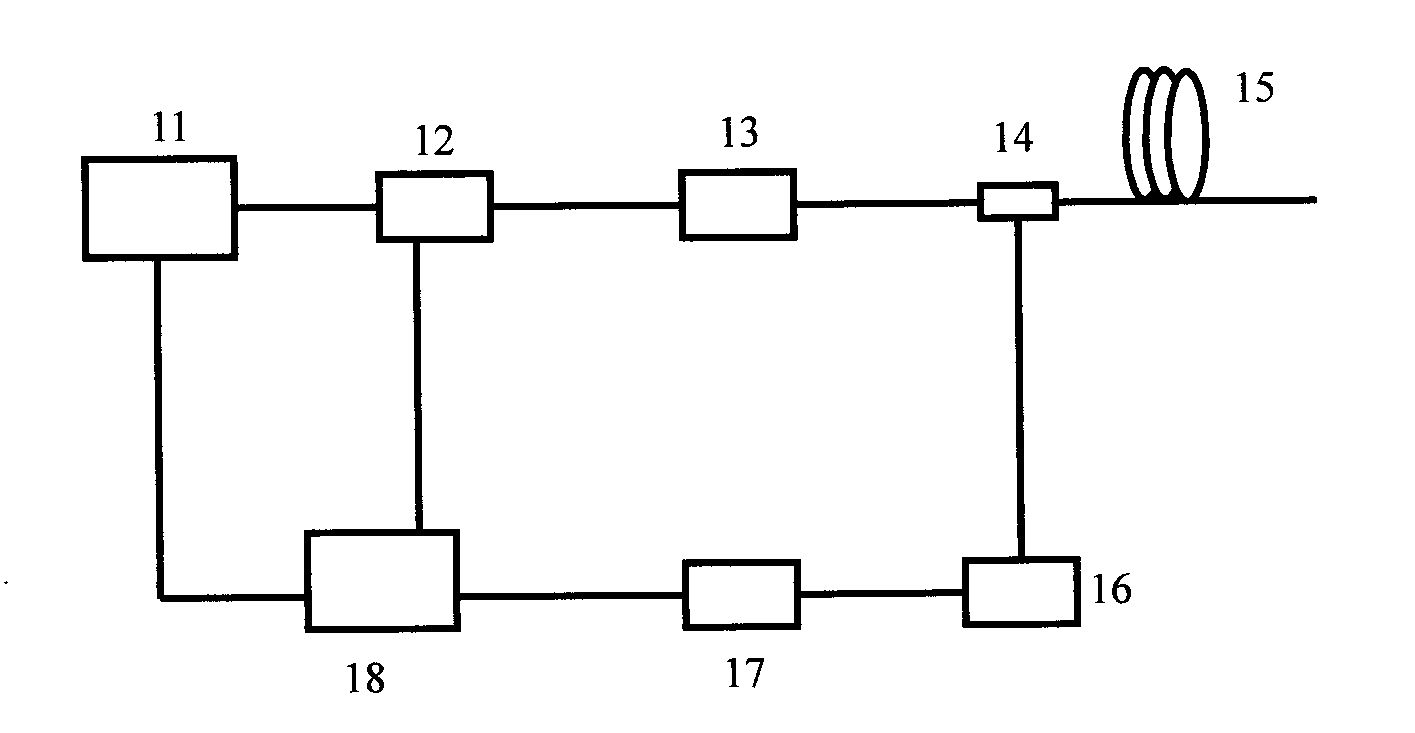
[0012] The present invention is about a new type of distributed optical fiber temperature and stress sensor. The specific implementations related to this sensor will be discussed in the following sections, but it should be understood that this patent is not limited to these specific implementations related to the present invention. Program. On the contrary, the present invention is intended to include all alternatives, modifications and equivalent embodiments, and these embodiments should be included in the characteristics and scope of the invention stated in the claims. according to image 3 As shown, a novel distributed optical fiber temperature and stress sensor invented describes a distributed temperature and stress measurement device based on optical fiber Rayleigh scattering, which includes a wavelength scanning laser (11), a pulse modulator (12), a doped An erbium fiber amplifier (13), a fiber optic circulator (14), a single-mode sensing fiber (15), a photodetector (16...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap