Physalis bitterin a extraction process and its medicinal application
A technology for physalis and melanoma, which is applied in the field of medicine, and can solve the problem of few studies on the pharmacological mechanism of physalis A
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1: Optimization of Physalis A extracting process
[0036] 1 Experimental method
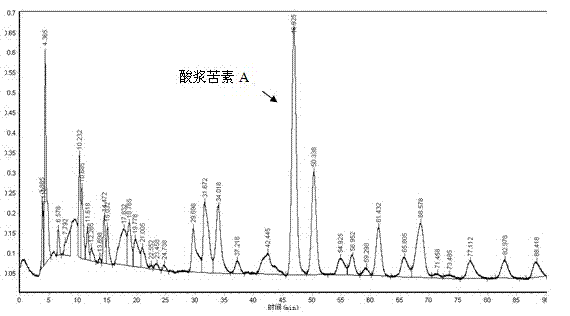
[0037] Physalis bitterin A is derived from Physalis ( Physalis alkekengi L. var. franchetii (Mast.) Makino) extracted and isolated. The extraction conditions of Physalis A were optimized, and the best process combination was determined through single factor investigation (extraction method, solvent, time, concentration, liquid-solid ratio) and orthogonal design experiments.
[0038] 2 Experimental results
[0039] Selection of extraction method (extraction time is 60 min):
[0040]
[0041]
[0042] According to the extraction method and solvent selection, it is finally determined to use 70% ethanol for reflux extraction.
[0043] Single factor experiments mainly investigated the effects of extraction time, liquid-to-solid ratio, and ethanol concentration on the extraction rate.
[0044] Factors and levels determined:
[0045]
[0046] Orthogonal experiment...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2: the refining process of Physalis A crude extract
[0052] 1 Experimental method
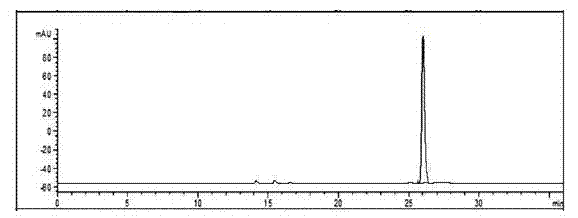
[0053] According to the results obtained from the above orthogonal experiments, the optimal combination process is used for extraction, specifically: using vegetable physalis ( Physalis alkekengi L. var. franchetii (Mast.) Makino) 1 kg of commercially available finished medicinal materials was used as a raw material, and reflux extraction was carried out by 70% ethanol, the ratio of liquid to material was 60:1, reflux extraction was carried out for 40 minutes, and a total of three extractions were carried out; the obtained extract was concentrated to obtain an extract of about 160 g, dispersed into 10 times the amount of water, extracted three times with the same volume of ethyl acetate; the ethyl acetate layer extract was evaporated to dryness to obtain about 34 g of extract, and an appropriate amount of acetone was slowly added to make it just completely dissolved. After...
Embodiment 3
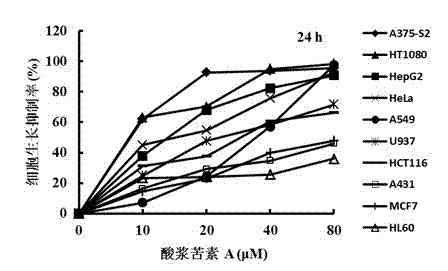
[0058] Example 3: The growth inhibitory effect of physalicin A on ten kinds of tumor cells in vitro
[0059] 1 Experimental method
[0060]Eight out of ten types of tumor cells (HT1080, A375-S2, HepG2, HeLa, A549, HCT116, A431, MCF7) adhered to the wall, and two types (U937, HL60) were grown in suspension with 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U / ml Penicillin, 100 μg / ml streptomycin in RPMI-1640 culture medium, placed in 5% CO 2 , cultured in a 37°C incubator.
[0061] For adherent cells, cells in the logarithmic growth phase were prepared to make 6×10 4 1 / ml concentration of cell suspension, 100 μl per well was inoculated in a 96-well plate and cultured overnight. After the cells were fully adhered to the wall, the original culture medium was removed and different concentrations of Physicine A or DMSO were added (final concentration less than 0.1 %, negative control), 100 μl per well. Incubate at 37°C for 24 hours. After the culture, add 10 μl of 5 mg / ml MTT to each well and c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com