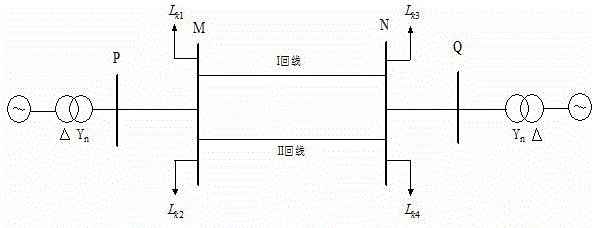
A single-ended traveling wave fault location method for double-circuit transmission lines on the same tower without relying on wave head identification
A technology of double circuits and transmission lines on the same tower, applied in the direction of the fault location, etc., can solve the problems of incorrect ranging results and large investment in equipment, and achieve reliable ranging results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
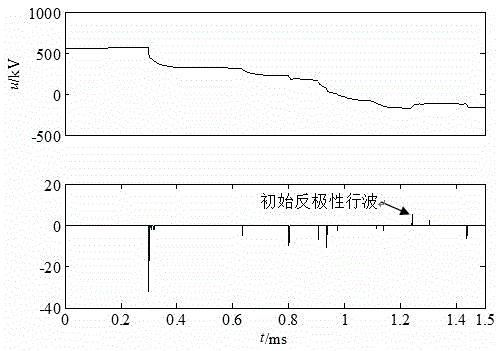
[0050] Example 1: Phase A metallic grounding fault occurred at the distance measuring terminal M50km from the I circuit of the double circuit transmission line on the same tower. The measuring terminal M detects and records the 1.5ms traveling wave data after the fault, the fault voltage traveling wave and its wavelet transform Modulus maximum such as image 3 Shown.
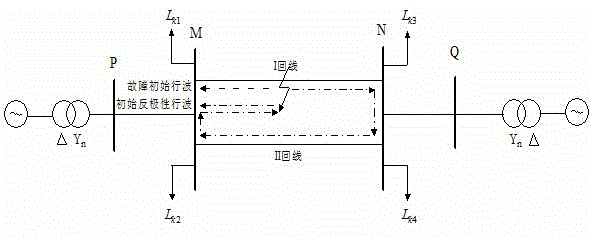
[0051] 1. According to step (2) of claim 2, using the arrival time of the initial traveling wave of the fault as the reference time, the distance reflected by the wave heads of the same polarity is calculated:
[0052] x=[50.36, 74.65, 89.70, 94.62, 100.87, 115.18, 121.29, 125.16]km;
[0053] Similarly, using the arrival time of the initial reverse polarity traveling wave as the reference time, calculate the distance reflected by the wave heads of the traveling waves of the same polarity:
[0054] x'=[89.85, 65.56, 50.51, 45.59, 39.34, 25.03, 18.92, 15.05] km.
[0055] 2. According to the step (3) of the claim, find out ...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2: Phase A metallic grounding fault occurred at a distance of 90km from the measuring terminal M to the I circuit of the double circuit transmission line on the same tower. The measuring terminal M detects and records the 1.5ms traveling wave data after the fault, the fault voltage traveling wave and its wavelet transform Modulus maximum such as Figure 5 Shown.
[0061] 1. According to step (2) of claim 2, using the arrival time of the initial traveling wave of the fault as the reference time, calculate the distance reflected by the wave heads of the same polarity:
[0062] x=[50.16, 74.64, 90.14, 94.76, 100.27, 115.03, 121.29, 124.71]km;
[0063] Similarly, using the arrival time of the initial reverse polarity traveling wave as the reference time, calculate the distance reflected by the wave heads of the traveling waves of the same polarity:
[0064] x'=[90.18, 65.56, 50.06, 45.44, 39.93, 25.18, 18.92, 15.49] km.
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap