A Radiation Network Fault Branch Identification Method Based on Full Coverage of Voltage Distribution and Traveling Wave Information Along the Line
A technology of voltage distribution and radiation network, applied in the fault location and other directions, can solve the problems of the difficulty of identifying, distinguishing and locating the reflected wave at the fault point, and the large attenuation of the initial traveling wave of the fault.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
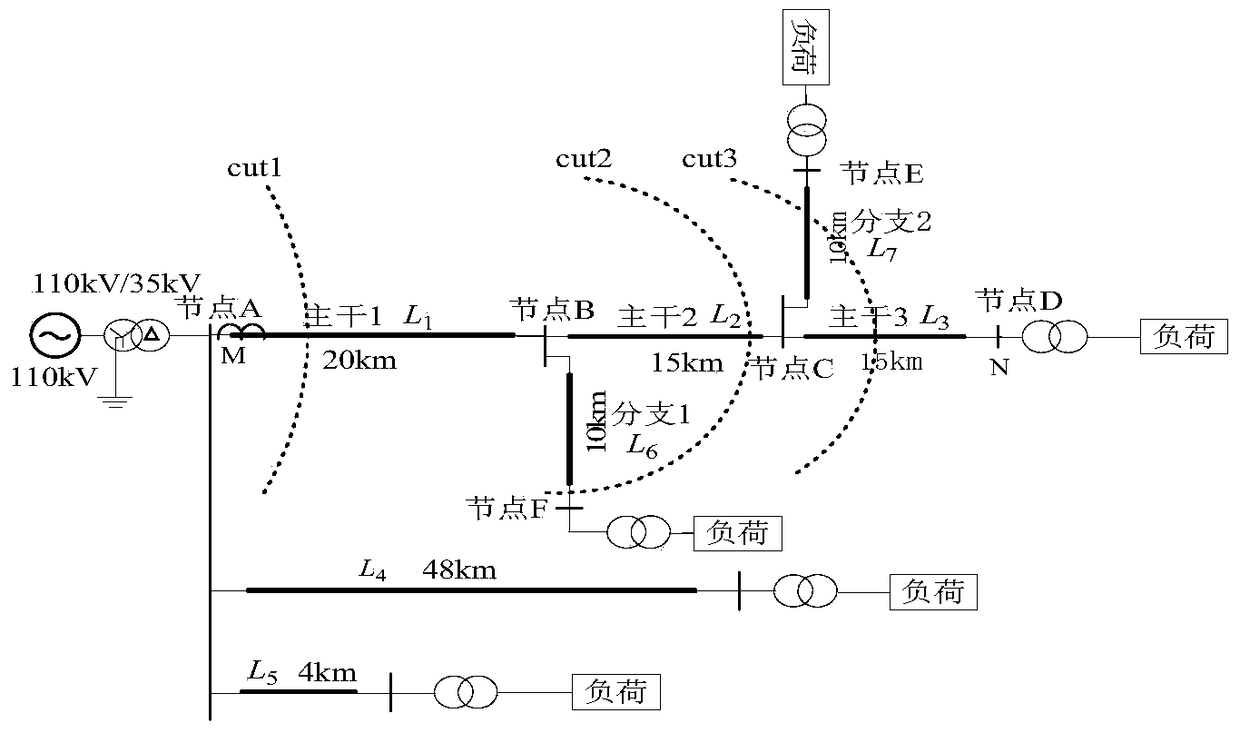
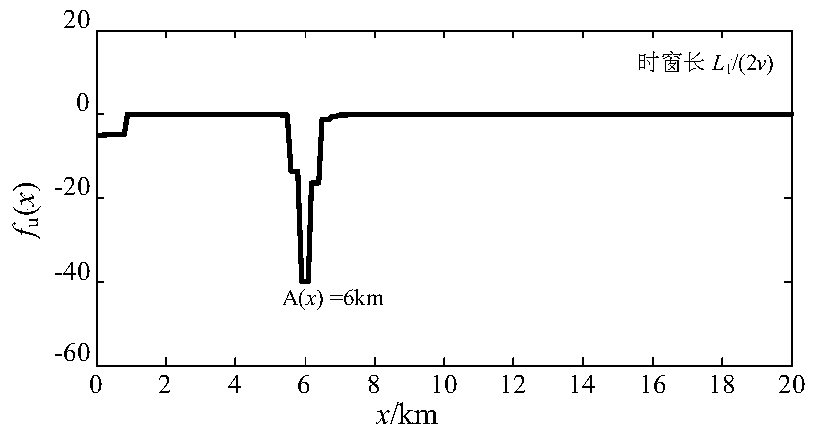
[0052] use as figure 1 The topology of the multi-branch radial power distribution network with multi-outlet wiring is shown, the measurement end is located at the head end M, and the healthy line L 4 = 48km, L 5 = 4km. Assume that the line MN is composed of trunk 1, trunk 2, trunk 3, branch 1 and branch 2, and the line lengths are L 1 =20km, L 2 = 15km, L 3 = 15km, L 6 = 10km, L 7 = 10km. Assuming that a phase A ground fault occurs at a distance of 26km from the M terminal within the half-line length of the trunk 2 (that is, 6km away from node B), first use PCA-SVM to identify that the fault is located in the cut set 2, and then in [k 0 ,k 0 +L 1 / (2v)] and [k 0 +L 1 / (2v),k 0 +L 1 / v] time window, using the line-mode current traveling wave and line-mode voltage traveling wave at the measurement end of trunk 1, the calculation step along the line is 0.1km, and the ranging function f of the measurement end M is calculated according to the transmission equation of t...
Embodiment 2
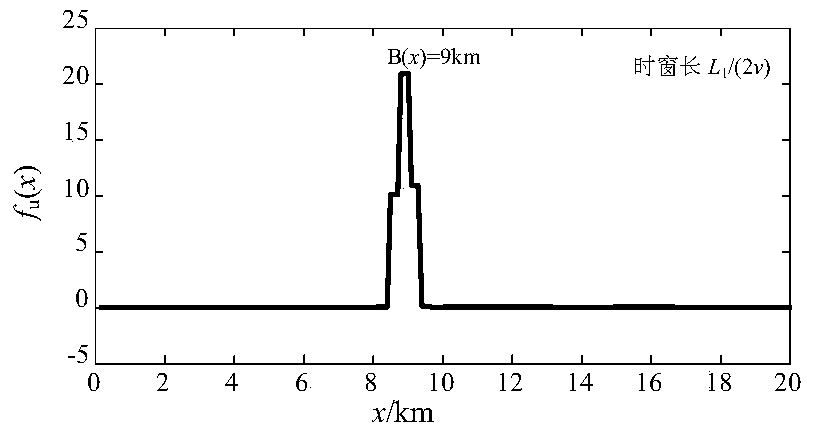
[0054] use as figure 1 The topology of the multi-branch radial power distribution network with multi-outlet wiring is shown, the measurement end is located at the head end M, and the healthy line L 4 = 48km, L 5 = 4km. Assume that the line MN is composed of trunk 1, trunk 2, trunk 3, branch 1 and branch 2, and the line lengths are L 1 =20km,L 2 = 15km, L 3 = 15km, L 6 = 10km, L 7 = 10km. Now suppose that when the phase A ground fault occurs at a distance of 45km away from the M terminal beyond the half-line length of the trunk line 3 (that is, 10km away from the C node), the PCA-SVM is first used to identify the fault location in the cut set 3, and then the faults are located in the [k 0 ,k 0 +L 1 / (2v)] and [k 0 +L 1 / (2v),k 0 +L 1 / v] time window, using the line-mode current traveling wave and line-mode voltage traveling wave at the measurement end of trunk 1, the calculation step along the line is 0.1km, and the ranging function f of the measurement end M is ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com