Railway concave-bottomed flatcar chassis
A flat car and railway technology, which is applied in the direction of railway car body parts, underframe, transportation and packaging, etc. It can solve the problems of small vertical rigidity of the underframe, can not use nail triangle gear, fix wheeled goods, etc., and achieve increased height Effects of range, interference avoidance, and rigidity improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
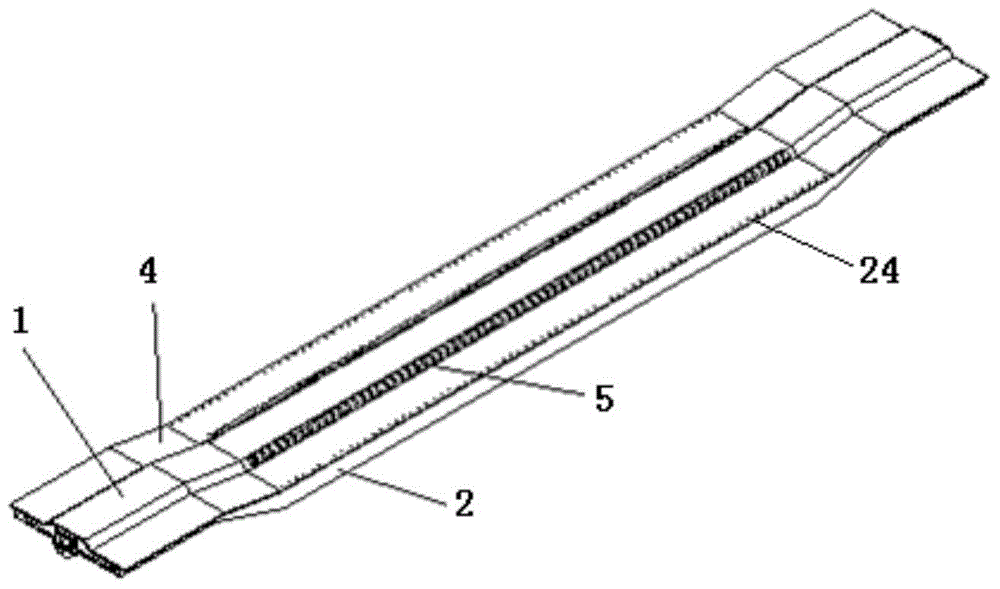
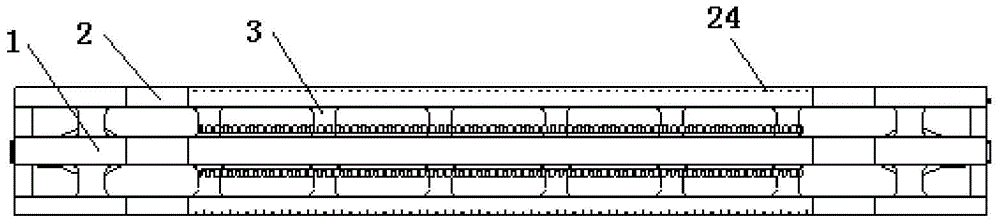
[0018] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, the present invention includes a middle beam 1, side beams 2, several transverse beams 3, a floor 4, two draw-in grooves 5 and a lower cover plate (not shown in the figure), wherein the middle beam 1 and the side beams 2 Both are concave structures in the middle, with slope transitions in the middle and both ends. The side beam 2 is fastened on both sides of the center beam 1 through several transverse beams 3 in parallel, the floor 4 is fastened to cover the center beam 1, the side beam 2 and the transverse beam 3, and the card slot 5 is fastened to the center beam 1 On the floor 4 on both sides of the concave bottom in the middle, the lower cover plate is fastened and connected under the concave bottom in the middle of the middle beam 1 and the side beam 2 .
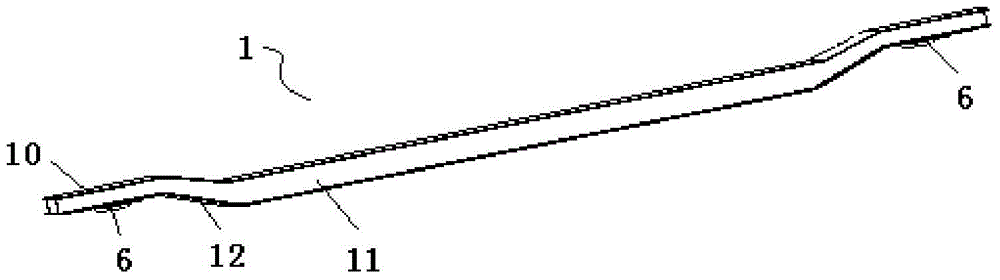
[0019] Such as image 3 As shown, the ce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com