Method for detection of a neurological disease
A neurological disease, disease technology, applied in disease diagnosis, biological testing, measurement devices, etc., can solve problems such as expensive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0228] 1. Sample Collection and Analysis
[0229] 1.1 Dataset
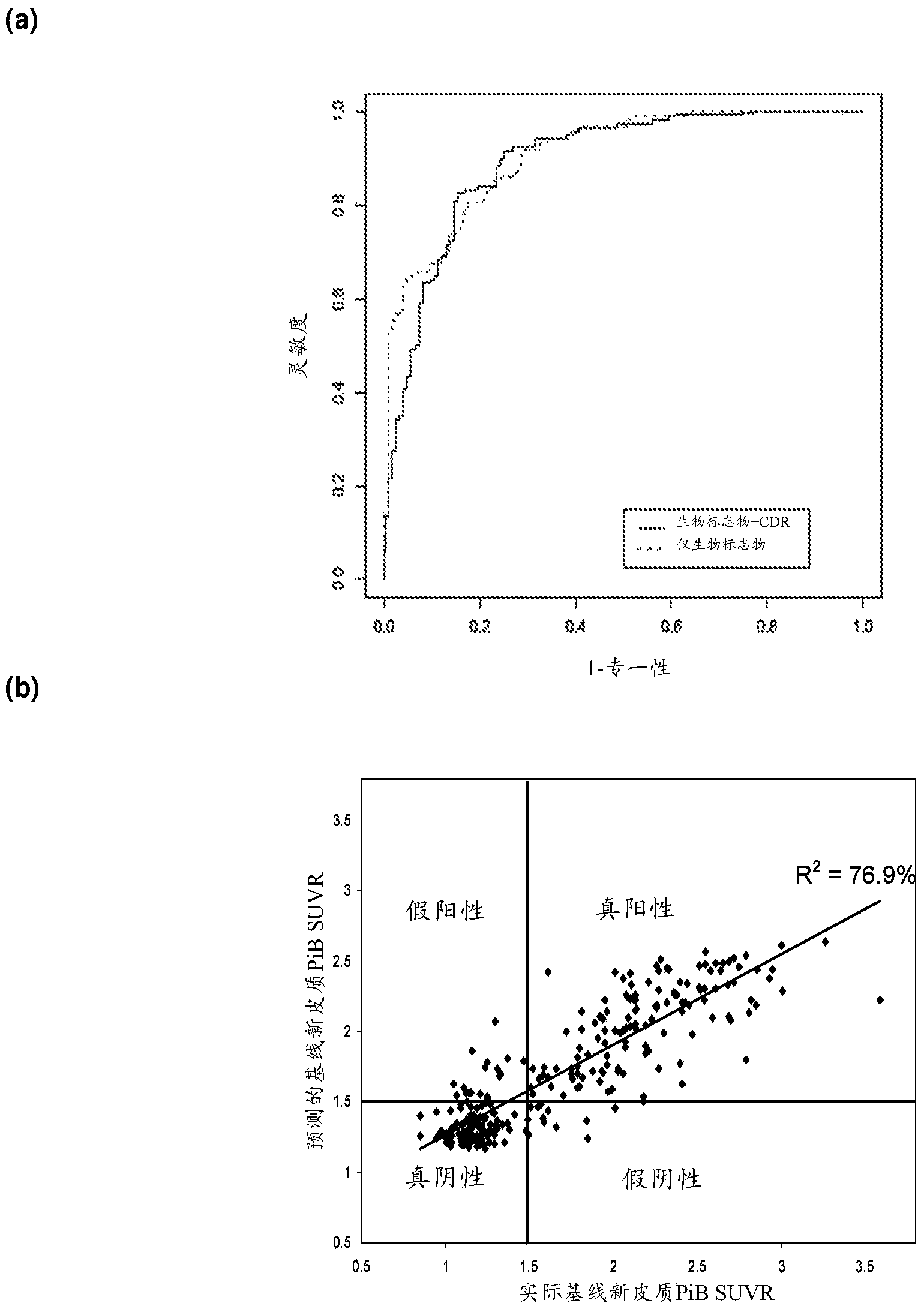
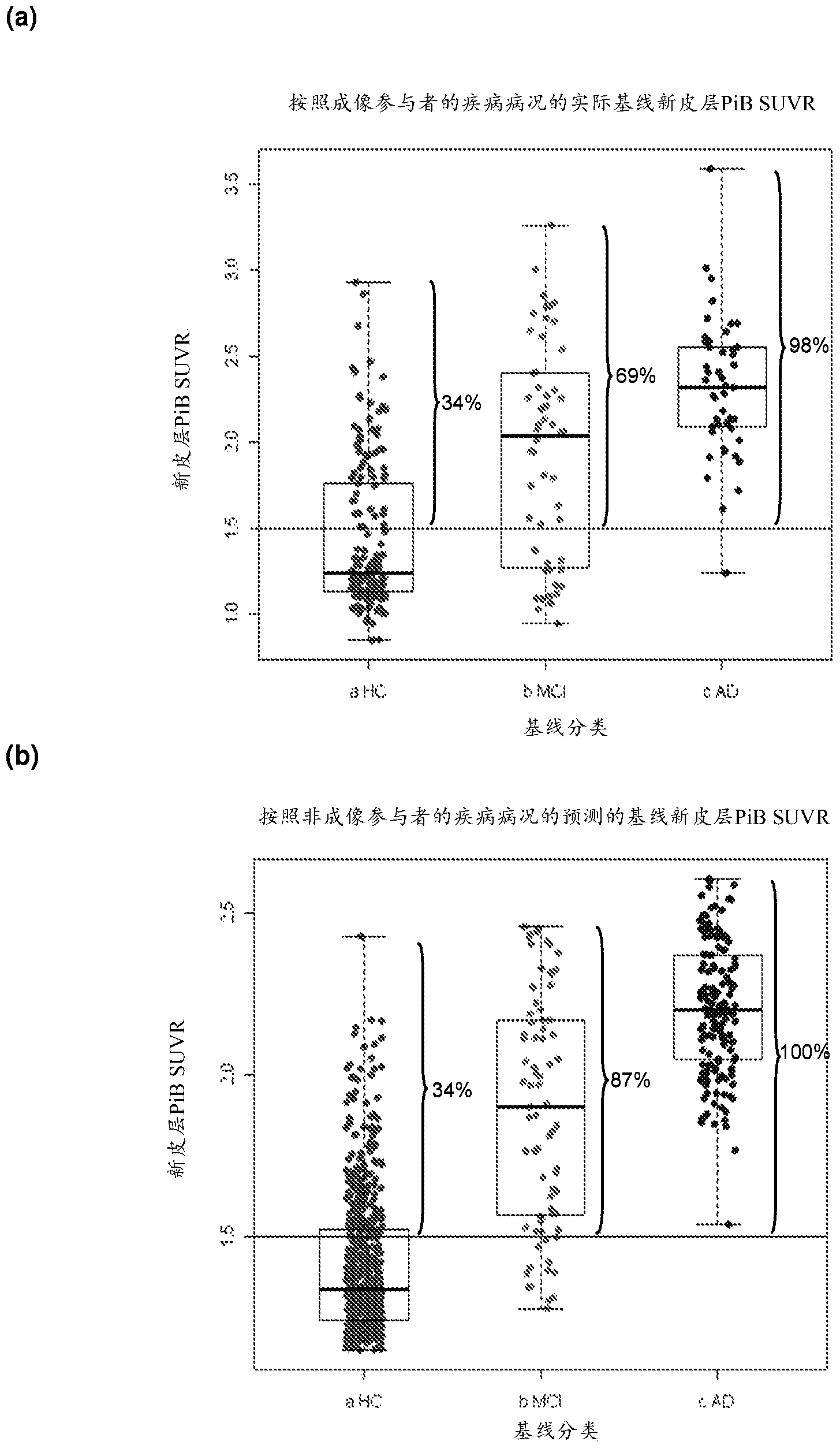
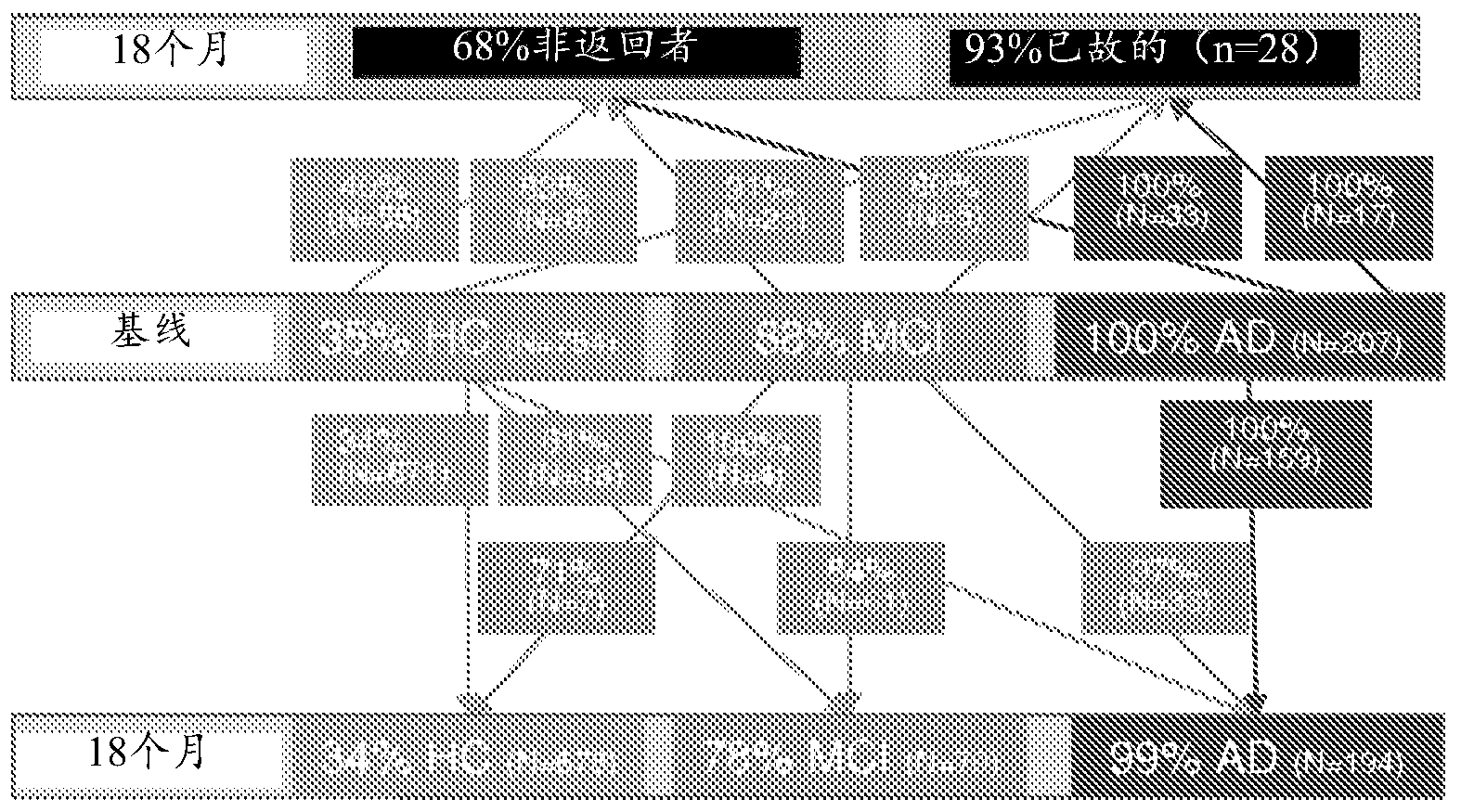
[0230] Two datasets are used. The first set was obtained from the Australian Imaging, Biomarkers, and Lifestyles (AIBL) Study. Details on the study design and registration procedures have been discussed (Ellis et al., 2009). The cohort consisted of 1090 subjects (207 with clinically established Alzheimer's disease (AD), 129 had mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and 754 were healthy controls (HC). 273 subjects underwent both blood measurements and imaging (PiB-PET). Over an 18-month time frame, acquisition PET images and samples are obtained for blood measurements, however blood measurements are yet to be determined.
[0231] The second set was obtained from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) database (http: / / www.loni.ucla.edu / ADNI). Each of these samples had baseline blood measurements and PET imaging at baseline or twelve-month follow-up. Information on ADNI studies has been detailed (M...
example 2
[0281] 1.1 Dataset
[0282] The same samples from the AIBL cohort discussed in Example 1 as well as ADNI were used for this second round of analysis.
[0283] Certain markers, as used in Example 1, are presented here in consideration of the difficulties that may be encountered when using certain markers in a clinical setting—difficulties due to their assay measurement being potentially unreliable, tricky to perform, or too variable. ignored in the second round of analysis. Instead, four other biomarkers of interest, demographic and clinical, were appended to the blood analytes; included markers were gender, ApoE ε4 carrier status, years of education, and CDR pen box.
[0284] The demographic composition of the two imaging (AIBL and ADNI) datasets split by high and low NAB for these four markers, age, and clinical class (HC, MCI, or AD) is given in Table 4. Demographic differences between high and low NAB were assessed using χ2 tests against categorical variables, and analy...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap