Refrigerator food storage position recording method, device and terminal and refrigerator
A technology of storage location and recording method, which is applied to household refrigeration devices, lighting and heating equipment, household appliances, etc., can solve the problem of low efficiency of entry of food storage location information, and achieve the effect of improving entry efficiency and ensuring accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] In Embodiment 1 of the present invention, the user only takes pictures of one subspace, that is, the storage space corresponding to a storage location. The user can take pictures of the whole subspace or a part of the subspace, but the subspace must be taken. Storage location sign for space.
[0037] figure 2 Shown is a flow chart of the method for recording food storage locations in a refrigerator provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, specifically including:
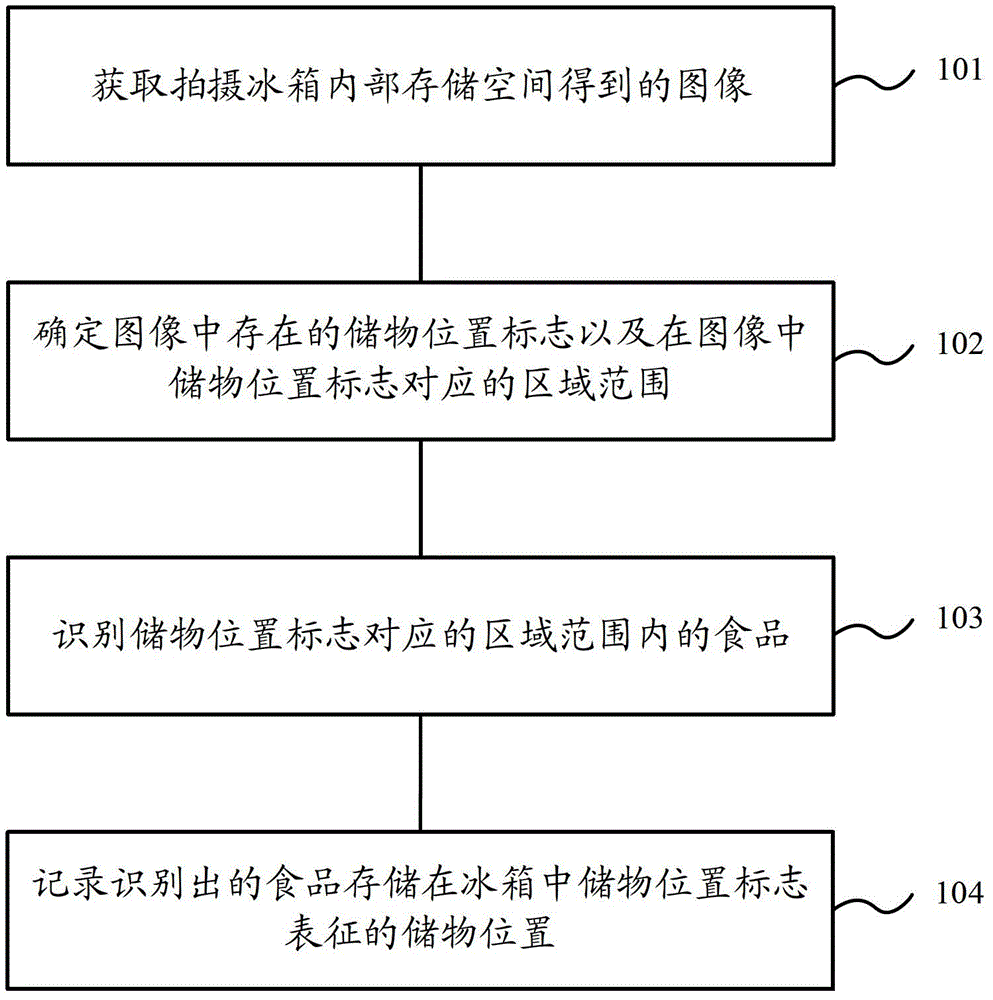
[0038] Step 201, acquire the captured food collection image.
[0039] Step 202: Determine a storage location mark existing in the food collection image, and determine that the range of the area corresponding to the storage location mark is the entire area in the food collection image.
[0040] There are many specific forms of the storage position mark, preferably, a barcode can be used. Furthermore, in order to distinguish the one-dimensional barcodes carried on the food in the refrigerator, the ...
Embodiment 2
[0069] In Embodiment 2 of the present invention, the user shoots a plurality of subspaces, that is, storage spaces corresponding to a plurality of storage locations, and may photograph all of the plurality of subspaces or a part of the plurality of subspaces.
[0070] Figure 4 Shown is the flow chart of the method for recording the food storage location in the refrigerator provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention, specifically including:
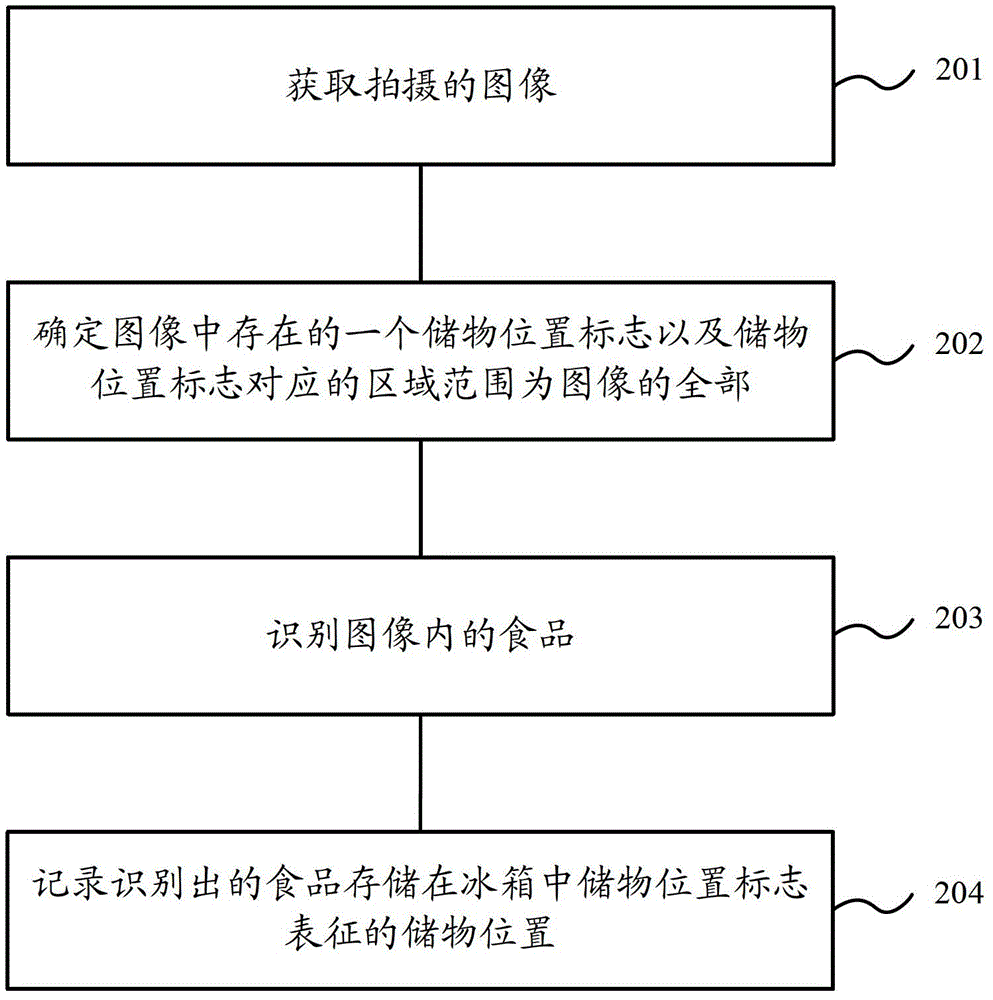
[0071] Step 401, acquire the captured food collection image.
[0072] Step 402: Determine the multiple storage location marks existing in the food collection image, and the area ranges corresponding to the multiple storage location marks in the food collection image.
[0073] Preferably, the storage location mark is a two-dimensional barcode.
[0074] Wherein, when determining the corresponding area range for each storage position mark, the specified range in the food collection image based on the storage position mark can be det...
Embodiment 3
[0083] Based on the same inventive idea, according to the method for recording the food storage location in the refrigerator provided by the above-mentioned embodiments of the present invention, correspondingly, Embodiment 3 of the present invention also provides a storage location recording device for food in the refrigerator, the structural diagram of which is as follows Figure 5 shown, including:
[0084] An acquisition unit 501, configured to acquire food collection images obtained by photographing the internal storage space of the refrigerator;
[0085] A determining unit 502, configured to determine the storage location mark existing in the food collection image, and the area range corresponding to the storage location mark in the food collection image;
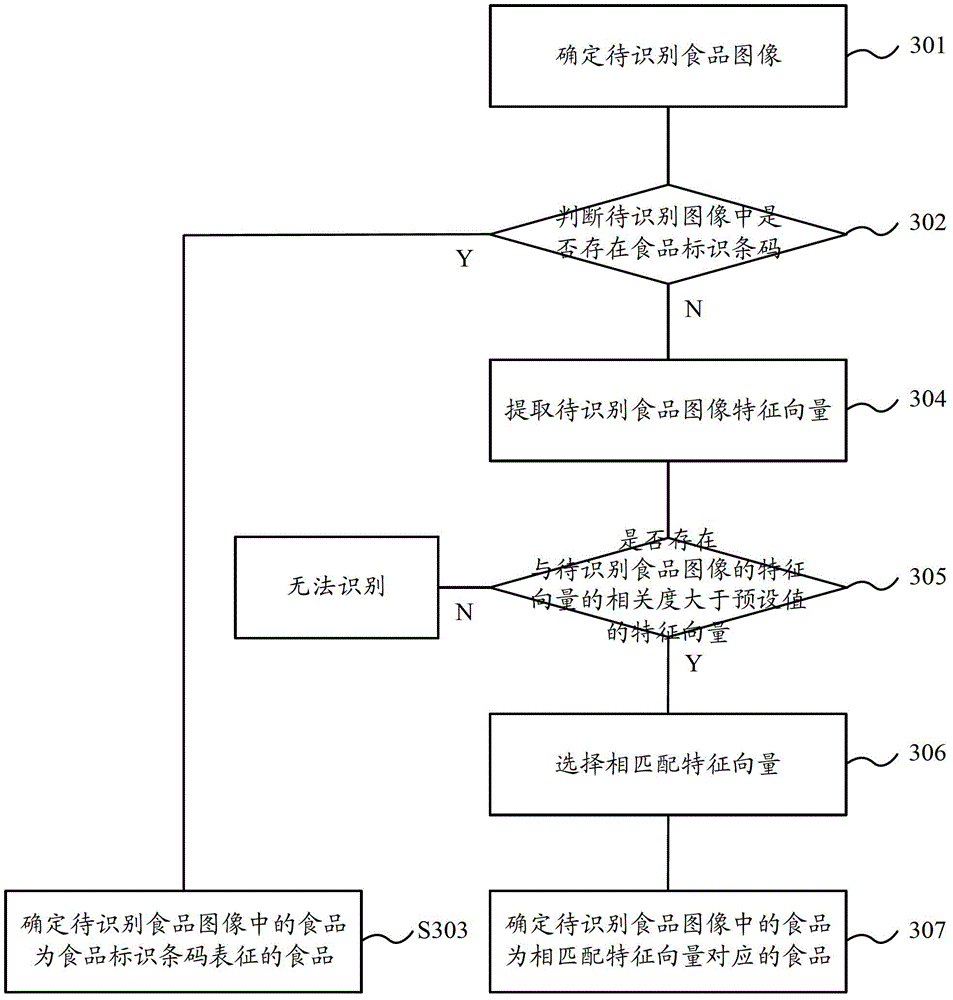
[0086] An identification unit 503, configured to identify the food existing in the area corresponding to the storage location mark;
[0087] The recording unit 504 is configured to record the identified storage locati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com