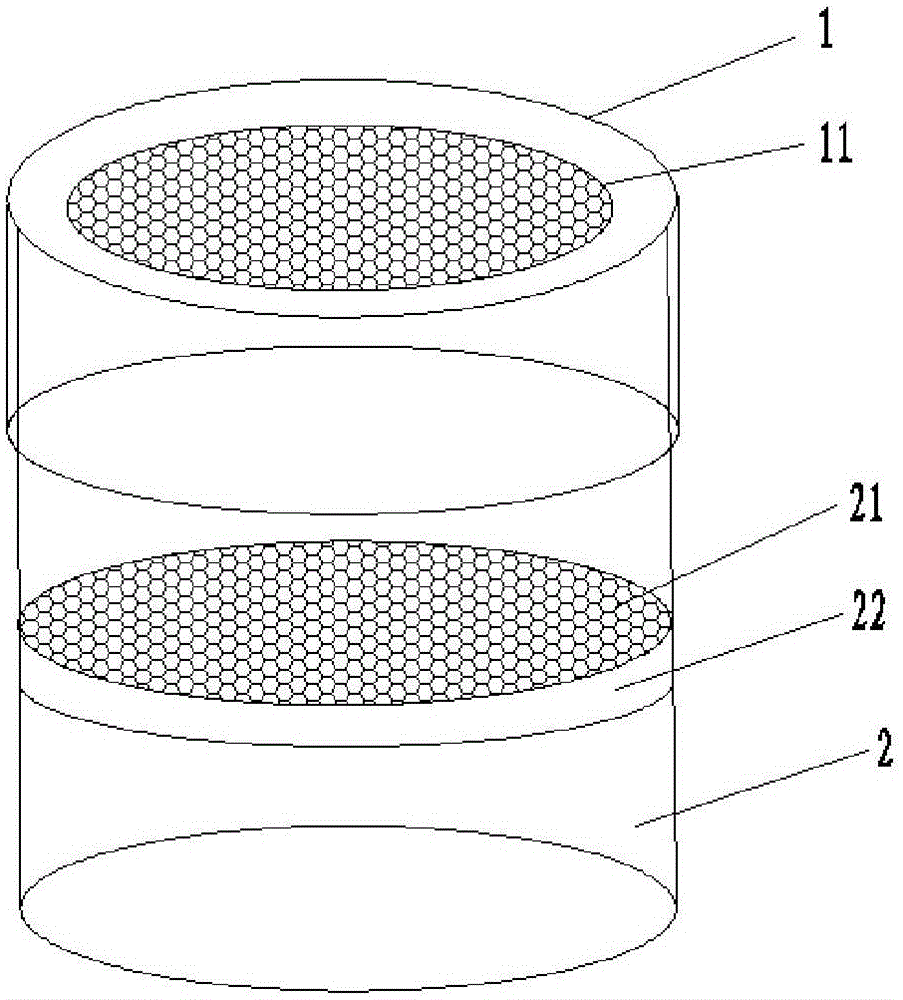
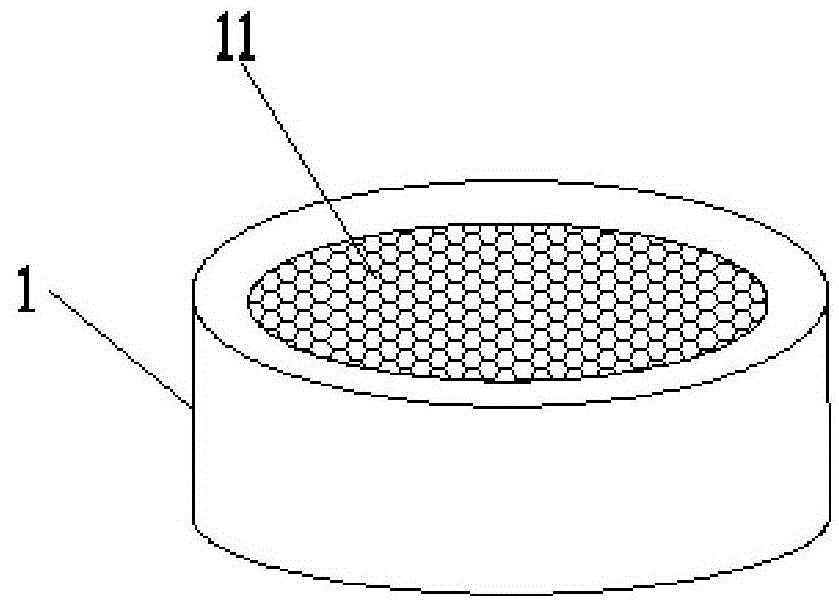
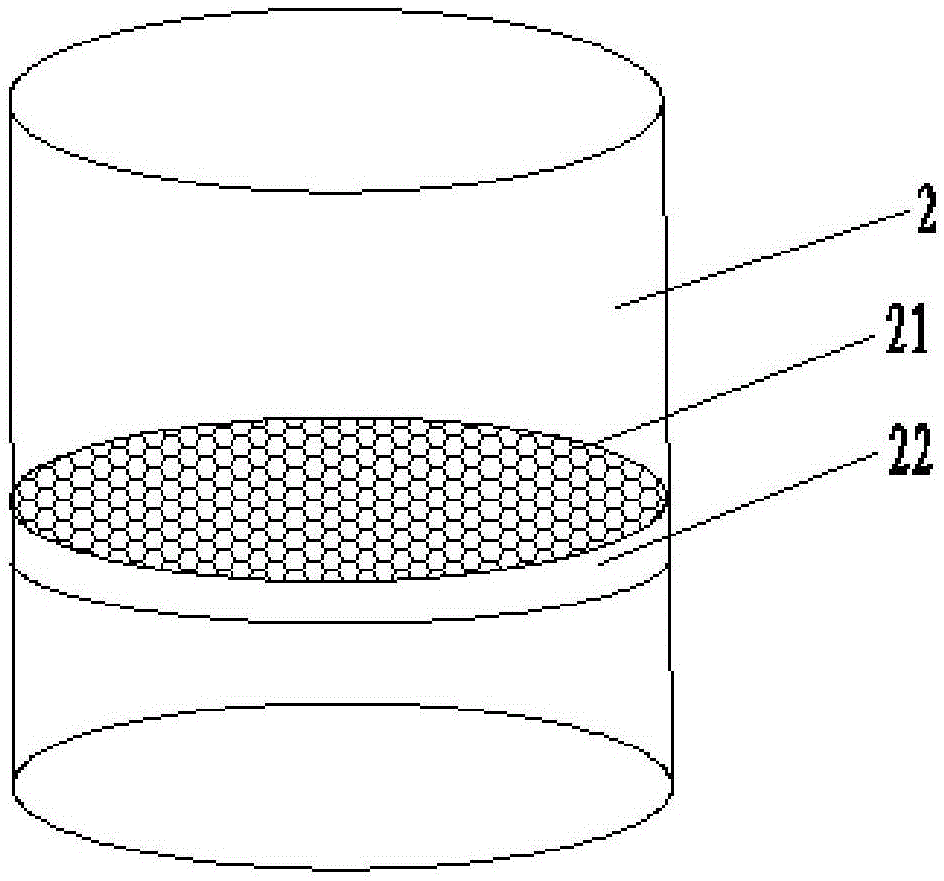
Method for Determining Virulence of Predator Mite
A measurement method, a technology of predatory mite, which is applied in measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high escape rate of predatory mite, strong self-activity, and difficult to guarantee the accuracy of results, so as to avoid suffocation and death, and is convenient to manufacture , the result is accurate and reliable
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 Determination of the toxicity of chlorpyrifos and lambda-cyhalothrin to Neoseius pasteurii
[0026] 1. Material
[0027] 1.1 Source of tested mite
[0028] The subject of the experiment was the new small seiusi Pasteur, collected from lemon leaves around the orchard of the Citrus Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
[0029] 1.2 Chemical reagents: see Table 1
[0030] Table 1 Chemical reagents to be tested
[0031]
[0032] 2 method
[0033] 2.1 Preparation of reagents with different concentration gradients
[0034] Different concentration gradients were prepared by diluting the field concentration of predatory mites in the instructions for use of the chemical reagents. The different concentration gradients of chlorpyrifos and lambda-cyhalothrin set in this experiment are shown in Table 2. Each reagent has 8 different settings The concentration gradient.
[0035] 2.2 Operation method for virulence determination
[0036] For each pesticide, 8 t...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2 Comparison of escape rate between the leaf residue method and the method of the invention
[0055] The escape rate of the traditional leaf residue method and the method of the present invention are compared. Each method was used to detect 40 new mites of Pasteurella mite, with 3 replicates for each method. After 24 hours, count the mites on the leaves and in the device of the present invention to calculate the escape rate.
[0056] As shown in Table 3, it can be seen from the results of the significance analysis that the escape rate of the new mites Pasteurii using the method of the present invention is significantly lower than that of the leaf residue method, indicating that the method of the present invention is used to detect the resistance of predator mites. More accurate and reliable.
[0057] Table 3 Comparison of escape rate between the leaf residue method and the predator mite virulence measuring device of the present invention
[0058]
[0059] Remarks: *As...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com