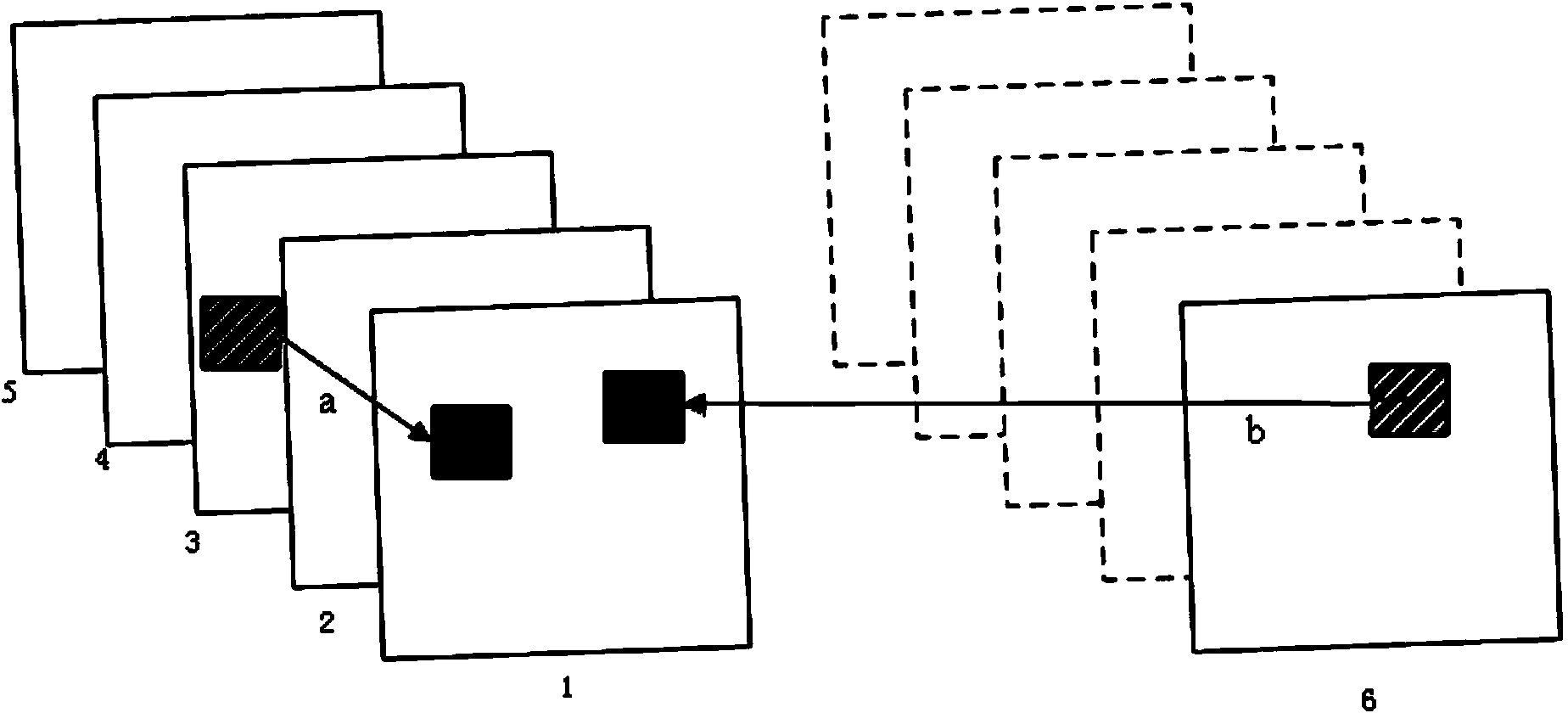
Method for acquiring parallax vector in multi-view video coding
A multi-view video and parallax vector technology, which is applied in the fields of digital video signal modification, electrical components, image communication, etc., can solve the problems that the current block prediction information is not accurate enough and affects parallelism.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0031] Specific Embodiment 1: A disparity vector acquisition method in multi-view video coding in this embodiment is specifically prepared according to the following steps:
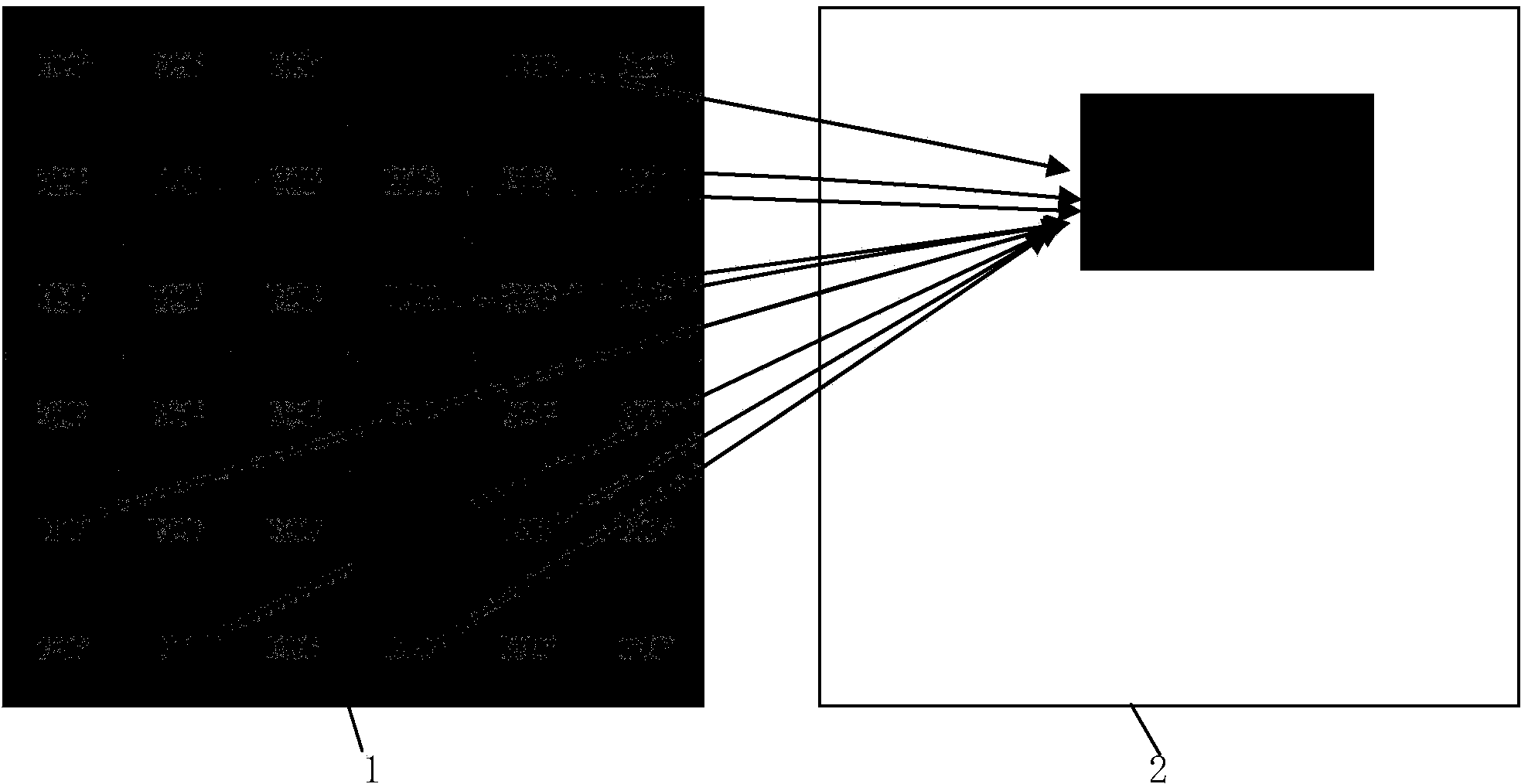
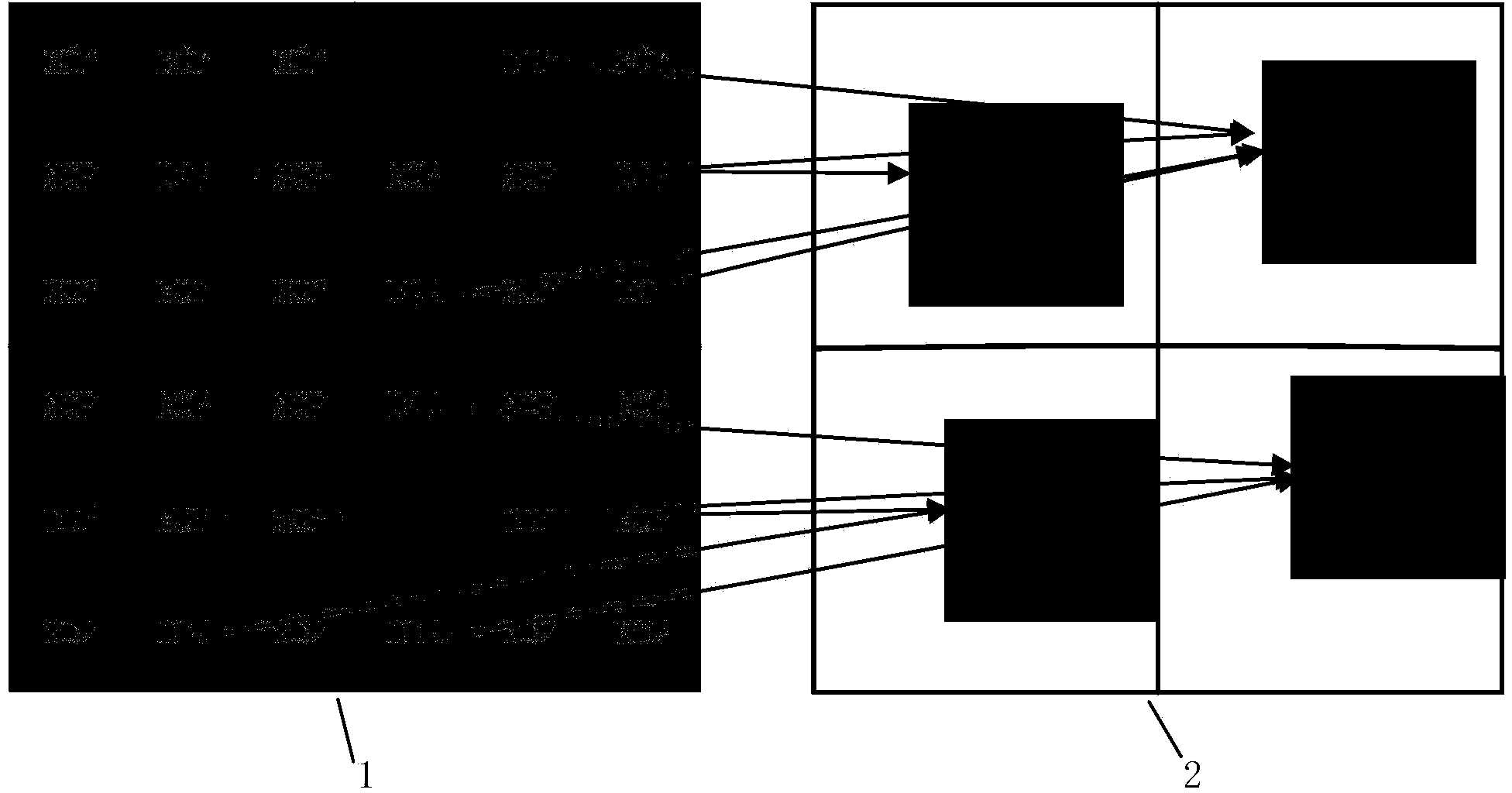
[0032] Step 1. Divide the current frame into any N parts; each part is divided into L*W (generally ensure that both W and L are greater than or equal to 4) unit area; the unit can be square, rectangular, or other shapes; L is each part of the current frame length, W is the width of each part of the current frame; N is an integer and N≥1; wherein, when N=1, such as figure 2 , when N=4, such as image 3 ;
[0033] Step 2. Divide each part of the L*W unit area of the current frame (when there is only one area, that is, the whole frame) into units of l*w, wherein, 4≤l≤L, 4≤w≤W;
[0034] Step 3, using the time domain reference frame to calculate the mean value, median, maximum value, minimum value or weighted average value of the disparity vector of the l*w unit to obtain the disparity vector (Disparity V...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0043] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in step 3, the disparity vector of the l*w unit is used to calculate the mean value of the disparity vector, and the disparity vector of the unit area of L*W is obtained. The specific process is:
[0044] (1) Determine the i partial area in the same position as the current frame in the time domain reference frame; wherein, i=1, 2, 3....N;
[0045] (2) Calculate the mean value of all or part of the disparity vectors of the N partial regions obtained in (1);
[0046] (3) Take the mean value of the disparity vector obtained in (2) as the disparity vector of the N part of the current frame, N=4 as image 3 shown; N=1 as figure 2 shown. Other steps and parameters are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0047] Embodiment 3: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 or 2 in that: in step 3, the disparity vector of the l*w unit is used to perform the median value of the disparity vector on the disparity vector of the l*w unit to obtain the disparity of the unit area of L*W The specific process of the vector is:
[0048] (1) Determine the i partial area in the same position as the current frame in the time domain reference frame; wherein, i=1, 2, 3....N
[0049] (2) Calculate the median of all or part of the disparity vectors of the N partial regions obtained in (1);
[0050] (3) Use the median value of the disparity vector obtained in (2) as the disparity vector of the N part of the current frame; N=4 as image 3 shown; N=1 as figure 2 shown. Other steps and parameters are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com