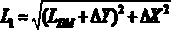AGV robot guide deviation correction method
A correction method and robot technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve the problems such as the inability to obtain the robot offset angle, the robot offset RFID center point distance, the wrong robot position information, etc., to reduce the probability of lost poses, the correction method is simple, and the efficiency is improved. sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] like Figure 6d As shown, assume that the current position of the robot is the path information contained in the two-dimensional code A, take the center point of the two-dimensional code A as the origin, and take the connection between the next destination two-dimensional code B and the current two-dimensional code A in the robot's planned path For the positive direction of the Y axis, establish a two-dimensional coordinate system.
[0066] The position of the robot pose and the two-dimensional code A is shown in the figure: the distance between the center point O of the robot and the center point of the two-dimensional code A in the horizontal direction is , the vertical distance is , the deviation angle between the current direction of the robot and the preset path is α. Assume that the linear velocity of the robot’s left wheel is V L , the linear velocity of the right wheel of the robot is V R , the linear velocity of the center point of the robot is V, the ang...
Embodiment 2
[0080] like Figure 7 As shown, when α is not less than 15°, the center of the robot is located in the fourth quadrant (the center of the robot is located in the third quadrant and the center of the robot is located in the fourth quadrant), then the AGV robot needs to stop the current movement, first correct the current deviation, and then continue to execute The specific implementation of the task is as follows:
[0081] Position ① The left wheel of the robot is ahead, and the right wheel is behind. ,
[0082] The first step is to correct the offset angle, the left wheel is backward, the right wheel is forward, and the angle a is rotated to reach the position ②, and the rotation arc length is ;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com