A Matrix Incremental Reduction Method Based on Knowledge Granularity
A knowledge granularity and matrix technology, applied in complex mathematical operations and other directions, can solve problems such as time-consuming, batch learning algorithms that are difficult to extract useful information and knowledge, and achieve the effect of easy implementation and simple calculation operations.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
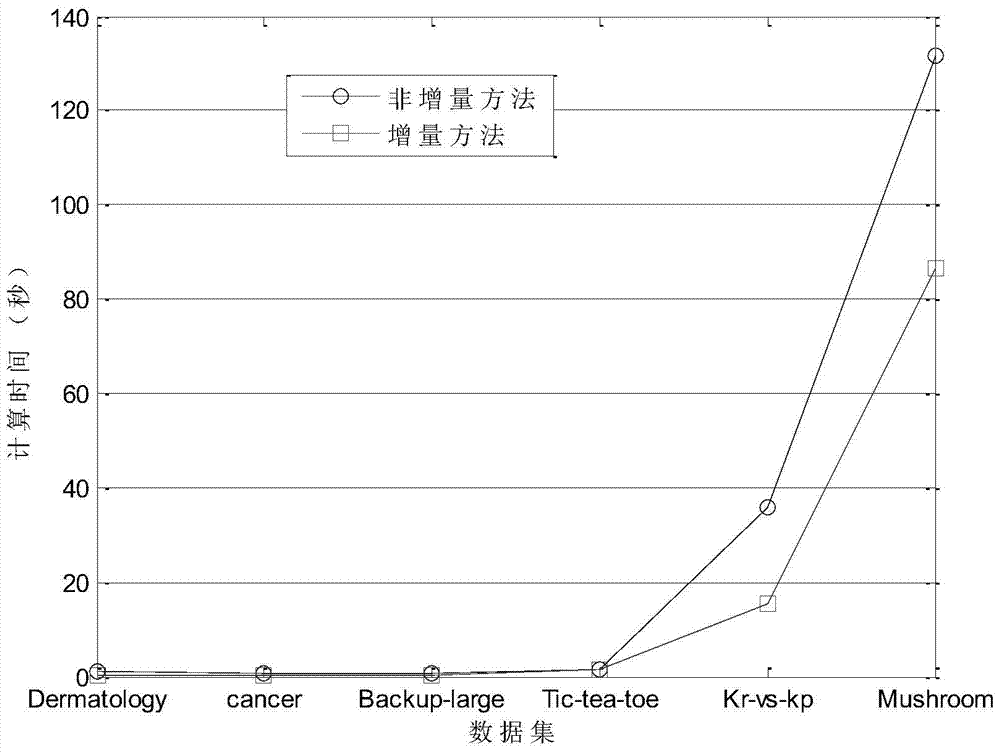
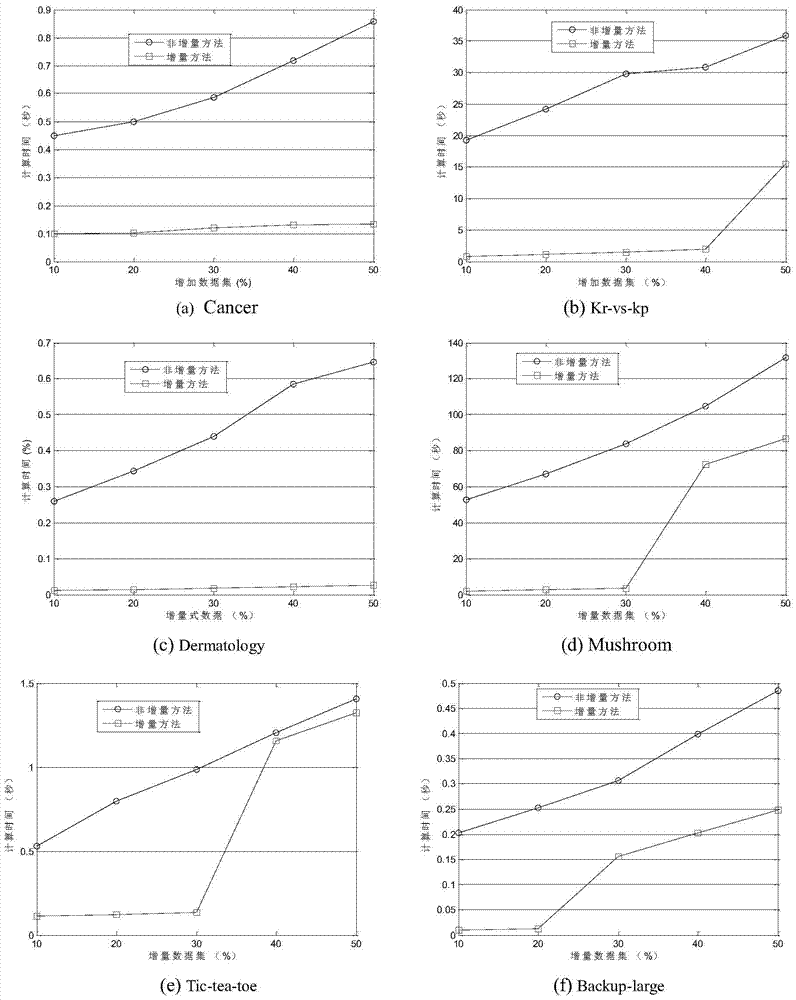
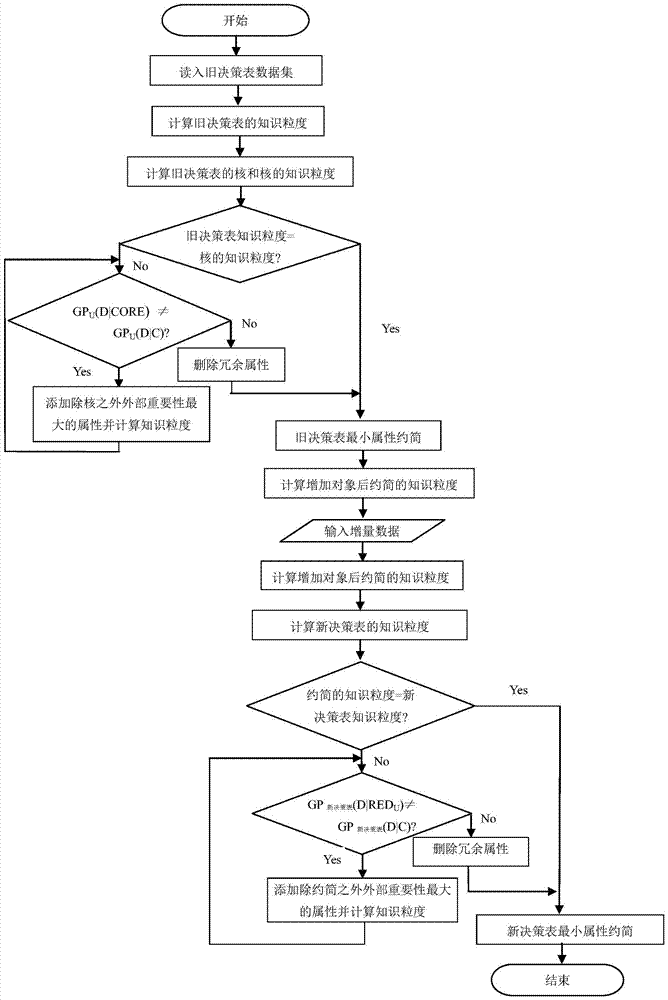
[0034] combine image 3 The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0035] Input: Existing decision table (including object set U, conditional attribute set C and decision attribute set D and object attribute values) (called old decision table), some new objects (denoted as incremental data set U X ={x n+1 ,x n+2 ,L,x n+t}) is added to the old decision table to form a new decision table.
[0036] Step 1: Use the matrix method to calculate the knowledge granularity of the old decision table Equivalence Relation Matrix of Old Decision Table is the arithmetic mean of the condition attribute equivalence matrix, is the arithmetic mean of the equivalence relation matrix of condition attribute and decision attribute;
[0037] Step 2: Calculate the core CORE of the old decision table using the matrix method;
[0038] The calculation method of the old decision table kernel is as follows: First, use the matrix method to calculate the internal importance of each attr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com