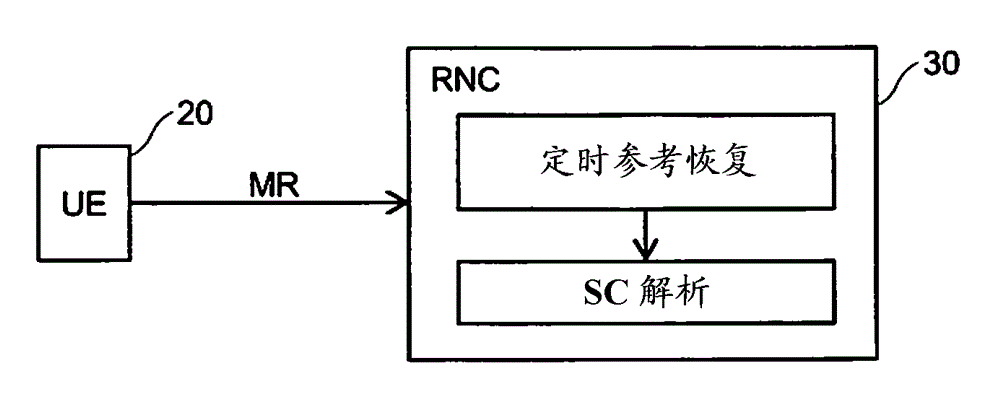
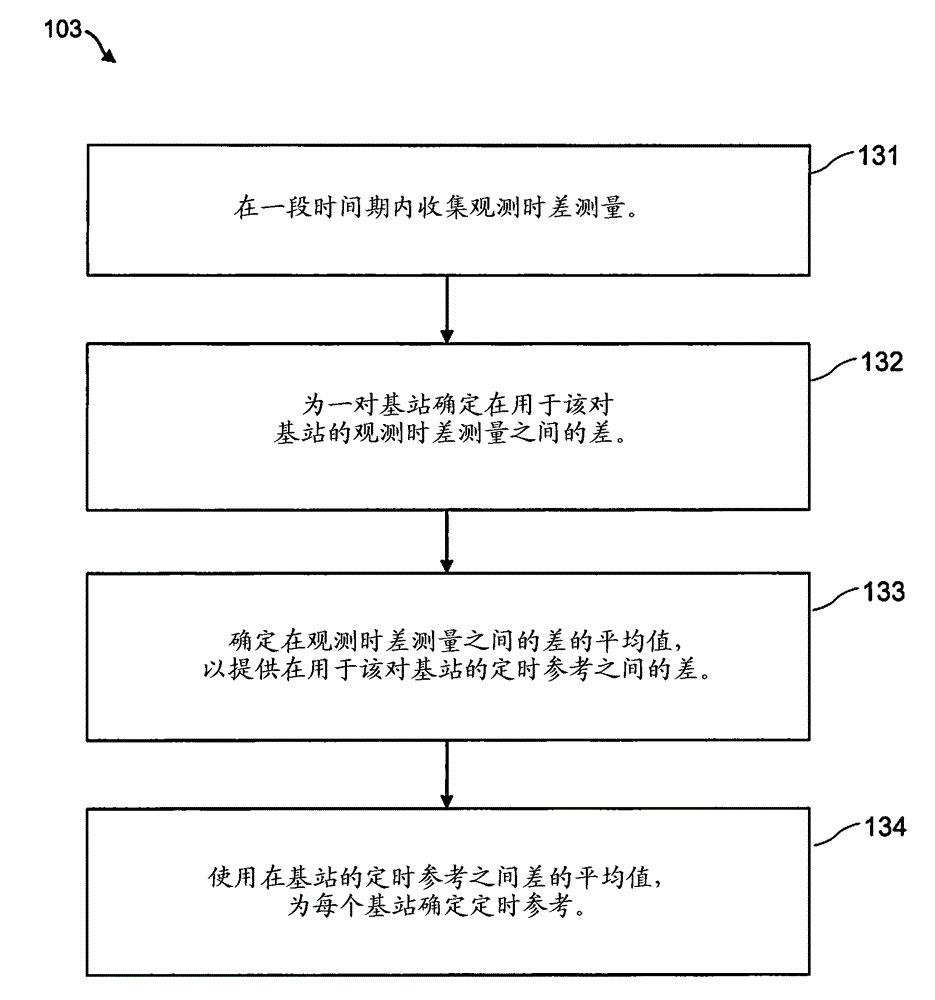
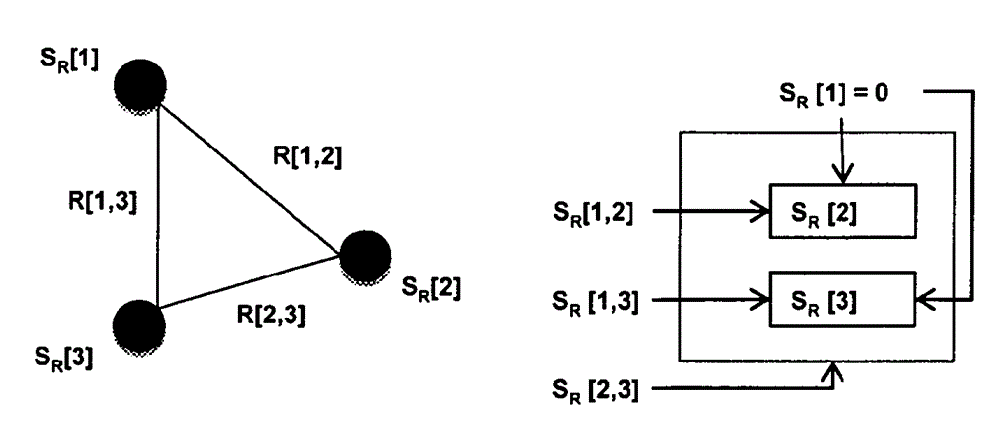
Scrambling code resolution
A code division multiple access and base station technology, applied in the direction of multiplexing code distribution, code division multiplexing system, signaling distribution, etc., can solve problems such as SHO failure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0089] A node (eg, RNC 30 ) receives a first type of measurement report (MR) reporting a scrambling code (SC)=450. It is known that SC=450 belongs to the sectors of the active set, so it is guaranteed to be sector 254. The node also receives a second type of measurement report (MR) with report scrambling code (SC)=48. There are two possible candidates for SC=48. The candidates are sector 751 and sector 79 .
[0090] The timing reference for each sector 254, 751 and 79 is known (via Figure 6 The timing of is obtained with reference to recovery step 101). MR received from terminal carries T for SC=450 and SC=48 m value. Timing reference for sector 254 = 10000 chips. Timing reference for sector 751 = 500 chips. Timing reference for sector 79 = 9351 chips. T for SC=48 m The value of is 2852 chips. T for SC=450 m The value of is 3500 chips.
[0091] Applying equation (2) above:
[0092] (5)
[0093] Candidate sectors = 751.
[0094] d[ i,j ]=(10000-500)–(3500-28...
example 2
[0102] Robust SC parsing. Unlike distance-based SC parsing, which assumes geometry to clarify uncertainty, the proposed scheme based on analyzing the relative distances between candidates is a robust approach, since it relies on the actual Network measurement. Figure 12 and Table 2 shows that SC=447 has two candidates, sectors 1242 and 1309. By comparing the relative distances between the two candidates (obtained using the method described above) and the reference sector, it is clear that sector 1309 is the correct choice for the candidate. However, relying only on the physical distance between sectors will lead to wrong decisions.
[0103]
[0104] Table 2. Example of radio distance dependence
example 3
[0106] Detect sectors that do not exist in the network topology. If the relative distance is not in the proper range, this means that there are some missing sectors in the network topology due to, for example, insufficient buffers. In Table 3, SC=172 has two candidates: sectors 308 and 1258. The relative distances for the two candidates are far from plausible, indicating that there are missing sectors for SC 172 .
[0107]
[0108] Table 3. Examples of missing sectors
[0109] Yet another use of the method is to detect SC collisions. When the SC rules are not designed properly, the terminal may measure two different sectors with the same SC. This is an undesirable situation which results in SHO failure and possible dropped connections. Embodiments of the present invention are able to detect this situation by noticing that MRs refer to two different sectors with the same SC at different times.
[0110] In the above example, the time-dependent quantity T m Reported by t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com