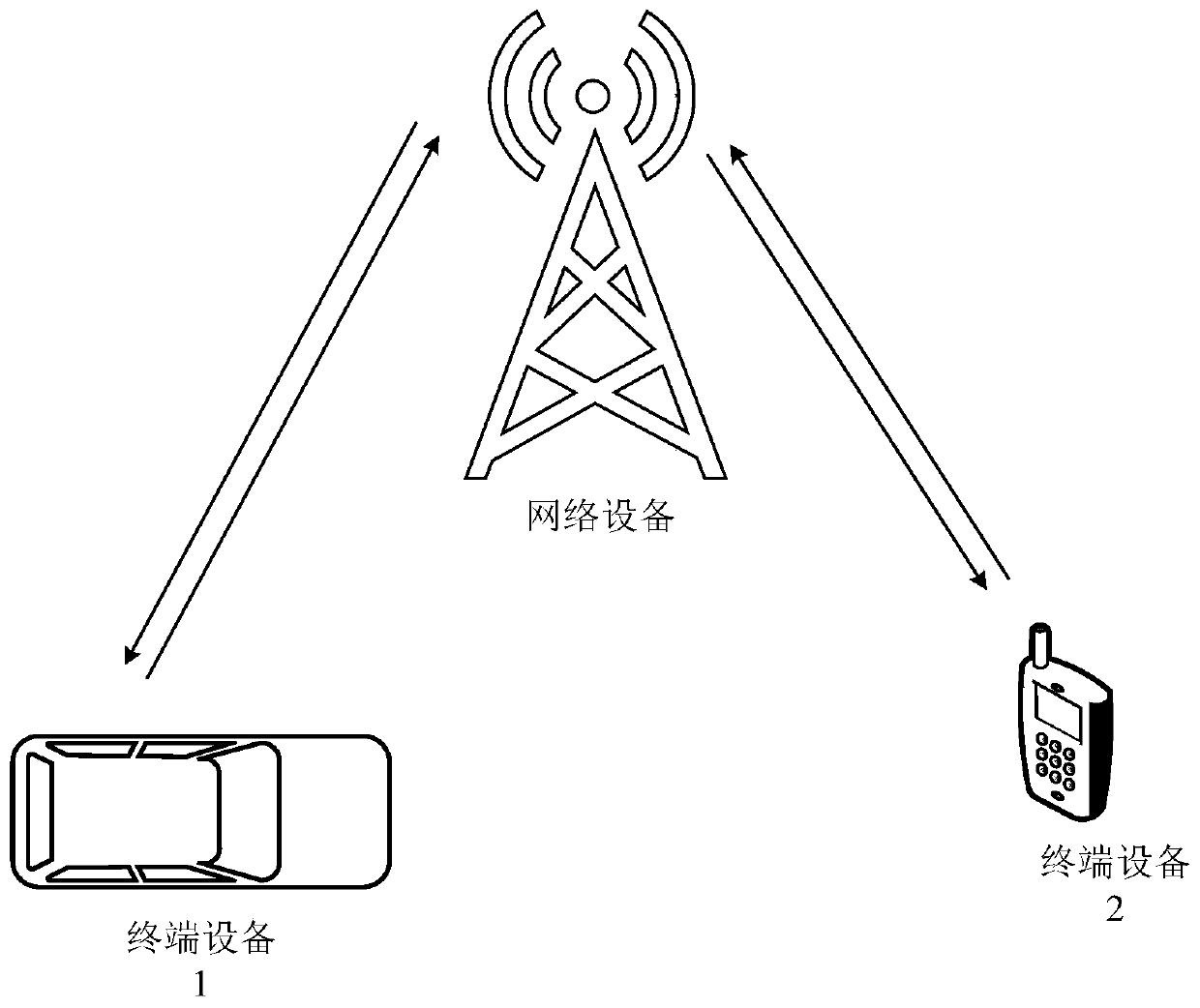
Patents
Literature
37results about "Network synchronisation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
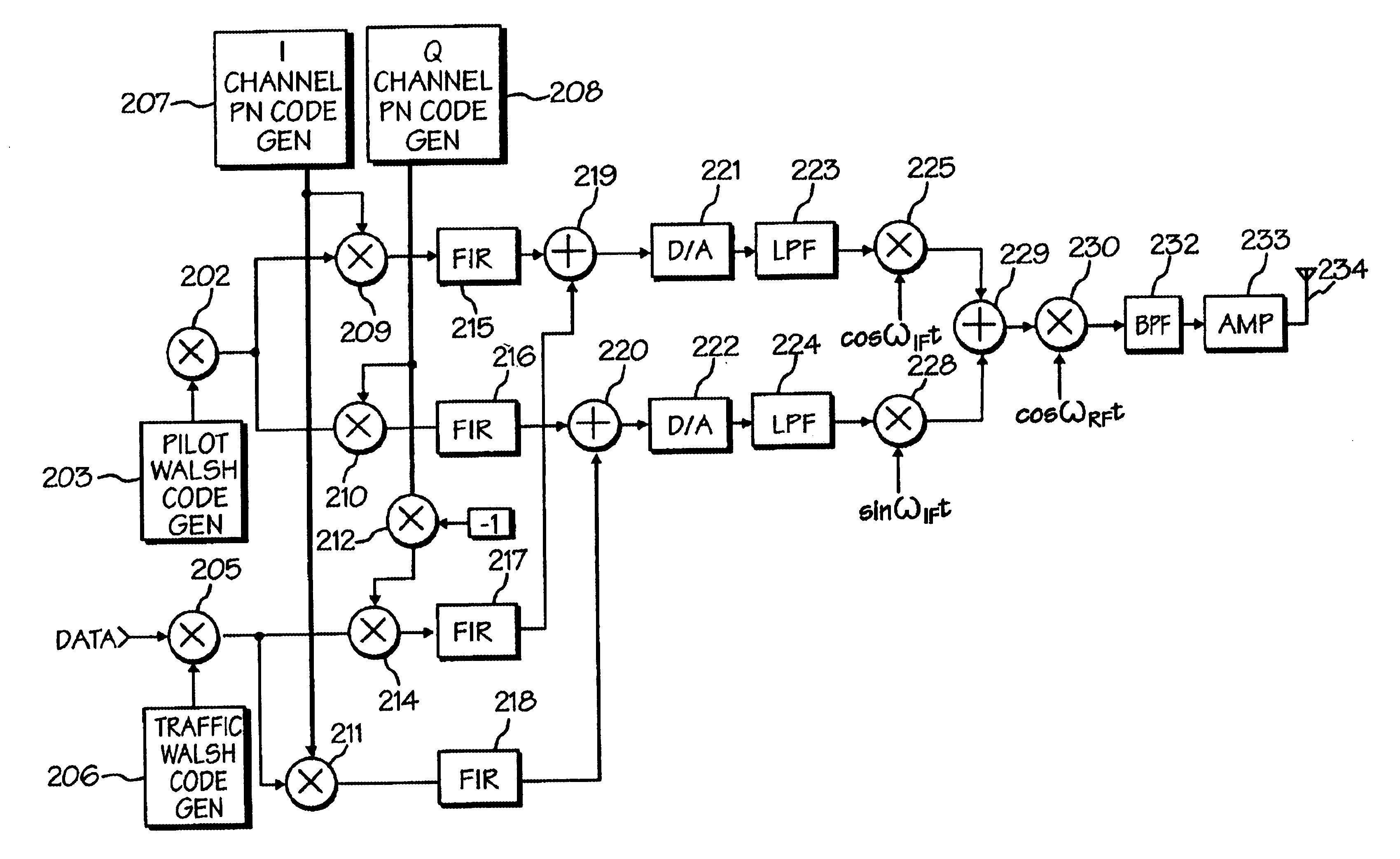
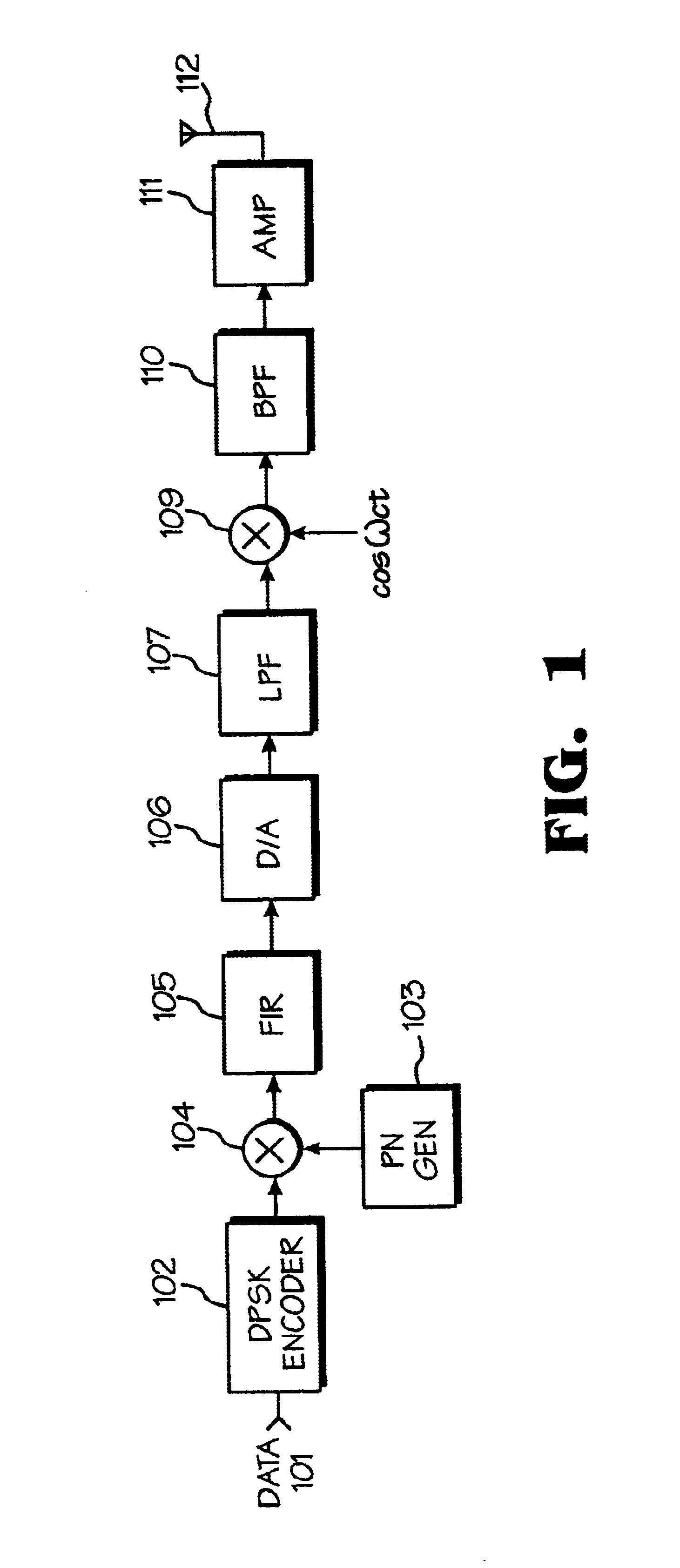
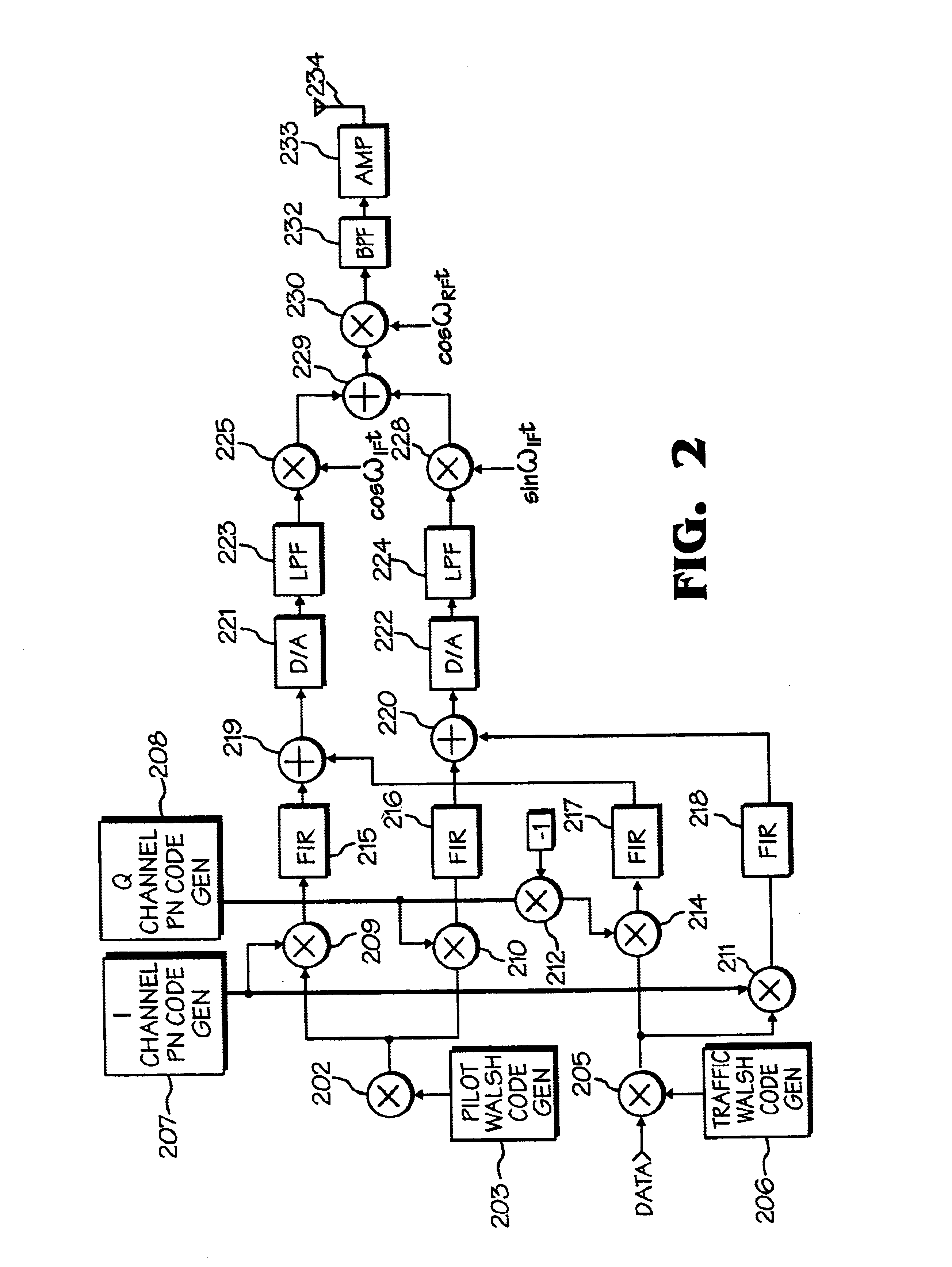
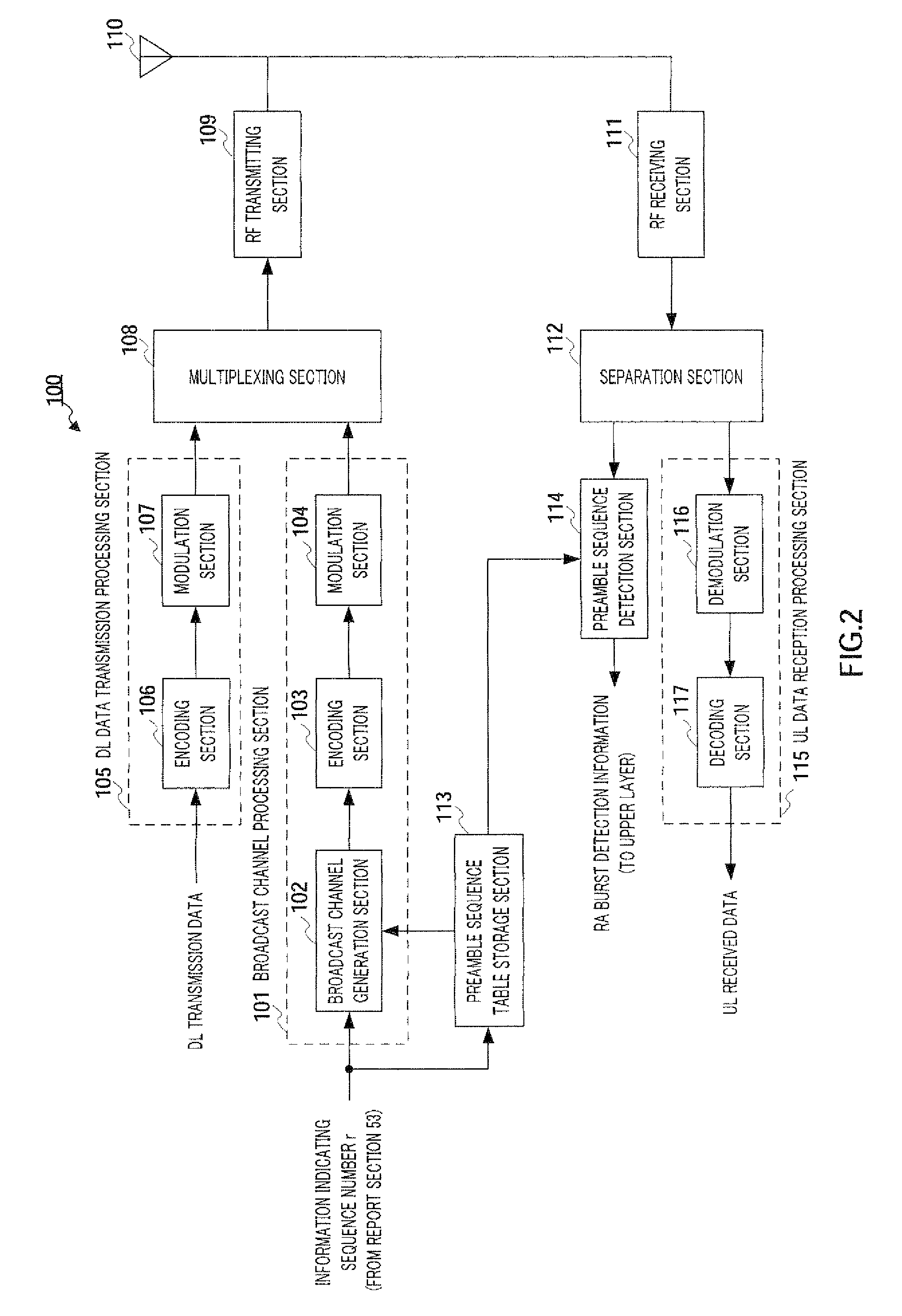
Data transmitter and receiver of a spread spectrum communication system using a pilot channel
InactiveUSRE38603E1The synchronization process is simpleMinimizing PN code acquisition timeSynchronisation information channelsMultiplex code generationFinite impulse responseIntermediate frequency
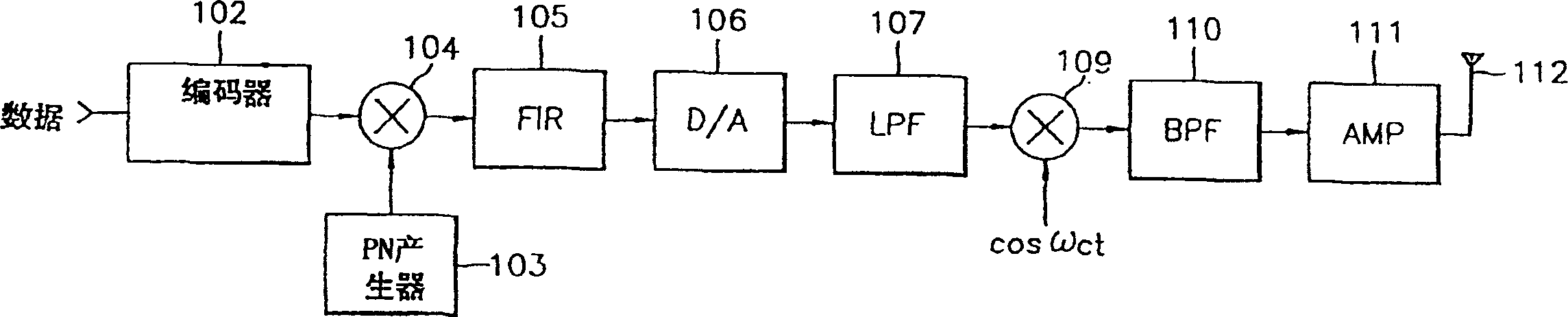
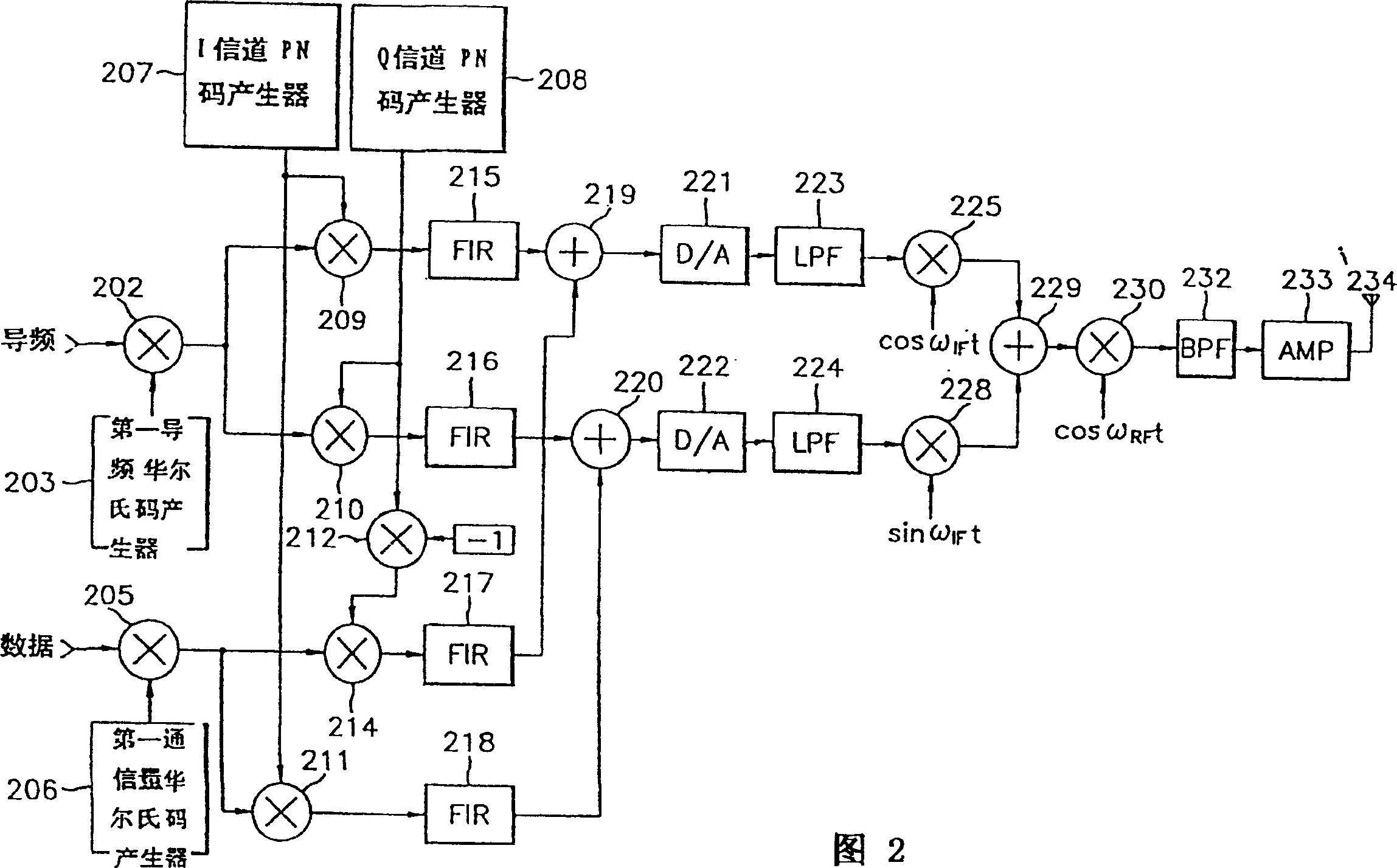
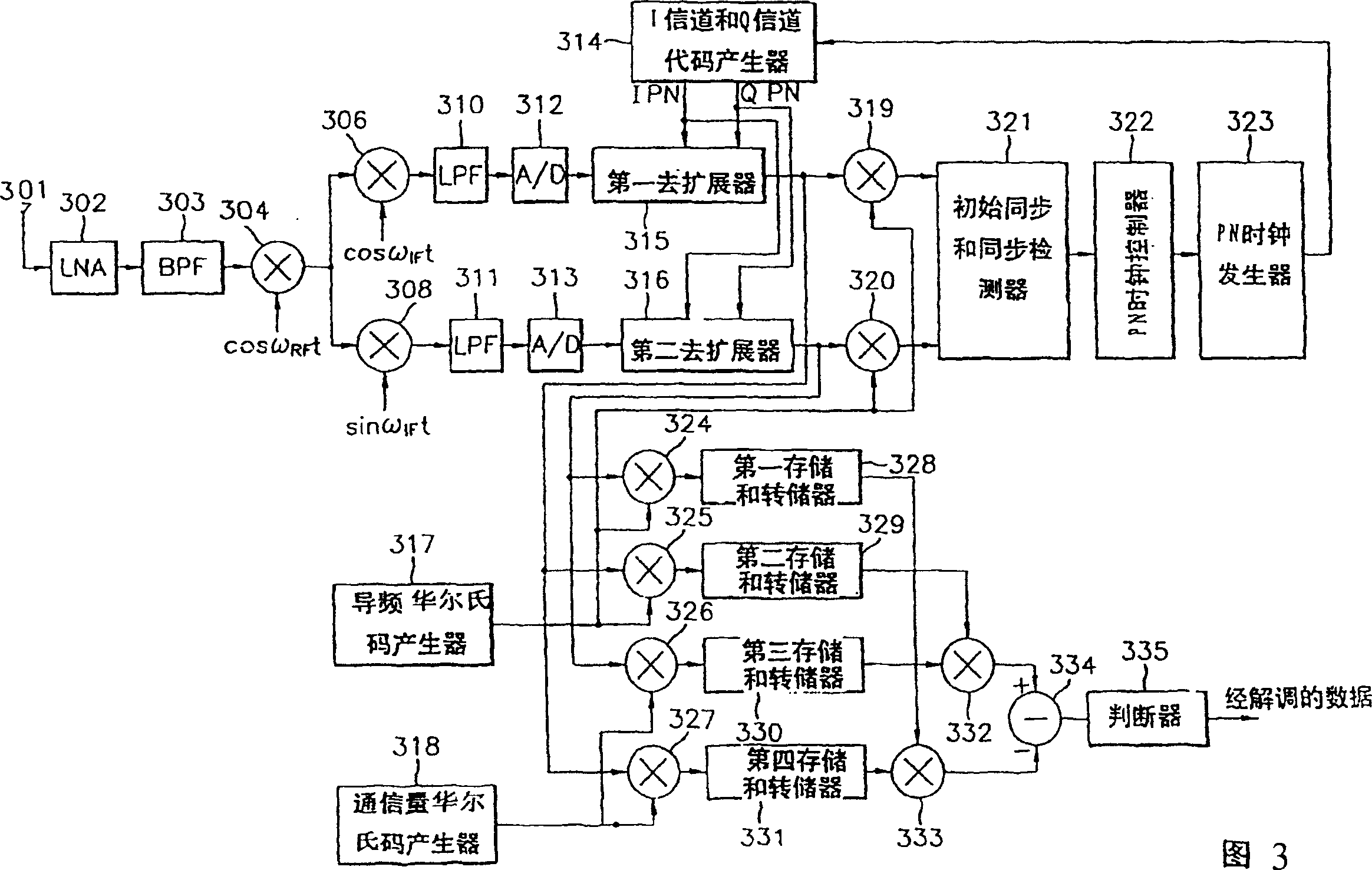
An improved spread spectrum communication system includes a transmitter and a receiver utilizing a pilot channel for the transmission of pure rather than modulated PN codes for code acquisition or tracking purposes with a lower bit error rate. The pilot signal is used to obtain initial system synchronization and phase tracking of the transmitted spread spectrum signal. At the transmitter side, a Walsh code generator, a Walsh modulator, a first PN code generator, a first band spreader, a second band spreader, finite impulse response filters, digital-analog converters, low-pass filters, an intermediate frequency mixer, a carrier mixer, a band-pass filter are used to transmit a spread spectrum signal. At the receiver side, a corresponding band-pass filter, a carrier mixer, an intermediate-frequency mixer, low-pass filters, analog-digital converters, a second PN code generator, an I channel despreader, a Q channel despreader, a PN code synchronization controller, a Walsh code generator, a first Walsh demodulator, a second Walsh demodulator, accumulator & dump circuits, a combiner, and a data decider are used to demodulate a received spread spectrum signal
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
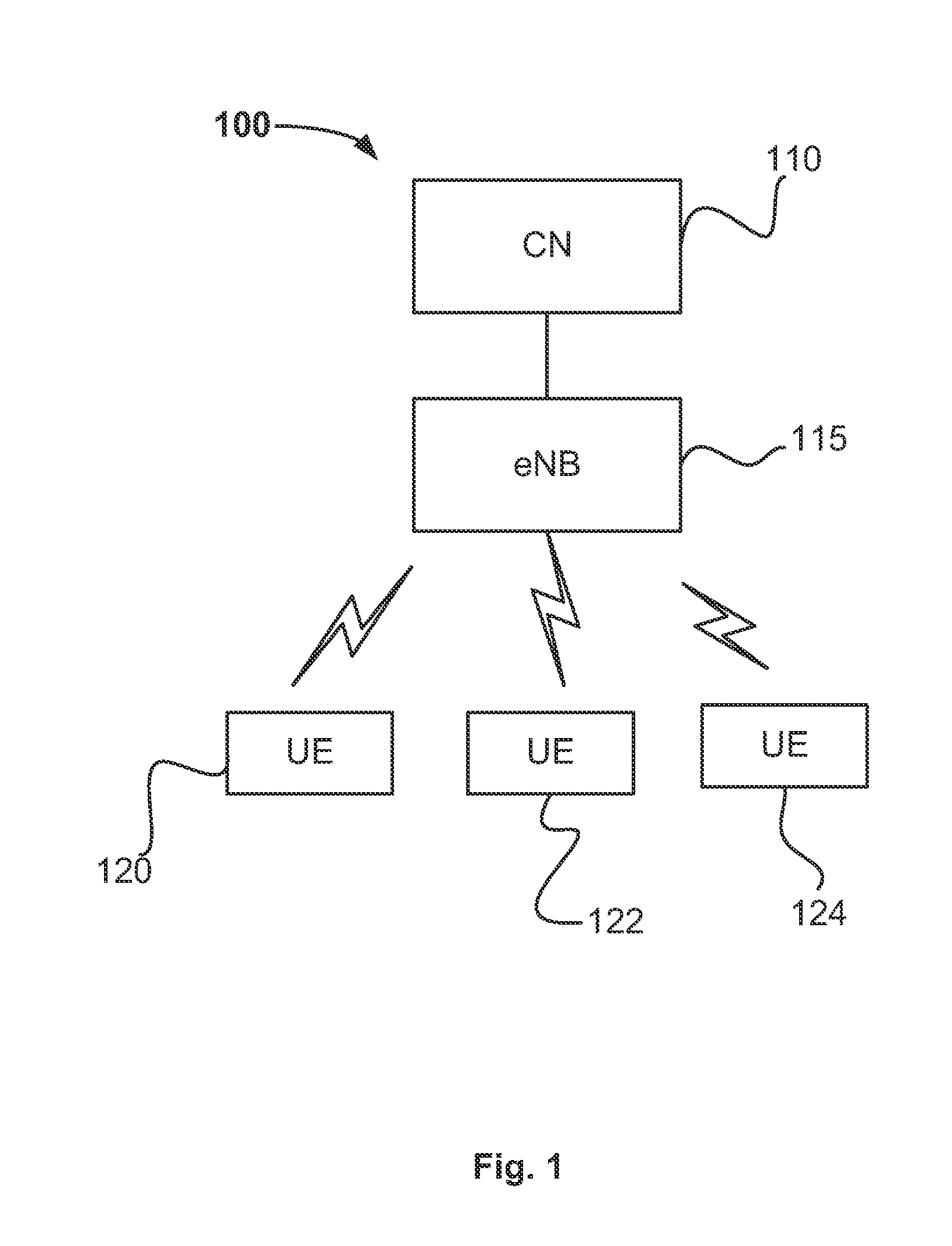
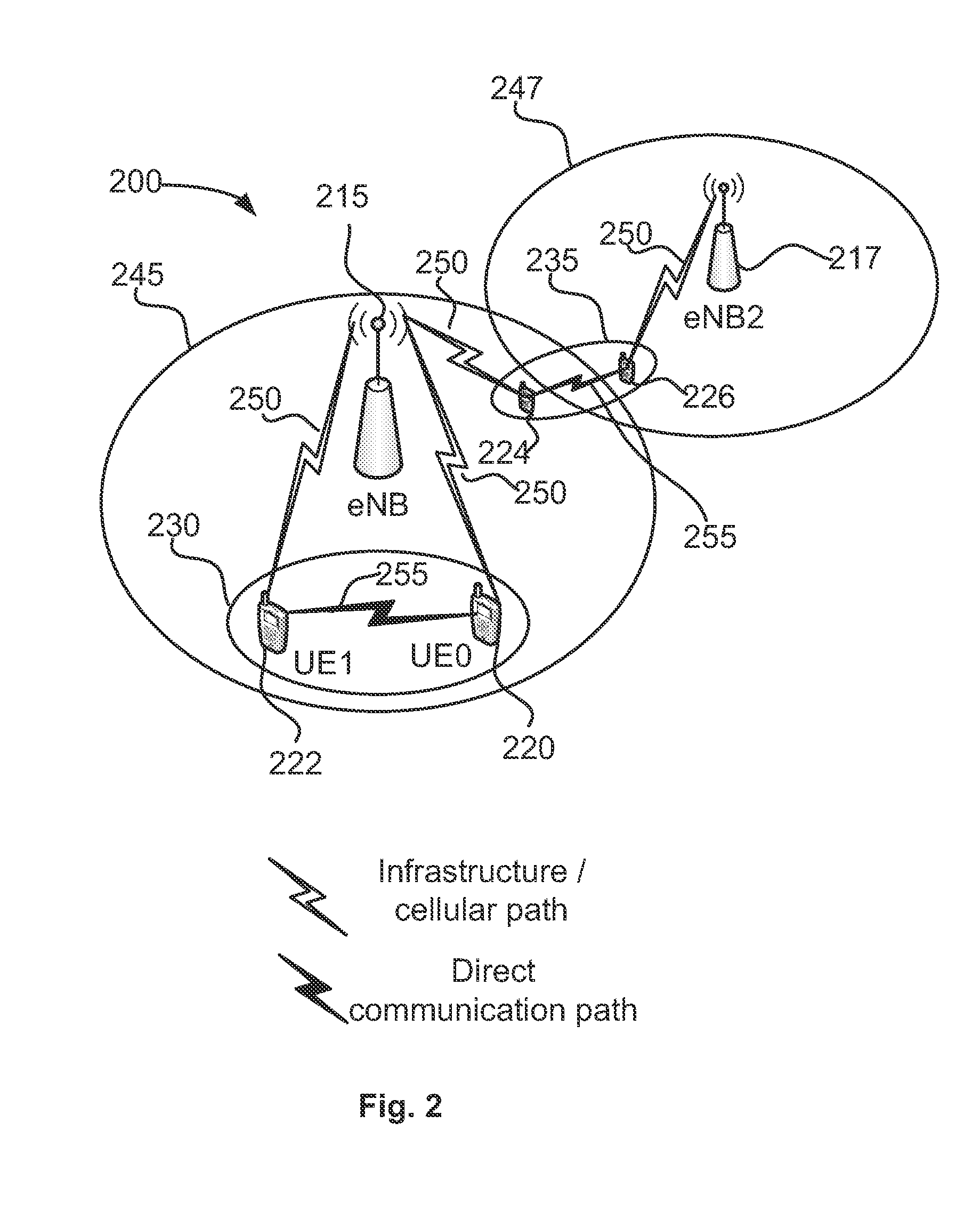
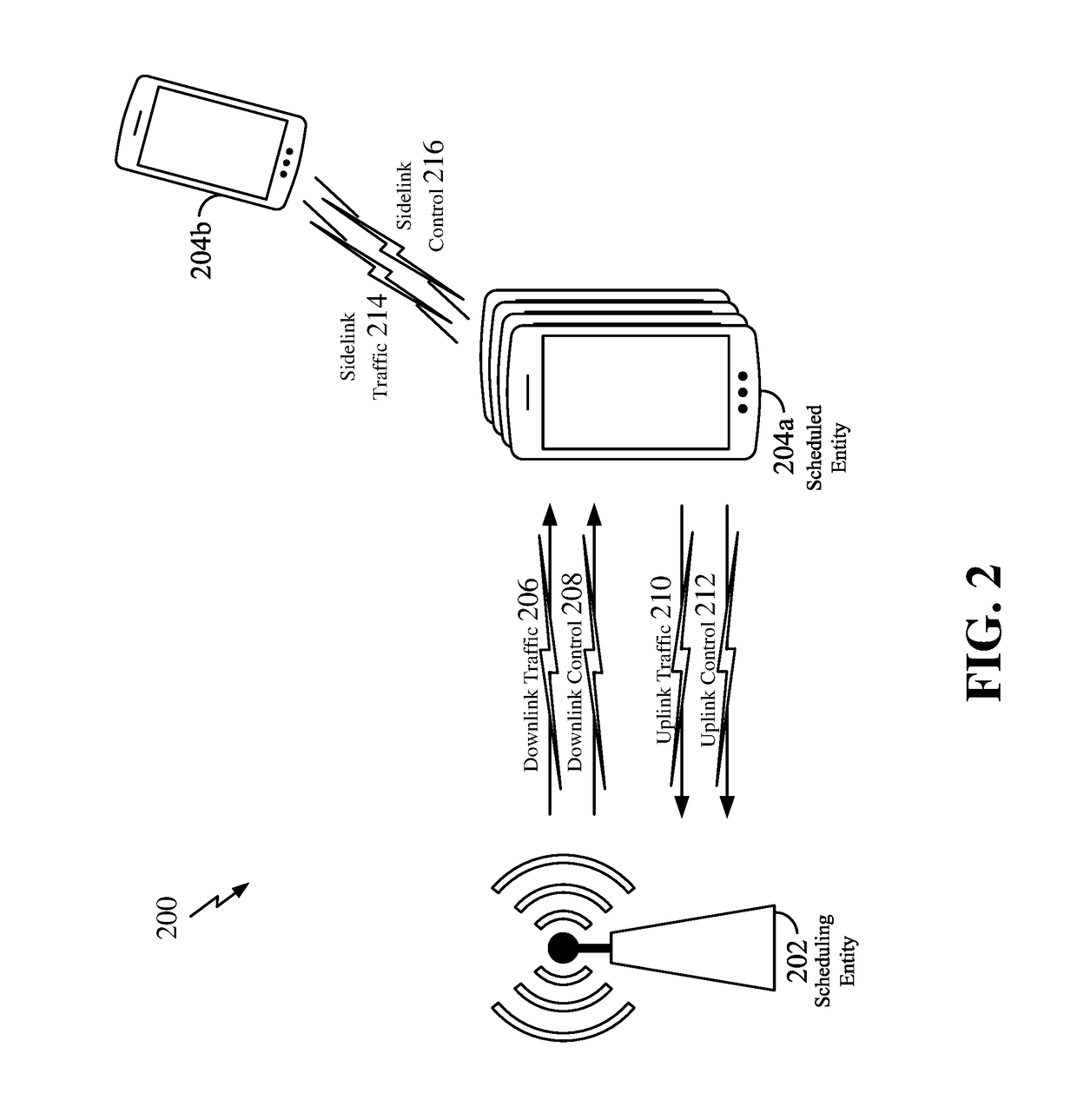
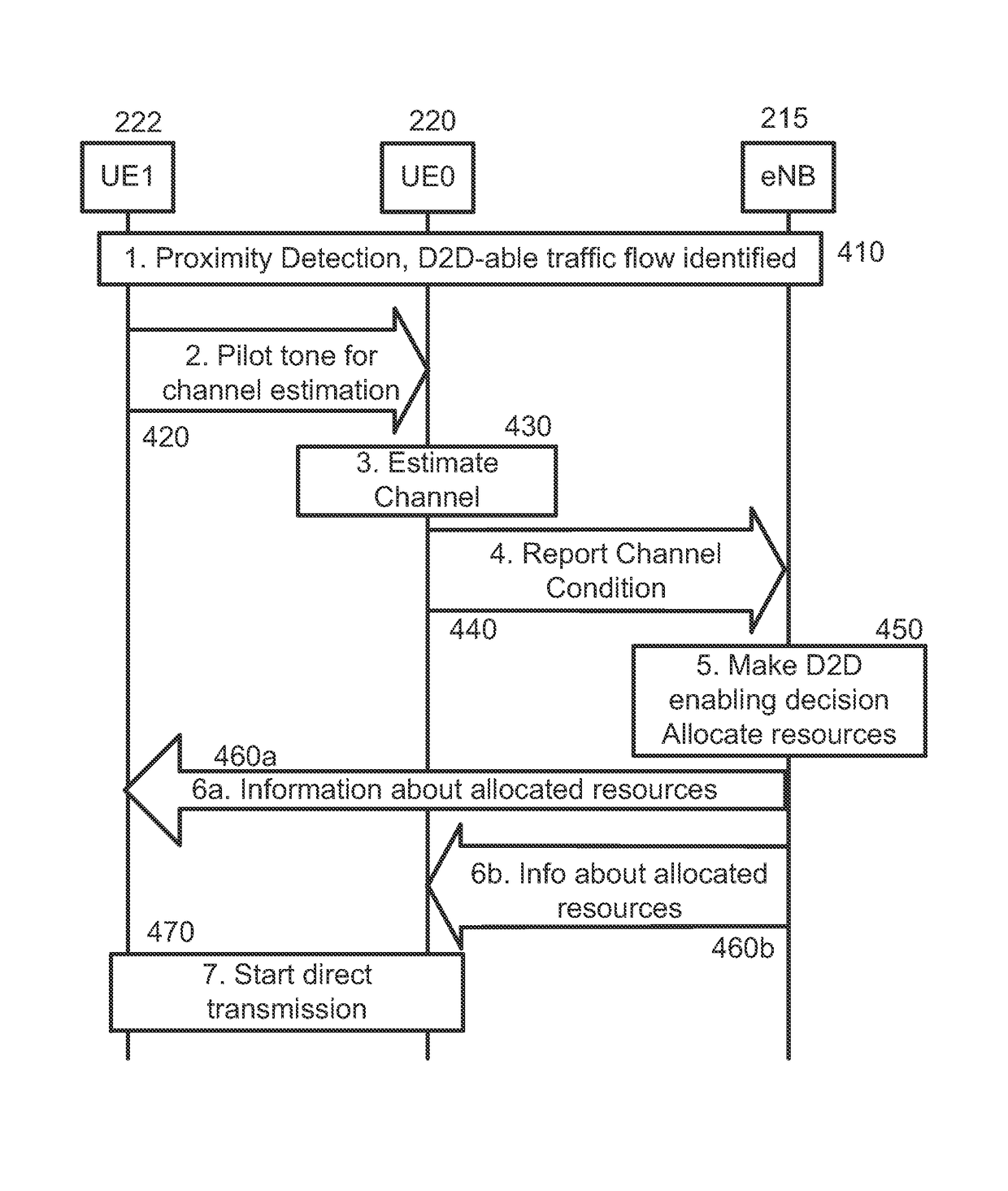
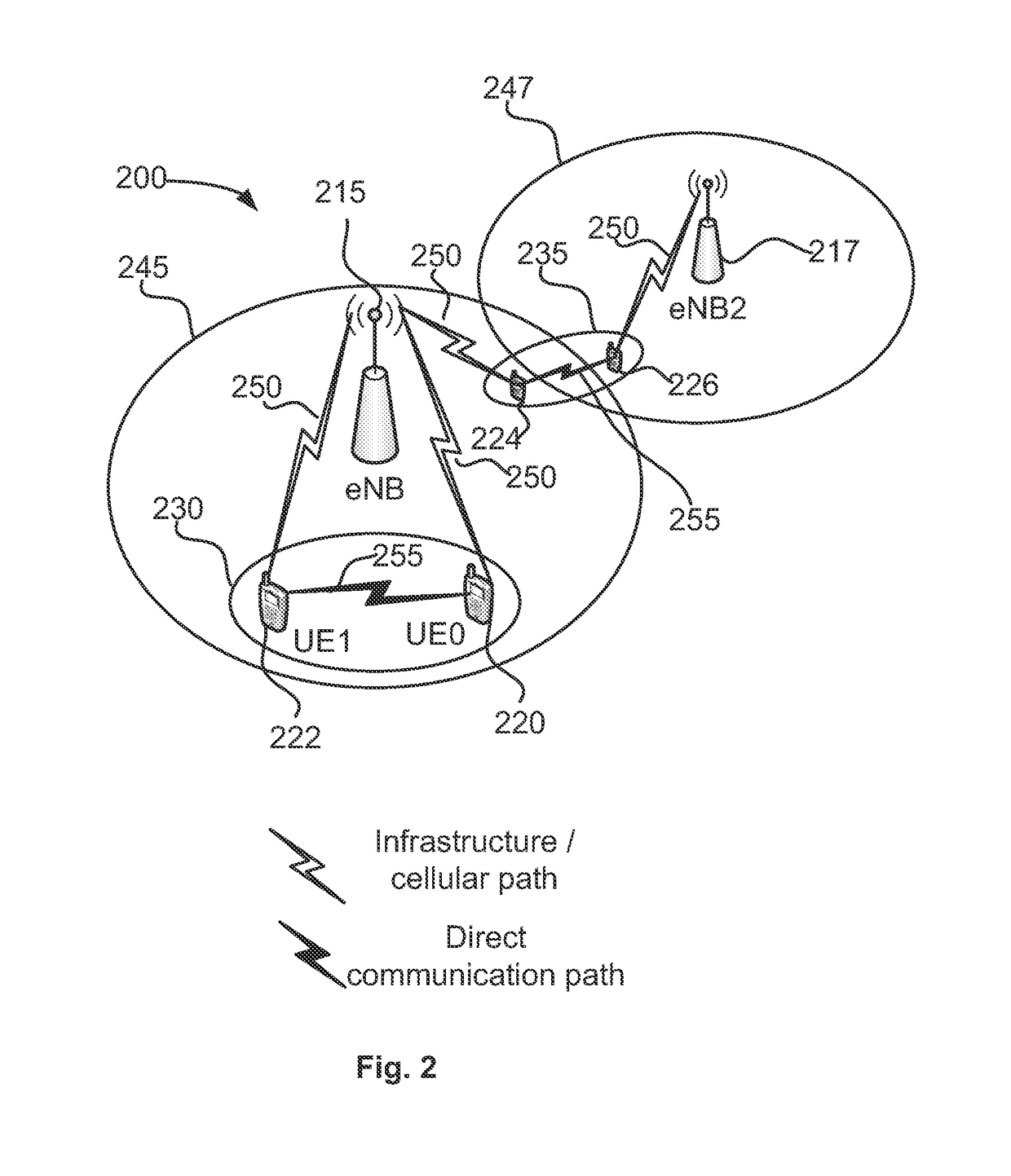
Device-to-device communication
An apparatus is provided for a device-to-device, D2D, communication enabled user equipment, UE, comprising a processing section to determine, based on a signal received from another UE, a channel condition between the UE and the another UE; the UE to report the determined channel condition to an evolved Node B, eNB. The processing section is to initiate D2D communication based on a communication from the eNB, received in response to the report. Also, an apparatus is provided for a network element, comprising An input to receive a describing a channel condition between a first UE and a second UE; a processor to determine, based on the channel condition, whether or not D2D communication between the first UE and the second UE is to be enabled; and an output to output a result of the determination when the processor determines D2D communication is to be enabled. Related methods are also provided.
Owner:APPLE INC
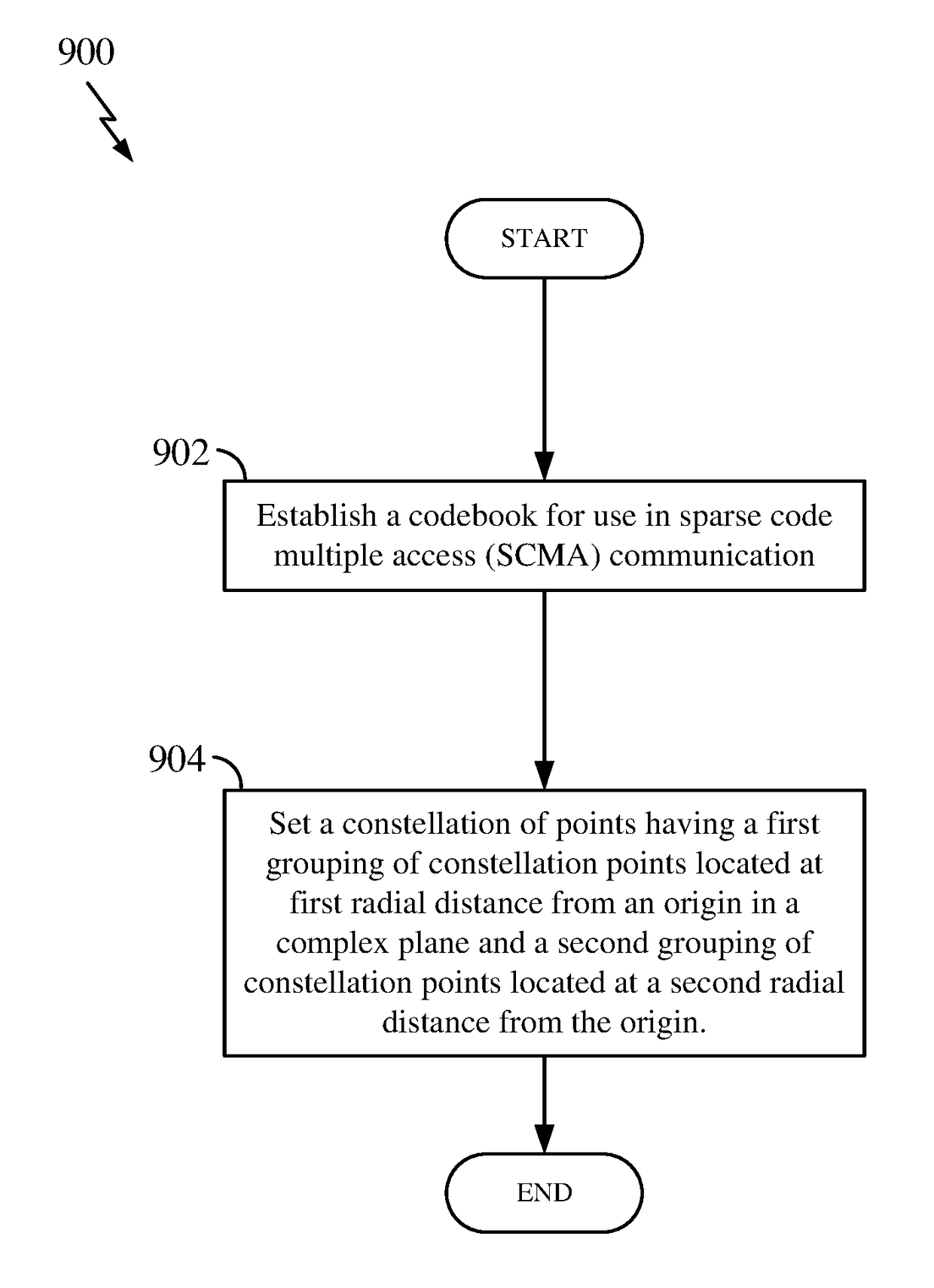
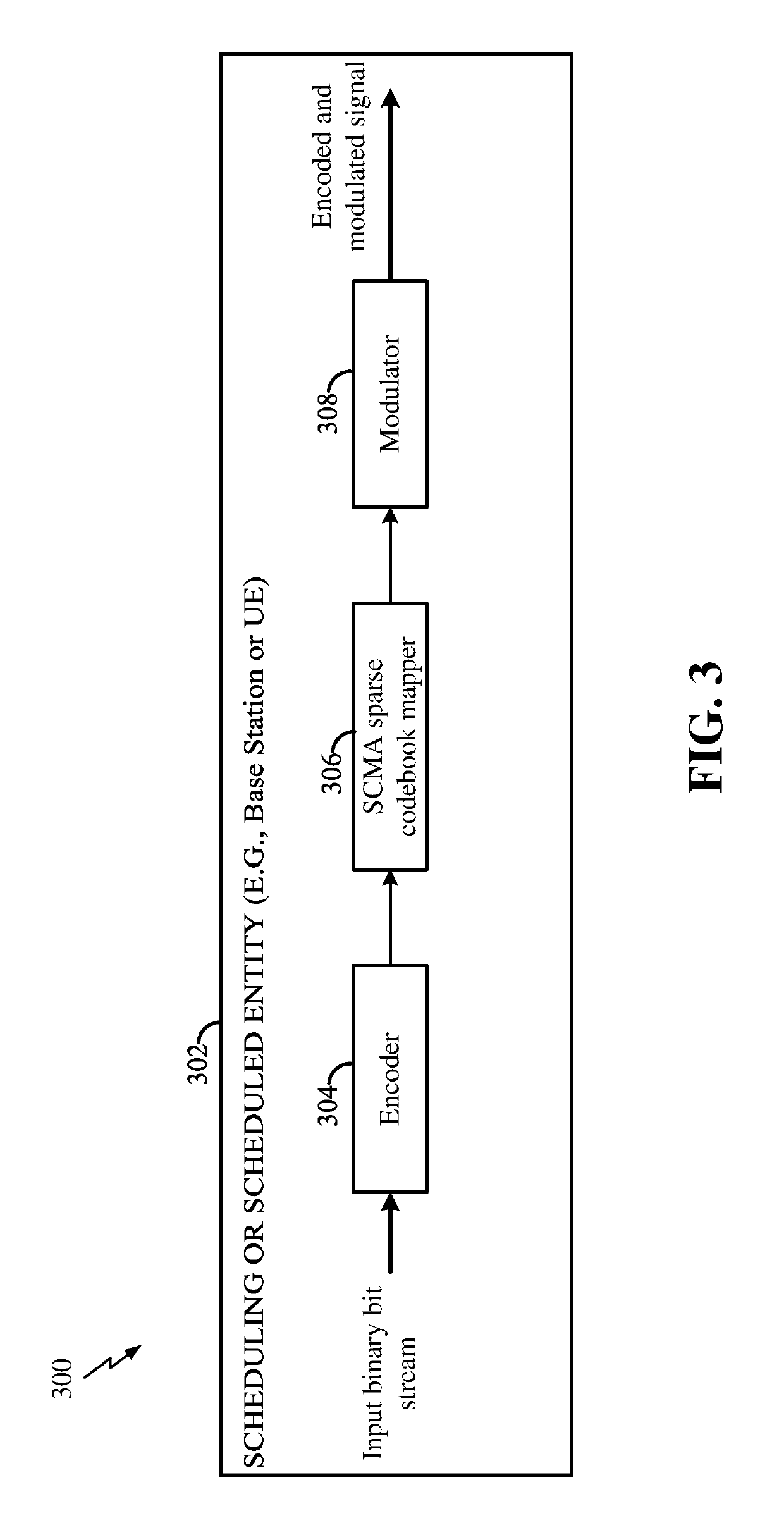
Methods and apparatus for construction of scma codebooks
Disclosed are methods and apparatus used in wireless communications. The methods and apparatus establish a codebook for use in sparse code multiple access (SCMA) encoded communications, in particular. The SCMA codebook is configured to set the codebook for at least one layer (i.e., a user) to include a constellation of points having a first grouping of constellation points located at first radial distance from an origin in a complex plane and a second grouping of constellation points located at a second radial distance from the origin. This codebook arrangement provides increased gains at receivers by optimizing the constellation shape to improve the distance between constellation points (i.e., SCMA codebook performance), and in particular more robust performance when encountering amplitude and phase misalignment in uplink (UL) multiple access.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
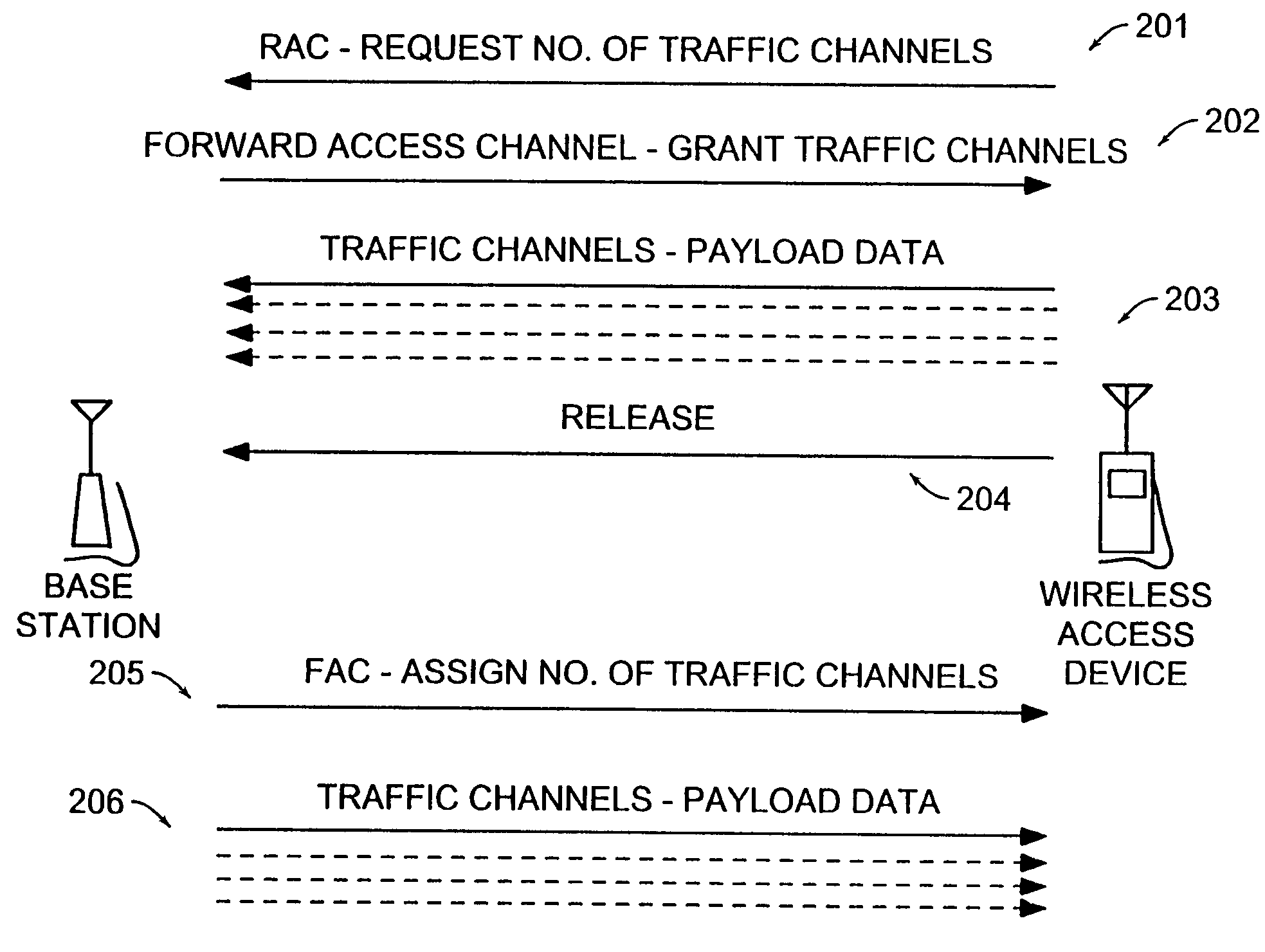
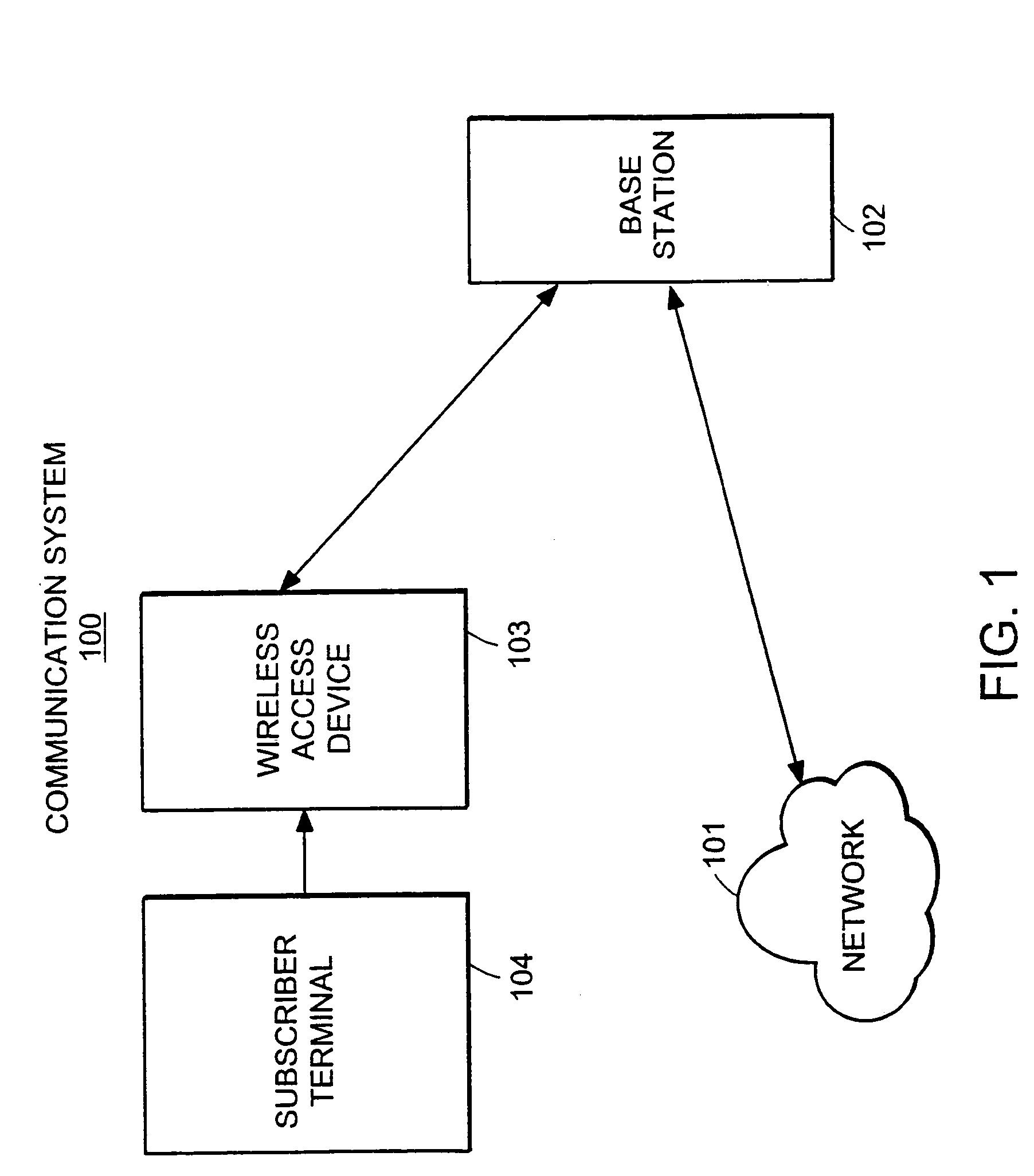
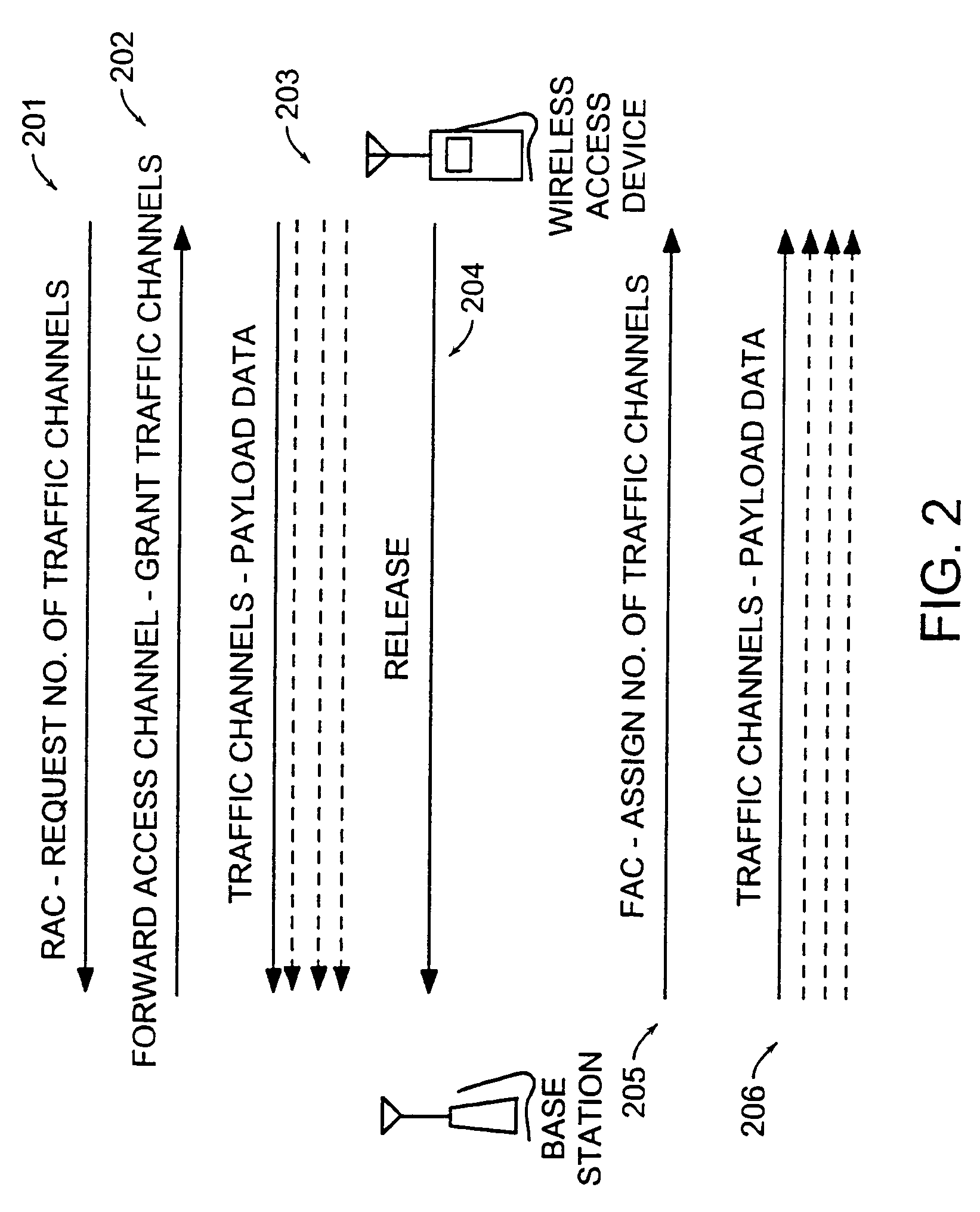
Maintenance of channel usage in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS6965778B1Network topologiesConnection managementCommunications systemTelecommunications link
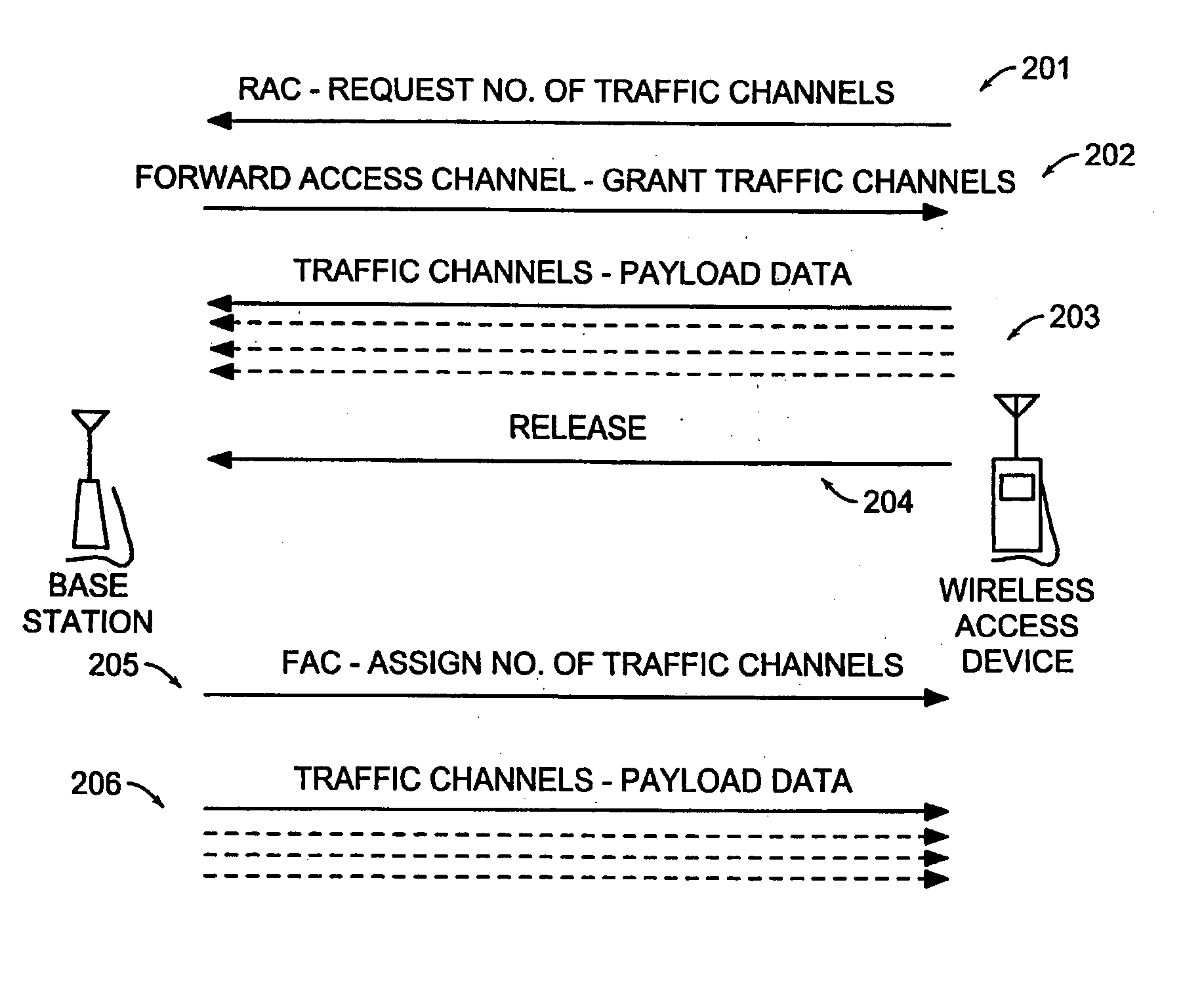
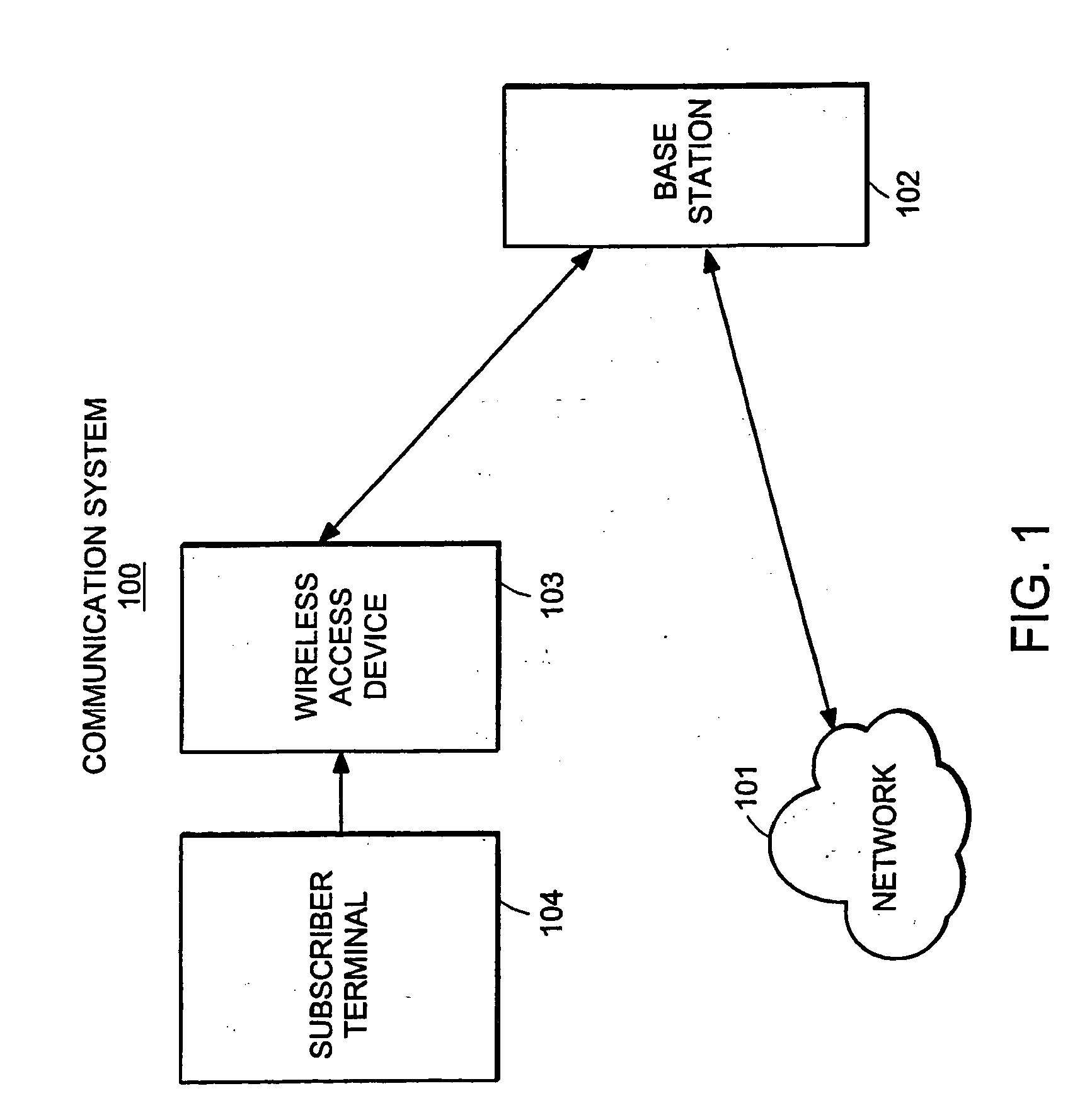
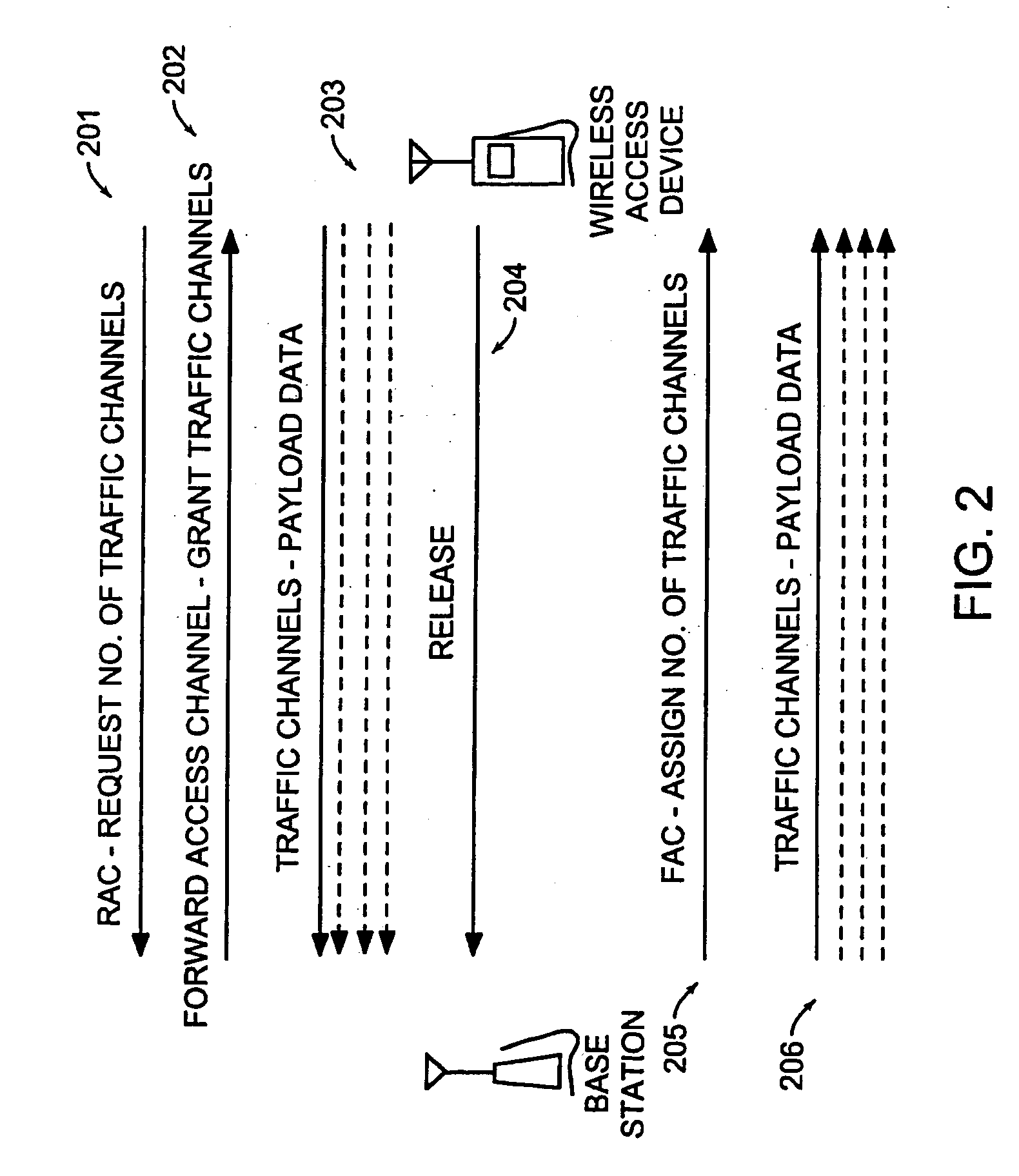
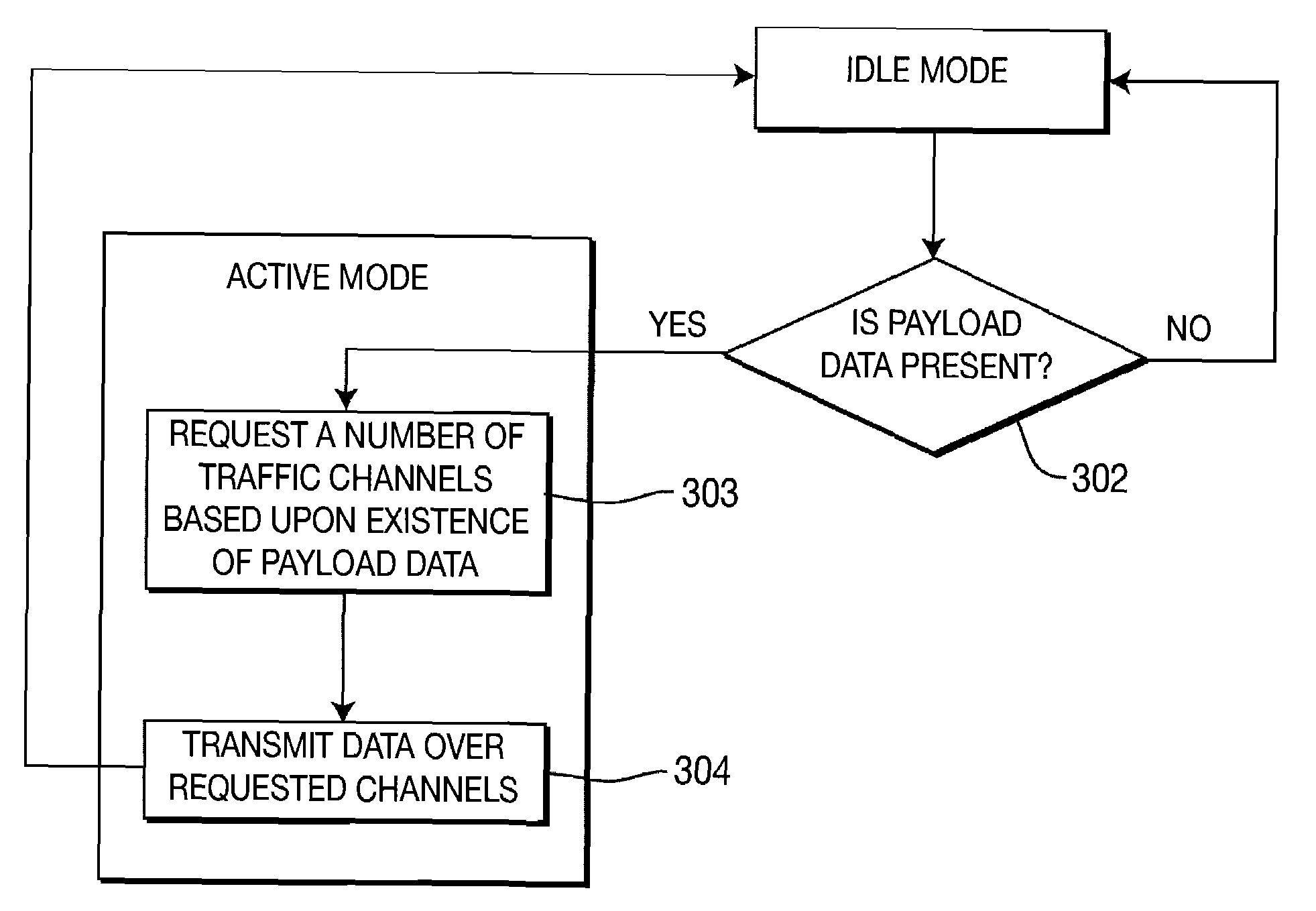
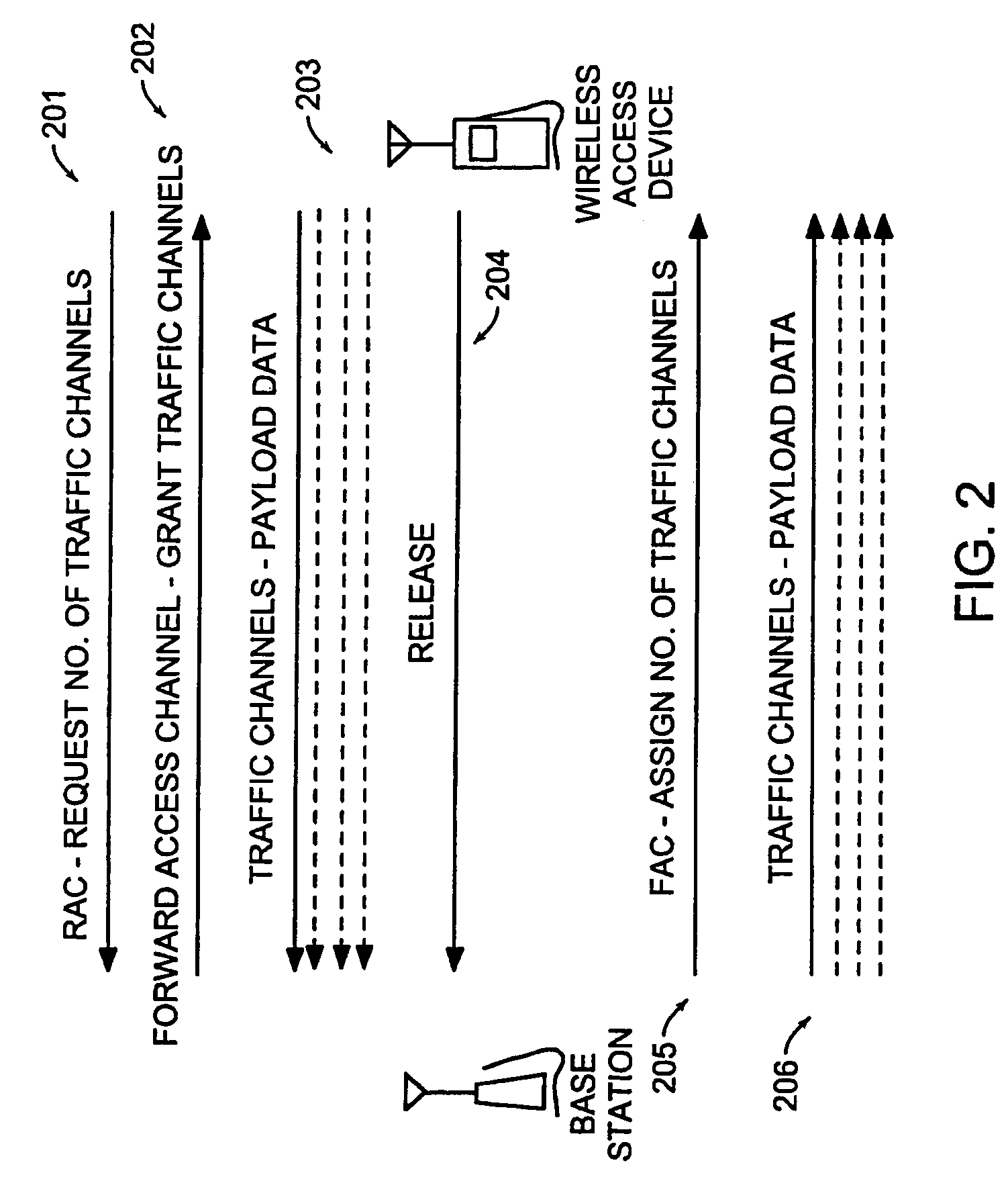
Data is accessed from a network via a wireless communication link. A determination is made as to whether payload data has been received from a subscriber's terminal. If so, then a request is sent for a first set of traffic channels, and the payload data is transmitted over the first set of traffic channels.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Deployment and communications test of intermediate-range devices using a short-range wireless mobile device
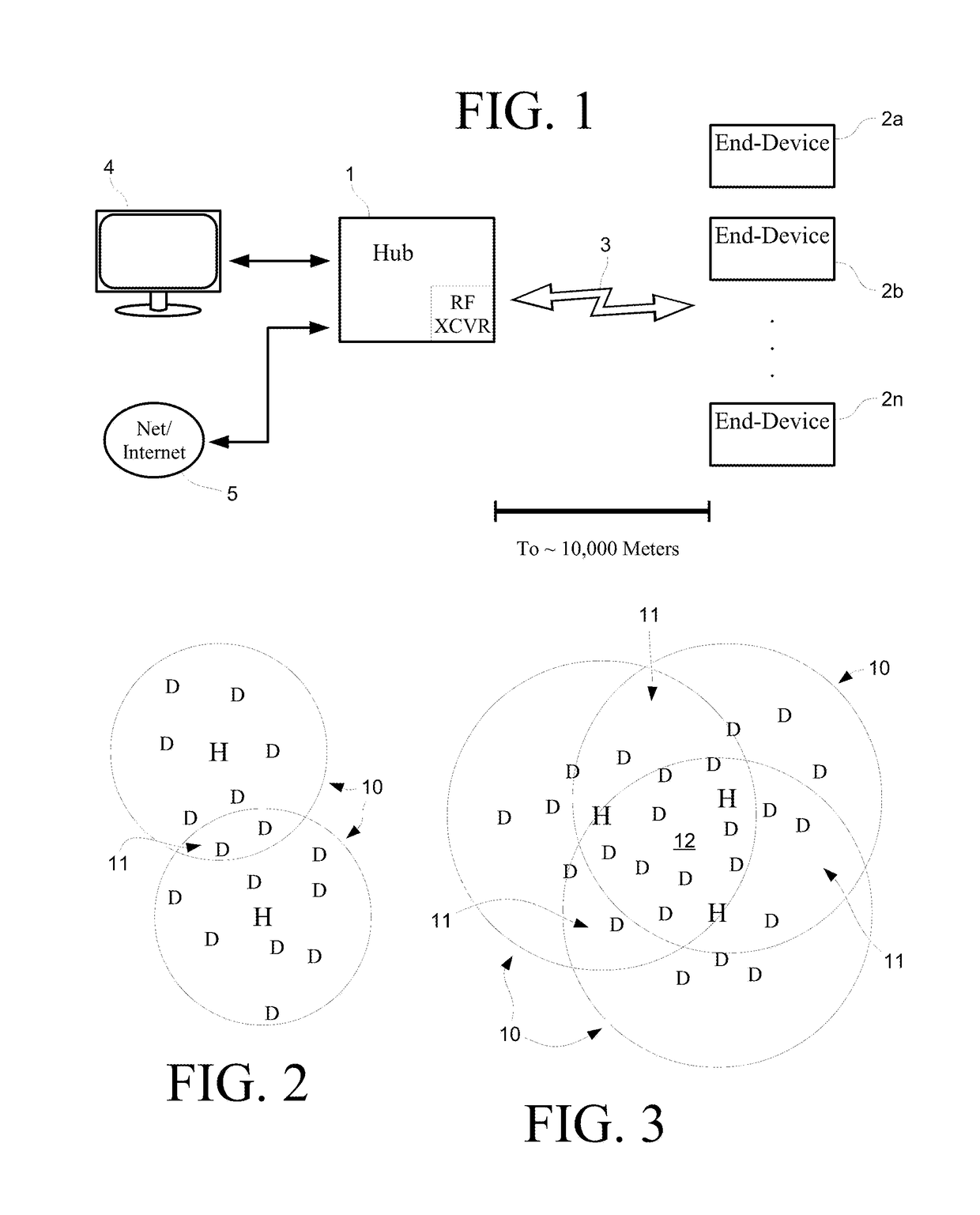
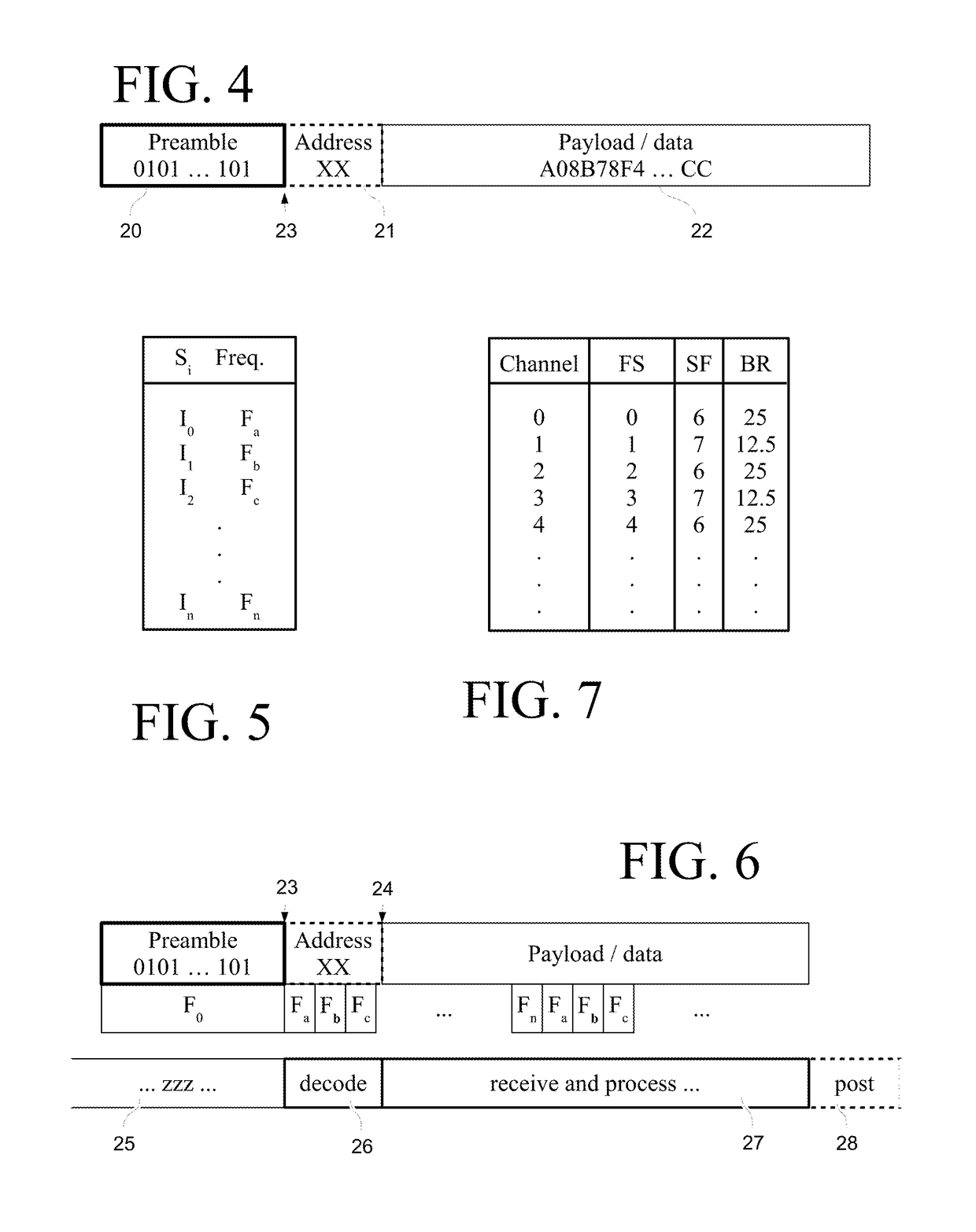
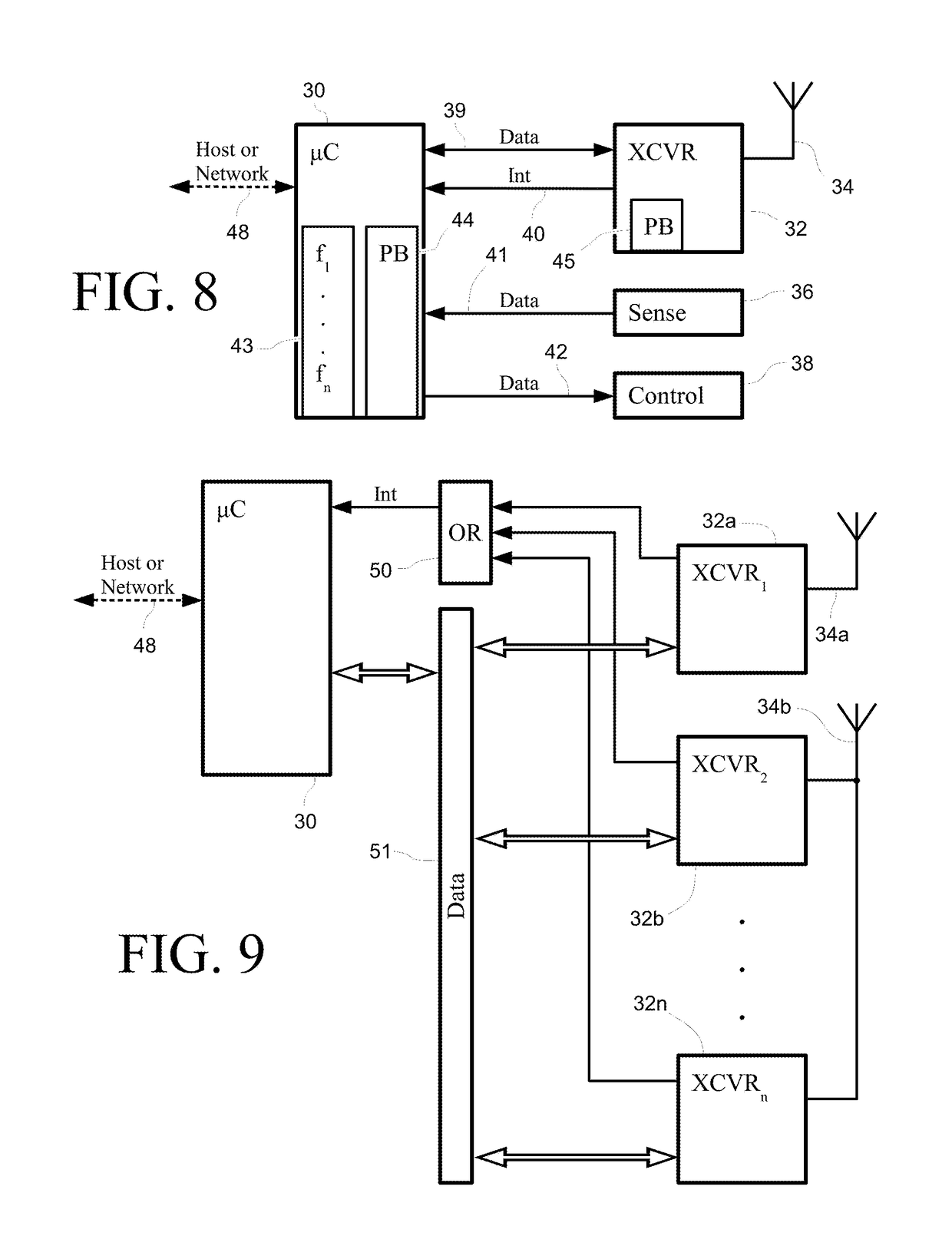
Disclosed herein are wireless devices operable at intermediate wireless at ranges of thousands of meters, utilizing packets that include a preamble and a data payload. Devices may be such things as keypads, door latches, occupancy monitors, sprinkler controllers and other devices needing a communications link. Devices include an intermediate-range transceiver and a separate short-range wireless transceiver accessible from a mobile device such as a cellular telephone or portable tablet. Devices may bear a scannable label bearing a code providing a means of identification, and can be registered in a database and deployed for use by means of an application running on the mobile device. Intermediate-range communications may be tested during deployment as directed from a mobile device. Detailed information on various example embodiments of the inventions are provided in the Detailed Description below, and the inventions are defined by the appended claims.
Owner:SURE FI INC
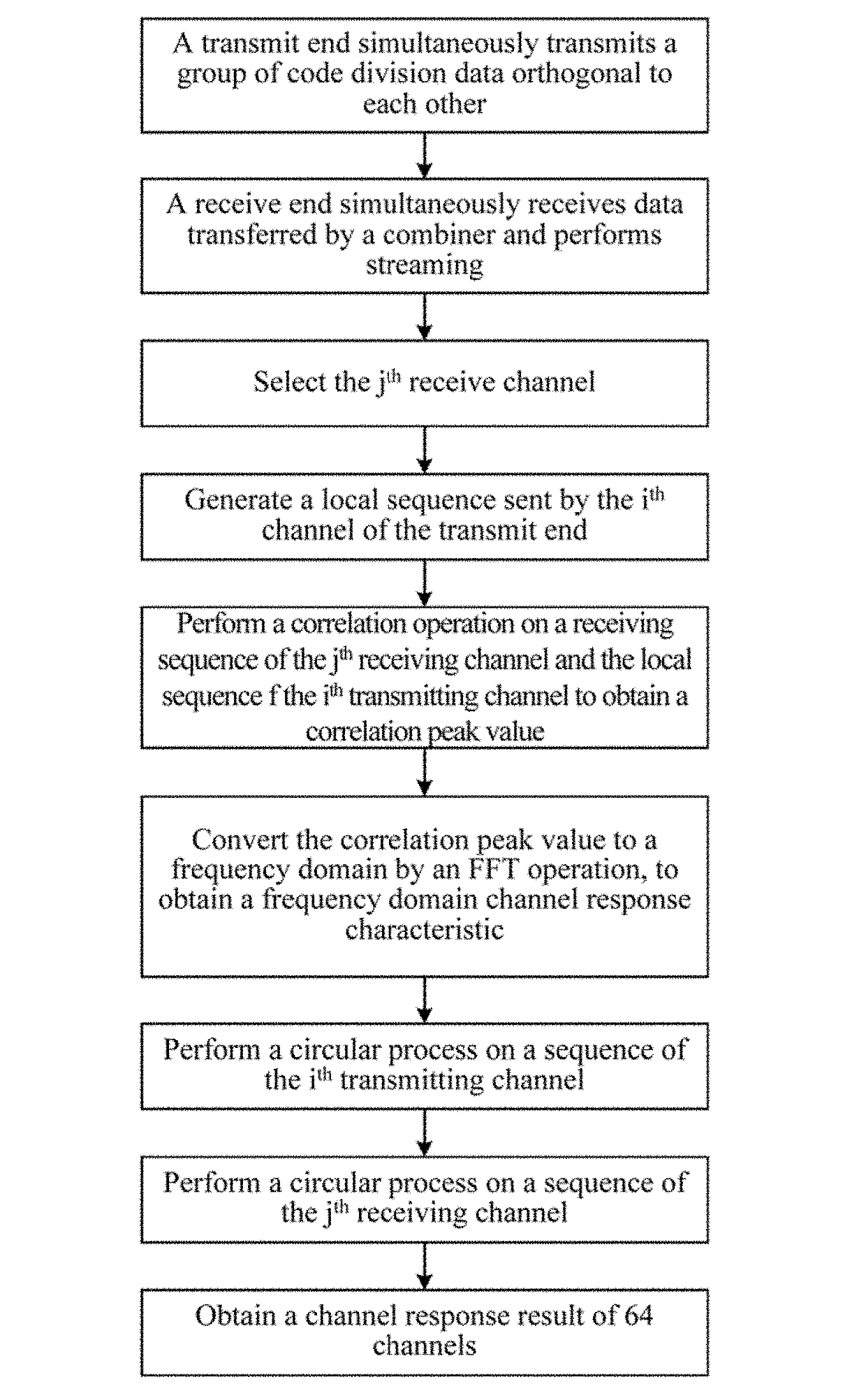
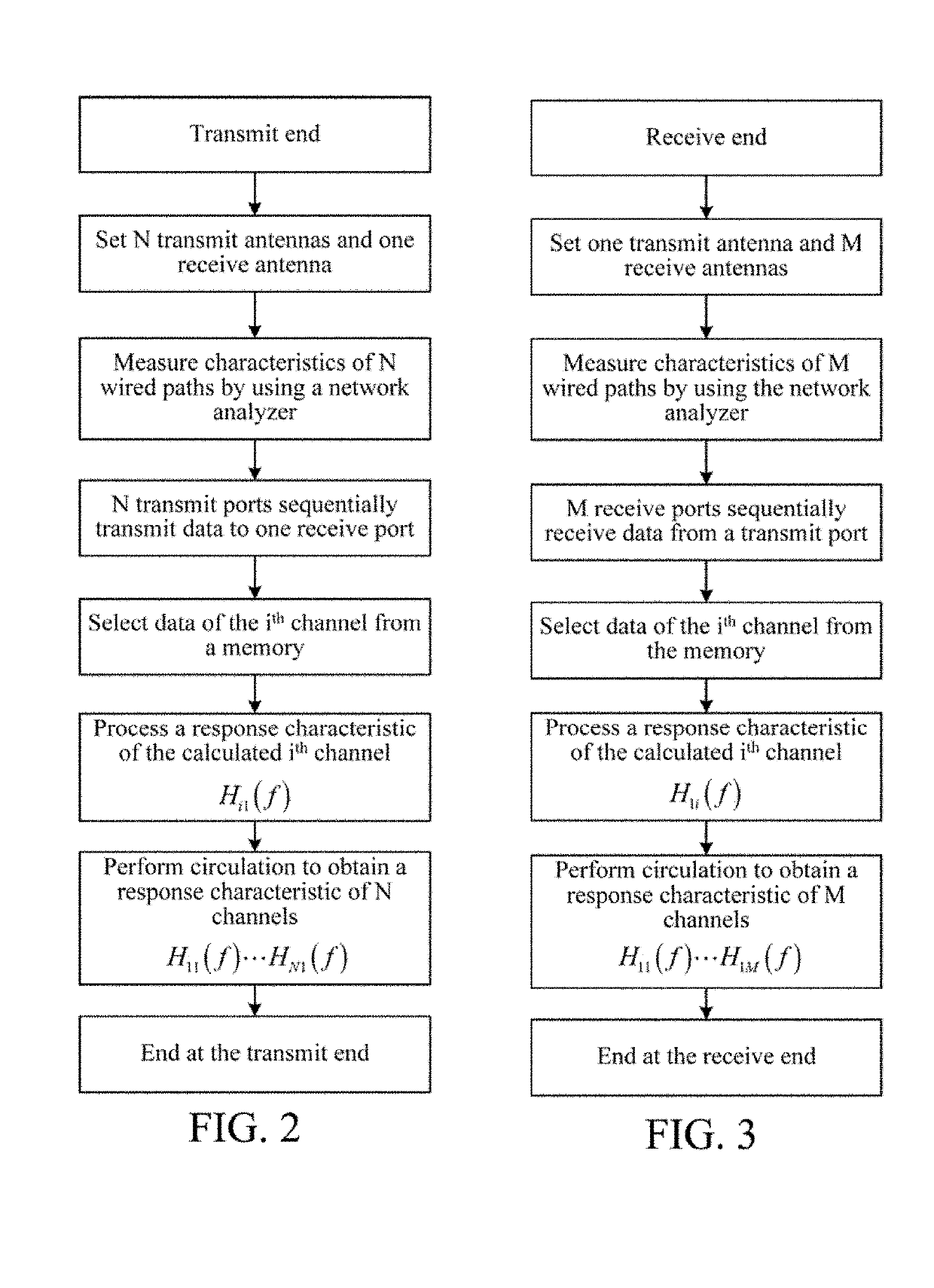
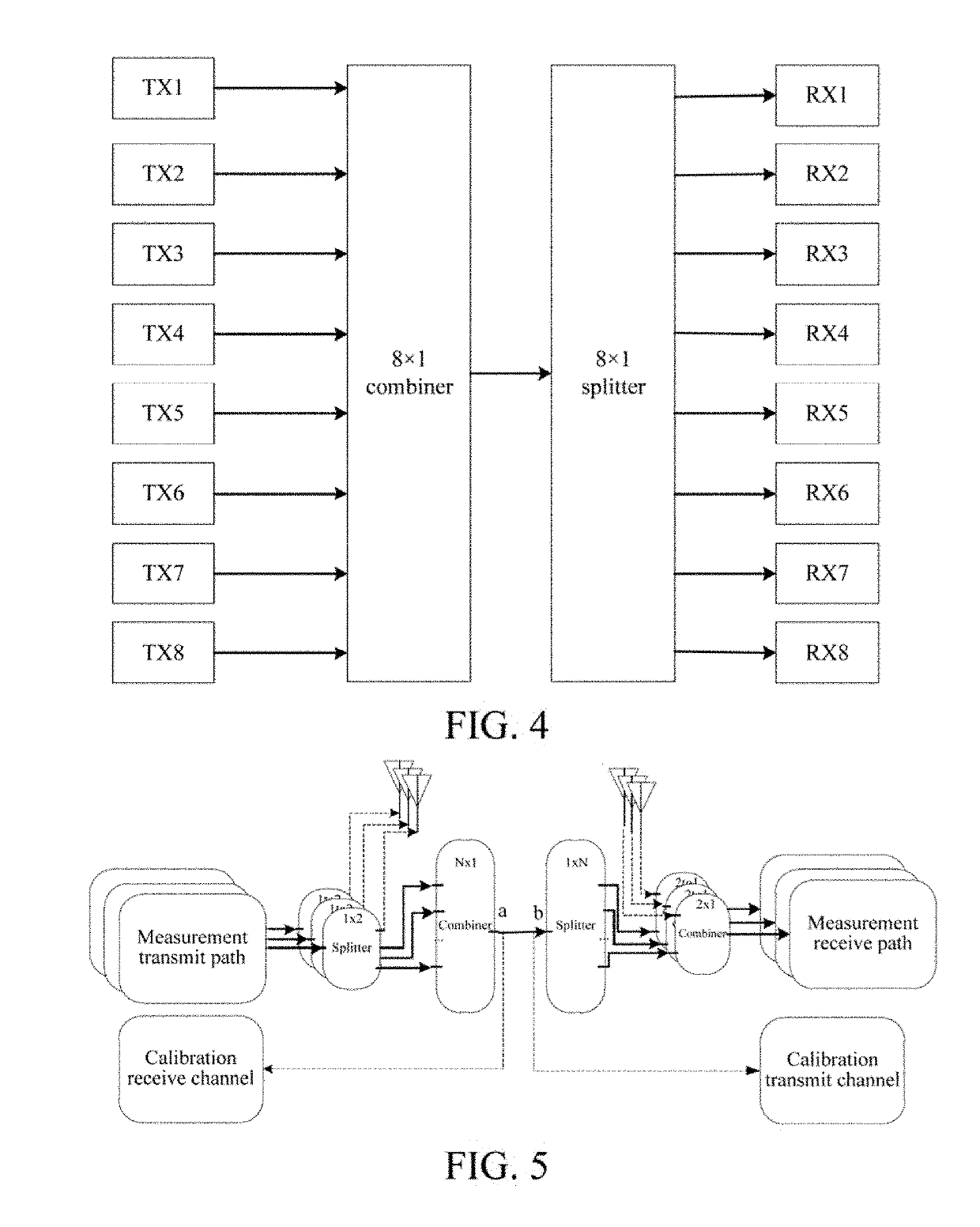
Method and system for calibration facing parallel multi-channel wireless channel measurement
InactiveCN107104742AMeet measurement needsReduce calibration timeTransmitters monitoringSynchronisation arrangementObservational errorRadio frequency
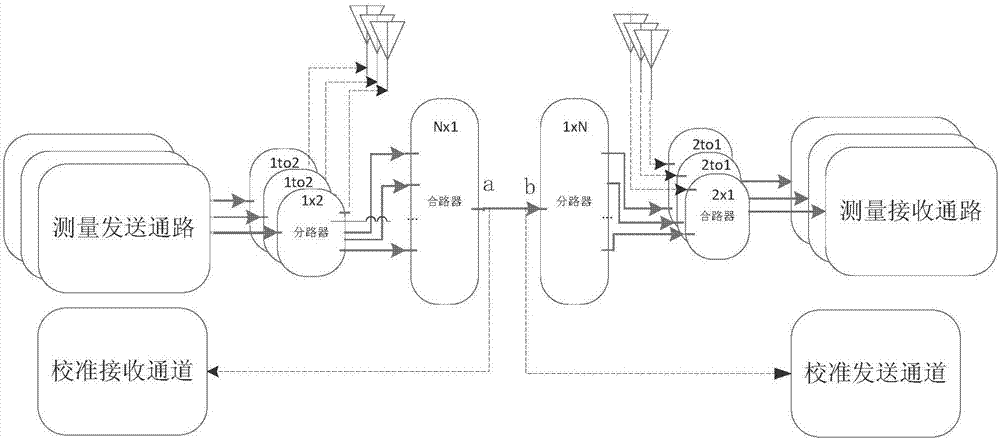
The present invention discloses a method for calibration facing parallel multi-channel wireless channel measurement, and a calibration system for realization of the calibration method. In the calibration method, a calibration receiving channel and a calibration sending channel are respectively added at a sending terminal and a receiving terminal. In the calibration process, a radio frequency line is directly communicated to the sending terminal and the receiving terminal, the calibration receiving channel and the calibration sending channel are disconnected and the response features of a passive device are tested; in the measurement process, the sending terminal is disconnected with the receiving terminal, the calibration receiving channel is connected with the calibration sending channel, and the calibration receiving channel / the calibration sending channel are employed to match measurement channels to calibrate the channel response features of the sending terminal and the receiving terminal. According to the invention, the method and system for calibration facing parallel multi-channel wireless channel measurement can perform real-time online supervision of the channel response features among multiple channels at the current moment to ensure that the measurement errors caused by mutual interference and influence among multiple channels can be avoided in the channel measurement process.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS COMM +1
Sequence report method and sequence report device
Disclosed are a sequence report method and a sequence report device for reducing a signaling amount for reporting a Zadoff-Chu sequence or a GCL sequence allocated for a cell. Indexes starting at 1 are correlated to different ZC sequences and are allocated for cells so that the indexes are continuous. When such ZC sequences are reported from BS to UE, a start index indicating the start of the continuous indexes is combined with the number of allocated sequences and they are reported as allocation sequence information by a report channel. The UE and the BS share the correlation between the ZC sequences and the indexes and the UE identifies a usable sequence number according to the correlation and the allocation sequence information reported from the BS.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
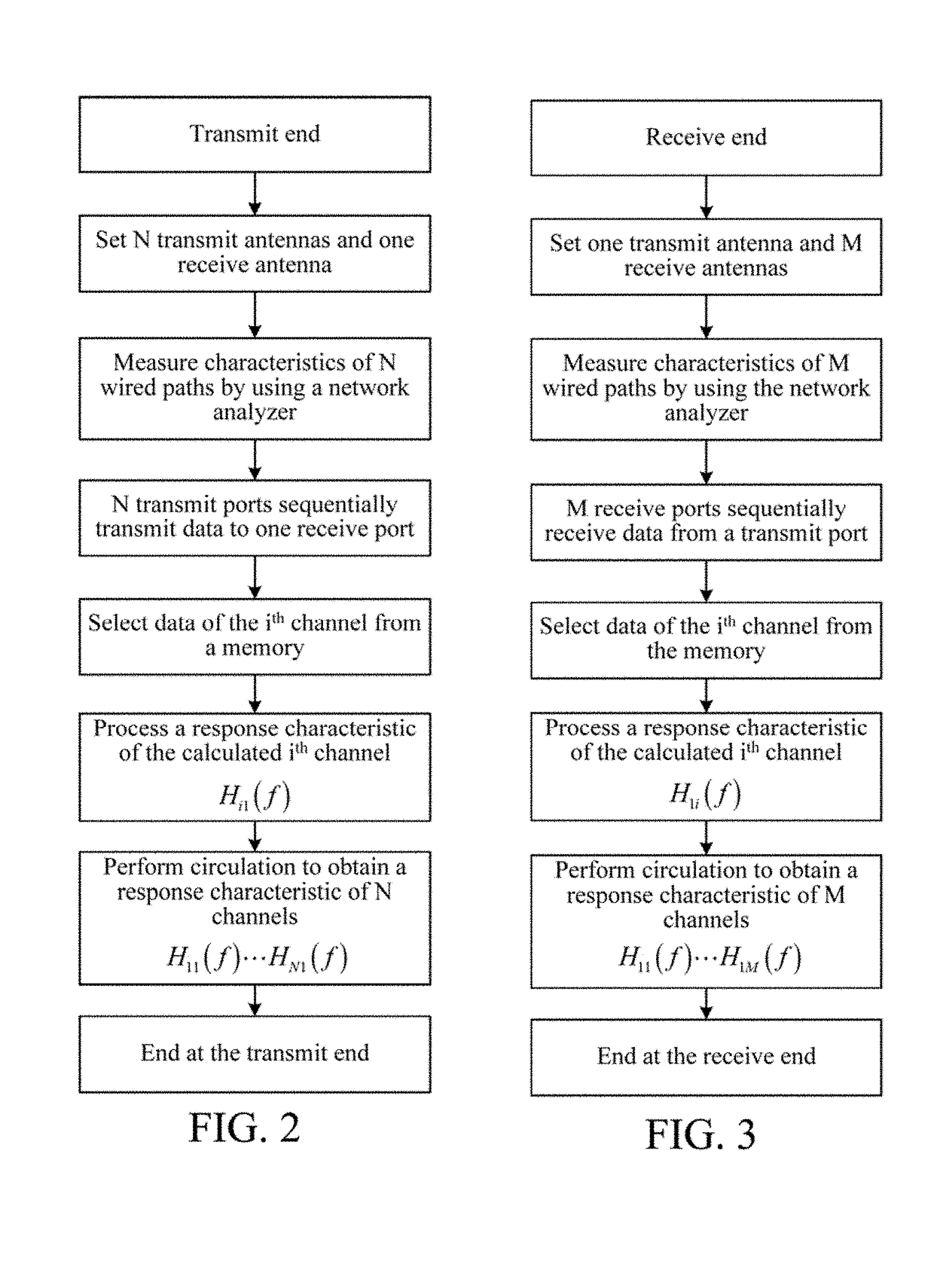
Calibration method for parallel multi-channel wireless channel measurement and system for the same
ActiveUS20180288723A1Reduce calibration timeAvoid measurement errorsTransmitters monitoringSynchronisation arrangementObservational errorCurrent channel
The present invention discloses a calibration method for parallel multi-channel wireless channel measurement and a calibration system thereof. The transmitting end and the receiving end are disconnected, and are respectively connected to the calibration receiving channel and the calibration transmitting channel, and the calibration receiving channel / calibration transmitting channel cooperates with a measurement channel in air interface measurement, to calibrate a channel response characteristic of the transmitting end and the receiving end. By means of the present invention, a current channel response characteristic between multiple channels can be online supervised in real time, so as to ensure that a measurement error because of an impact of mutual interference between multiple channels can be avoided in the channel measurement process.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS COMM
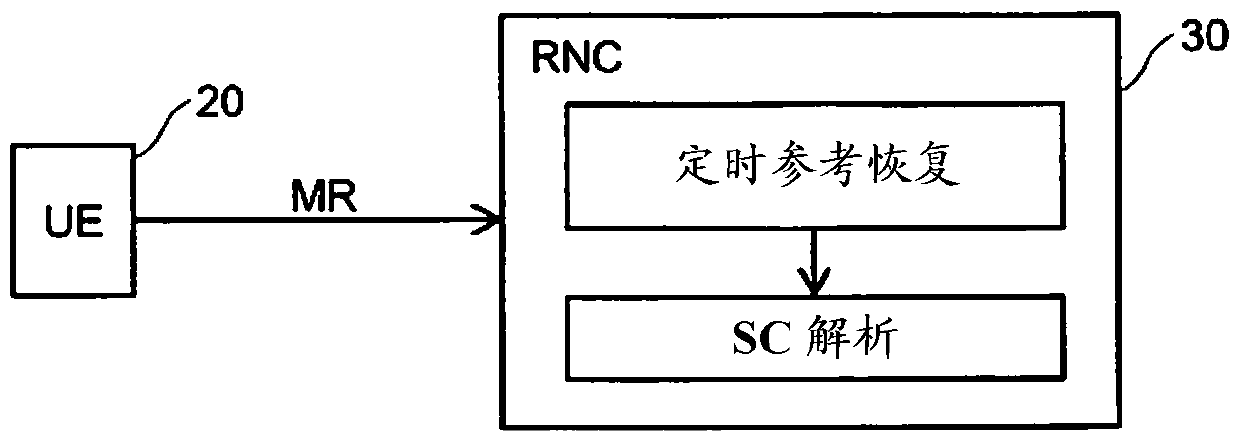
Scrambling code resolution
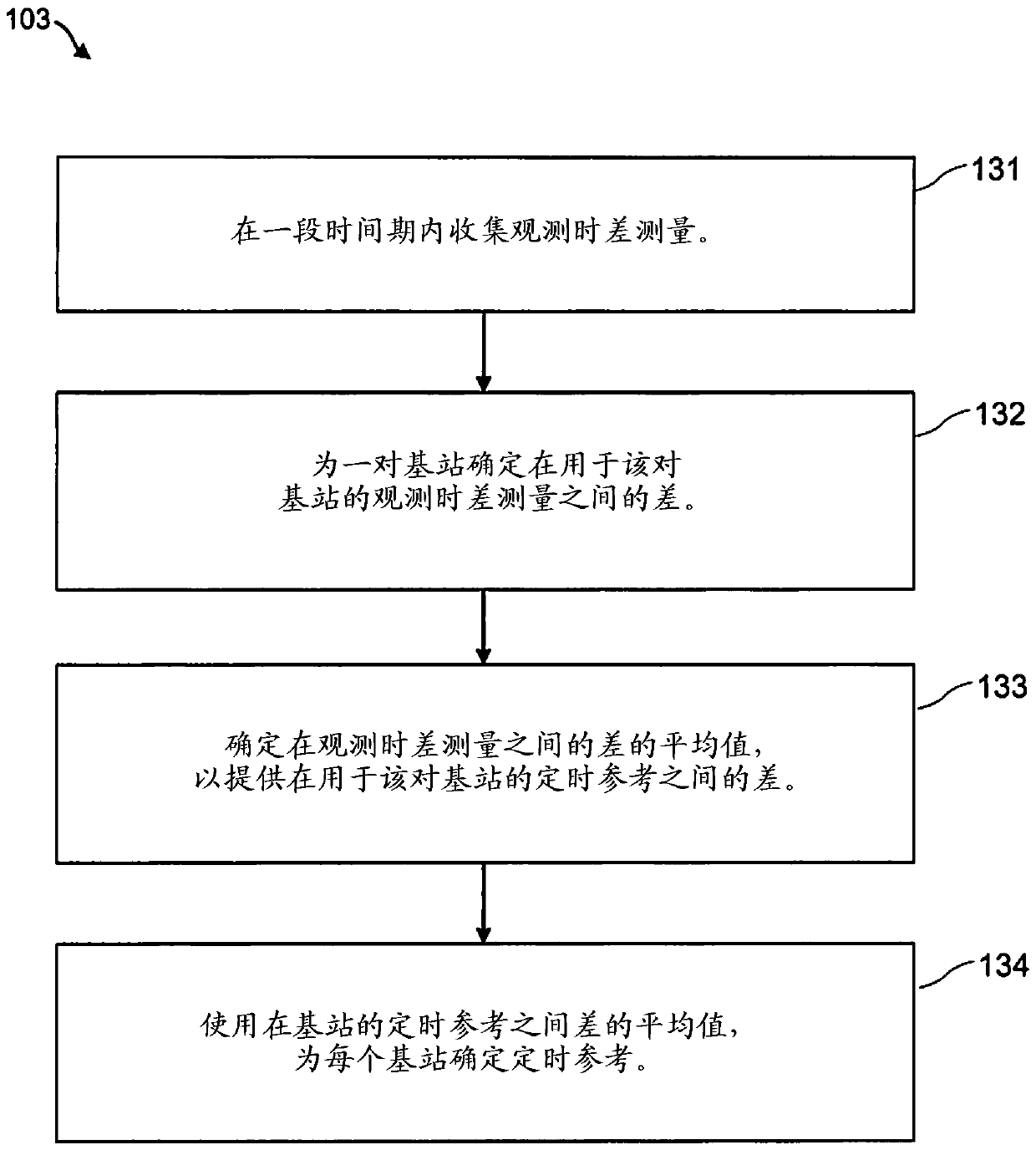
ActiveCN104488317AReliable Measurement MappingSoft Handoff ProcessSynchronisation arrangementSignal allocationAsynchronous operationCode division multiple access
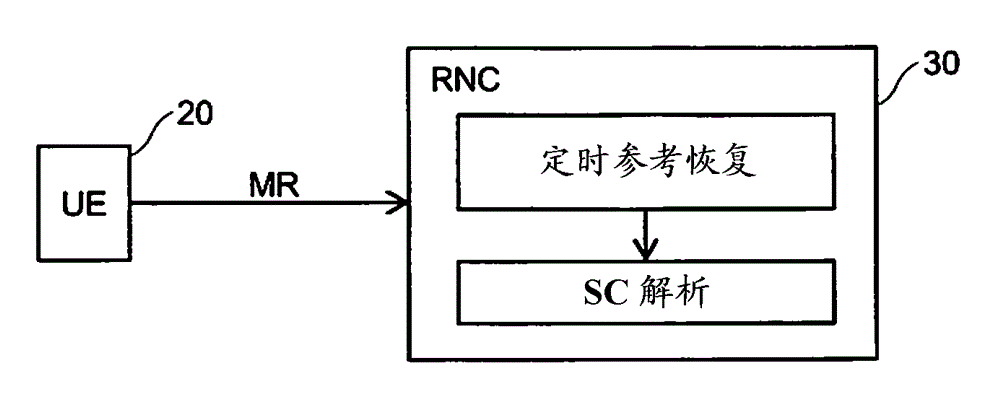
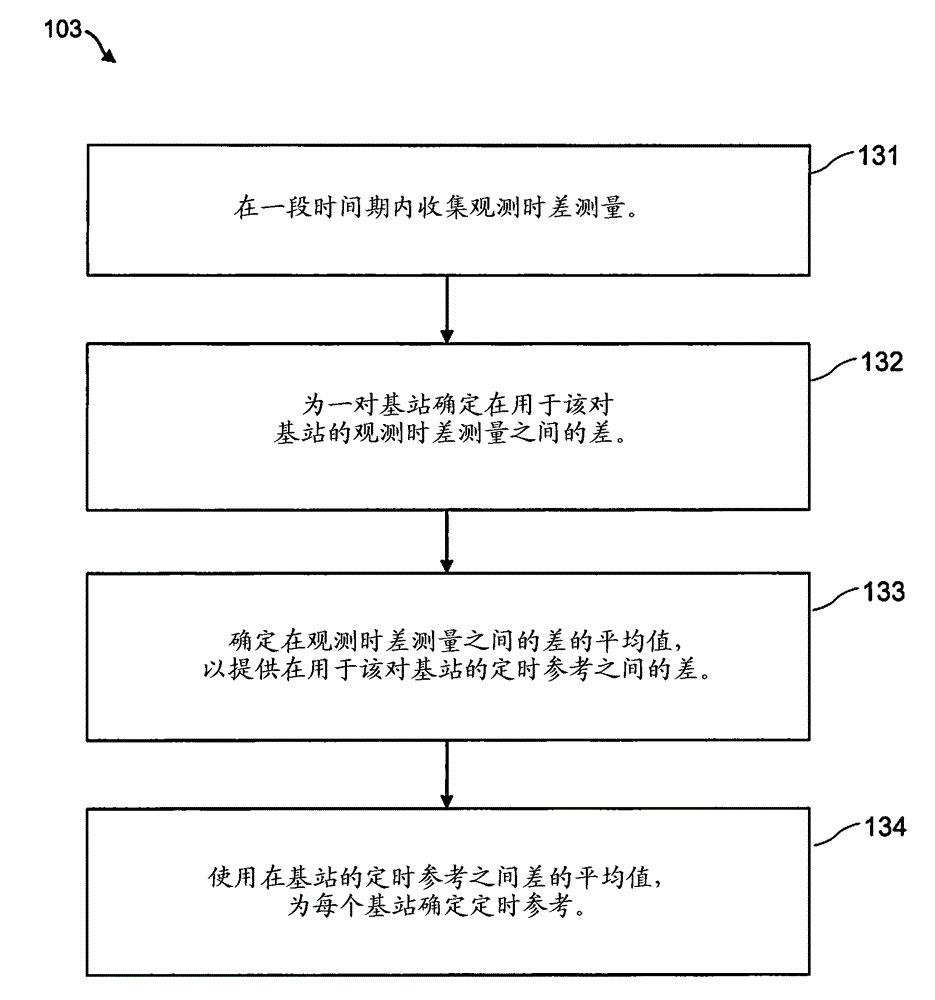
A code division multiple access wireless network (10) comprises a plurality of base stations (11-14) which operate asynchronously with respect to one another. A set of scrambling codes are allocated to the base stations for scrambling signals transmitted from the base stations. A node (30) of the wireless network receives (102) a first type of measurement report from wireless terminals (20), which comprises an observed time difference measurement acquired by the wireless terminal (20) for a signal received from one of an active set of base stations (11, 12, 13) that currently serve the wireless terminal. A timing reference is determined (103) for each of the base stations using a plurality of the observed time difference measurements. A second type of measurement report is received (105) from a wireless terminal (20) which comprises an observed time difference measurement acquired by the wireless terminal for a signal received from a base station (14) which is not currently serving the wireless terminal and a scrambling code of the received signal. An identity of the base station (14) in the second type of measurement report is determined by using the scrambling code of the signal received from the base station (14) which is not currently serving the wireless terminal and the observed time difference measurement in the second type of measurement report and the determined timing reference for that base station.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Signal sending and receiving method and device thereof
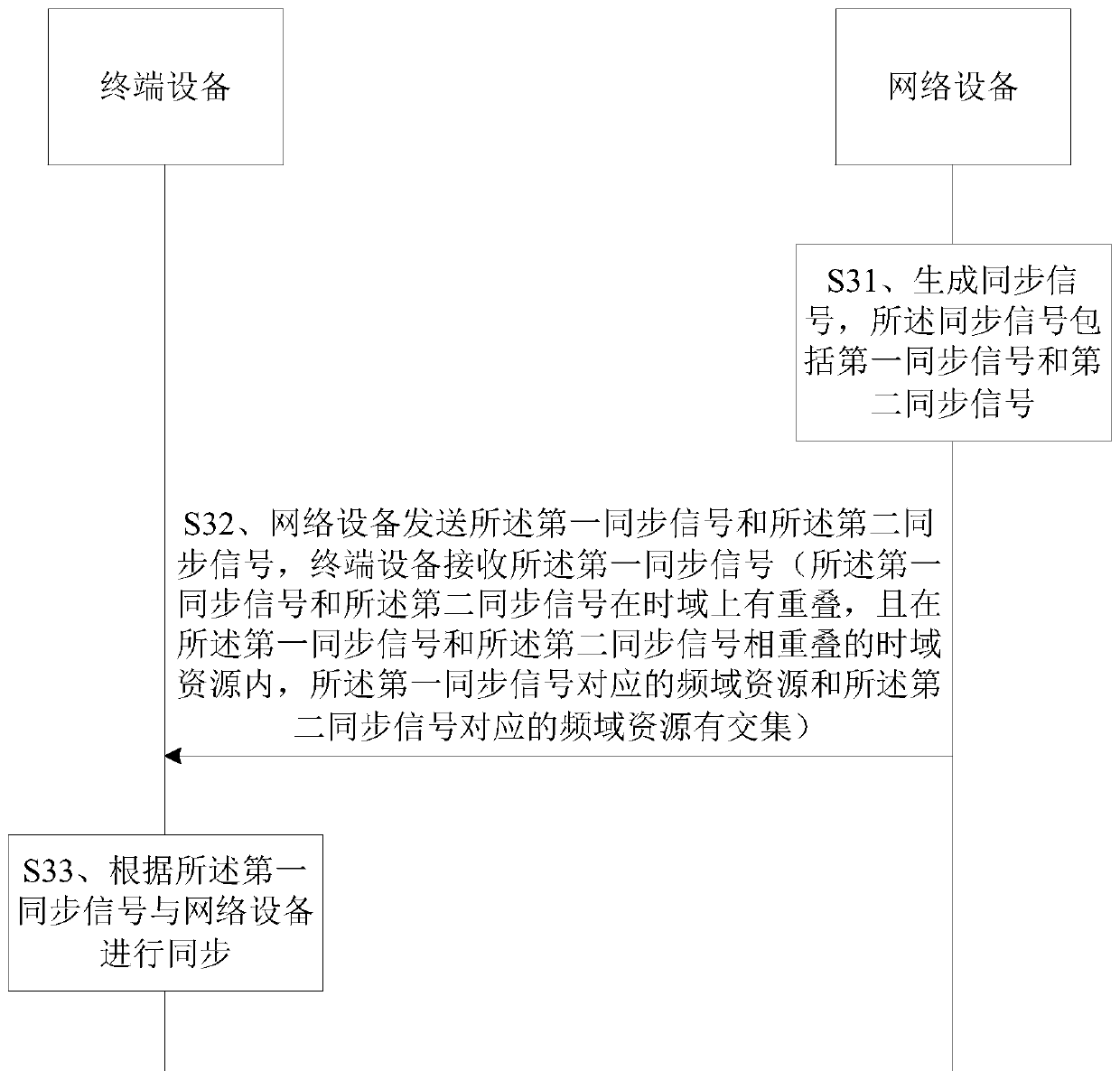
ActiveCN111465022AIncrease profitReduce occupancySynchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsTime domainData transmission
The invention relates to a signal sending and receiving method and a device thereof, the signal sending method comprises the following steps: generating synchronization signals, the synchronization signals comprising a first synchronization signal and a second synchronization signal; and sending the synchronization signal, wherein the first synchronization signal and the second synchronization signal are overlapped in the time domain, and in the overlapped time domain resource of the first synchronization signal and the second synchronization signal, the frequency domain resource correspondingto the first synchronization signal and the frequency domain resource corresponding to the second synchronization signal have an intersection. According to the embodiment of the invention, the two synchronization signals are not completely independent, but are partially overlapped on the frequency domain, so that the frequency domain resources occupied by the synchronization signals can be reduced, the frequency domain resources are saved for other data transmission processes, the two synchronization signals can also share one part of frequency domain resources, and the utilization rate of the resources is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Signal frame receiving method for aviation telemetering channel
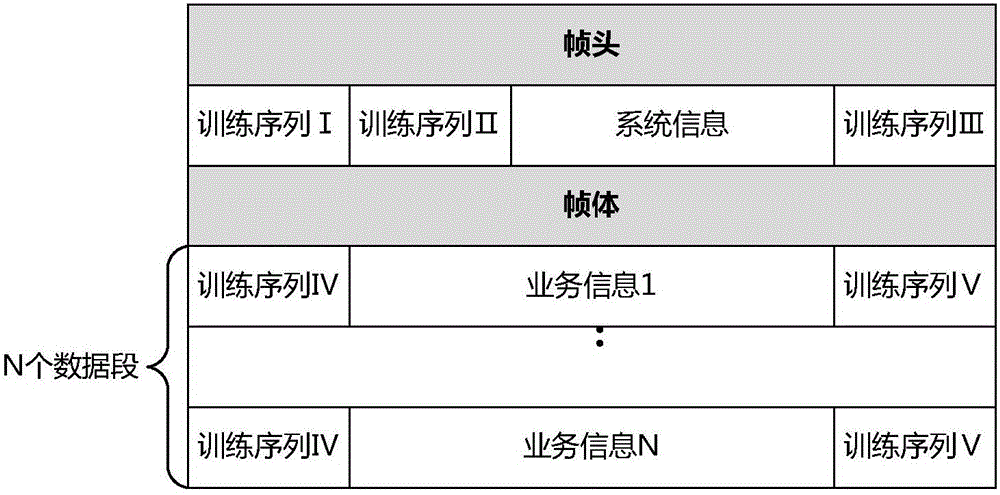
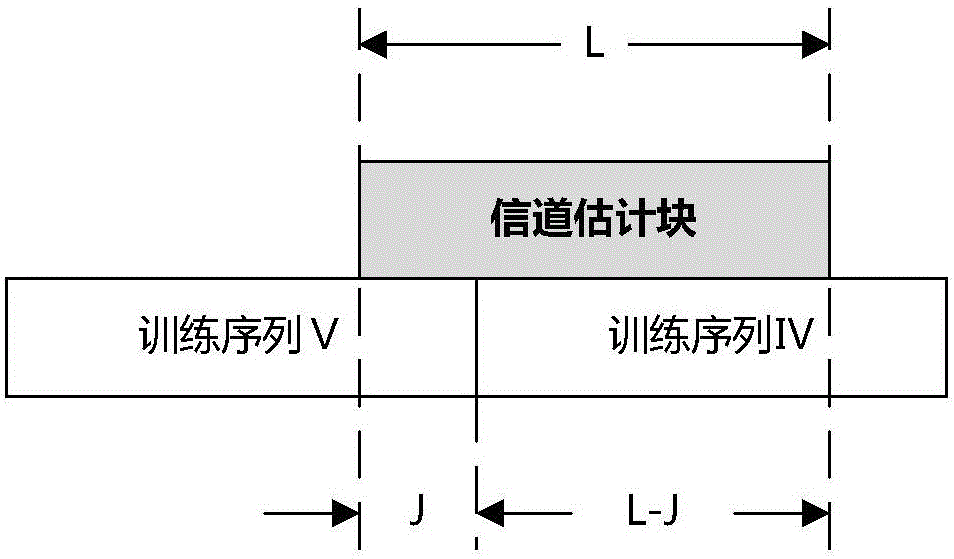
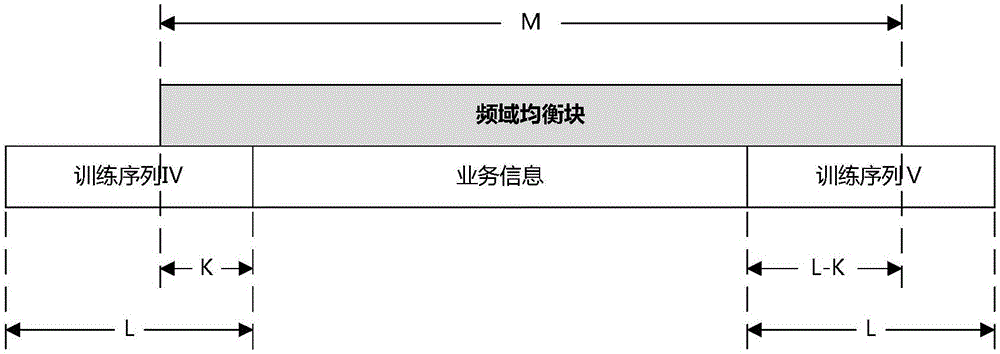
InactiveCN106572037AImprove synchronicityThe selection position parameter is adjustableChannel estimationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksAviationData segment
The invention discloses a signal frame receiving method for an aviation telemetering channel. The method comprises: with a training sequence I, a training sequence II, a training sequence III in a frame header, system initial synchronization during channel access is carried out; accessed system working information is determined by using system information in the frame header; wave carrying, regular tracking and compensation, channel estimation, and frequency domain equalization are carried out by using training sequences IV, business information, and training sequences V of all data segments of a frame body part; and demodulation and decoding are carried out on business information of all data segments of the frame body part. Therefore, a problem of realization of reliable transmission of telemetering information under high-dynamic multi-path fading channel can be solved.
Owner:CHINESE AERONAUTICAL RADIO ELECTRONICS RES INST
Sequence Report Method and Sequence Report Device
ActiveUS20100113046A1Reducing sequenceSignal allocationMultiplex code allocationData miningBioinformatics
Disclosed are a sequence report method and a sequence report device for reducing a signaling amount for reporting a Zadoff-Chu sequence or a GCL sequence allocated for a cell. Indexes starting at 1 are correlated to different ZC sequences and are allocated for cells so that the indexes are continuous. When such ZC sequences are reported from BS to UE, a start index indicating the start of the continuous indexes is combined with the number of allocated sequences and they are reported as allocation sequence information by a report channel. The UE and the BS share the correlation between the ZC sequences and the indexes and the UE identifies a usable sequence number according to the correlation and the allocation sequence information reported from the BS.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Anti-interference high-precision signal synchronization method based on access code in Bluetooth receiver
ActiveCN111988108AImprove work efficiencyHigh Signal Detection AccuracyMulti-frequency code systemsOrthogonal multiplexInterference (communication)Communications system
The invention discloses an anti-interference high-precision signal synchronization method based on an access code in a Bluetooth receiver. The method comprises the following steps: taking the access code agreed by two parties as a local training sequence; sampling received signals, and continuously performing delay differential operation on the two sampling values at an interval of one code element period, obtaining a to-be-correlated sequence according to a result of the delay differential operation, performing sliding correlation operation on the to-be-correlated sequence and a local training sequence, searching a peak value of a correlation value, and taking a sampling moment corresponding to the peak value as an initial position of an access code, thereby realizing frame timing synchronization. According to the invention, signal synchronization is carried out by using the Bluetooth access code, interference of other signals in the same frequency band is not liable to occur, the signal detection accuracy is high, and the problem of missing detection or false detection is greatly reduced, so that the working efficiency of the Bluetooth receiver is improved, the Bluetooth communication accuracy and safety are ensured, and the communication system is more stable and reliable.
Owner:NANJING QINHENG MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
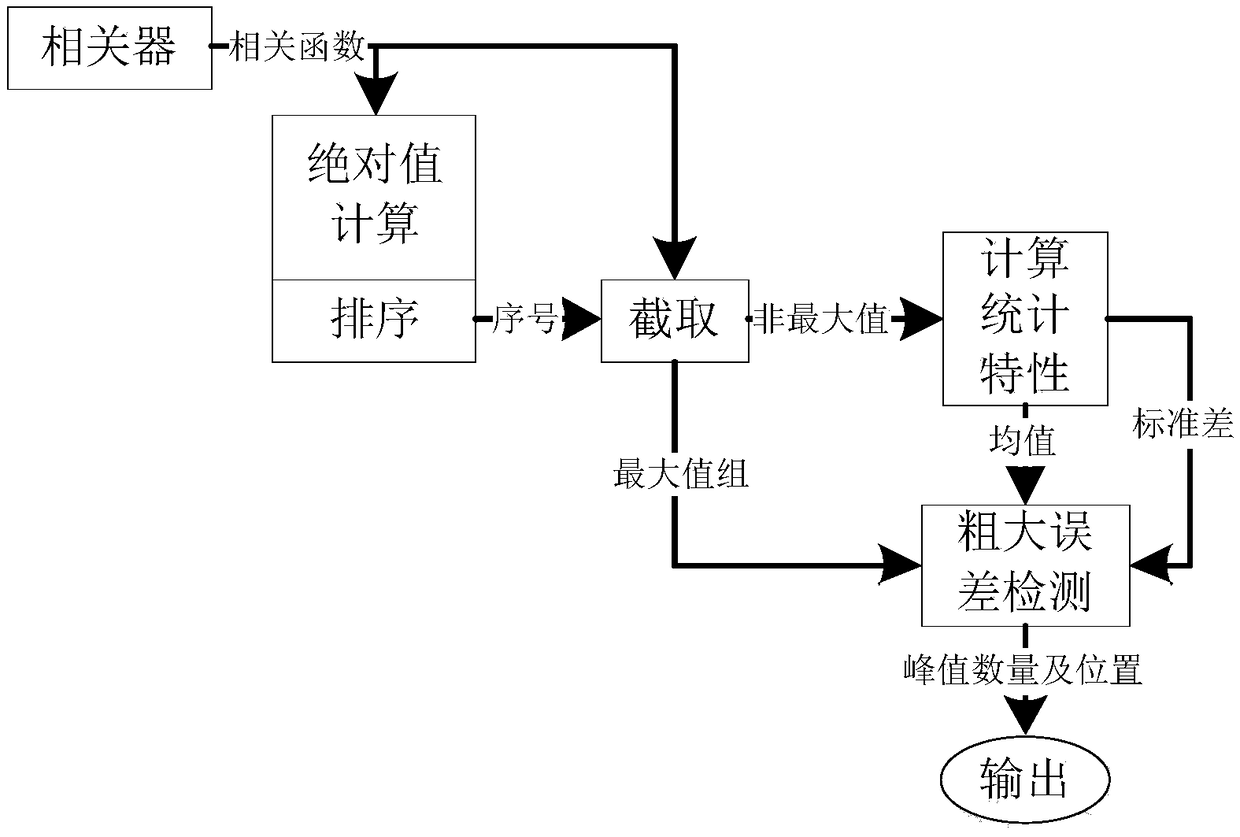
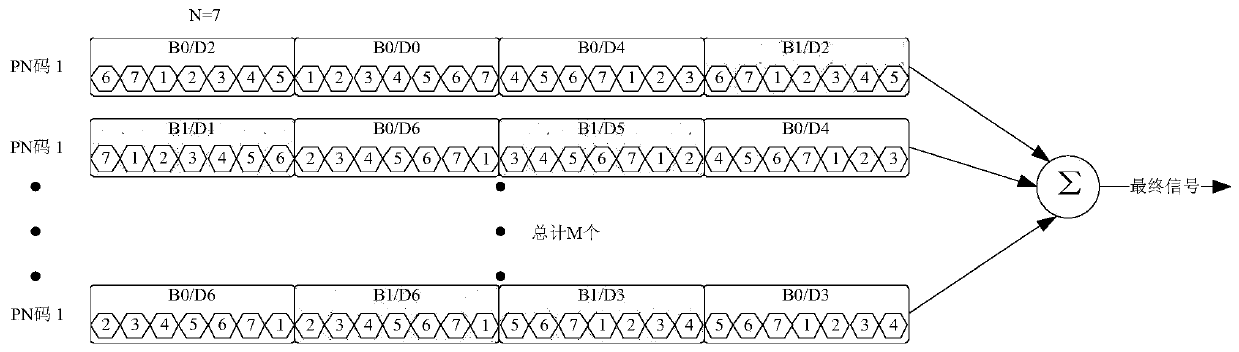
CCSK signal improvement method based on dynamic multi-peak combination
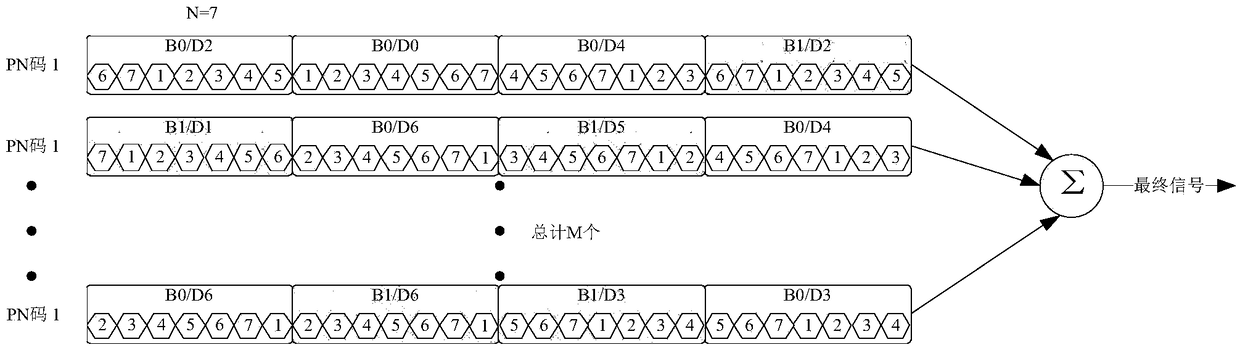
ActiveCN108616323ADoes not affect delivery methodIncrease transfer rateNetwork synchronisationMultiplex code applicationInformation transmissionCorrelation function
The invention discloses a CCSK signal improvement method based on dynamic multi-peak combination, which belongs to the technical field of communication engineering. The method comprises steps: in thecase of signal transmission, the transmitting end adjusts the properties of positive and negative of a to-be-transmitted PN code C(0), the offset s of the to-be-transmitted PN code is adjusted throughcyclic displacement, in a mode of stacking at most M groups of PN codes, the possible states of each group of spread spectrum codes can be enhanced to 2*C<N><M>2*sigma<m=1><M>C<N><m>; and signals arefinally transmitted under assistance of a synchronization strategy. When a receiver receives the signals, under help of the synchronization strategy, the original spread spectrum sequence C(0) is used, the received signals are subjected to correlation operation, and the receiver obtains the original information based on the combination condition of m peaks obtained from the correlation function and the positive and negative condition. The traditional CCSK information transfer mode is not influenced, the information amount is extraly loaded on the basis, the states contained in each spread spectrum code cycle is improved to 2*sigma<m=1><M>C<N><m> from 2*N, and the information transmission rate is greatly improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Device to-device communication
An apparatus is provided for a device-to-device, D2D, communication enabled user equipment, UE, comprising a processing section to determine, based on a signal received from another UE, a channel condition between the UE and the another UE; the UE to report the determined channel condition to an evolved Node B, eNB. The processing section is to initiate D2D communication based on a communication from the eNB, received in response to the report. Also, an apparatus is provided for a network element, comprising An input to receive a describing a channel condition between a first UE and a second UE; a processor to determine, based on the channel condition, whether or not D2D communication between the first UE and the second UE is to be enabled; and an output to output a result of the determination when the processor determines D2D communication is to be enabled. Related methods are also provided.
Owner:APPLE INC
Maintenance of channel usage in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS20060030331A1Network topologiesConnection managementTelecommunications linkCommunications system
Owner:INTEL CORP
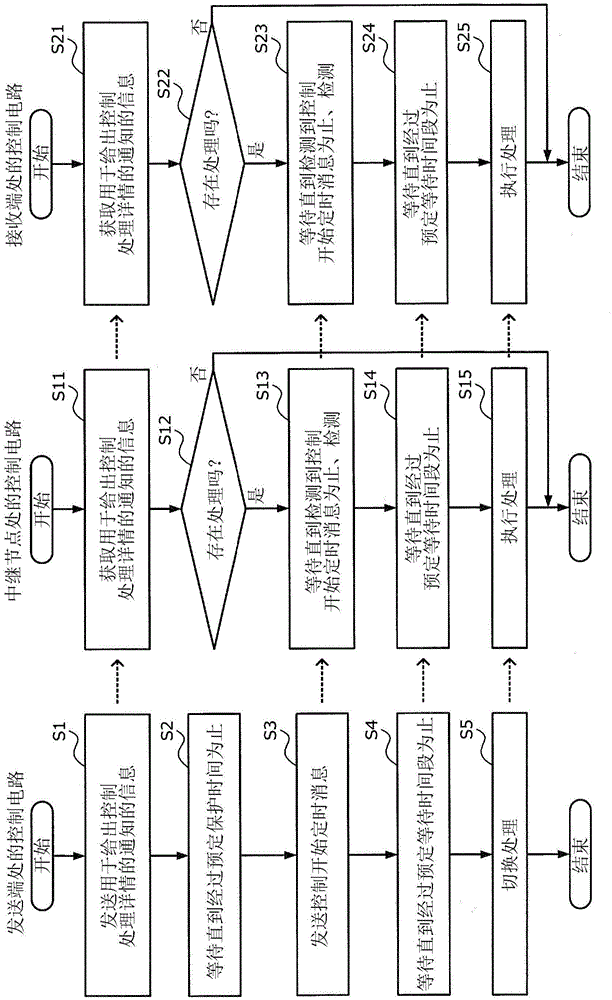
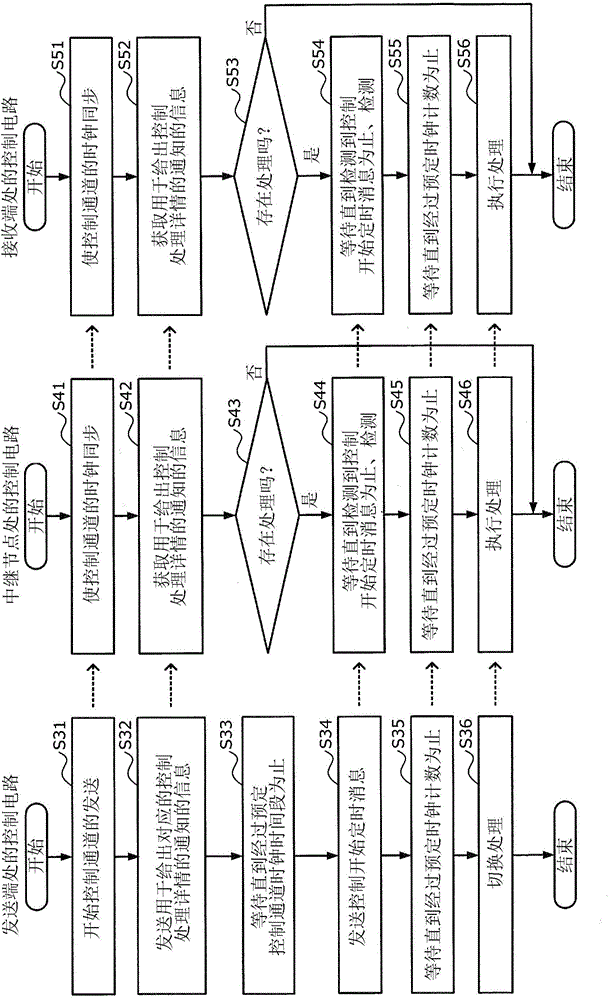
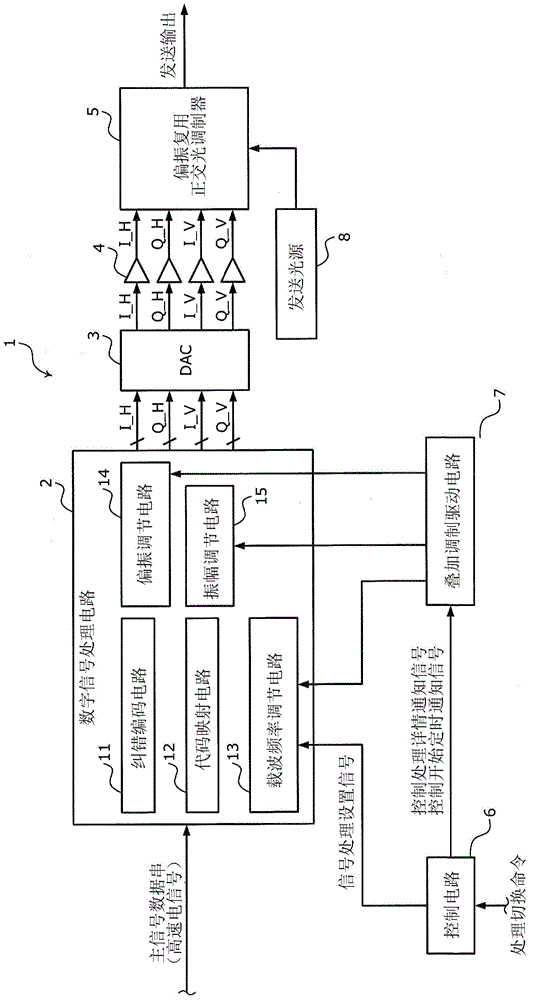
Control timing synchronization method, optical transmission system, and optical transmission apparatus
ActiveCN104052563ASolve the above-mentioned problems in the conventional technologyMultiplex system selection arrangementsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansComputer hardwareTransmission system
A control timing synchronization method is executed by a first and a second optical transmission apparatus. The first optical transmission apparatus: superimposes on a main signal and transmits, information of control process details; waits for a first period; subsequently, superimposes on the main signal and transmits, a message giving notification of control start timing; waits for a second period; and subsequently switches a process of the first optical transmission apparatus to a process corresponding to the control process details. The second optical transmission apparatus: acquires the information on the main signal; waits until detection of the message on the main signal, when a process is present that is to be executed by the second optical transmission apparatus based on the information; waits for the second period when the message is detected while waiting for the detection of the message; and subsequently, executes a process corresponding to the information.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Methods and apparatus for construction of SCMA codebooks
Disclosed are methods and apparatus used in wireless communications. The methods and apparatus establish a codebook for use in sparse code multiple access (SCMA) encoded communications, in particular. The SCMA codebook is configured to set the codebook for at least one layer (i.e., a user) to include a constellation of points having a first grouping of constellation points located at first radial distance from an origin in a complex plane and a second grouping of constellation points located at a second radial distance from the origin. This codebook arrangement provides increased gains at receivers by optimizing the constellation shape to improve the distance between constellation points (i.e., SCMA codebook performance), and in particular more robust performance when encountering amplitude and phase misalignment in uplink (UL) multiple access.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Calibration of a synthesiser in a radio receiver
ActiveUS11445505B2Quickly change frequencyShorten the timeOrthogonal multiplexTransmission path multiple useTelecommunicationsRadio receiver
A method of operating a radio receiver arranged to receive a plurality of data symbols transmitted on one of a predetermined set of frequencies. The method comprises receiving a first set of data symbols at a first transmission frequency. The first set of data symbols comprises a message indicating a first frequency sub-set. A synthesiser is calibrated for the one or more frequencies in the first frequency sub-set. A second set of data symbols transmitted on at least one of said one or more frequencies from the first sub-set is received. It is determined from the second set of data symbols whether a network quality metric exceeds a threshold. The synthesiser is calibrated for one or more frequencies in a second frequency sub-set when the network quality metric exceeds the threshold. The second sub-set comprises frequencies that are not in the first sub-set.
Owner:NORDIC SEMICONDUCTOR
Anti-interference high-precision signal synchronization method based on access code in Bluetooth receiver
ActiveCN111988108BImprove work efficiencyHigh Signal Detection AccuracyMulti-frequency code systemsOrthogonal multiplexInterference (communication)Communications system
The invention discloses an anti-interference high-precision signal synchronization method based on an access code in a Bluetooth receiver. The method comprises the following steps: taking the access code agreed by two parties as a local training sequence; sampling received signals, and continuously performing delay differential operation on the two sampling values at an interval of one code element period, obtaining a to-be-correlated sequence according to a result of the delay differential operation, performing sliding correlation operation on the to-be-correlated sequence and a local training sequence, searching a peak value of a correlation value, and taking a sampling moment corresponding to the peak value as an initial position of an access code, thereby realizing frame timing synchronization. According to the invention, signal synchronization is carried out by using the Bluetooth access code, interference of other signals in the same frequency band is not liable to occur, the signal detection accuracy is high, and the problem of missing detection or false detection is greatly reduced, so that the working efficiency of the Bluetooth receiver is improved, the Bluetooth communication accuracy and safety are ensured, and the communication system is more stable and reliable.
Owner:NANJING QINHENG MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and network for sending multiple signals
ActiveCN110419179BImprove efficiencyReduce power consumptionMultiplex code generationMultiplex code allocationComputer networkEncoder decoder
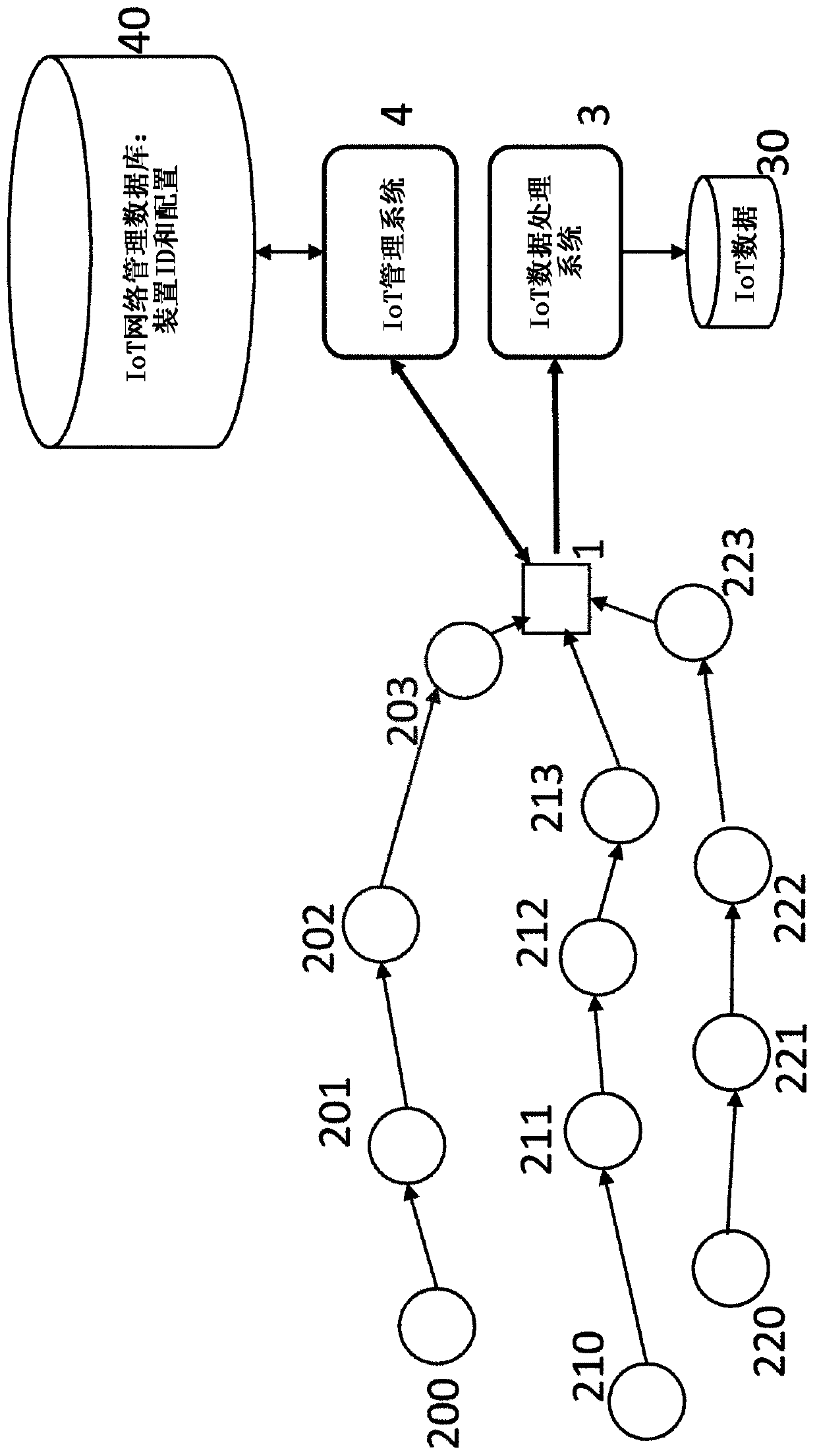
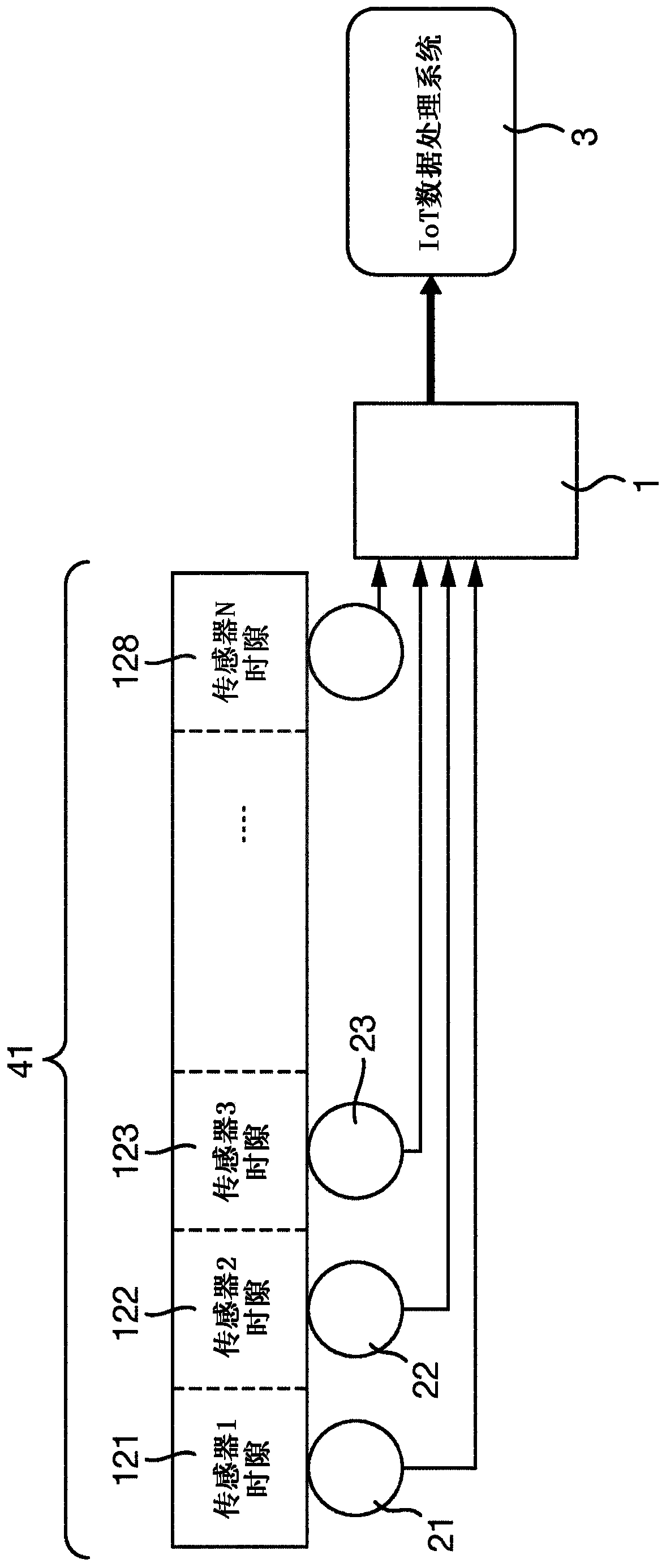
Spread spectrum systems are used to transmit data to and from devices in a distributed system that are capable of operating as sensors and actuators. Communication occurs through a series of aggregation nodes in a branched hierarchical network. Each device and aggregation node has a corresponding spreading code and in the central control system 4 a corresponding encoder / decoder (401, 402, . . . , 252, 352, 452, 552) operating on the same spreading code, with The device-dependent coded data is aggregated over a shared channel. At each level of the hierarchy, the aggregated signal to / from the next level is re-encoded. This allows the same code (153, 253) to be reused at different levels and in different sub-branches of the same level, thereby increasing the number of devices that can be served on one channel.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Multi-user interference elimination method and system
ActiveCN105530696ASynchronisation arrangementNetwork synchronisationMulti user interferenceTime delays
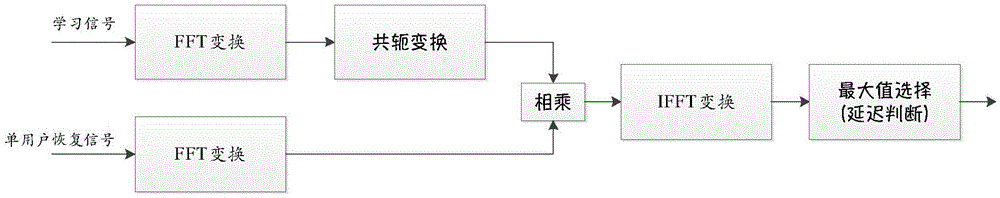
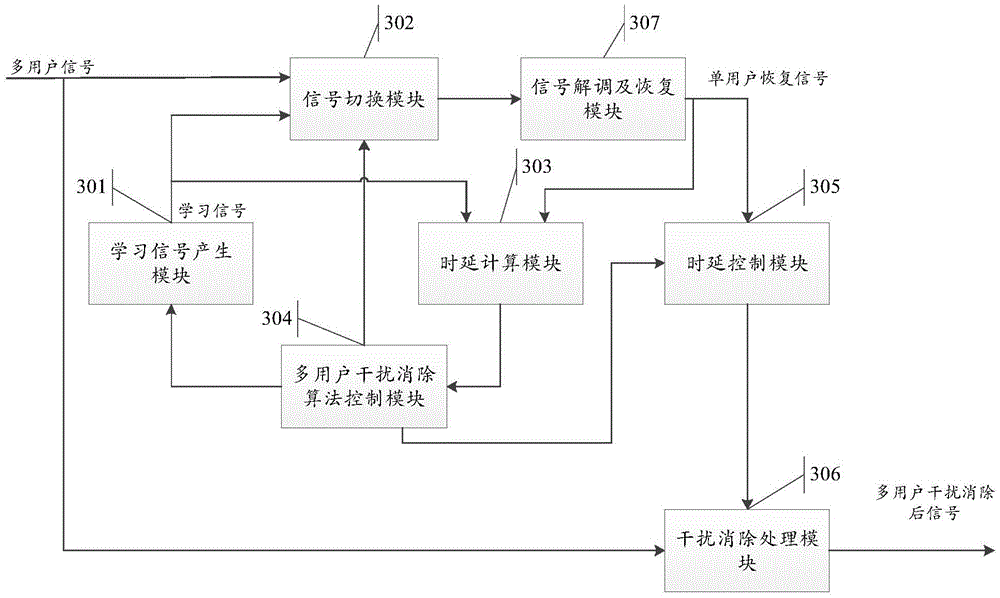
The invention discloses a multi-user interference elimination method. The method comprises: generating analog signals according to set parameters and related parameters appointed by users, demodulating and recovering analog learning signals to obtain single-user recovery signals; calculating the analog learning signals and the single-user recovery signals according to a preset algorithm to obtain the delay values of the single-user recovery signals relative to the analog learning signals; obtaining the delay calculation results of appointed users according to the delay values; obtaining the delay calculation result of every appointed user; taking the maximum in the delay calculation results as a calculation reference value; adjusting the multi-user signals and the single-user recovery signals to align in time delay according to the reference value. Through the method provided by the embodiment of the invention, estimation and recovery are automatically realized, every user signal and the receiving signal are caused to strictly align in time, and therefore, the expandable general multi-user interference processing system compatible with different users is realized.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
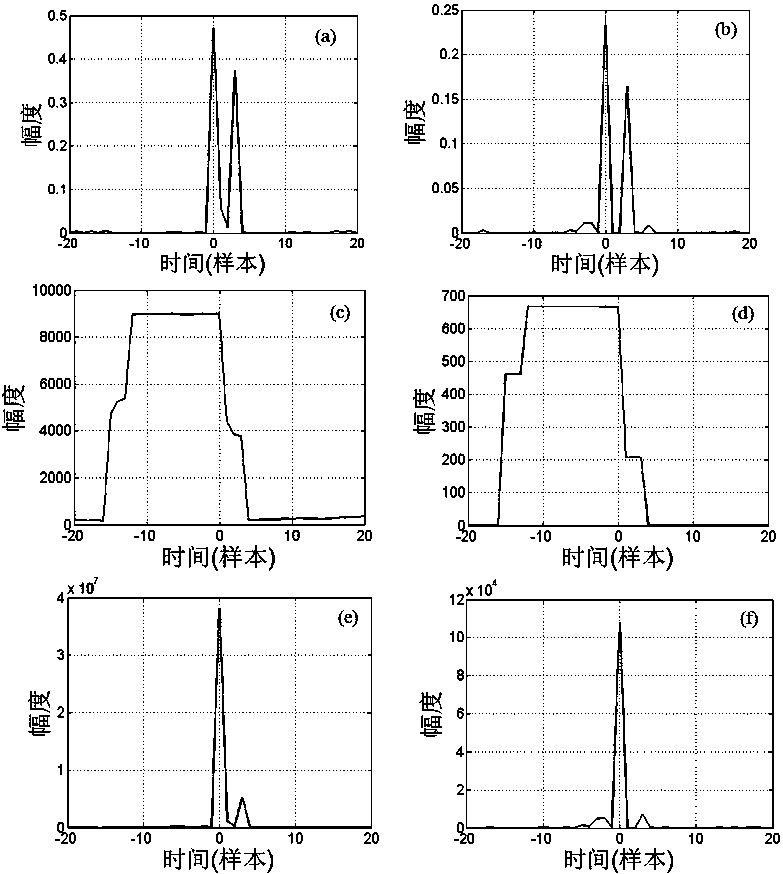
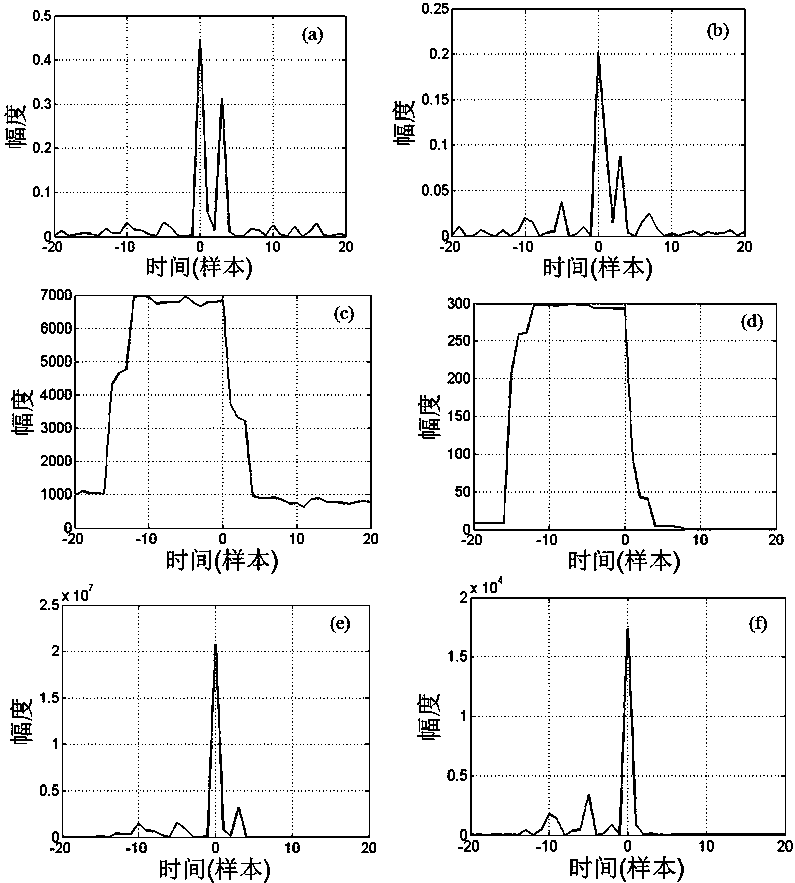
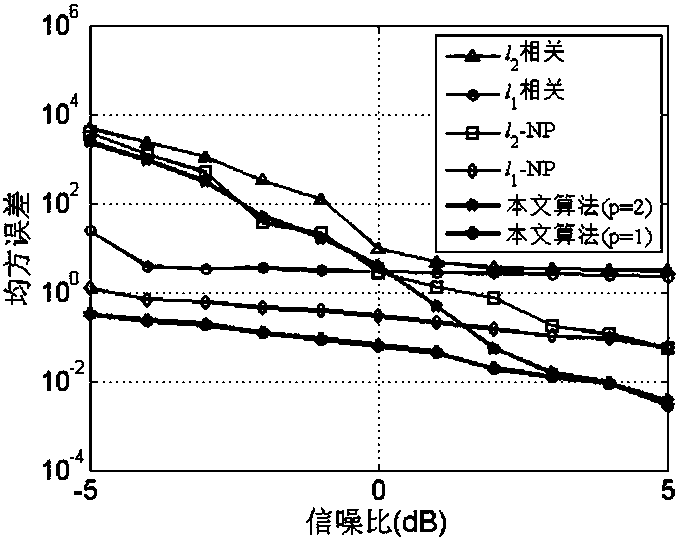
Weighted lp correlation synchronization method
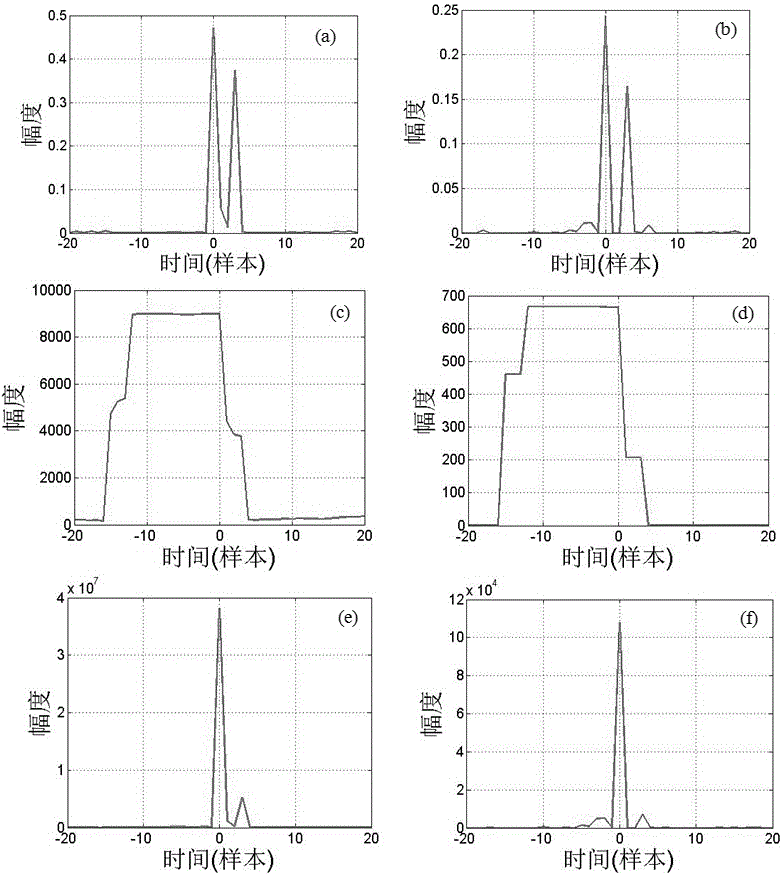
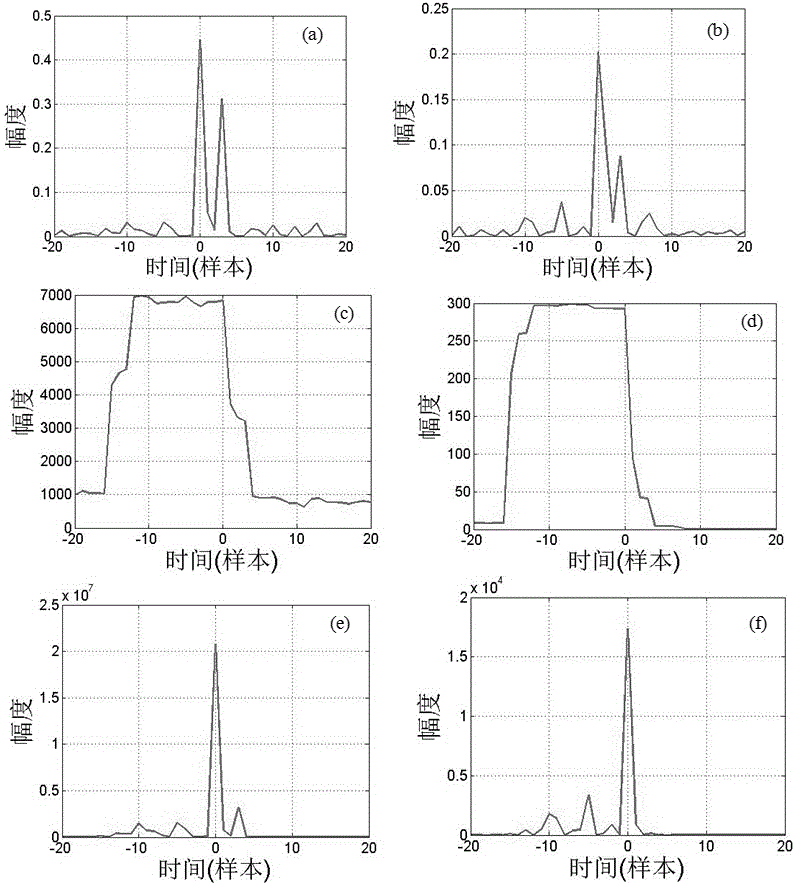
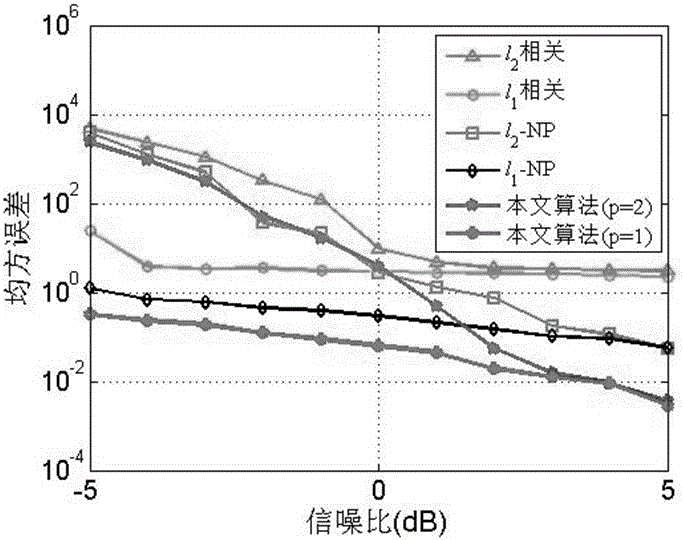
ActiveCN106534024AEliminate the effects ofReduce complexityMulti-frequency code systemsNetwork synchronisationMultiplexingCorrelation coefficient
The invention belongs to the technical field of communication and satellite navigation, and in particular relates to a weighted lp correlation synchronization method (p=1 or 2). According to the method, a special weight function is used, and lp correlation coefficients are weighted to effectively suppress the influence of a multipath effect on a traditional lp correlation synchronization algorithm. The analysis shows that the weight function used in the invention has the effect of time domain filtering and can filter out pseudo-peak generated by the multipath effect. In particular, when p is equal to 1, the algorithm provided by the invention has strong robustness to heavy tail distribution noise. A simulation result shows the correctness and validity of theoretical analysis, and shows that in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) and code division multiplexing (CDMA) systems, the method has higher synchronization accuracy and performance than the existing algorithms.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Calibration method for parallel multi-channel wireless channel measurement and system for the same
InactiveUS10362551B2Satisfying channel measurement requirementReduce calibration timeTransmitters monitoringSynchronisation arrangementCurrent channelAir interface
The present invention discloses a calibration method for parallel multi-channel wireless channel measurement and a calibration system thereof. The transmitting end and the receiving end are disconnected, and are respectively connected to the calibration receiving channel and the calibration transmitting channel, and the calibration receiving channel / calibration transmitting channel cooperates with a measurement channel in air interface measurement, to calibrate a channel response characteristic of the transmitting end and the receiving end. By means of the present invention, a current channel response characteristic between multiple channels can be online supervised in real time, so as to ensure that a measurement error because of an impact of mutual interference between multiple channels can be avoided in the channel measurement process.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS COMM
Improved method of ccsk signal based on dynamic multi-peak combination
ActiveCN108616323BDoes not affect delivery methodIncrease transfer rateNetwork synchronisationMultiplex code applicationInformation transmissionCorrelation function
The invention discloses a CCSK signal improvement method based on dynamic multi-peak combination, which belongs to the technical field of communication engineering. The method comprises steps: in thecase of signal transmission, the transmitting end adjusts the properties of positive and negative of a to-be-transmitted PN code C(0), the offset s of the to-be-transmitted PN code is adjusted throughcyclic displacement, in a mode of stacking at most M groups of PN codes, the possible states of each group of spread spectrum codes can be enhanced to 2*C<N><M>2*sigma<m=1><M>C<N><m>; and signals arefinally transmitted under assistance of a synchronization strategy. When a receiver receives the signals, under help of the synchronization strategy, the original spread spectrum sequence C(0) is used, the received signals are subjected to correlation operation, and the receiver obtains the original information based on the combination condition of m peaks obtained from the correlation function and the positive and negative condition. The traditional CCSK information transfer mode is not influenced, the information amount is extraly loaded on the basis, the states contained in each spread spectrum code cycle is improved to 2*sigma<m=1><M>C<N><m> from 2*N, and the information transmission rate is greatly improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Maintenance of channel usage in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS8045990B2Network topologiesConnection managementTelecommunications linkCommunications system
Data is accessed from a network via a wireless communication link. A determination is made as to whether payload data has been received from a subscriber's terminal. If so, then a request is sent for a first set of traffic channels, and the payload data is transmitted over the first set of traffic channels.
Owner:INTEL CORP
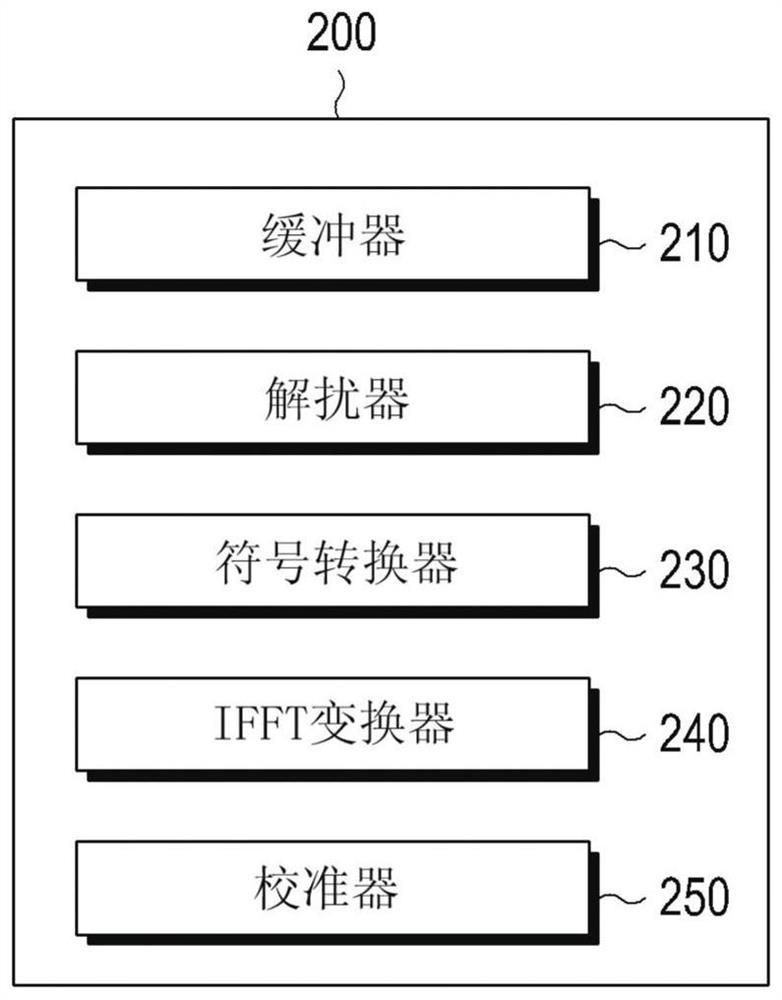
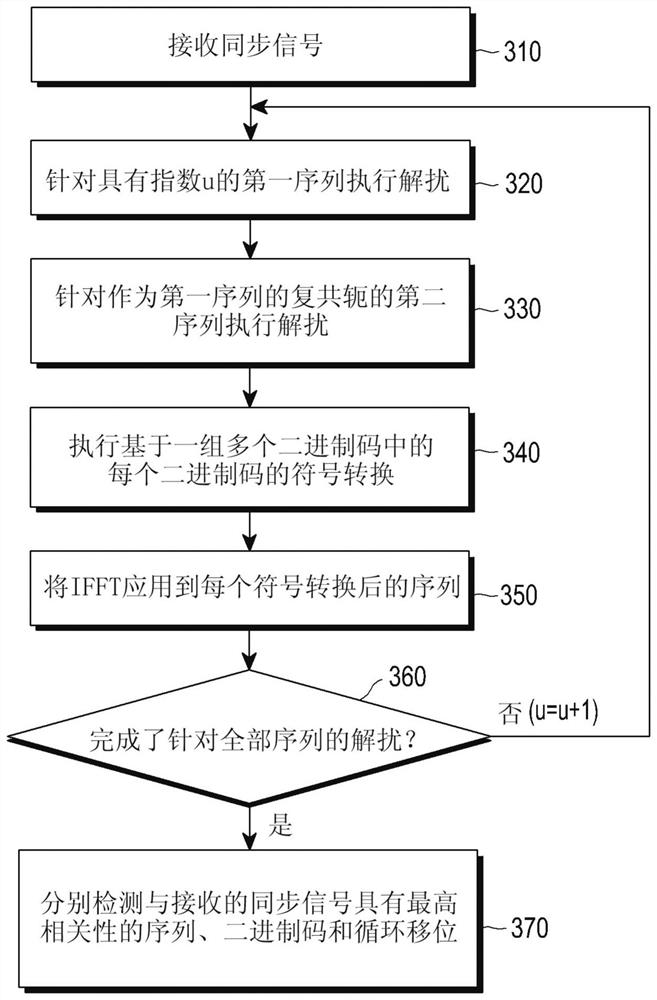
Method and device for detecting synchronization signals
A method and apparatus for detecting synchronization signals. A chip for detecting a synchronization signal generated based on one of a plurality of sequences generated by a sequence generator, the chip comprising a memory and a processor connected to the memory may be provided. The processor may be configured to: receive a synchronization signal; perform a first descrambling of the received synchronization signal for the first sequence by multiplying the received synchronization signal with a first sequence from the plurality of sequences ; performing a second descrambling of the received synchronization signal for a second sequence from the plurality of sequences of the received synchronization signal by changing the sign of at least one element of the descrambling sequence of the first sequence, wherein the first The second sequence is the complex conjugate of the first sequence.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Scrambling code analysis
ActiveCN104488317BReliable Measurement MappingSoft Handoff ProcessSynchronisation arrangementSignal allocationWireless mesh networkCode division multiple access
A code division multiple access wireless network (10) network includes a plurality of base stations (11-14) operating asynchronously with respect to each other. Sets of scrambling codes are assigned to the base stations in order to scramble signals transmitted from the base stations. A node (30) of the wireless network receives (102) a first type of measurement report from a wireless terminal (20), the first type of measurement report includes , 13) Observational time difference measurements of signals received by a base station in the active set. A timing reference is determined (103) for each base station using the plurality of observed moveout measurements. receiving (105) from a wireless terminal (20) a second type of measurement report comprising observed time difference measurements collected by the wireless terminal for signals received from base stations (14) not currently serving the wireless terminal and the scrambling code of the received signal. By using the observed time difference measurement in the second type of measurement report and the scrambling code of the signal received from the base station (14) not currently serving the wireless terminal and the determined timing reference for this base station, it is determined The identity of the base station (14) in the measurement report of .
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
weighted l p Related Synchronization Methods
ActiveCN106534024BEliminate the effects ofReduce complexityMulti-frequency code systemsNetwork synchronisationMultiplexingTime domain
The invention belongs to the technical field of communication and satellite navigation, and in particular relates to a weighted lp correlation synchronization method (p=1 or 2). According to the method, a special weight function is used, and lp correlation coefficients are weighted to effectively suppress the influence of a multipath effect on a traditional lp correlation synchronization algorithm. The analysis shows that the weight function used in the invention has the effect of time domain filtering and can filter out pseudo-peak generated by the multipath effect. In particular, when p is equal to 1, the algorithm provided by the invention has strong robustness to heavy tail distribution noise. A simulation result shows the correctness and validity of theoretical analysis, and shows that in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) and code division multiplexing (CDMA) systems, the method has higher synchronization accuracy and performance than the existing algorithms.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com