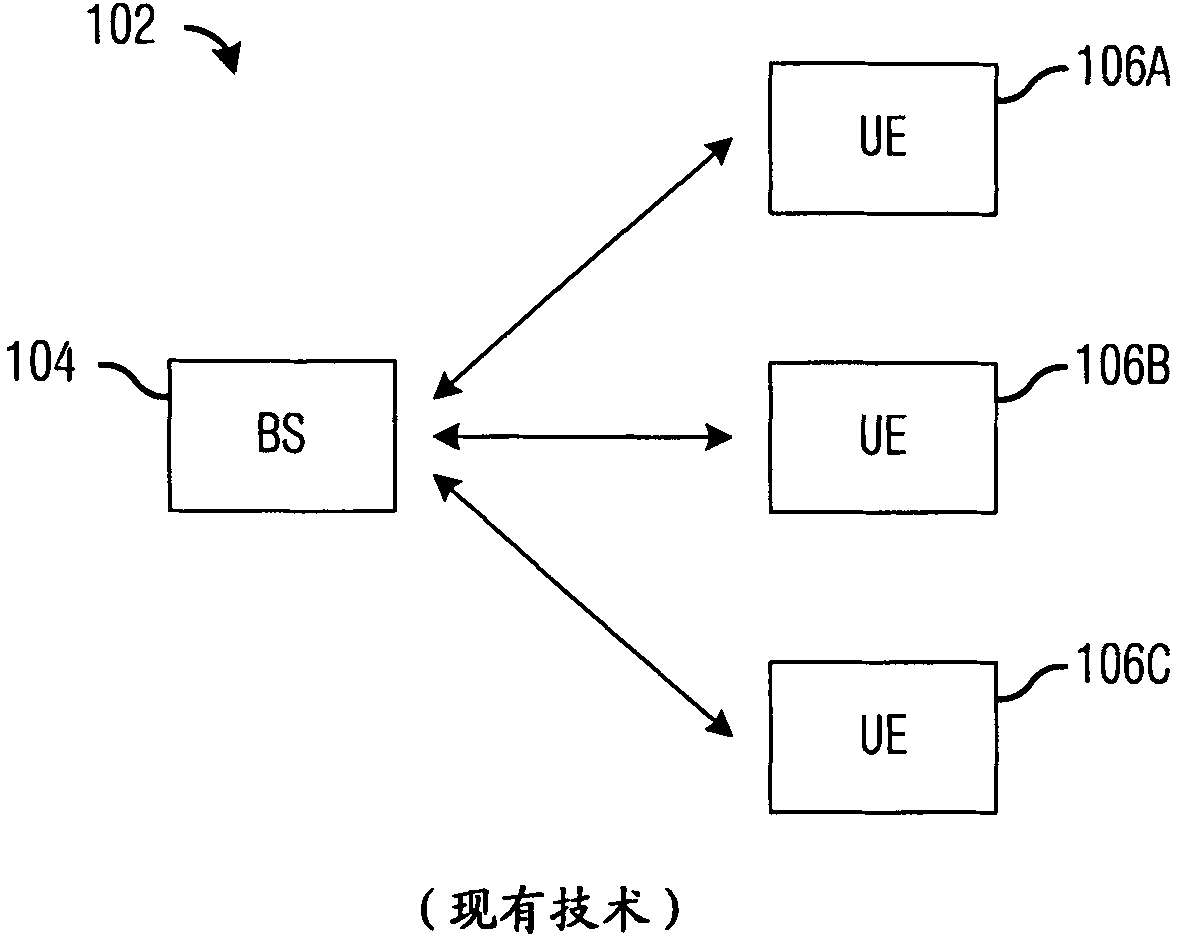
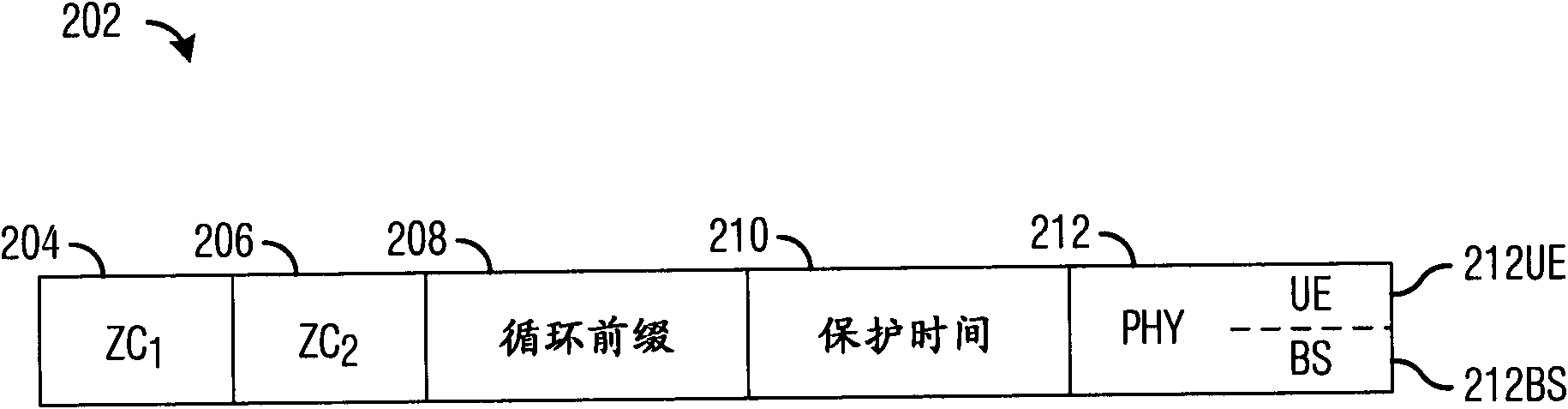
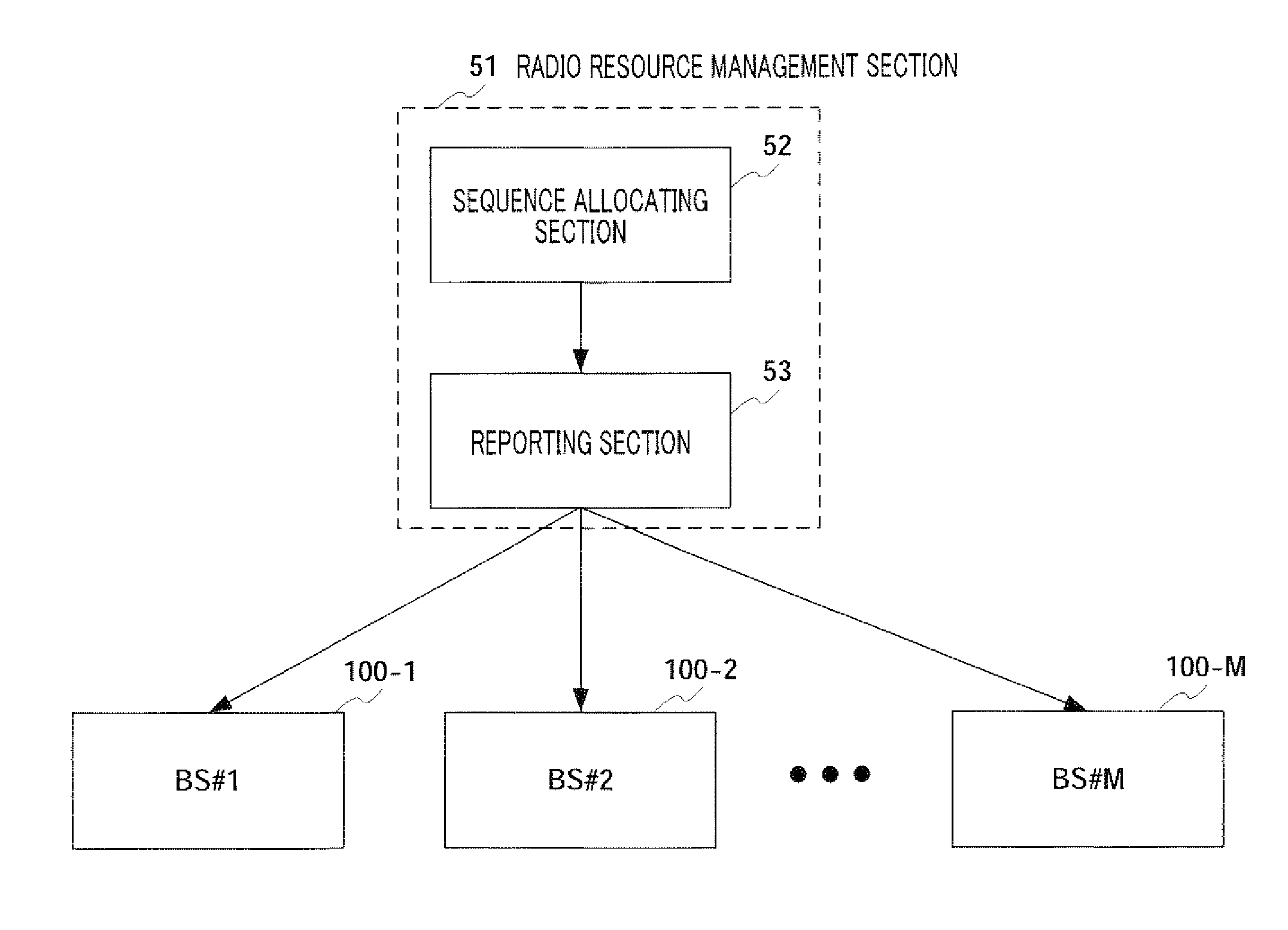
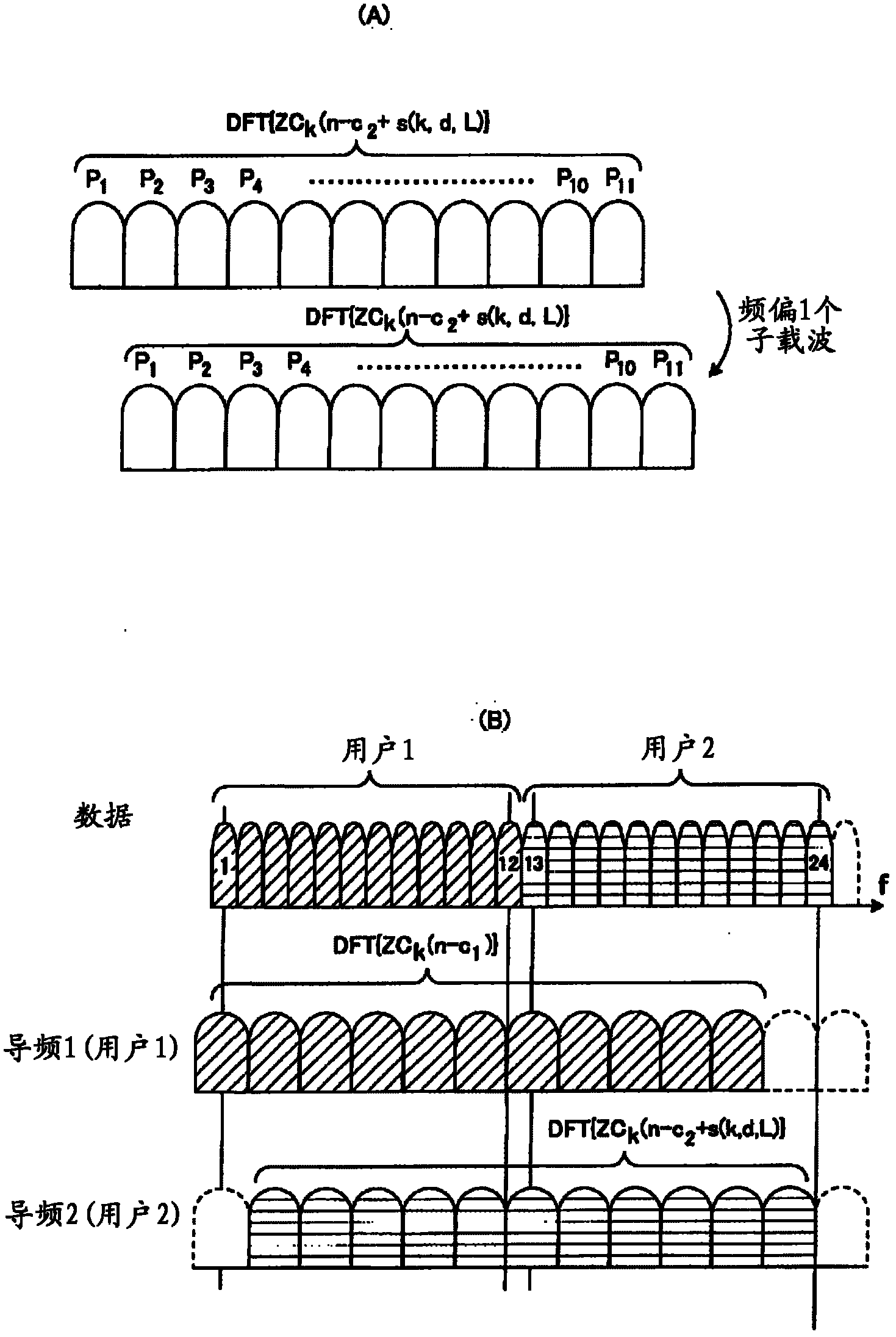
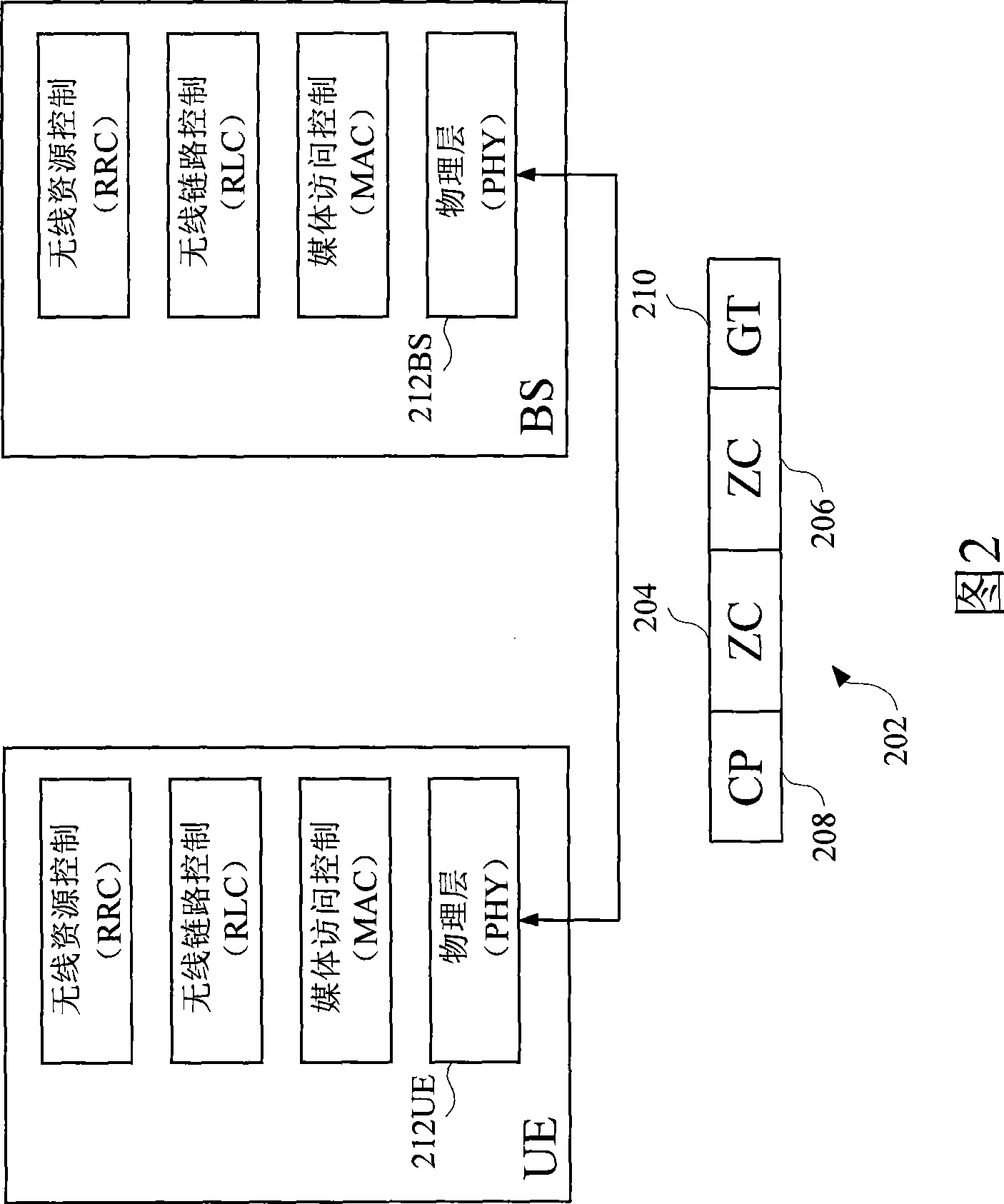
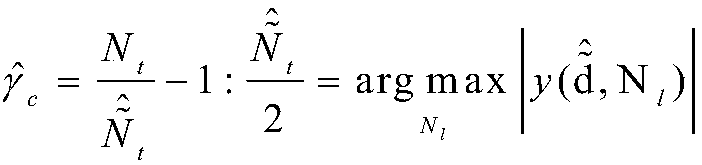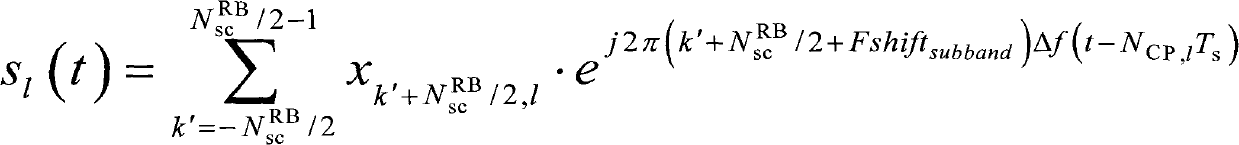Patents
Literature
86 results about "Zadoff–Chu sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A Zadoff–Chu (ZC) sequence, also referred to as Chu sequence or Frank–Zadoff–Chu (FZC) sequence, is a complex-valued mathematical sequence which, when applied to a signal, gives rise to a new signal of constant amplitude. When cyclically shifted versions of a Zadoff-Chu sequence are imposed upon a signal the resulting set of signals detected at the receiver are uncorrelated with one another.
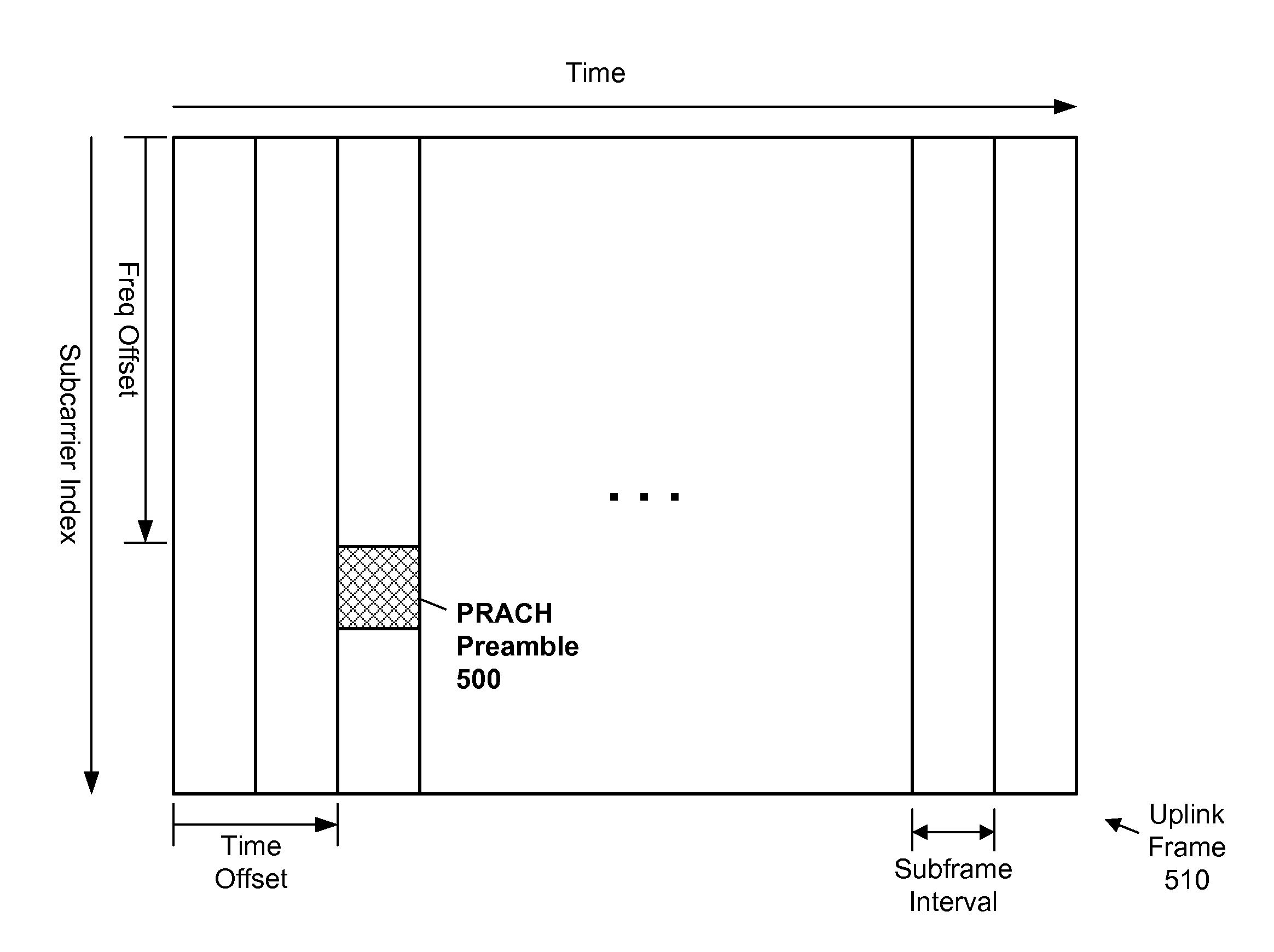
Enhanced PRACH Scheme for Power Savings, Range Improvement and Improved Detection
ActiveUS20150365977A1Big spaceLarge temporal widthError prevention/detection by using return channelPower managementTelecommunicationsRandom-access channel
Enhanced random access procedures for link-budget-limited user equipment (UE) devices are disclosed. A user equipment device may transmit a first message containing a Physical Random Access Channel (PRACH). The PRACH contains instances of a Zadoff-Chu sequence, and may be transmitted repeatedly as part of a single random attempt, to facilitate correlation data combining at the base station. The available Zadoff-Chu sequences may be partitioned among a plurality of sets, each set being associated with a respective Doppler shift range (or frequency hop pattern or time repetition pattern). A UE device may signal Doppler shift (or other information) to the base station by selection of one of the sets. The first PRACH transmission and the following PRACH transmission may occur in consecutive subframes. A UE device may select from a special set of Zadoff-Chu sequences (different from a conventional set of sequences), to signal its status as a link-budget-limited device.
Owner:APPLE INC
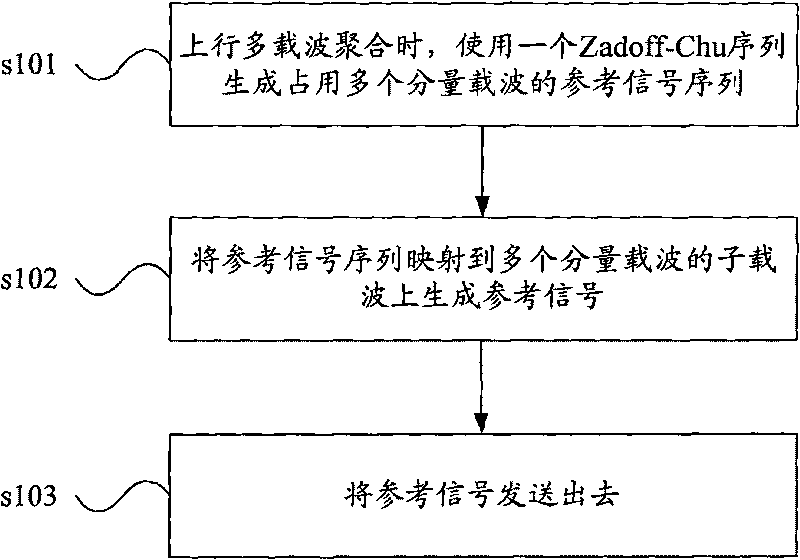
Method, system and equipment for transmitting uplink reference signals
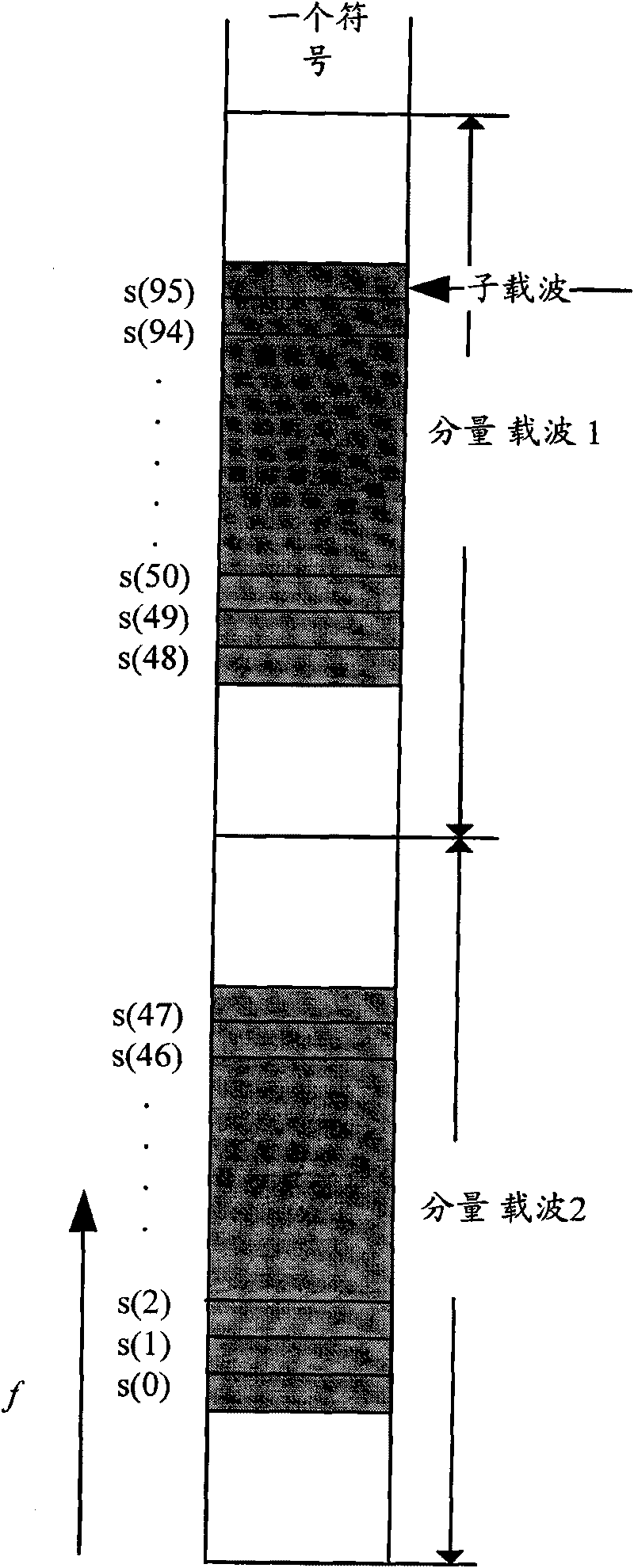
InactiveCN101741793AReduce CM/PAPRMulti-frequency code systemsMultiple carrier systemsCarrier signalComputer science
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method, a system and equipment for transmitting uplink reference signals. The method comprises: using a Zadoff-Chu sequence to generate a reference signal sequence occupying a plurality of component carriers during uplink multi-carrier polymerization; and mapping the reference signal sequence onto sub-carriers of the component carriers so a to generate and send reference signals. In the embodiment of the invention, the reference signal sequence is generated by use of one ZC sequence, and the reference signal sequence is mapped onto the sub-carriers of the component carriers so as to generate the reference signals when the reference signals are mapped onto the component carriers, so that the aim of reducing uplink reference signal CM / PAPR is achieved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Communications device
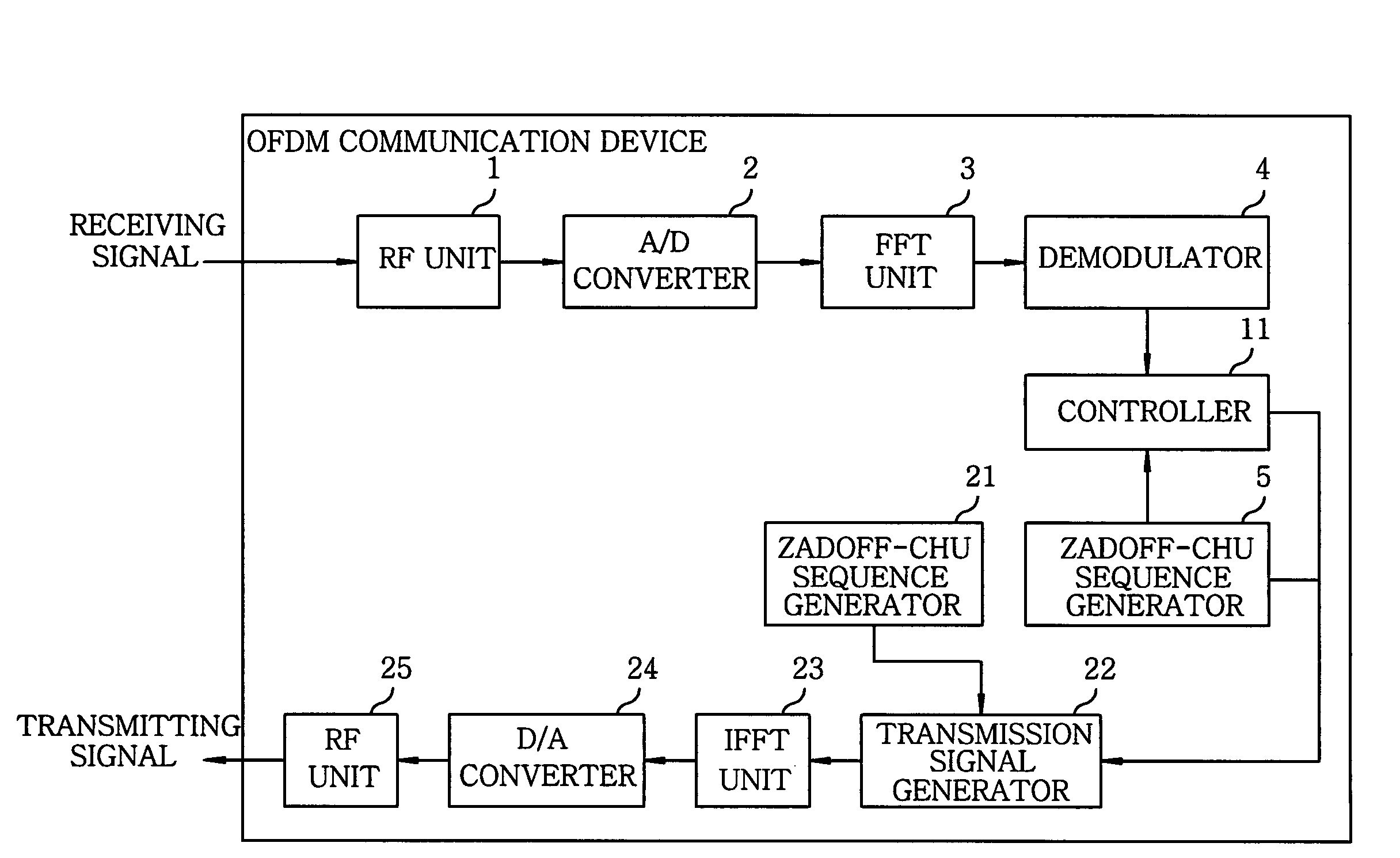
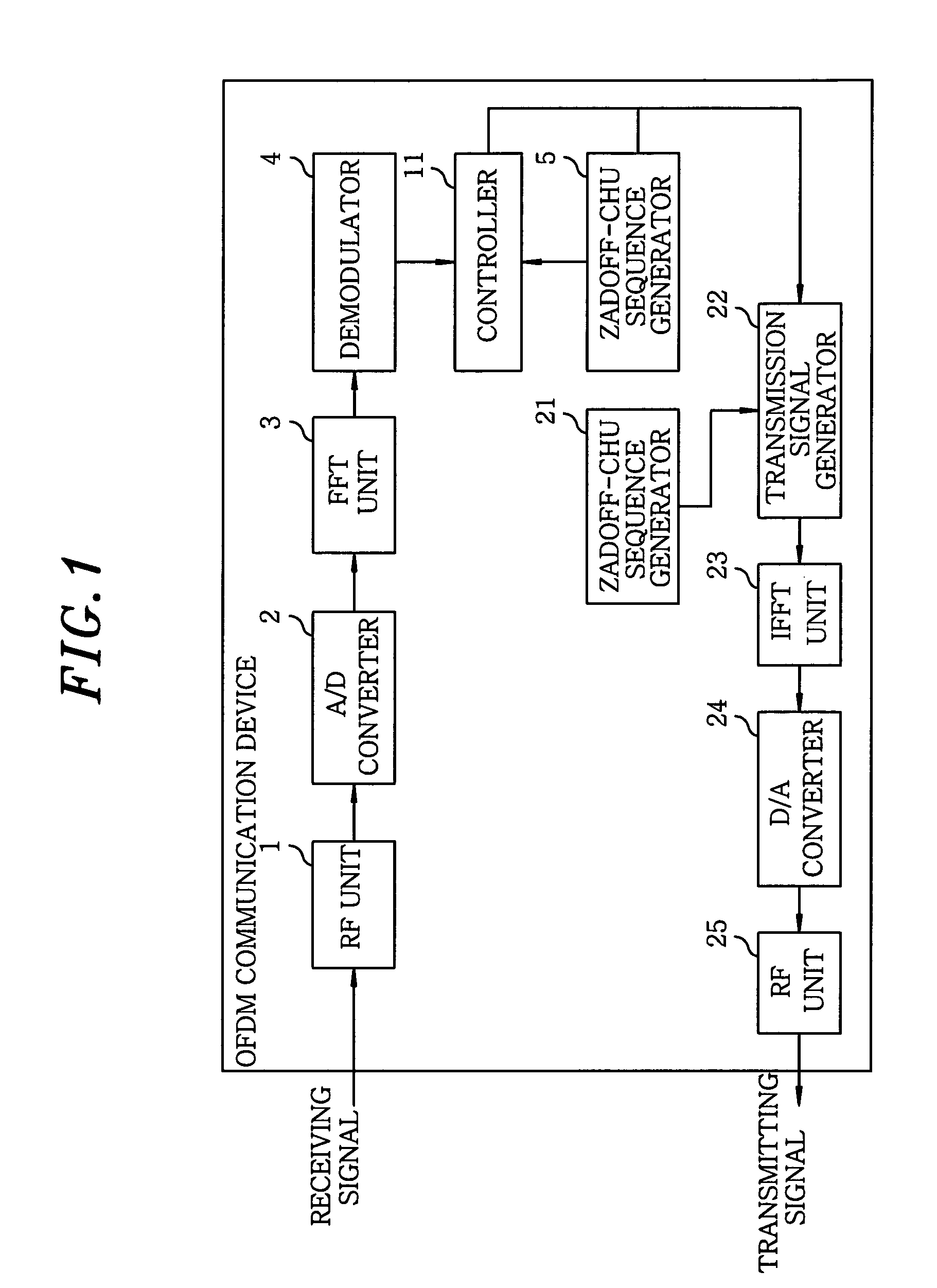
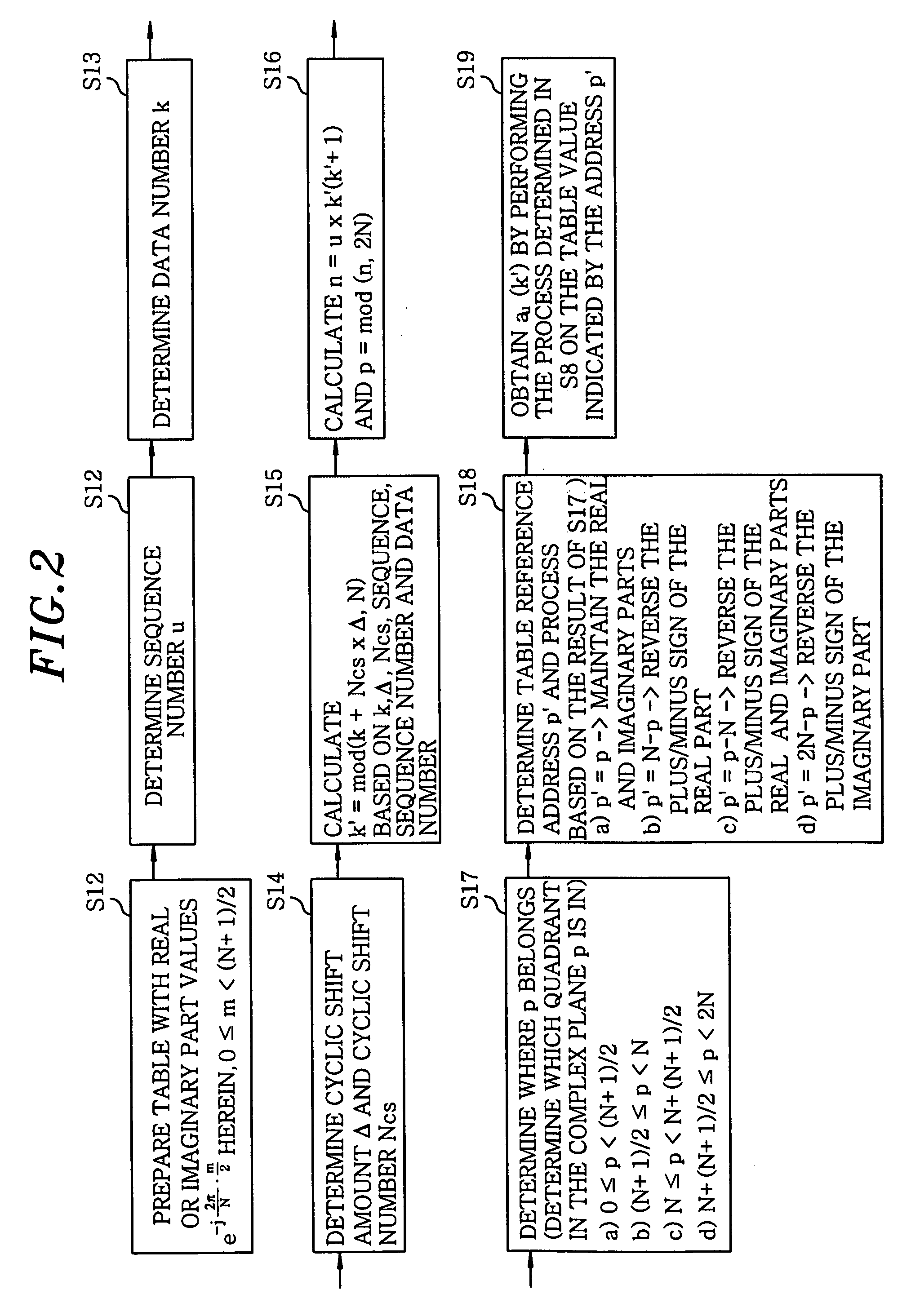
ActiveUS20090080550A1Generate efficientlyImprove accuracyCode division multiplexDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSequence determinationComputer science
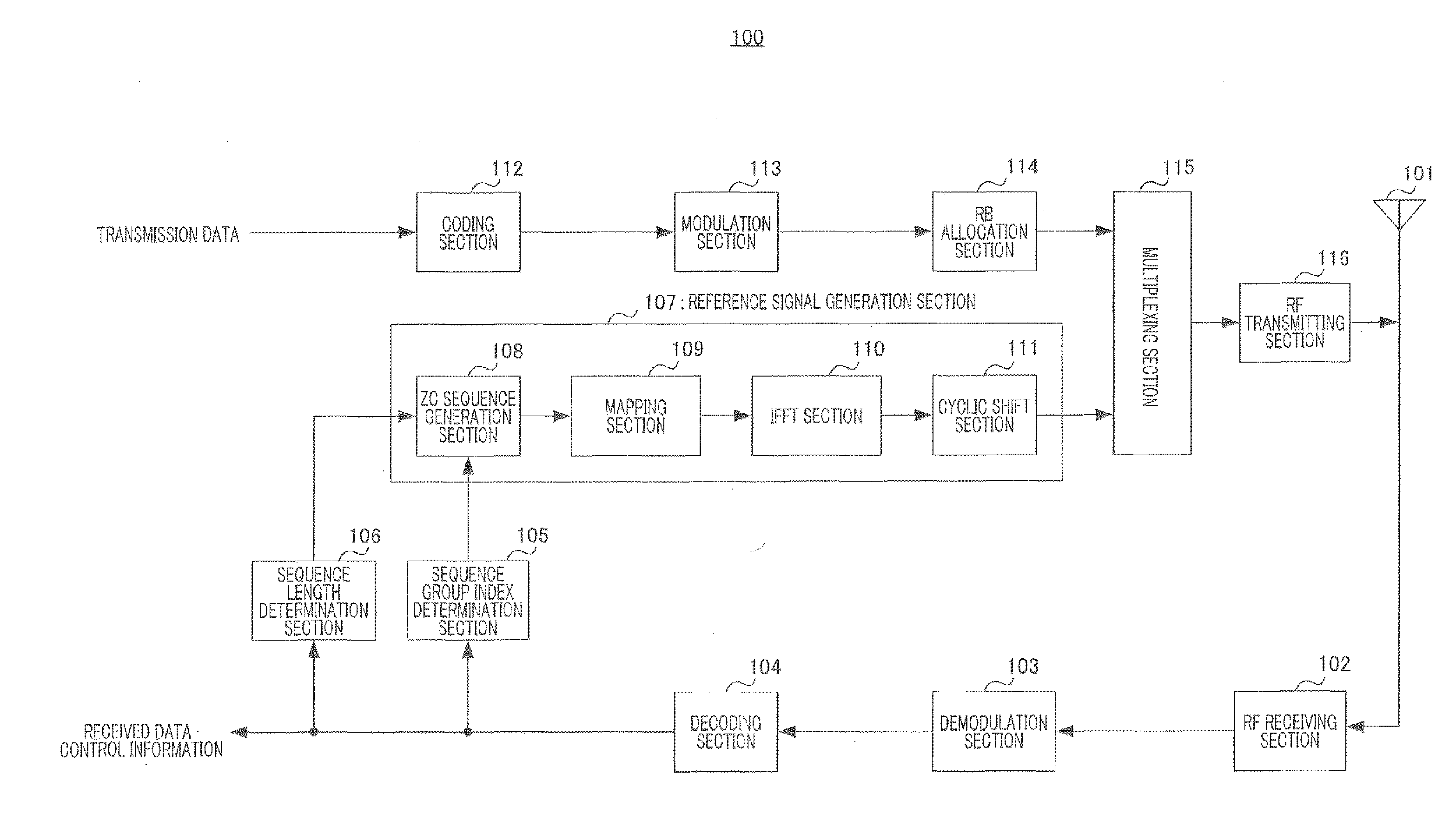
A communications device for generating a Zadoff-Chu sequence includes a storage unit storing real and imaginary part values of exp{−j·(2π / N)·(m / 2)} for the Zadoff-Chu sequence of the sequence length N, wherein m is an integer (0≦m<(N+1) / 2); a parameter acquisition unit acquiring a sequence number u, data number k, cyclic shift amount Δ and cyclic shift number Ncs; a phase position detecting unit detecting a phase position of the Zadoff-Chu sequence with acquired parameters; and a sequence determination unit determining m to read a real and an imaginary part value in the storage unit based on the phase position and determining a plus / minus sign of each of the real and the imaginary part value. The device further includes a sequence acquisition unit acquiring the Zadoff-Chu sequence by using the real and the imaginary part values according to m determined by the sequence determination unit and the signs thereof determined.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Sequence hopping method, wireless communication terminal apparatus and wireless communication base station apparatus
InactiveUS20100272022A1Good effectReduce distractionsMultiplex code allocationWireless commuication servicesTerminal equipmentZadoff–Chu sequence
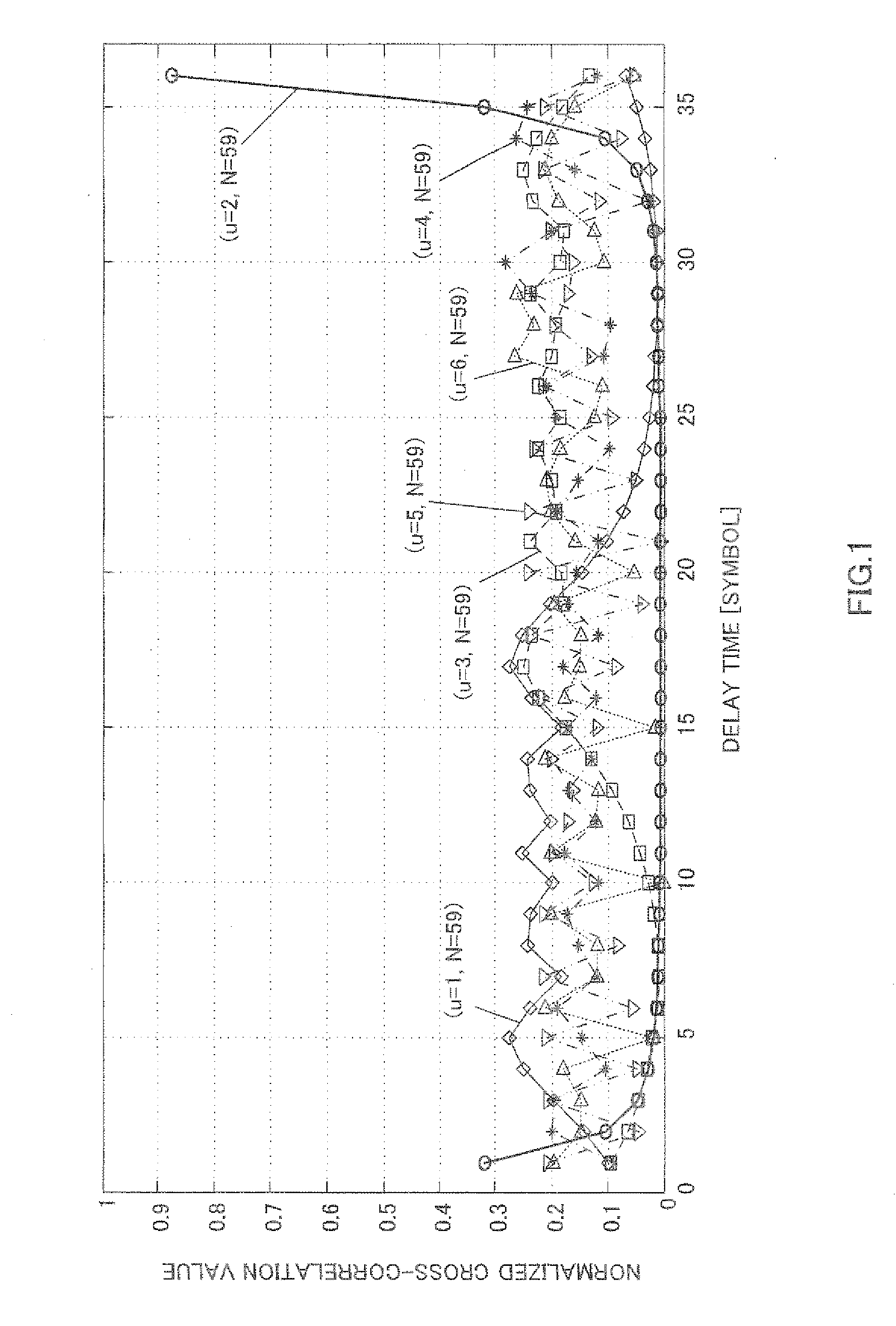
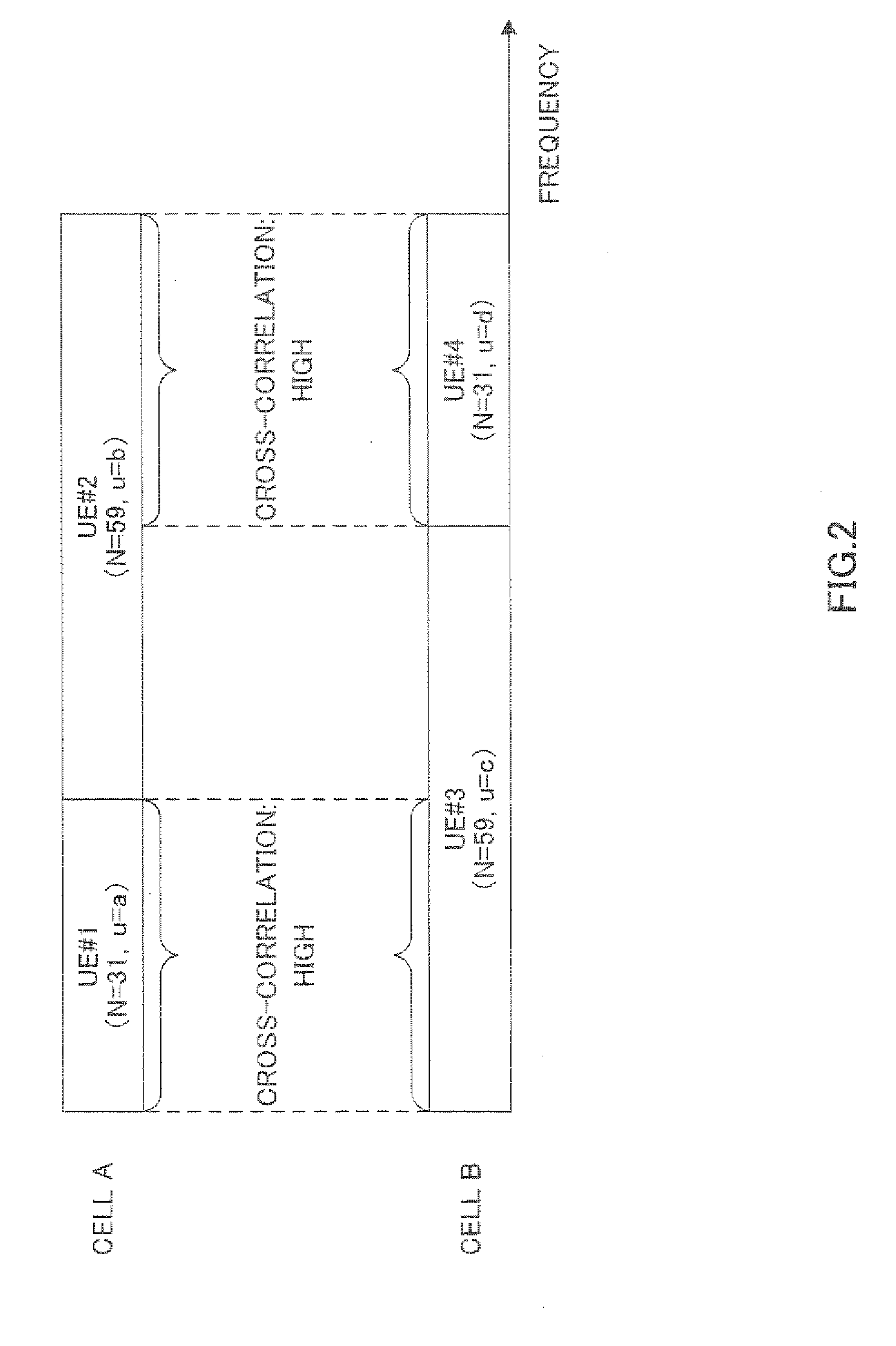
A wireless communication terminal apparatus wherein the occurrences of inter-sequence interferences between a reference signal preceding a sequence hopping and a reference signal following the sequence hopping can be reduced so as to improve the randomizing effect achieved by the sequence hopping. In this apparatus, a sequence number deciding part (105) has a table in which the sequence lengths of Zadoff-Chu sequences used for reference signals are associated with the sequence numbers of Zadoff-Chu sequences used for reference signals of a slot #1 and with the sequence numbers of Zadoff-Chu sequences used for reference signals of a slot #2. In accordance with a sequence length according to a transmission bandwidth received from a decoding part (104), the sequence number deciding part (105) refers to the table to decide the sequence number of a Zadoff-Chu sequence. In the table of the sequence number deciding part (105), different hopping amounts are provided to a plurality of slot-#2-specific Zadoff-Chu sequences having different sequence lengths.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
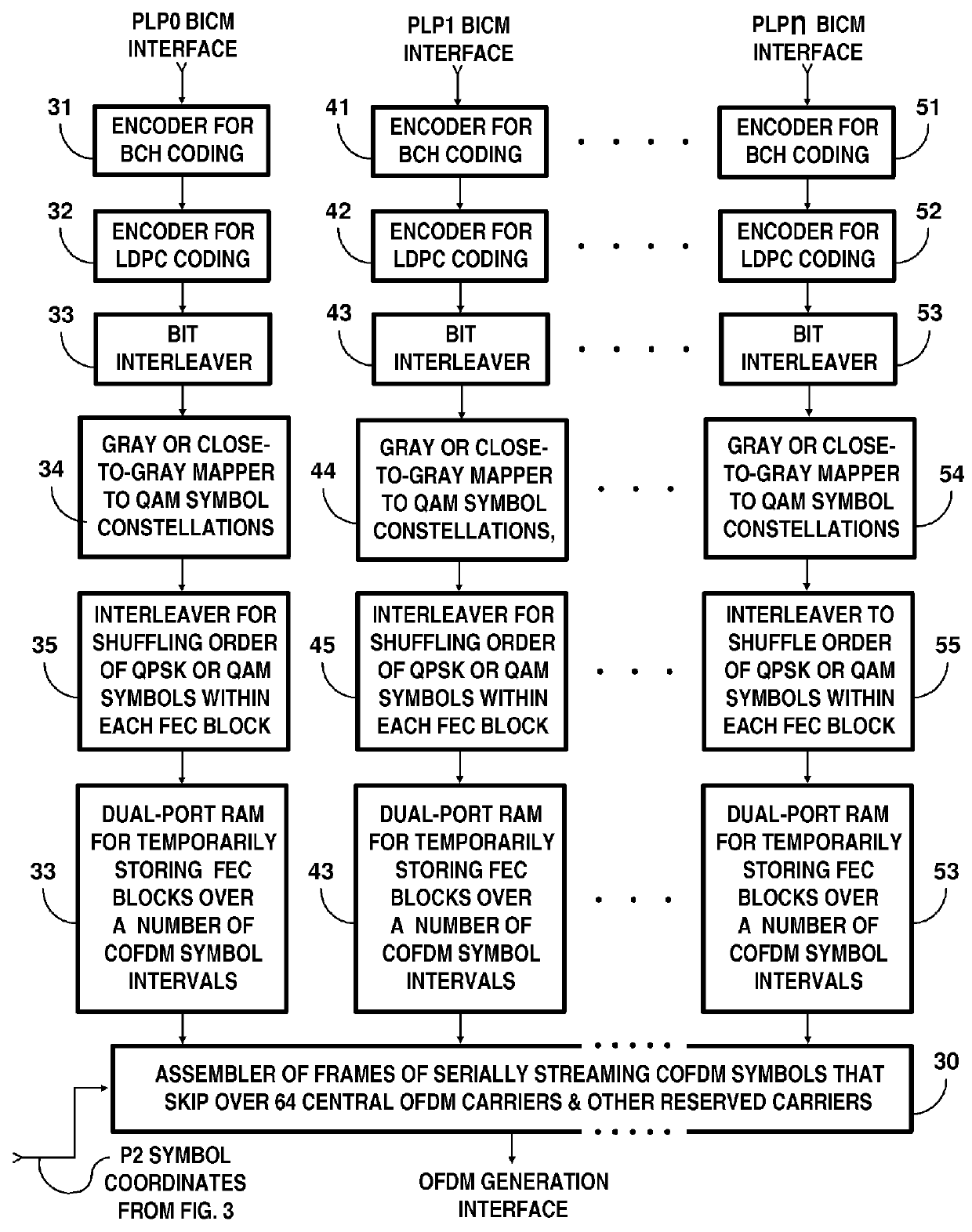
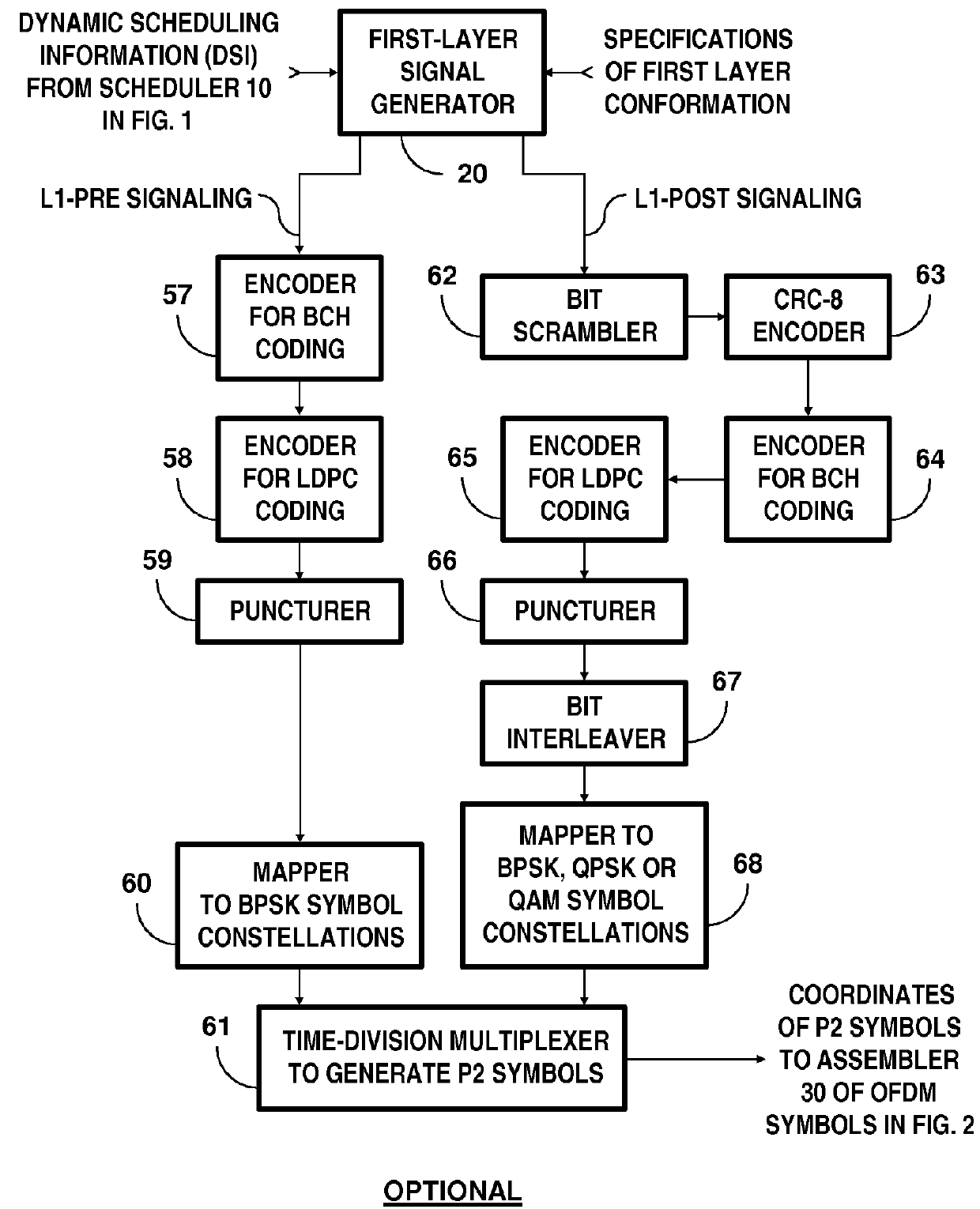
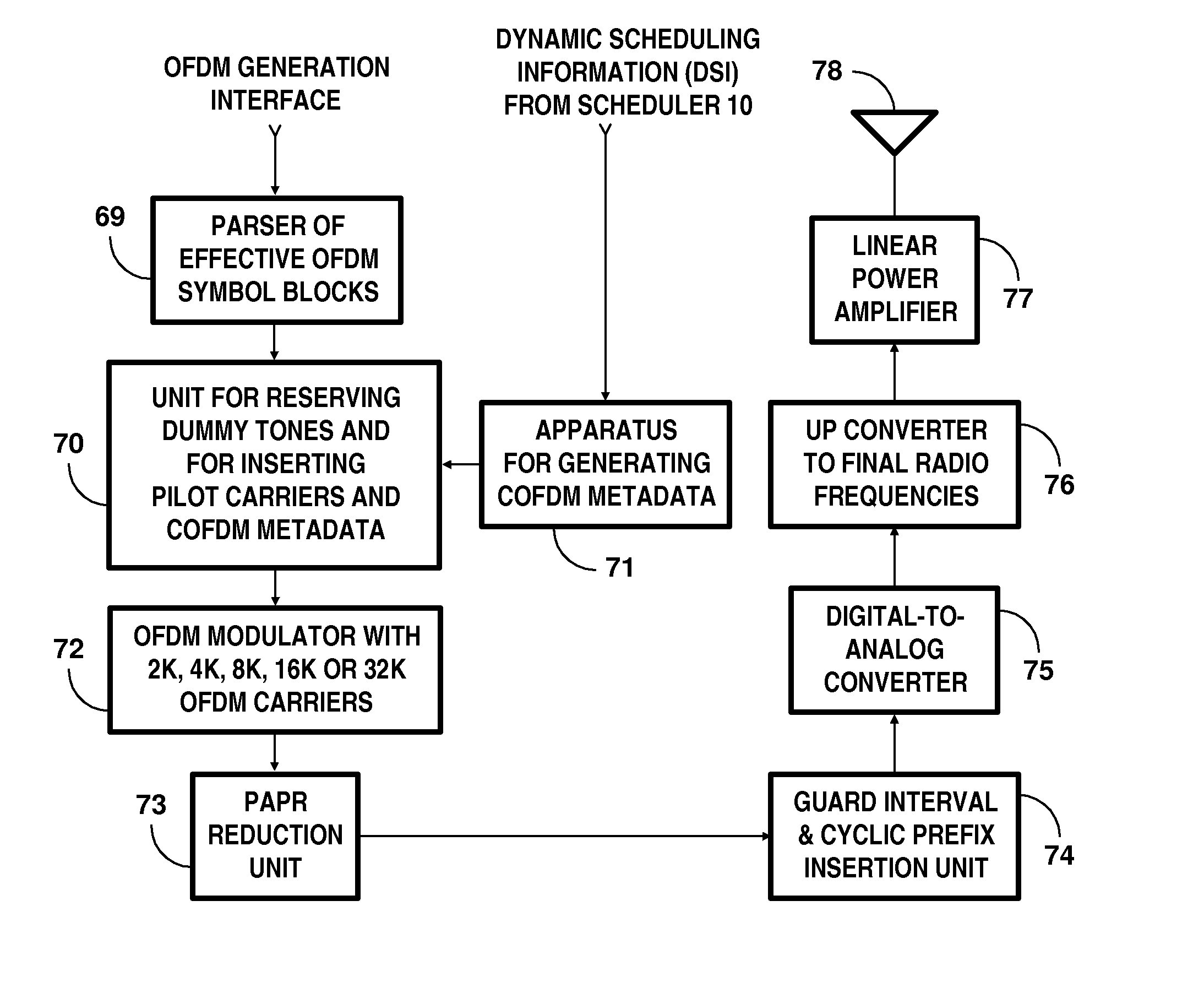
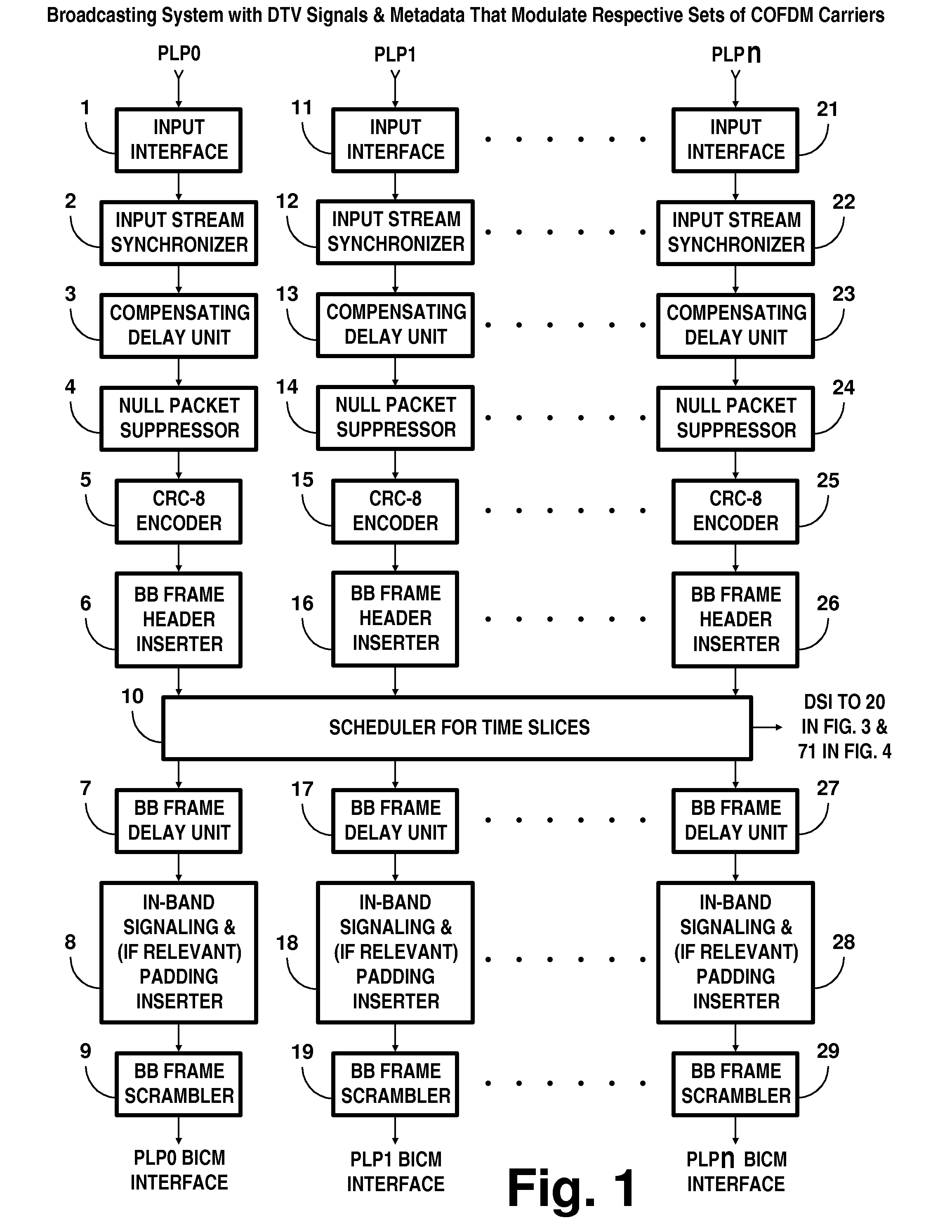
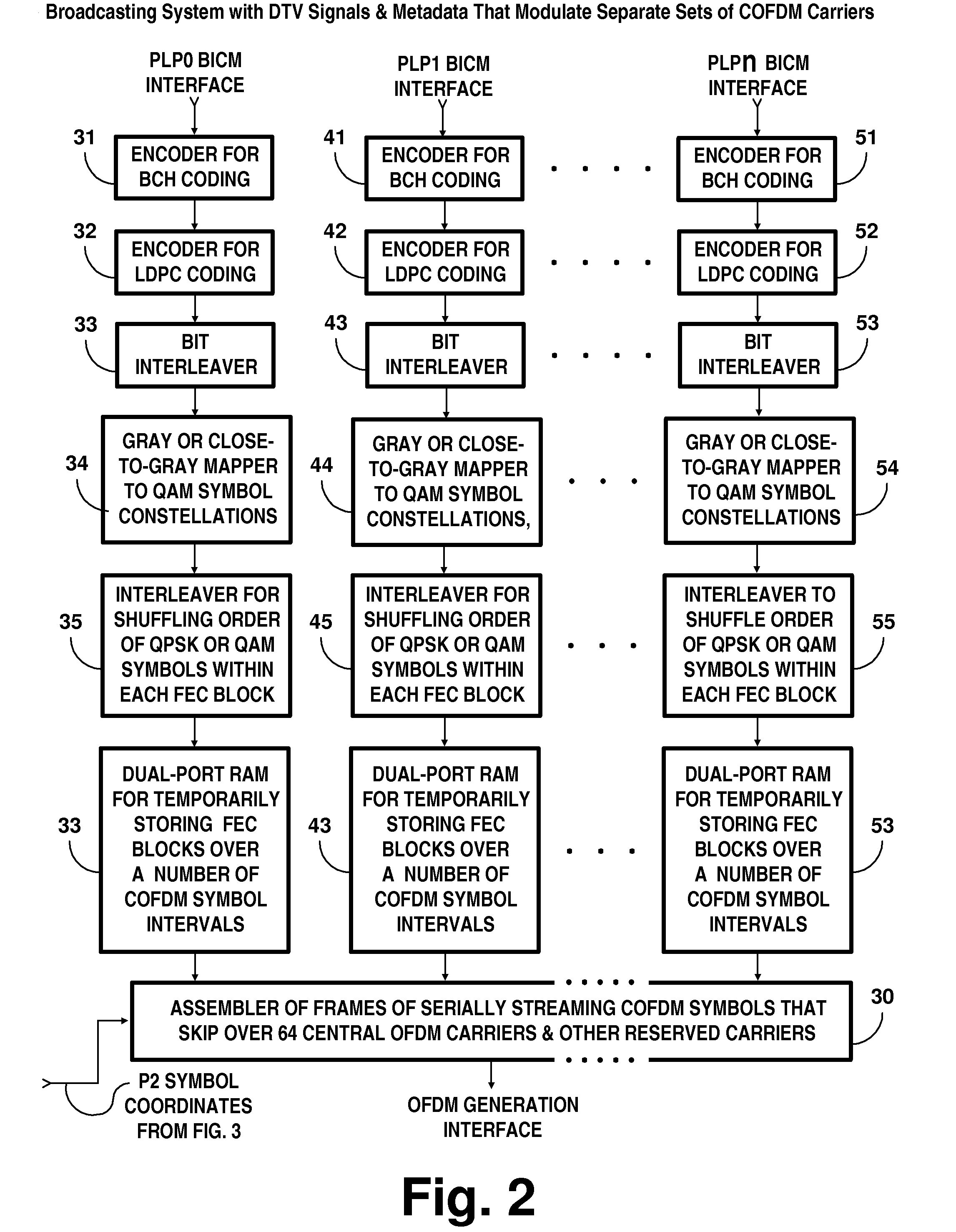
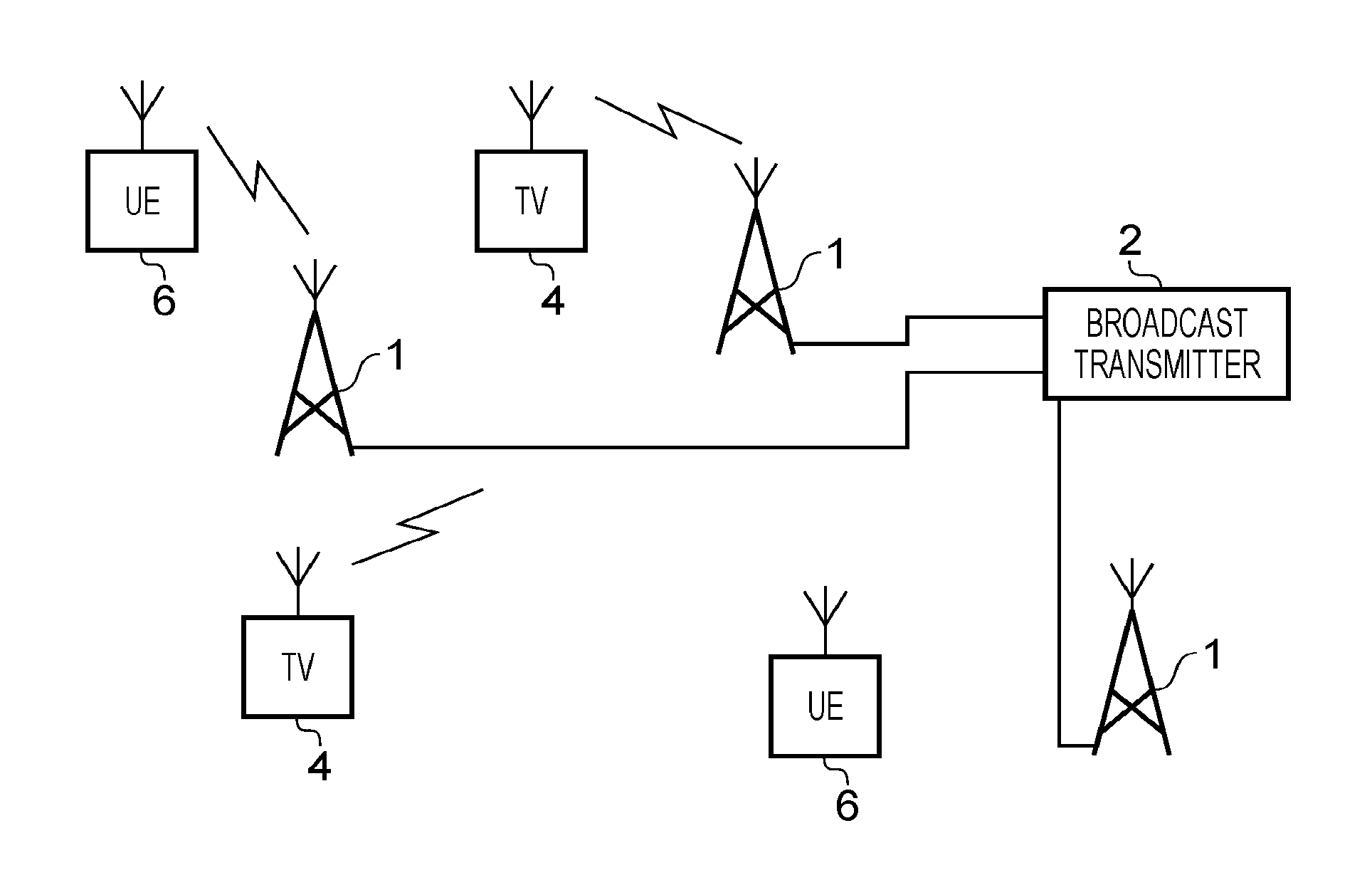
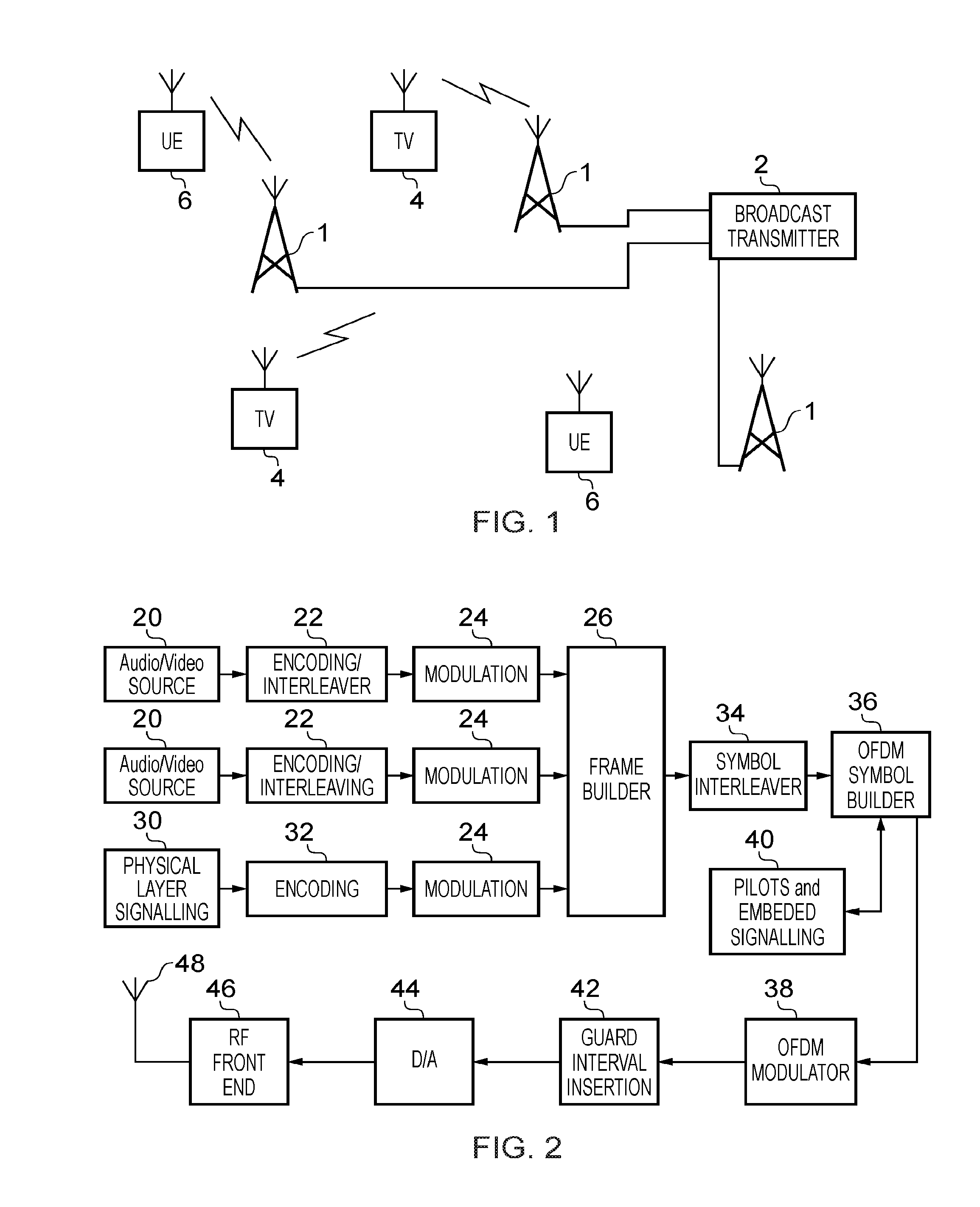
Broadcasting system with digital television signals and metadata that modulate respective sets of OFDM carriers
ActiveUS9253428B2Television system detailsMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsFrequency spectrumIntermediate frequency
Digital television (DTV) broadcasting using COFDM modulation is designed to modulate orthogonal frequency-division-multiplexed (OFDM) mid-band carriers with metadata including synchronization signals and transmission-mode signals. DTV signals modulate OFDM carriers occupying portions of the frequency spectrum of the transmission channel that extend in frequency both below and above these mid-band carriers. The OFDM midband carriers are capable of signaling when a new broadcast service is used that differs from the one disclosed. The signaling is provided by modulating the midband carriers with respective elements of signature sequences, each of which signature sequences is composed of Zadoff-Chu sequences and repetitive pseudo-random sequences scrambled by a Zadoff-Chu sequence.
Owner:CERINET USA
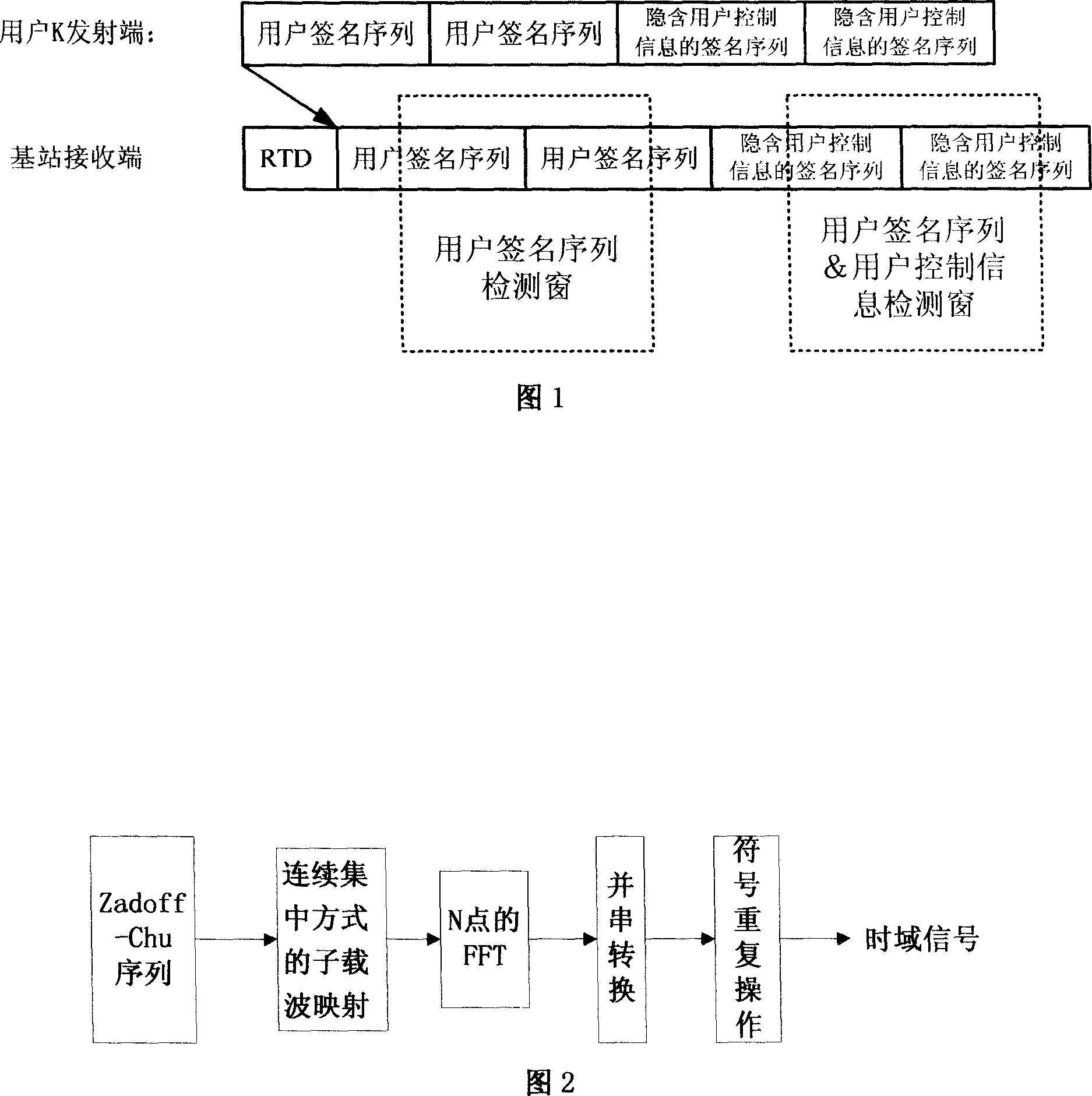
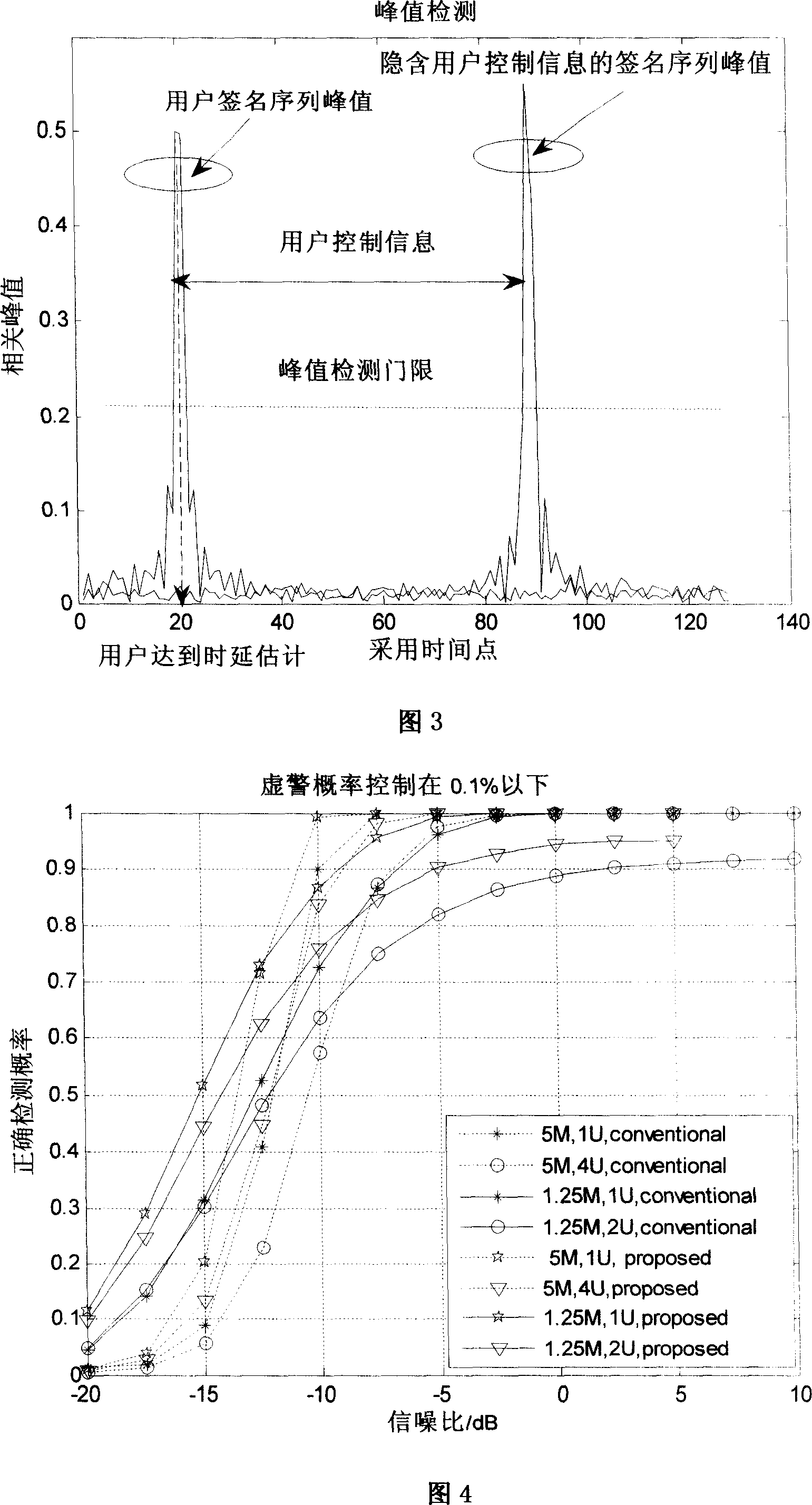
Signature sequence of sending structure of implying userí»s control information, transmitting and receiving method
ActiveCN101094027AAvoid interferenceTransmission method is reliableUser identity/authority verificationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTime domainComputer science
The mentioned sending structure includes a user signature sequence (USS) and user-control info (UCI). The time domain circular shift, between the mentioned signature sequence with implicit user-control info and USS, is an integer multiplied by Ns, the step length of circular shift. At the integer locates the control info. This invention provides a reliable way to transmit user-control info in the multi-user competing channel. It takes full advantage of the excellent related characteristics of the Zadoff-chu sequence to overcome interference from multi-user. In addition, this invention can be simply realized. Due to the sameness of the detection of the user signature sequence (USS) with a special structure as the detection of the traditional USS, the former USS can carry user-control information without adding extra complication to the user detection.
Owner:上海赟璟信息技术有限公司
Broadcasting system with digital television signals and metadata that modulate respective sets of OFDM carriers
ActiveUS20150341586A1Television system detailsMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsFrequency spectrumIntermediate frequency
Digital television (DTV) broadcasting using COFDM modulation is designed to modulate orthogonal frequency-division-multiplexed (OFDM) mid-band carriers with metadata including synchronization signals and transmission-mode signals. DTV signals modulate OFDM carriers occupying portions of the frequency spectrum of the transmission channel that extend in frequency both below and above these mid-band carriers. The OFDM midband carriers are capable of signaling when a new broadcast service is used that differs from the one disclosed. The signaling is provided by modulating the midband carriers with respective elements of signature sequences, each of which signature sequences is composed of Zadoff-Chu sequences and repetitive pseudo-random sequences scrambled by a Zadoff-Chu sequence.
Owner:CERINET USA
Equipment and method for transmitting and receiving random access preamble
InactiveCN102036408AMulti-frequency code systemsWireless communicationTelecommunicationsPhysical layer
The invention provides equipment and a method for transmitting and receiving a random access preamble. The equipment comprises a physical layer for transmitting burst comprising the preamble. The preamble comprises a first Zadoff-Chu sequence and a second Zadoff-Chu sequence, and each sequence has the length of N. The first Zadoff-Chu sequence is a periodic sequence of a first sequence index, and the period of the periodic sequence is equal to N; and the second Zadoff-Chu sequence is a periodic sequence of a second sequence index, and the period of the periodic sequence is equal to N.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Sequence allocating method and sequence allocating apparatus
ActiveUS20100039998A1Reducing of circuit scaleReducing amount of calculation and circuit scale of circuitModulated-carrier systemsMultiplex code generationTelecommunicationsZadoff–Chu sequence
A sequence allocating method and a sequence allocating apparatus wherein in a system where a plurality of different Zadoff-Chu sequences or GCL sequences are allocated to a single cell, the arithmetic amount and circuit scale of a correlating circuit at a receiving end can be reduced. According to these method and apparatus, in ST201, a counter (a) and a number (p) of current sequence allocations are initialized, and in ST202, it is determined whether the number (p) of current sequence allocations is coincident with a number (K) of allocations to one cell. In ST203, it is determined whether the number (K) of allocations to the one cell is odd or even. If K is even, in ST204-ST206, sequence numbers (r=a and r=N−a), which are not currently allocated, are combined and then allocated. If K is odd, in ST207-ST212, for sequences that cannot be paired, one of sequence numbers (r=a and r=N−a), which are not currently allocated, is allocated.
Owner:PANASONIC HLDG CORP
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving a pilot sequence in a broadcasting communication system
InactiveUS20130170333A1Reduce power consumptionSync fastModulated-carrier systemsCode division multiplexCommunications systemCarrier signal
A method and an apparatus for transmitting and receiving a pilot sequence in an Single Carrier-Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (SC-OFDM) scheme of a broadcasting communication system. The method includes determining seed values for Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) symbols; generating pilot sequences including information related to an OFDM symbol index by applying a Zadoff-Chu sequence to each of the seed values; inserting the pilot sequences into a determined subcarrier position in a frame according to a pilot pattern; and transmitting the frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
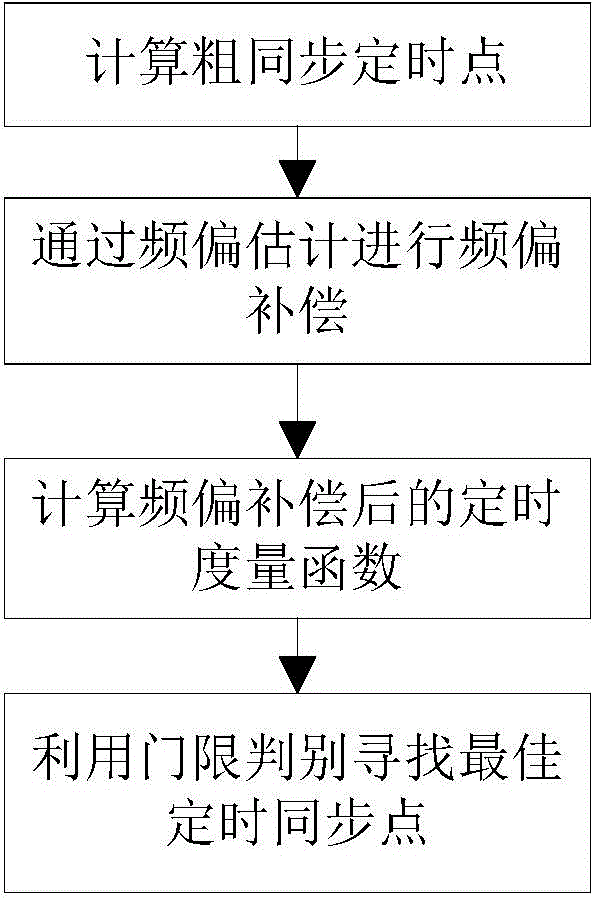
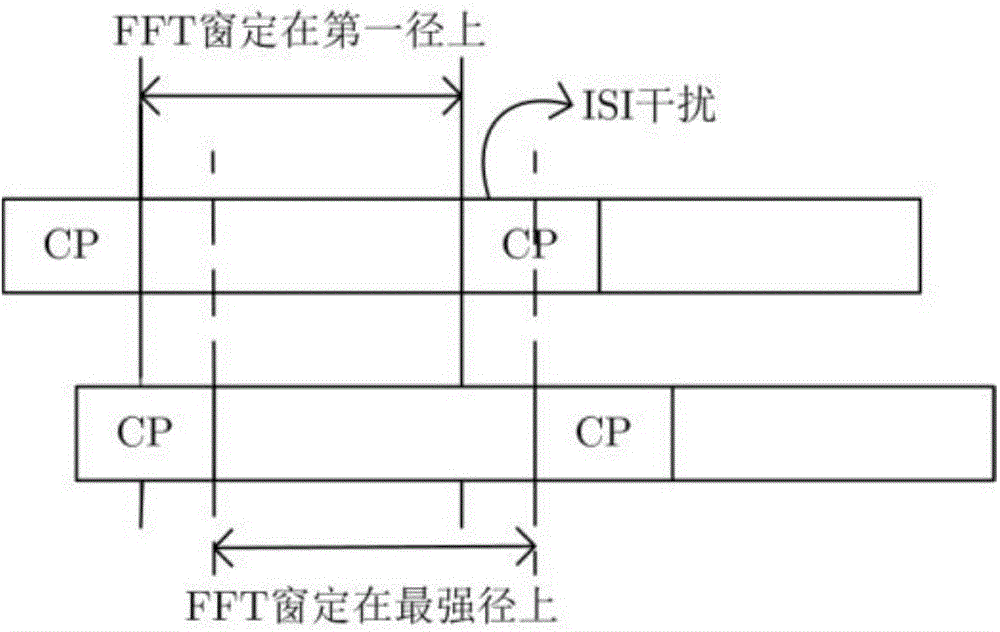
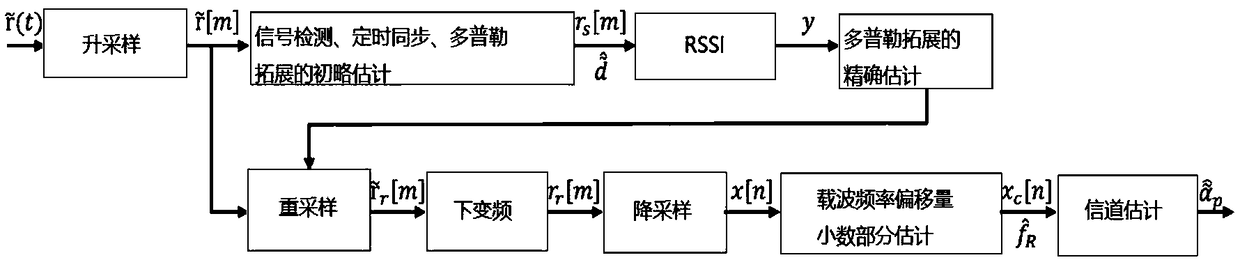
OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) precise timing synchronous method based on Zadoff-Chu sequence
ActiveCN104022995AImprove detection rateReduce mean square errorMulti-frequency code systemsSynchronising arrangementProblem of timeSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
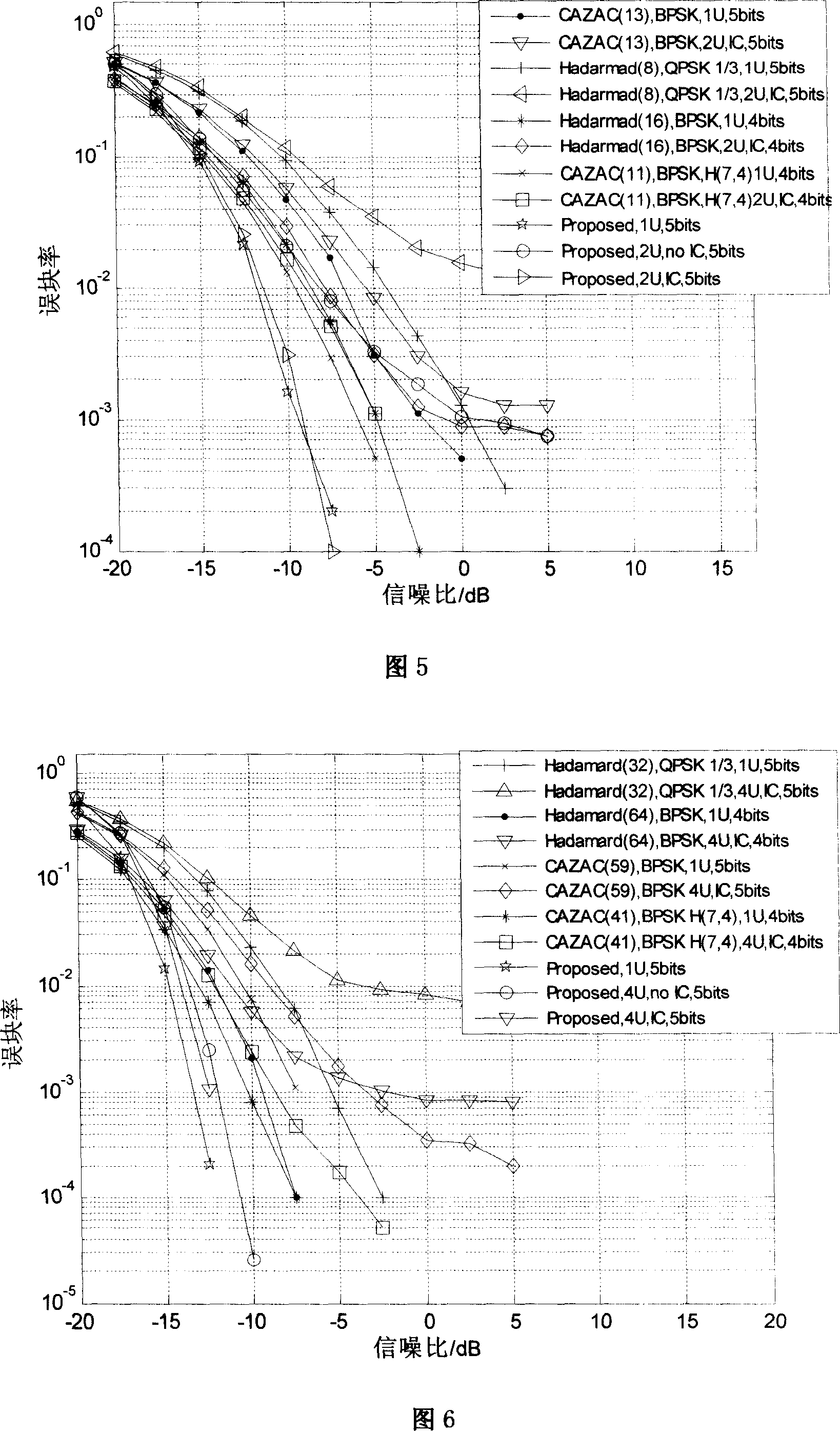
The invention discloses an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) precise timing synchronous method based on a Zadoff-Chu sequence, which belongs to the technical field of communication and mainly aims at solving the problem of timing deviation caused by the fact that a path with the maximum energy in a multi-path fading channel of an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system is not a first path. Channel impulse response is estimated through Zadoff-Chu sequence correlation, and a self-adaptive threshold detection algorithm for withstanding residual frequency deviation is established, then the achieving time of the first path is accurately judged, moreover the self-adaptive threshold is modified aiming at the problem that the false alarm probability is increased because of the residual frequency deviation, and verification shows that in a high speed moving multi-path environment, the algorithm detection probability is high, the mean square error is small, the detection probability can be greater than 99% in an SUI-3 channel when the signal to noise ratio is greater than 3dB, and then the method can be applied to a wideband OFDM communication system in the high speed moving environment.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
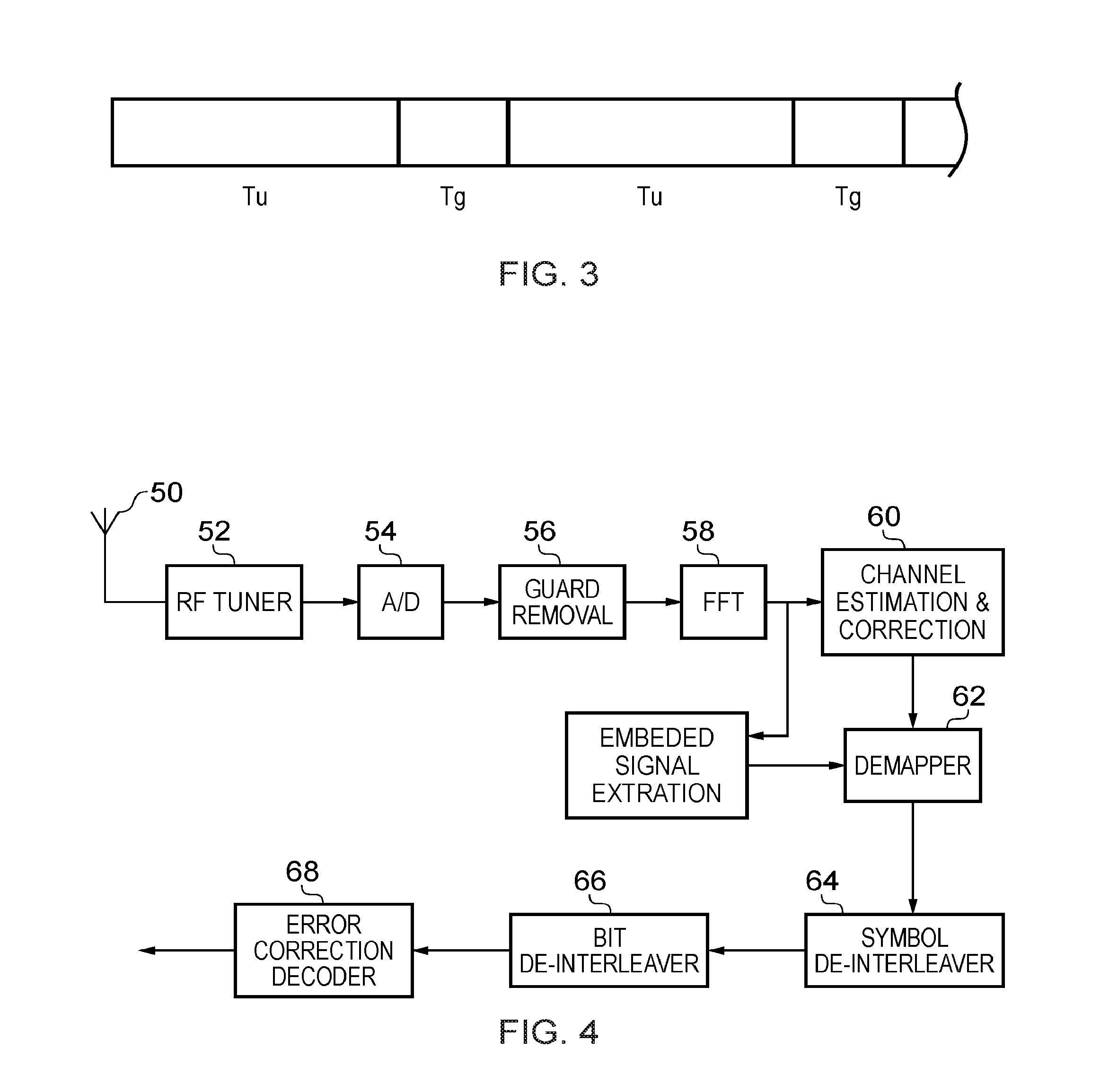
Receiver and method of receiving
ActiveUS20170026152A1Accurate estimateAccurate detectionTransmission path divisionSignal allocationDetector circuitsEngineering
A receiver for detecting and recovering payload data from a received signal, the receiver comprising: a radio frequency demodulation circuit configured to detect and to recover the received signal, the received signal having been formed and transmitted by a transmitter relative to which the receiver is moving at a speed less than or equal to a predetermined maximum speed, the received signal having been formed and transmitted by the transmitter to carry the payload data as Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexed (OFDM) symbols in one or more of a plurality of time divided frames, each frame including a preamble including a plurality of bootstrap OFDM symbols, one or more of the bootstrap OFDM symbols of the preamble carrying a signature sequence, and each of the one or more of the bootstrap OFDM symbols carrying a signature sequence carrying signalling data represented as a relative cyclic shift of the bootstrap OFDM symbol, wherein the signature sequence carried by each of the one or more of the bootstrap OFDM symbols comprises a combination of a Zadoff-chu sequence and a pseudorandom-noise sequence, a detector circuit configured to detect and to convert a useful part of the bootstrap OFDM symbols into the frequency domain, a bootstrap processor configured to detect the signalling data from the one or more of the bootstrap OFDM symbols in the frequency domain, and a demodulator circuit configured to recover the payload data from the payload OFDM symbols using the signalling data, wherein the bootstrap processor comprises: a divider configured to divide a first bootstrap OFDM symbol in the frequency domain by a second bootstrap OFDM symbol in the frequency domain, the first and second bootstrap OFDM symbols being adjacent OFDM bootstrap symbols in the received signal, and one of the first and second bootstrap OFDM symbols being a subject bootstrap OFDM symbol which is one of the bootstrap OFDM symbols carrying signalling data; a divider and multiplier unit configured to divide the output of the divider by the pseudorandom-noise sequence of the signature sequence of the first bootstrap OFDM symbol and multiply the output of the divider by the pseudorandom-noise sequence of the signature sequence of the second bootstrap OFDM symbol; a phase change estimator configured to detect an average change in phase between adjacent sub-carriers of the subject bootstrap OFDM symbol on the basis of the output of the divider and multiplier unit, and a signalling data detector configured to identify the signalling data of the subject bootstrap OFDM symbol based on the detected average change in phase which is representative of the cyclic shift applied to the subject bootstrap OFDM symbol.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
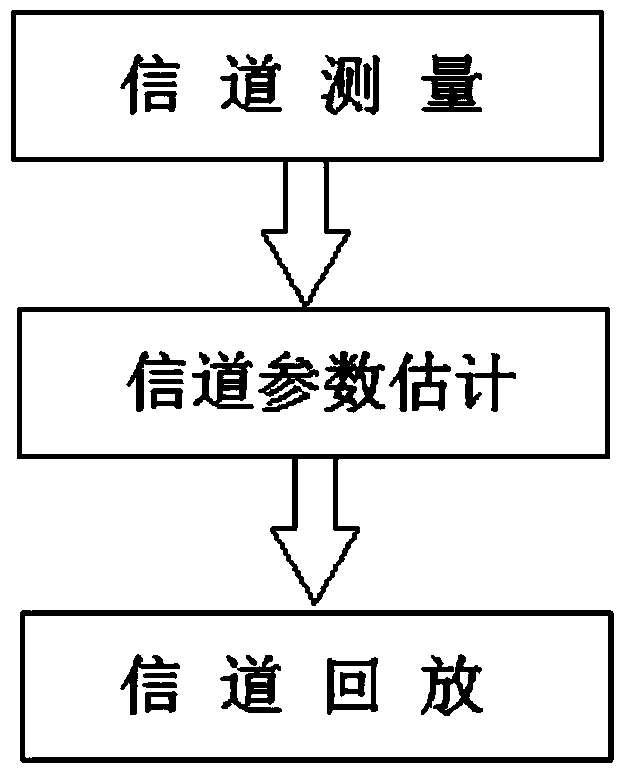
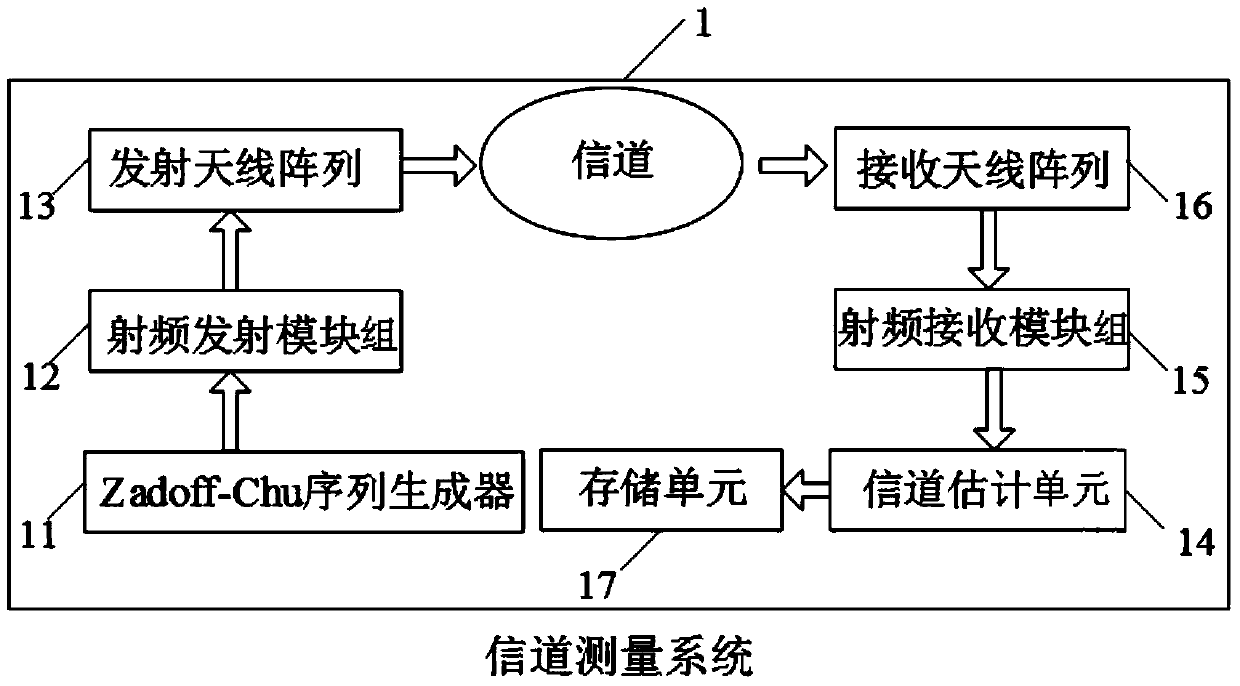
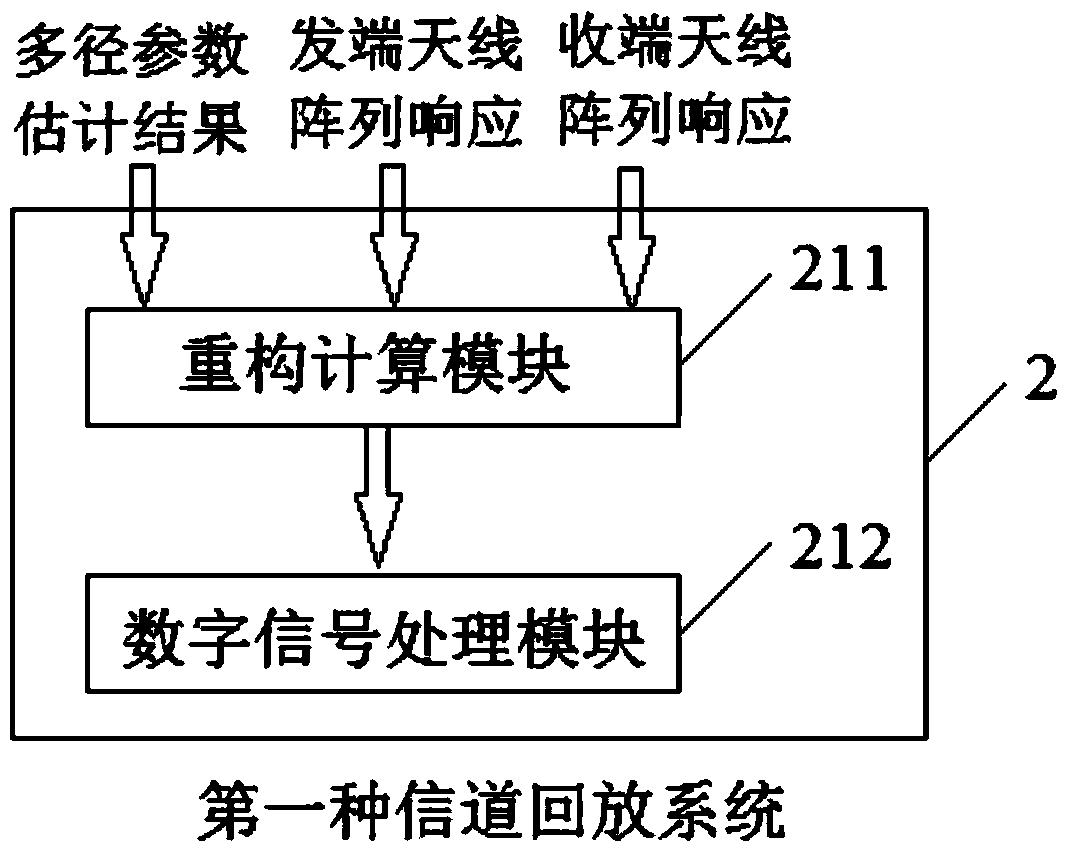
Channel data playback method and device
ActiveCN104618041AFully documentedEliminate the effects of measuring antenna responsePropogation channels monitoringChannel parameterRadio frequency
The invention discloses a channel data playback method and device. The method includes the steps: measuring a channel; estimating channel parameters; playing back the channel. The device comprises a channel measurement and channel playback system. Two playback methods and corresponding playback systems are provided according to whether a microwave chamber is used for OTA (over-the-air) playback or not. An antenna array in the measuring system is optimized, and multipath channel characteristics are sufficiently recorded by the aid of technologies such as Zadoff-Chu sequence and parallel reception, the multipath channel characteristics are accurately estimated by the aid of multipath parameter estimation algorithms such as particle swarm optimization, so that antenna response in recorded channel impact response is eliminated. In channel playback, an equivalent channel between transmitting and receiving radio frequency ports can be directly reconstructed for recovery, a channel between a base station radio frequency port and a terminal communication field can be reconstructed, and the microwave chamber with an intensive antenna probe and a corresponding antenna switching unit is used for playback by the aid of OTA technology.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
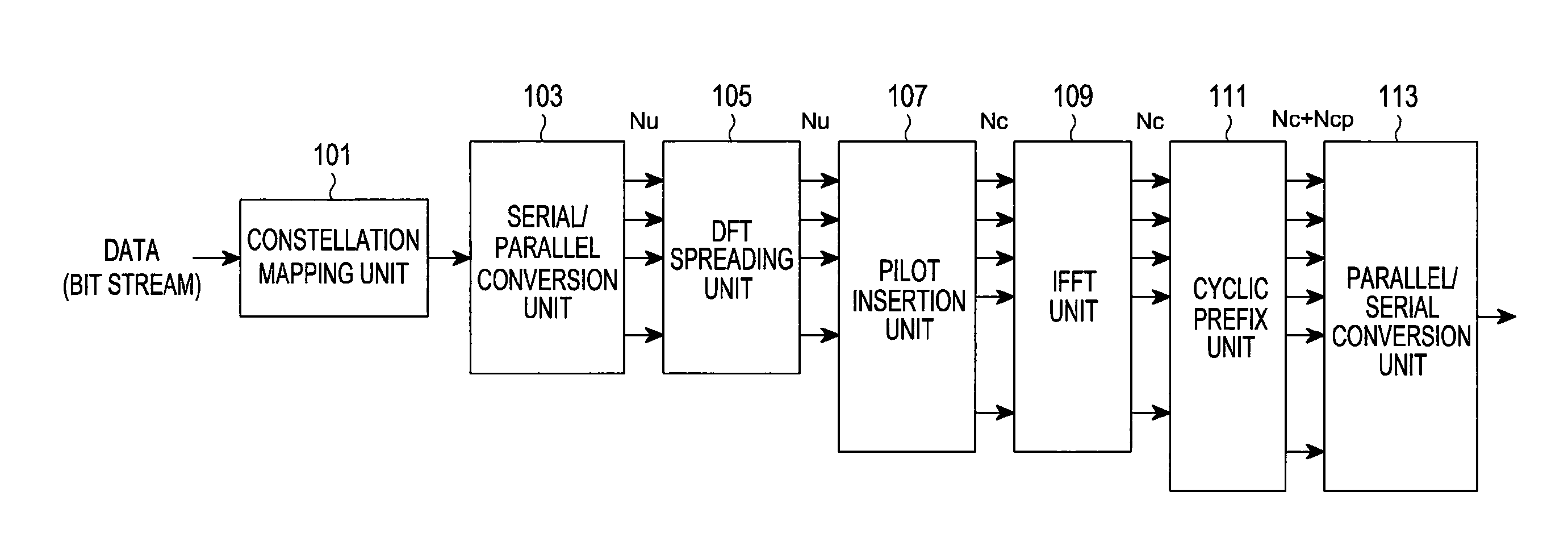
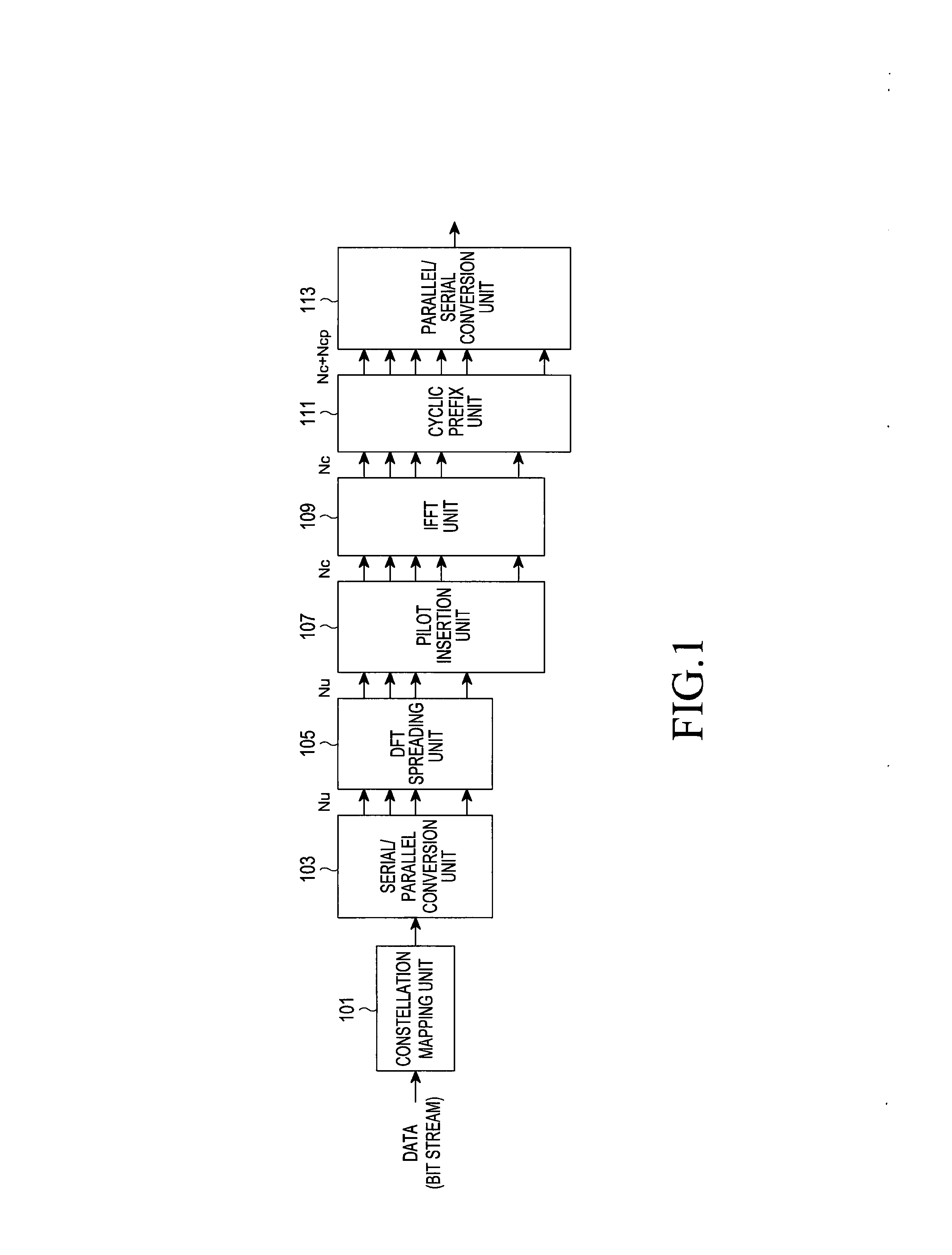
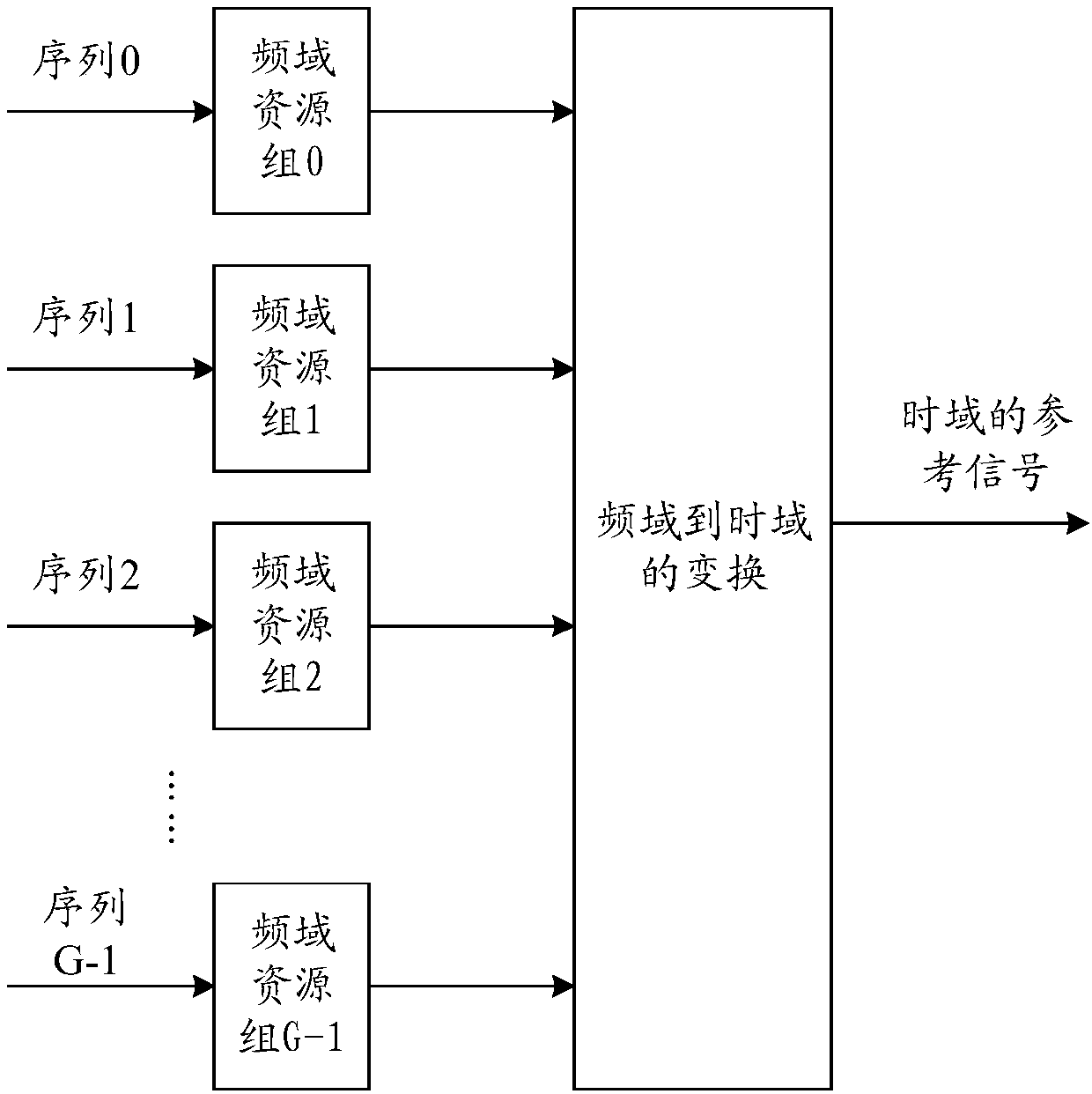
Reference signal transmission method and equipment
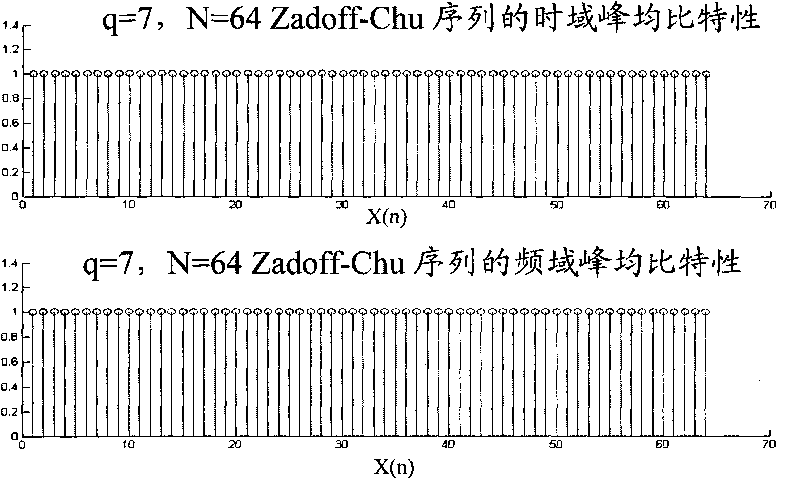
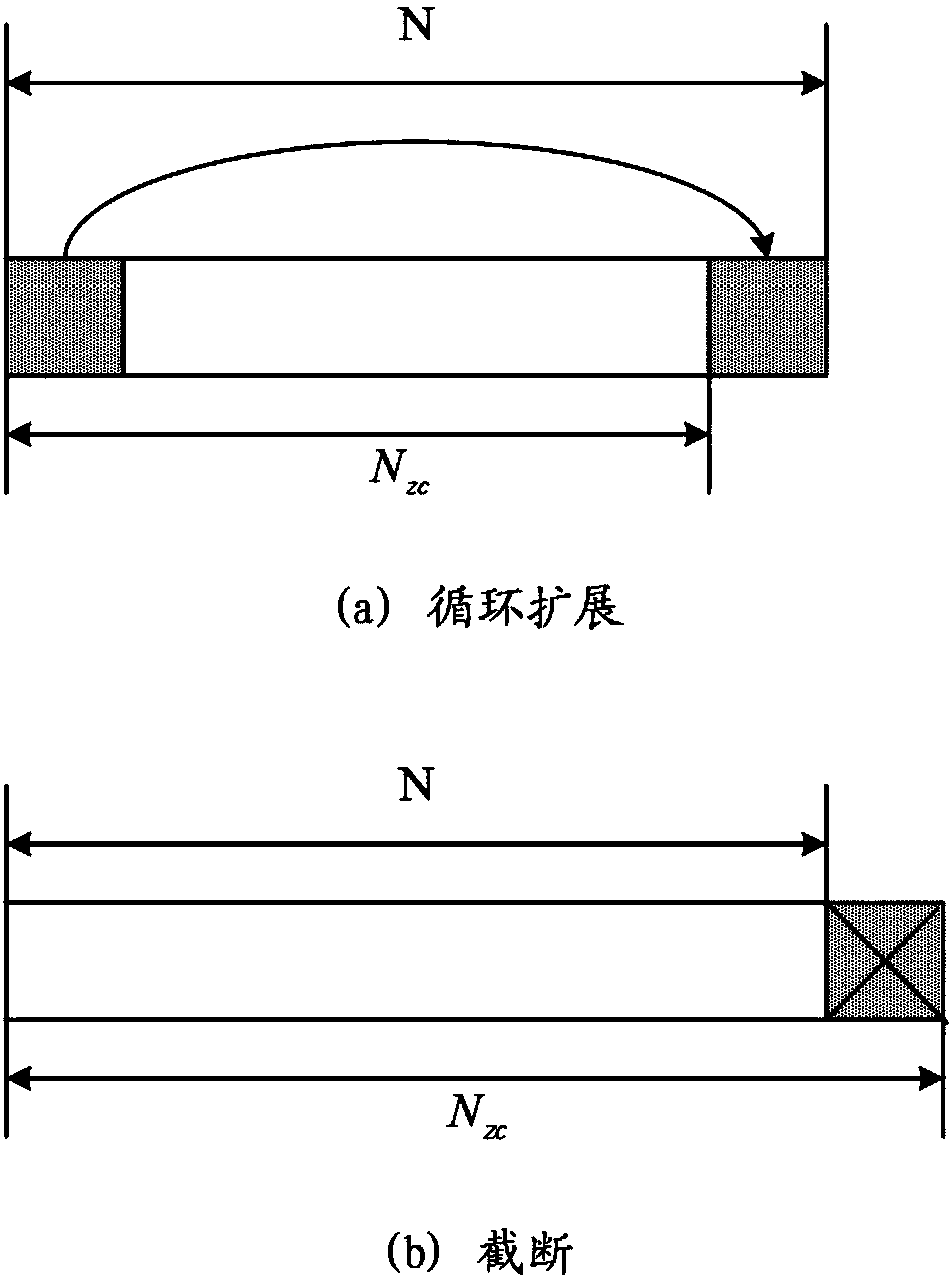
The invention provides a reference signal transmission method and equipment. The method comprises the steps that a sending device transforms reference signals of a frequency domain into a time domain,thereby generating the reference signals of the time domain, wherein the reference signals of the frequency domain comprise a reference signal sequence mapped on a frequency domain resource, the reference signal sequence is determined by a Zadoff-Chu sequence, and a length value of the Zadoff-Chu sequence is selected from at least two length values; and the sending device sends the reference signals of the time domain. According to the reference signal transmission method provided by the invention, the ZC (Zadoff-Chu) sequence is selected from at least two ZC sequences with different lengthsand is used for generating the reference signal sequence, so the generated reference signal sequence has the characteristic of low PRPR (peak-to-average power ratio) and low RCM (Raw Cubic Metric). According to the reference signals generated by the reference signal sequence, the data transmission performance can be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
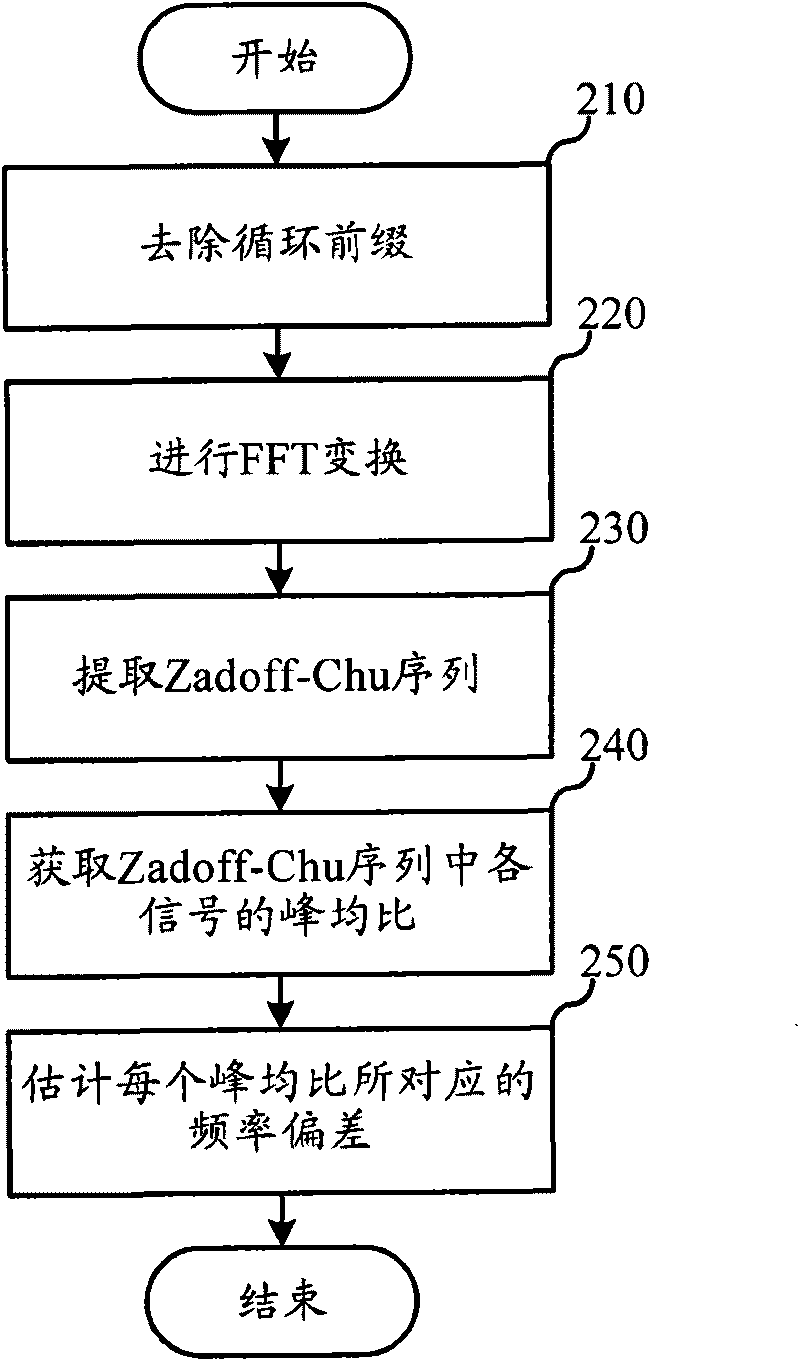
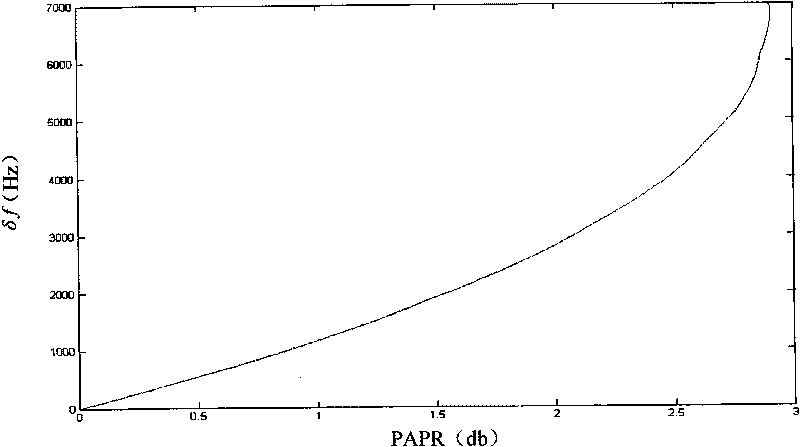
Frequency deviation estimating method and system
ActiveCN101741796ALower requirementAvoid calculationMulti-frequency code systemsOrthogonal multiplexCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a communication system and discloses frequency deviation estimating method and system. In the invention, a Zadoff-Chu sequence is extracted from a received signal, and a peak-to-mean ratio of signals in the Zadoff-Chu sequence is utilized to estimate a frequency deviation (namely frequency offset), thereby avoiding converting a frequency deviation estimating problem into a single frequency estimating problem, thus the invention has small operand, lower complexity and convenient ASIC realization. Moreover, because a concrete pilot frequency signal does not need to be known, blind estimation can be realized.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
5G waveform system synchronization method based on index modulation
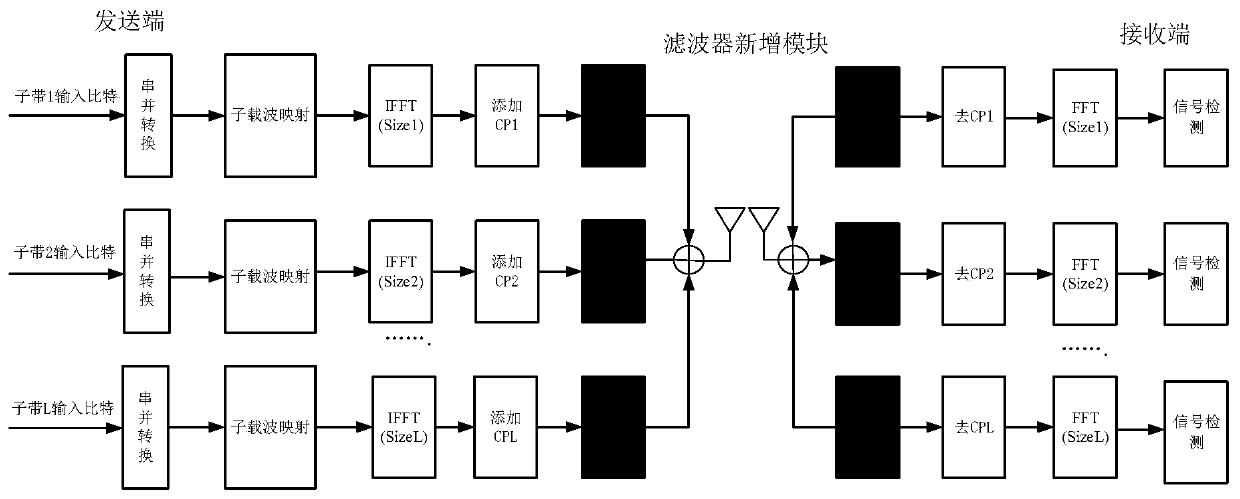
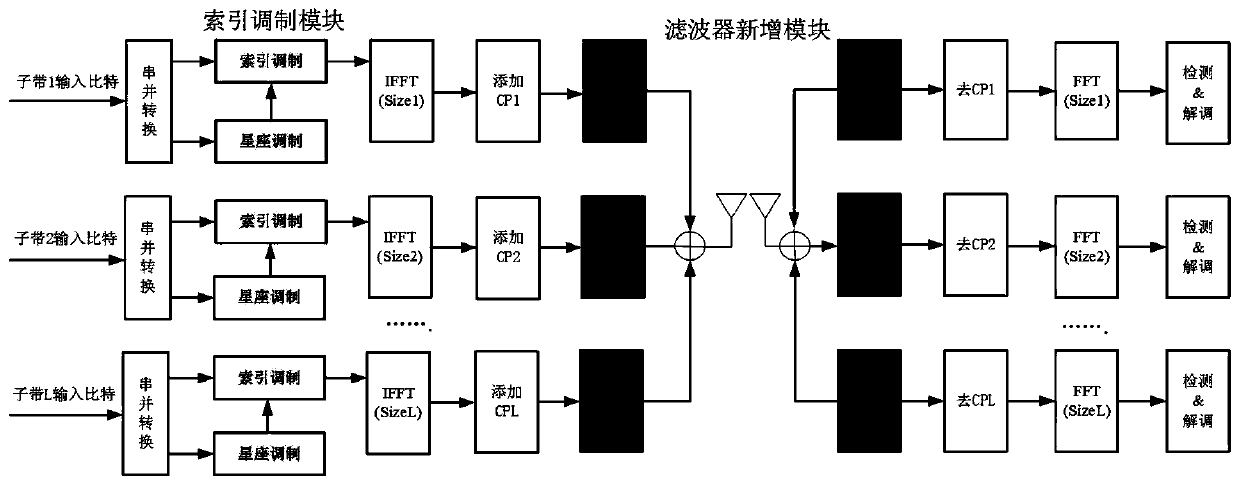
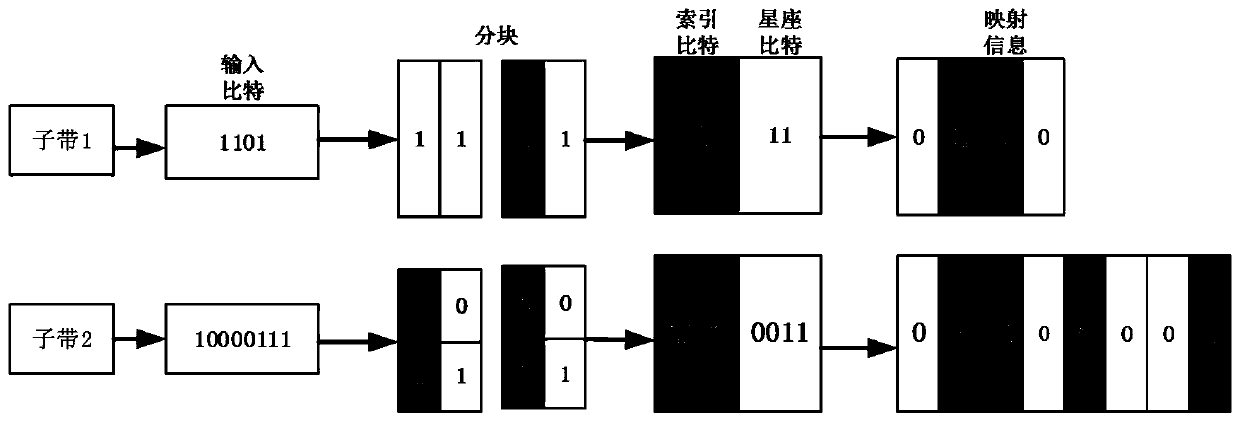
ActiveCN110636024AImprove performanceReduce bit error rateMulti-frequency code systemsCyclic prefixCarrier signal
The invention discloses a 5G waveform system synchronization method based on index modulation. The method comprises the following steps: dividing sending end parallel data of a filter orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system based on index modulation into index bit data and constellation modulation data, performing sub-band matching filtering processing, cyclic prefix removal and Fouriertransform at a receiving end, detecting the position of an activated sub-carrier, estimating an index bit, and demodulating constellation symbol information; establishing a training sequence based ona pseudo-random sequence and a Zadoff-Chu sequence, and performing timing and frequency offset estimation based on a pilot frequency data aided method; and completing timing estimation, performing fractional frequency offset estimation, performing integer frequency offset estimation by using the power difference between the activated subcarrier and the silent subcarrier, determining a receiving end Fourier transform starting window according to timing estimation information, determining a receiving end demodulation carrier frequency according to an estimated frequency offset value, and completing system synchronization. According to the invention, on the premise of not reducing the transmission efficiency, the influence of frequency offset on the system performance is effectively reduced.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV +1
Reference signal transmission method and device
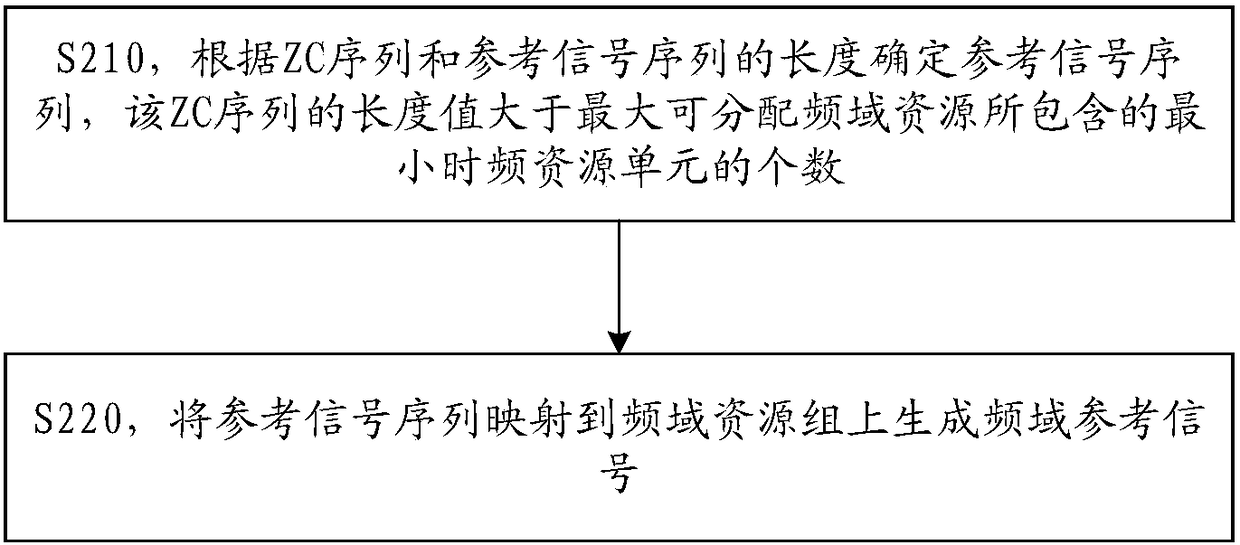
The invention provides a reference signal transmission method and device. The method comprises the following steps: a sending device transforms a reference signal in a frequency domain into a time domain to generate a reference signal in the time domain, wherein the reference signal in the frequency domain comprises a reference signal sequence mapped on a frequency domain resource group, the reference signal sequence is related to the lengths of a Zadoff-Chu sequence and the reference signal sequence, and the length value of the Zadoff-Chu sequence is greater than the number of minimum time-frequency resource units contained in a maximum assignable frequency domain resource; and the sending device sends the reference signal in the time domain. By adoption of the reference signal transmission method provided by the invention, the PAPR / RCM of the reference signal can meet the performance requirements, meanwhile, the number of blind detections of the reference signal can be reduced, and the system performance can be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
User terminals, wireless communication method and wireless communication system
ActiveCN102209061ABaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemResource information
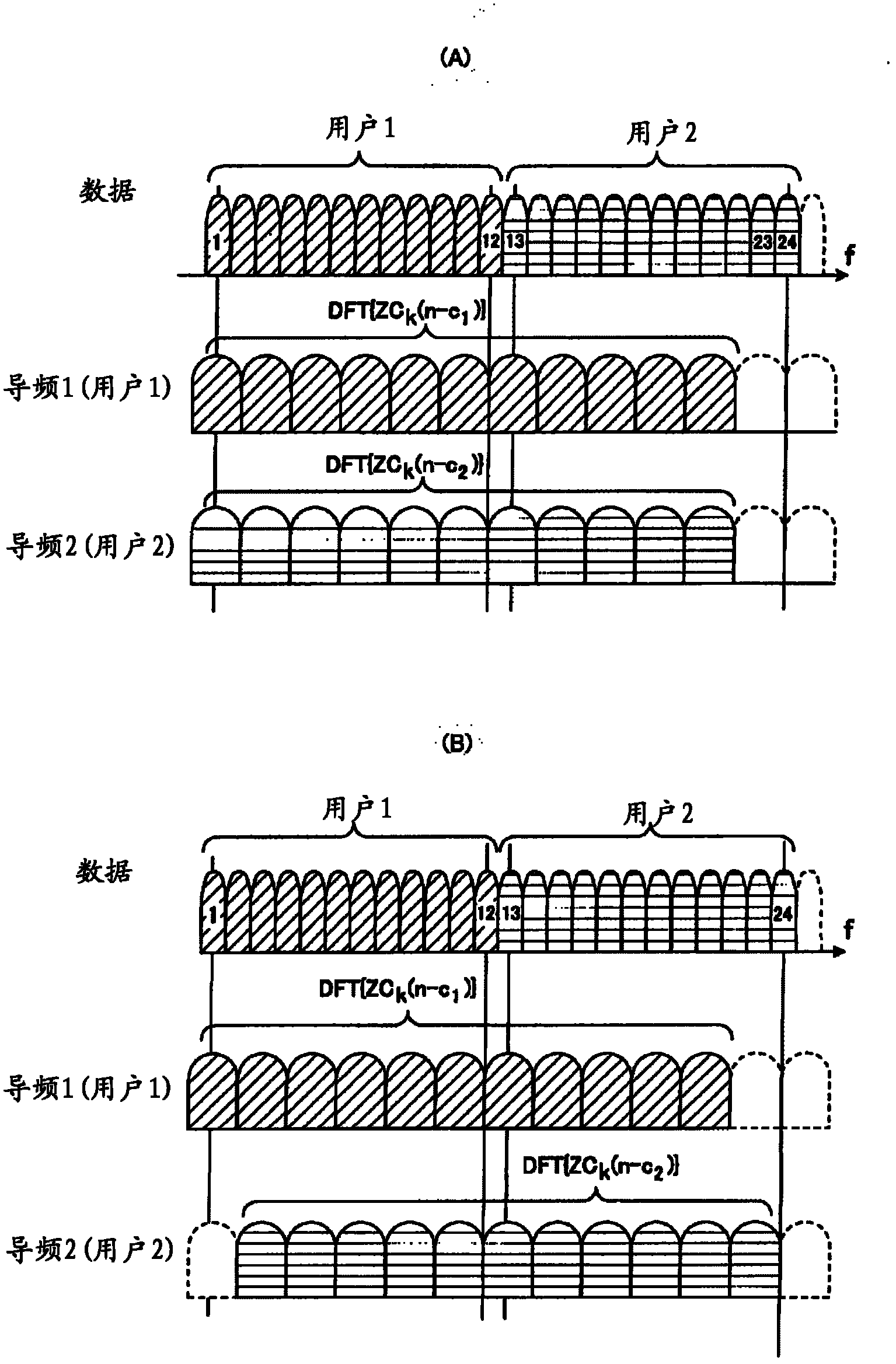
The invention provides user terminals, a wireless communication method and a wireless communication system. For the user terminals in the wireless communication system, all the user terminals in the wireless communication system use the frequency of different data transmitting frequency bands distributed by a base station to transmit data signals to the base station, and simultaneously multiplex pilot frequency signals corresponding to the data signals and transmit the multiplexed pilot frequency signals to the base station. The user terminals are characterized in that each user terminal comprises a receiving part, a pilot frequency generating part, a transmitting part and a subcarrier mapping part, wherein the receiving part is used for receiving uplink resource information from the base station, the pilot frequency generating part is used for generating pilot frequency signals according to the indication of the uplink resource information, the transmitting part is used for transmitting the pilot frequency signals to the base station, the pilot frequency generating part comprises a CAZAC sequence generating part used for generating a Zadoff-Chu sequence to be used as a pilot frequency signal according to the resource information, and the subcarrier mapping part is used for mapping sequences generated by circularly copying the Zadoff-Chu sequence.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Random access preamble having multiple Zadoff-Chu sequence for cellular telephone system
InactiveCN101394226AModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionRandom-access channelCellular telephone
The invention discloses a cellular telephone system, wherein random access channel burst pulse series are provided with a preamble which comprises two Zadoff-Chu sequences so as to lessen the Doppler frequency shift effect, and when a base station receives the random access channel burst pulse series, the cellular telephone system does division to the two sequences reacquired from the preamble of the received burst pulse series, so as to provide a factor sequence. As for some embodiments, the base station interrelates the factor sequence with the Zadoff-Chu sequences so as to identify the user equipment which sends the random access channel burst pulse series. Furthermore, the invention describes and claims other embodiments.
Owner:NXP BV
Method and device for timing shift estimation
ActiveCN102104951ASolve problems with high computational complexityReduce complexitySynchronisation arrangementRadio transmission for post communicationPeak valueRandom-access channel
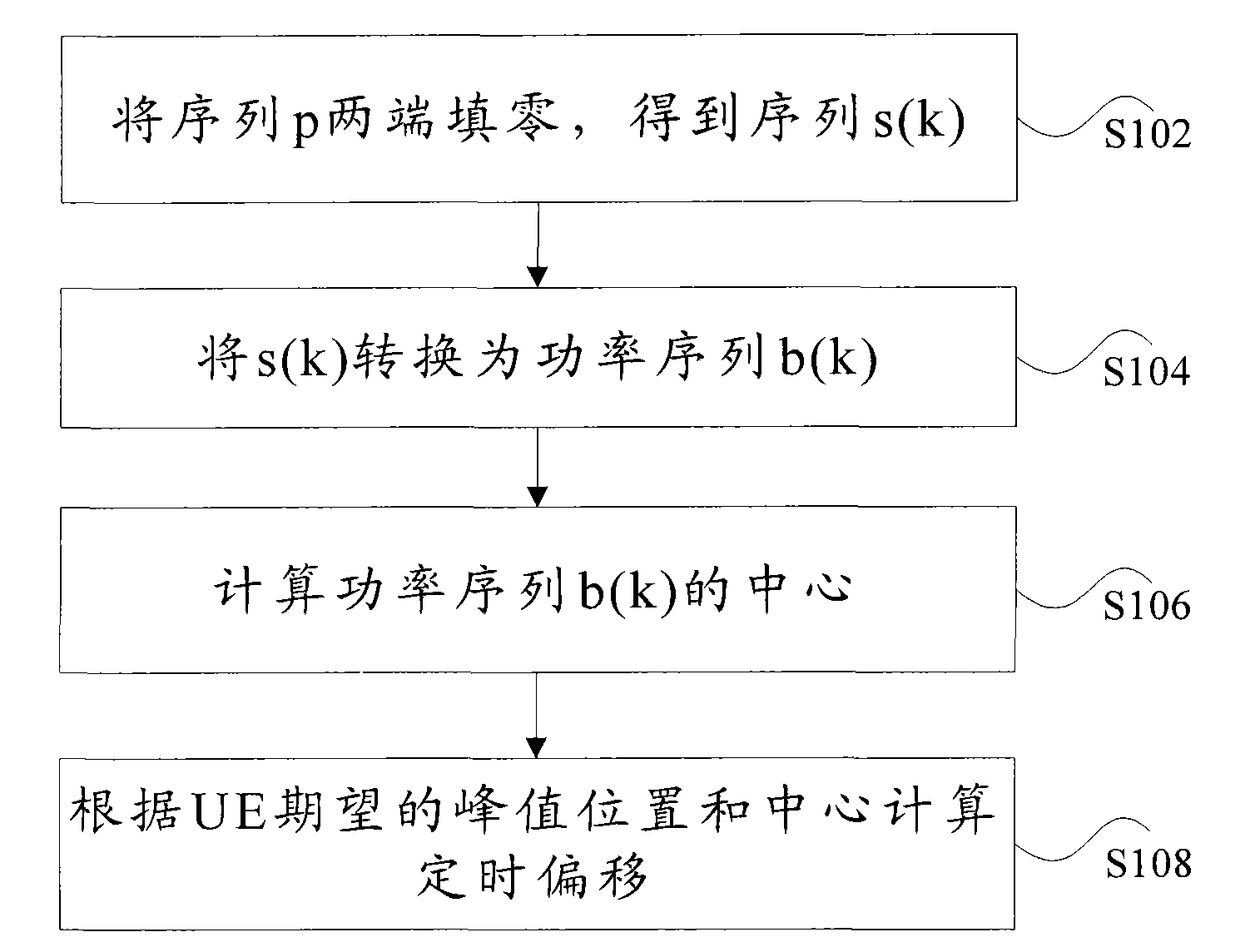
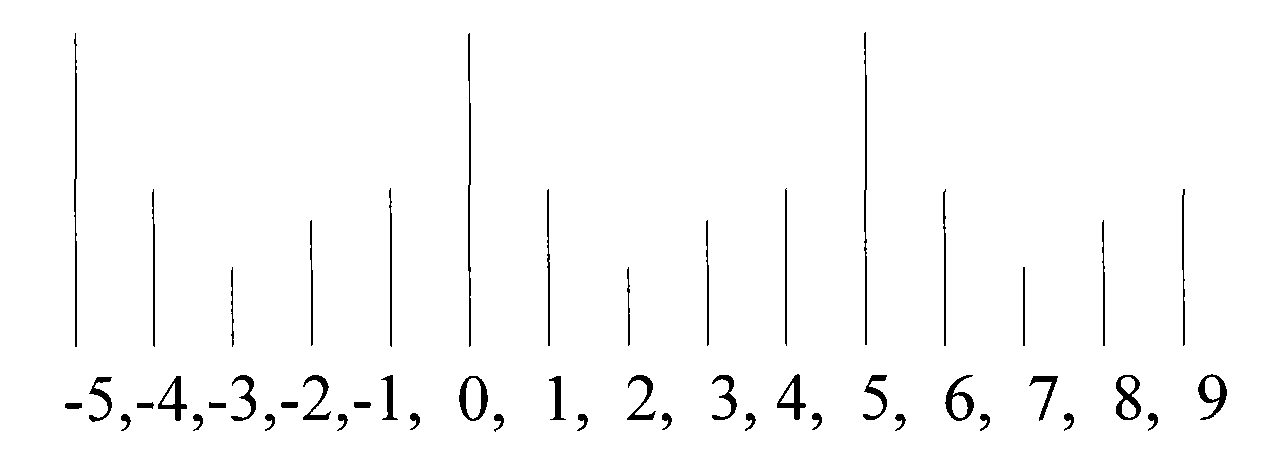
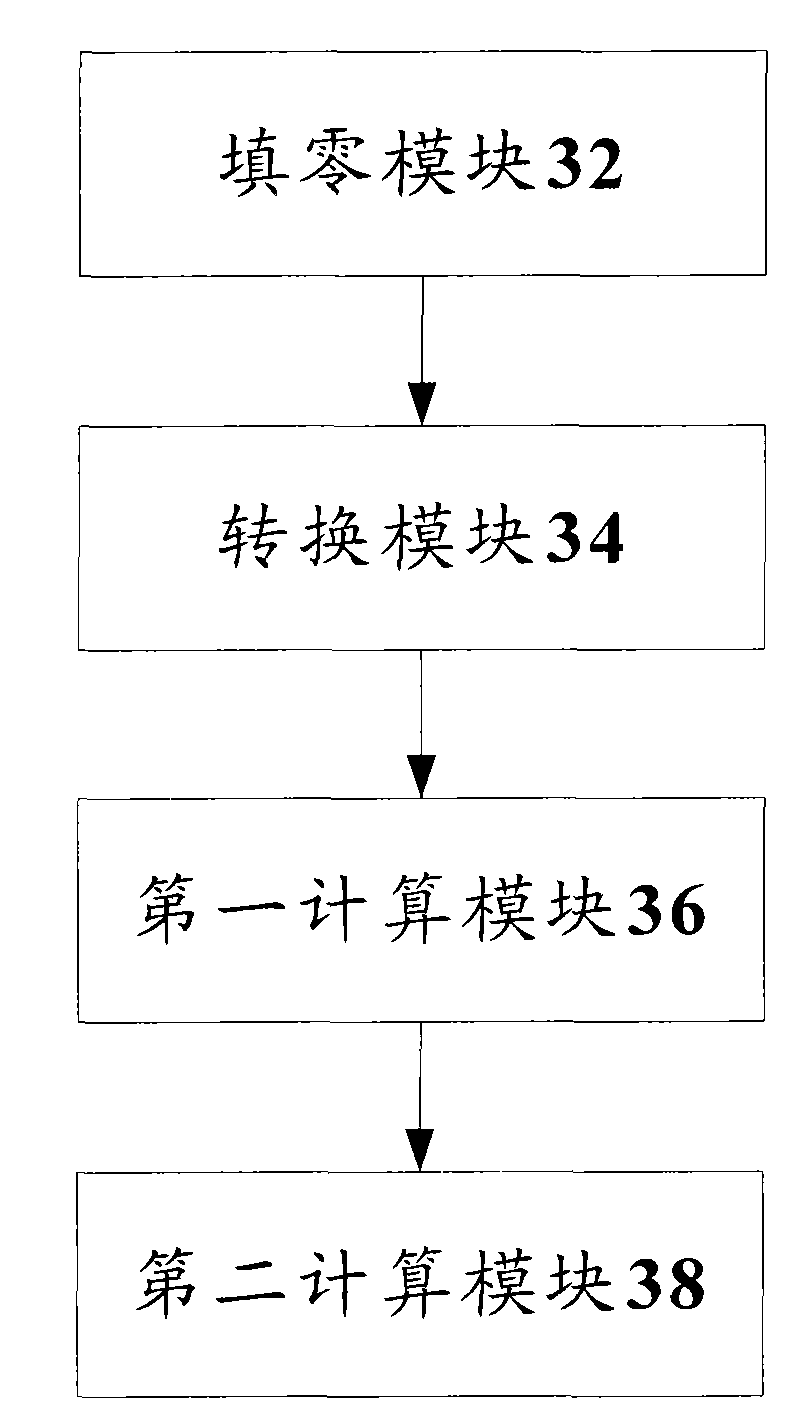
The invention discloses a method and device for timing shift estimation. The method comprises a step of filling zero at two ends of a sequence p, so as to acquire a sequence s(k), wherein the sequence p is a result of conjugate multiplication between a frequency domain mark received on a preset channel by user equipment (UE) and a Zadoff-Chu sequence; k is equal to 0,...,M-1; M is the number of sub-carriers occupied by signals in the preset channel; and the preset channel comprises a PRACH (physical random access channel) or a PUSCH (physical uplink shared channel). The method further comprises the following steps: converting s(k) into a power sequence b(k); calculating the center of the power sequence b(k); and calculating the timing shift according to the expected peak position of UE and the center. By using the method and device provided by the invention, the complex rate of calculation is reduced.
Owner:ZTE CORP
A signal synchronization method based on Dual-Zadoff-Chu sequence in underwater acoustic OFDM communication is presented
ActiveCN109104387AReduce operational complexityBaseband system detailsCode division multiplexDoppler spreadComputer science
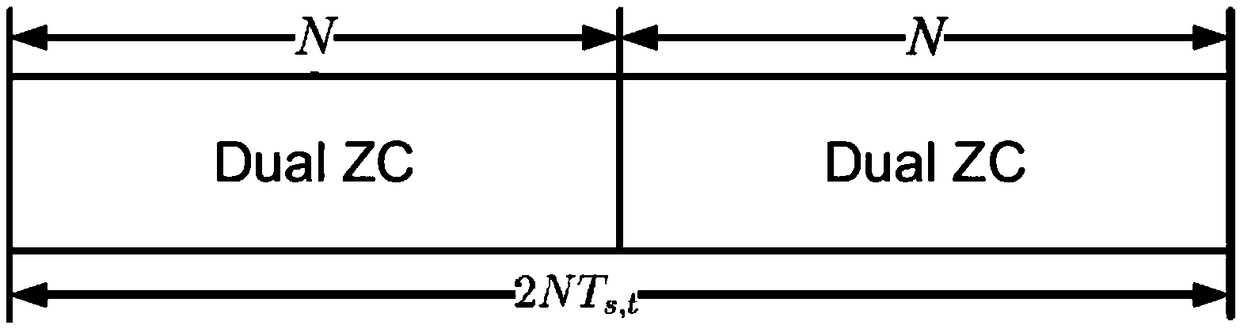
The invention discloses an underwater acoustic OFDM communication method based on Dual-Zadoff. The invention relates to a signal synchronization method of a Chu sequence, which relates to the field ofunderwater acoustic OFDM communication, comprising a transmitter and a receiver, wherein the transmitter sends a preamble with a length of 2N, and the preamble is composed of two Dual codes with thesame length of N; ZC sequence in series, Dual-ZC sequence is composed of two ZC sequences with N length, same parameter setting and g (0 (g (N)) frequency difference. The receiver can simultaneously complete signal synchronization, Doppler spread estimation, channel estimation and other tasks through the corresponding receiving steps.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
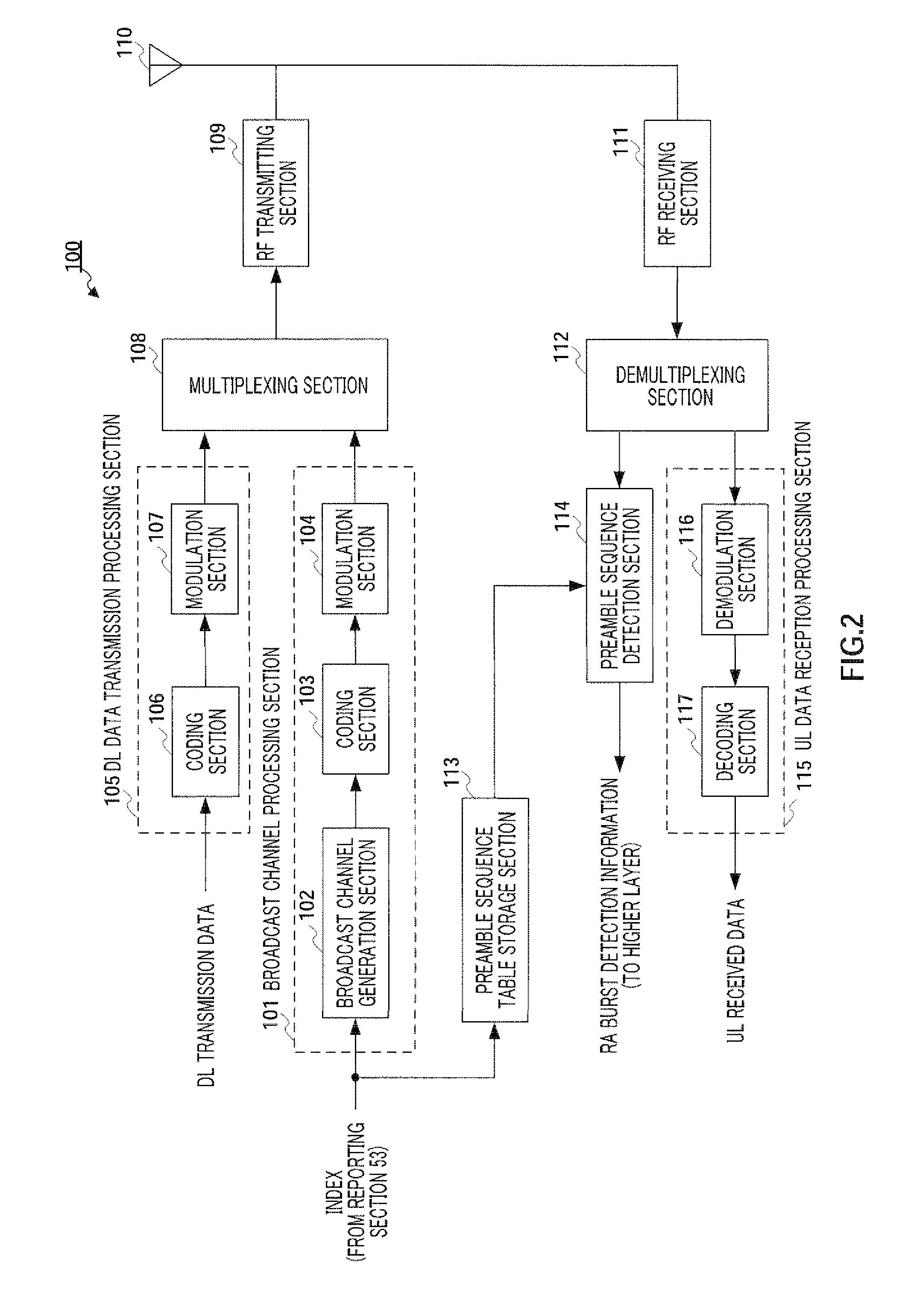
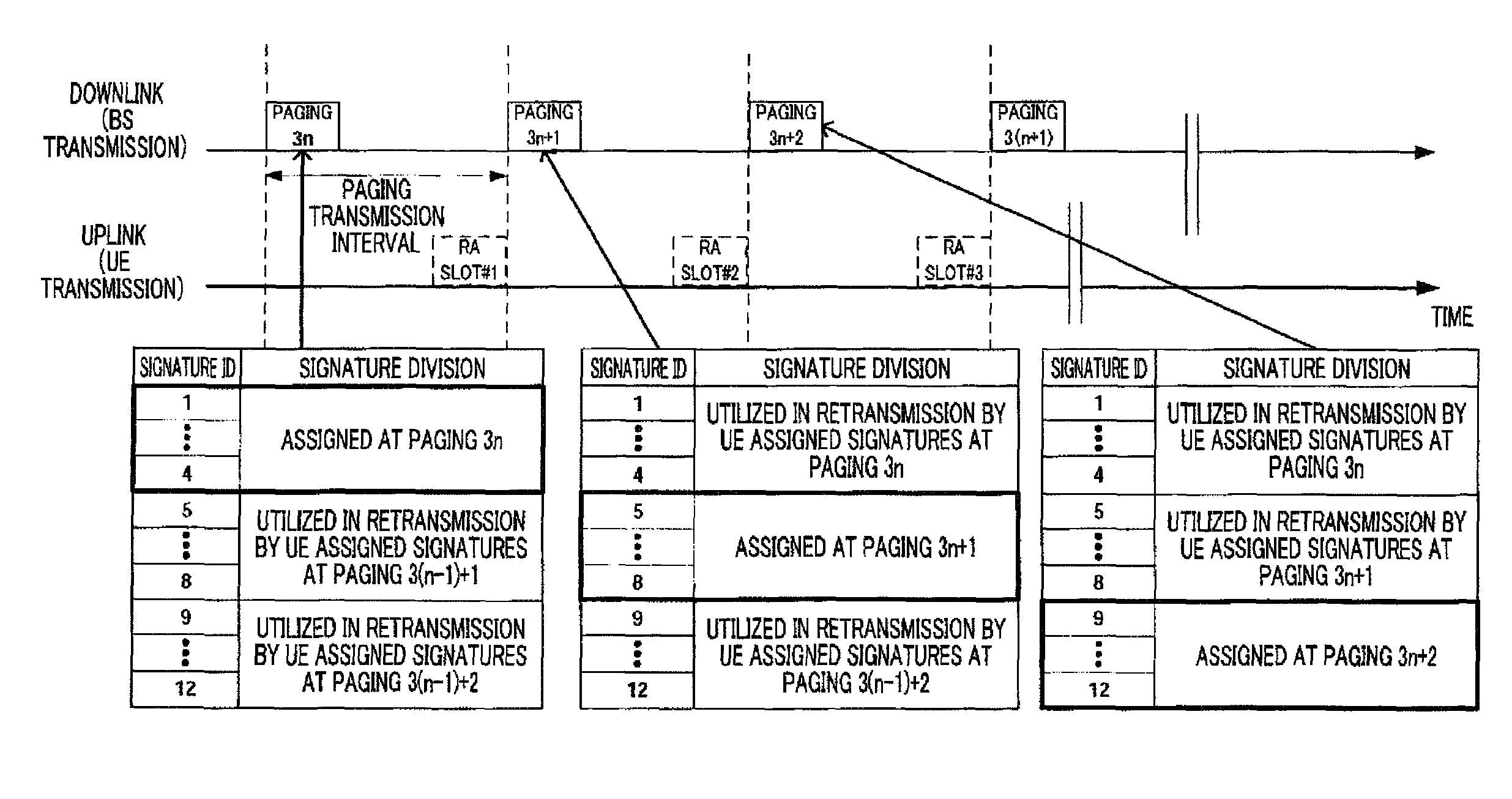
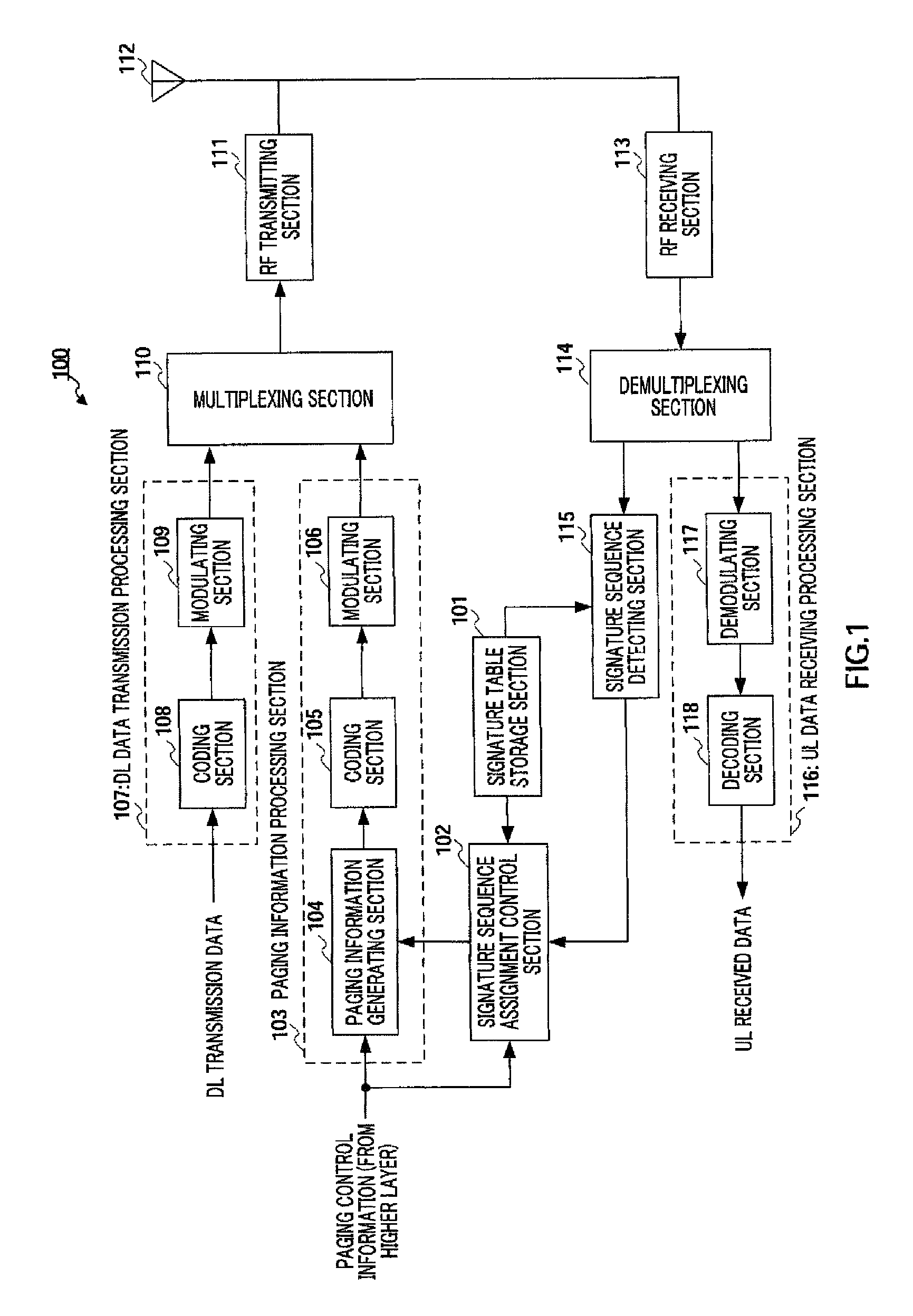
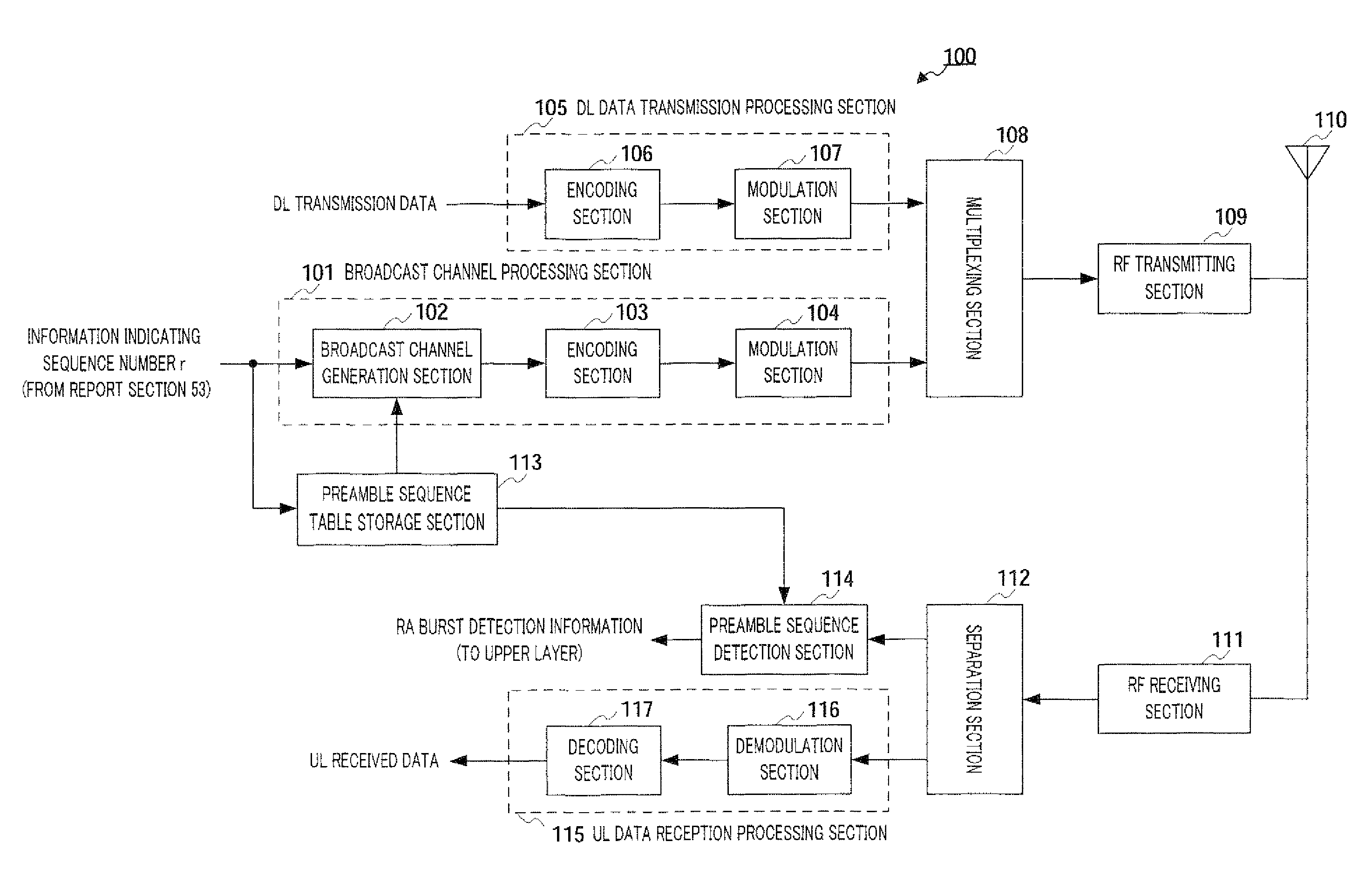
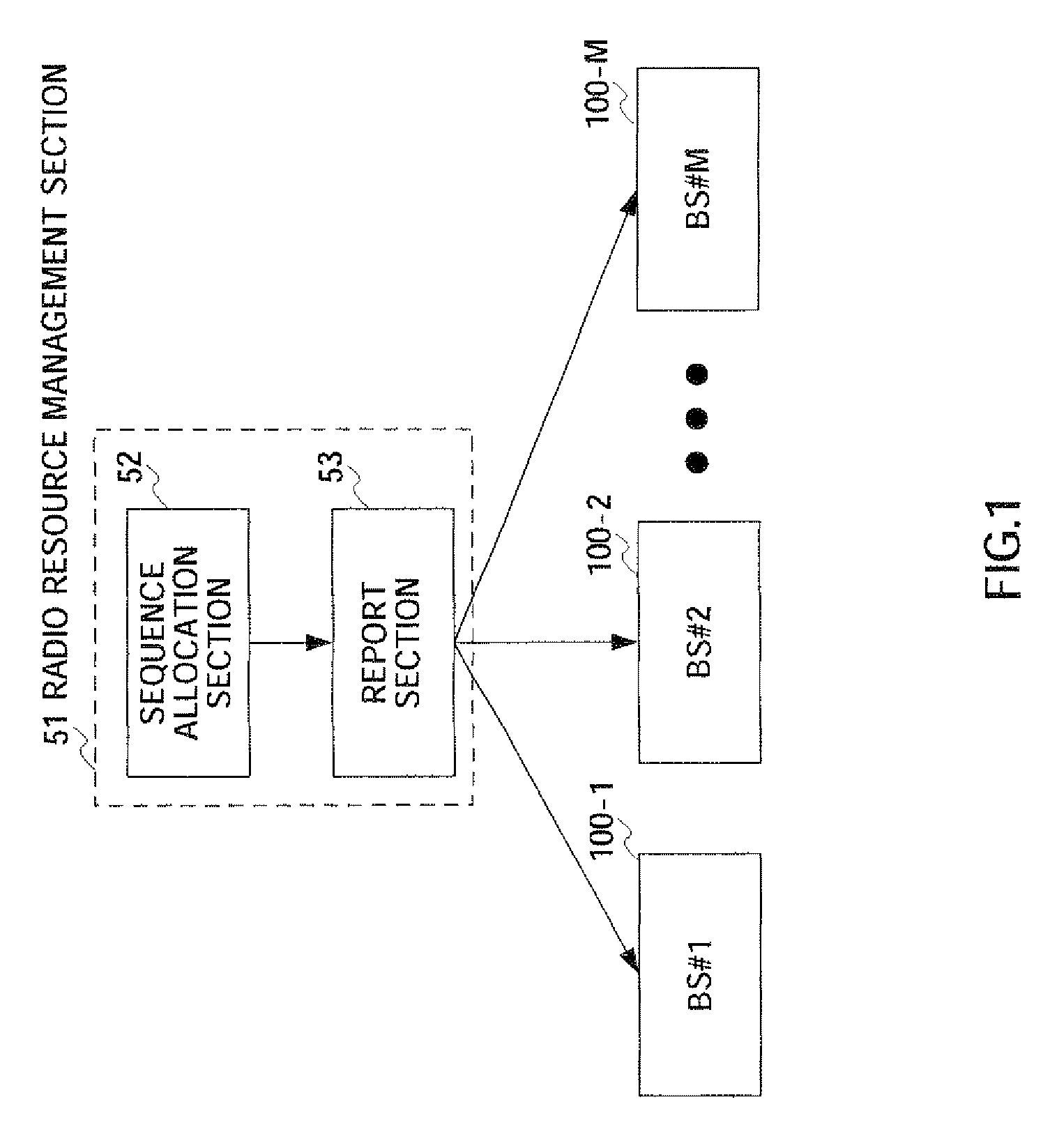
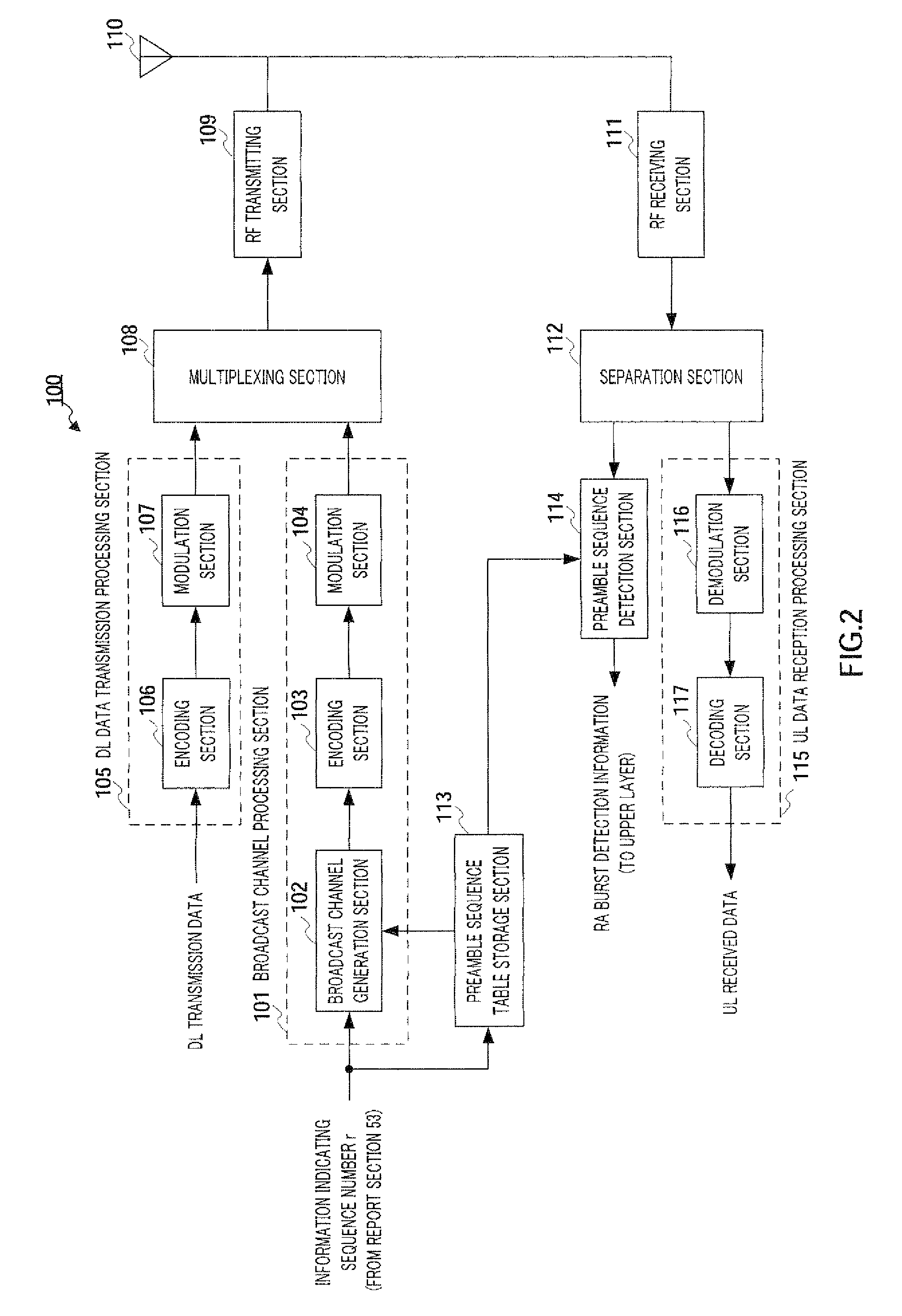
Radio transmitting apparatus and radio transmitting method
InactiveUS8379662B2Improve throughputFast processingAssess restrictionTime-division multiplexDistribution controlTelecommunications
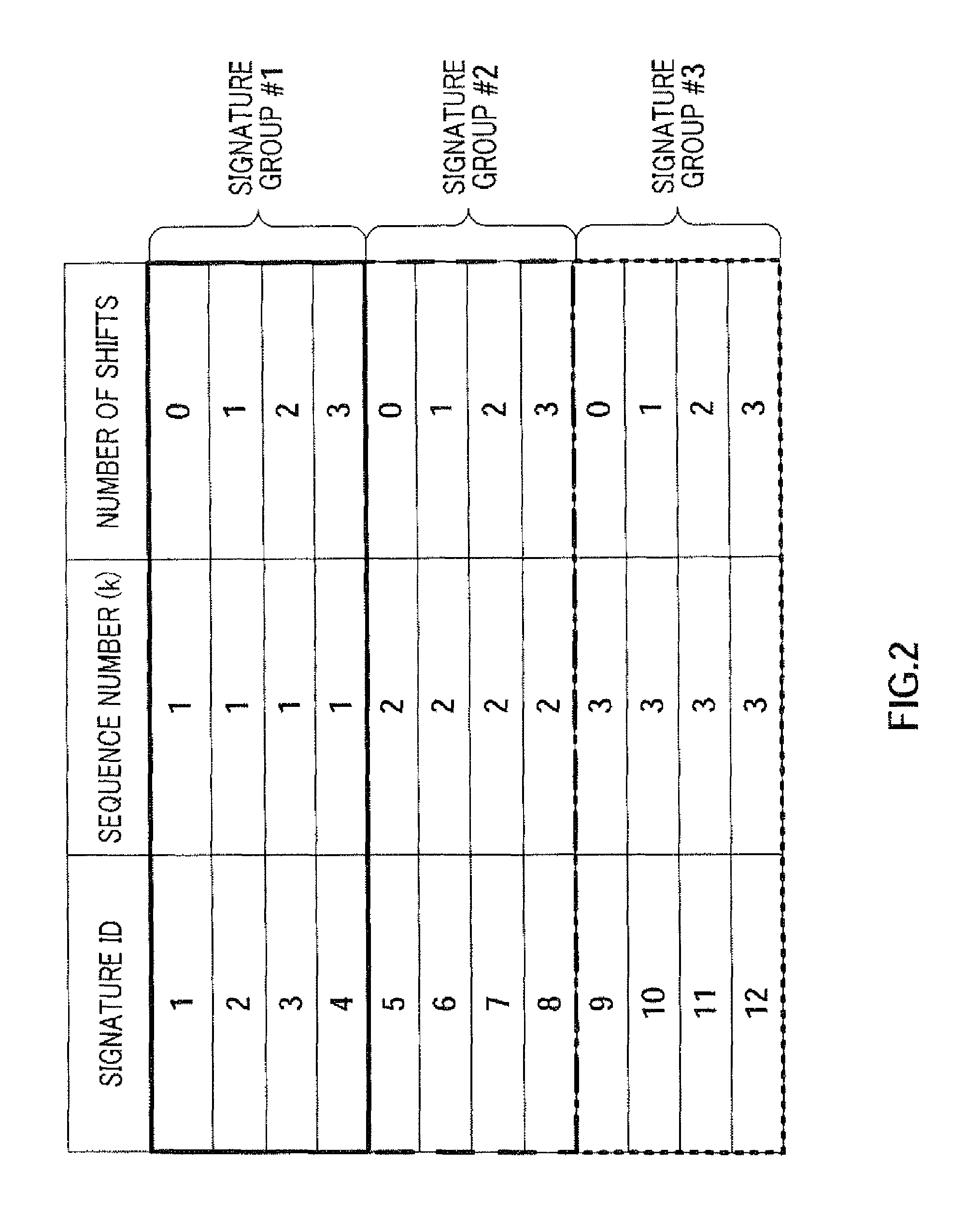
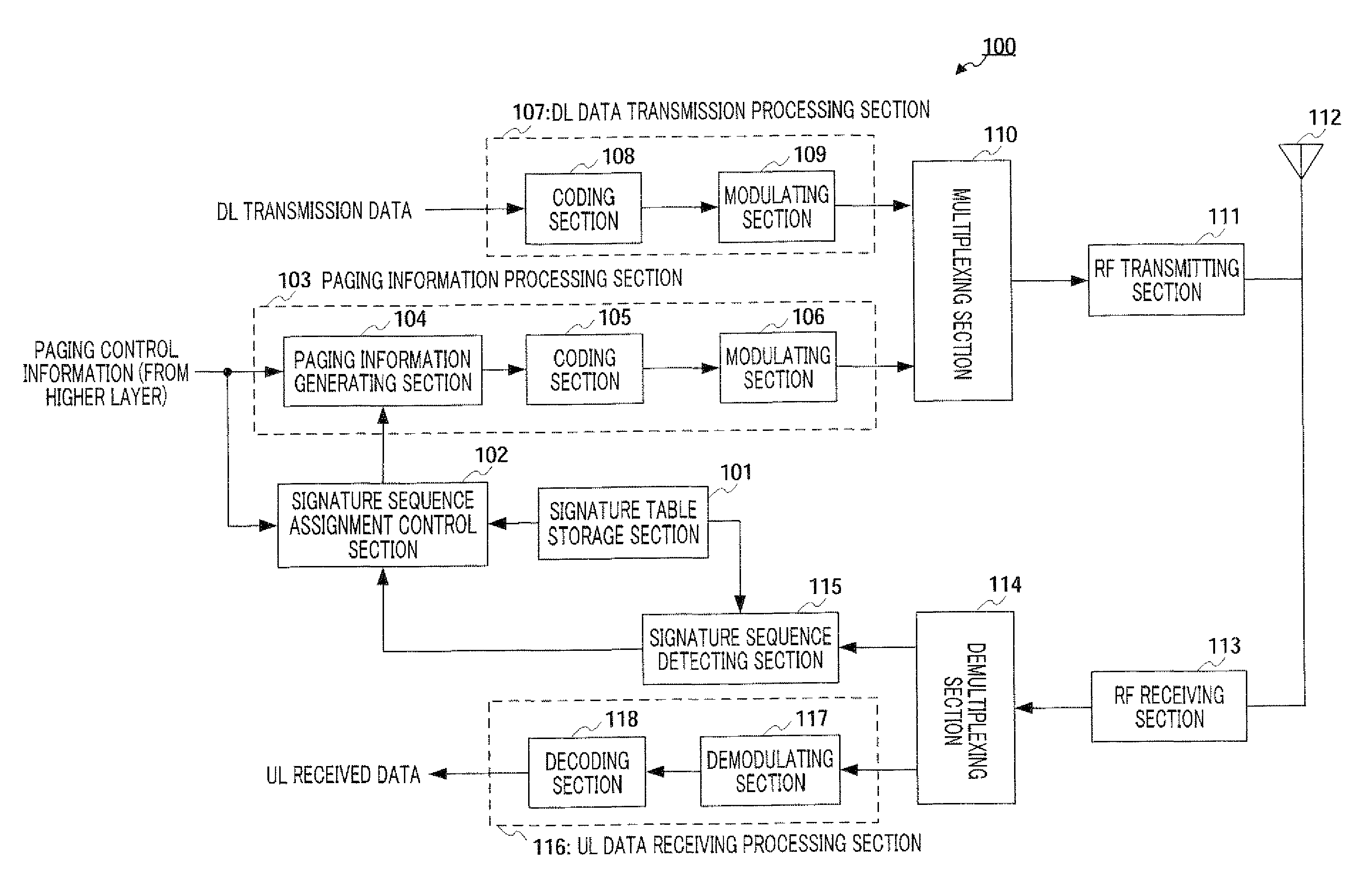
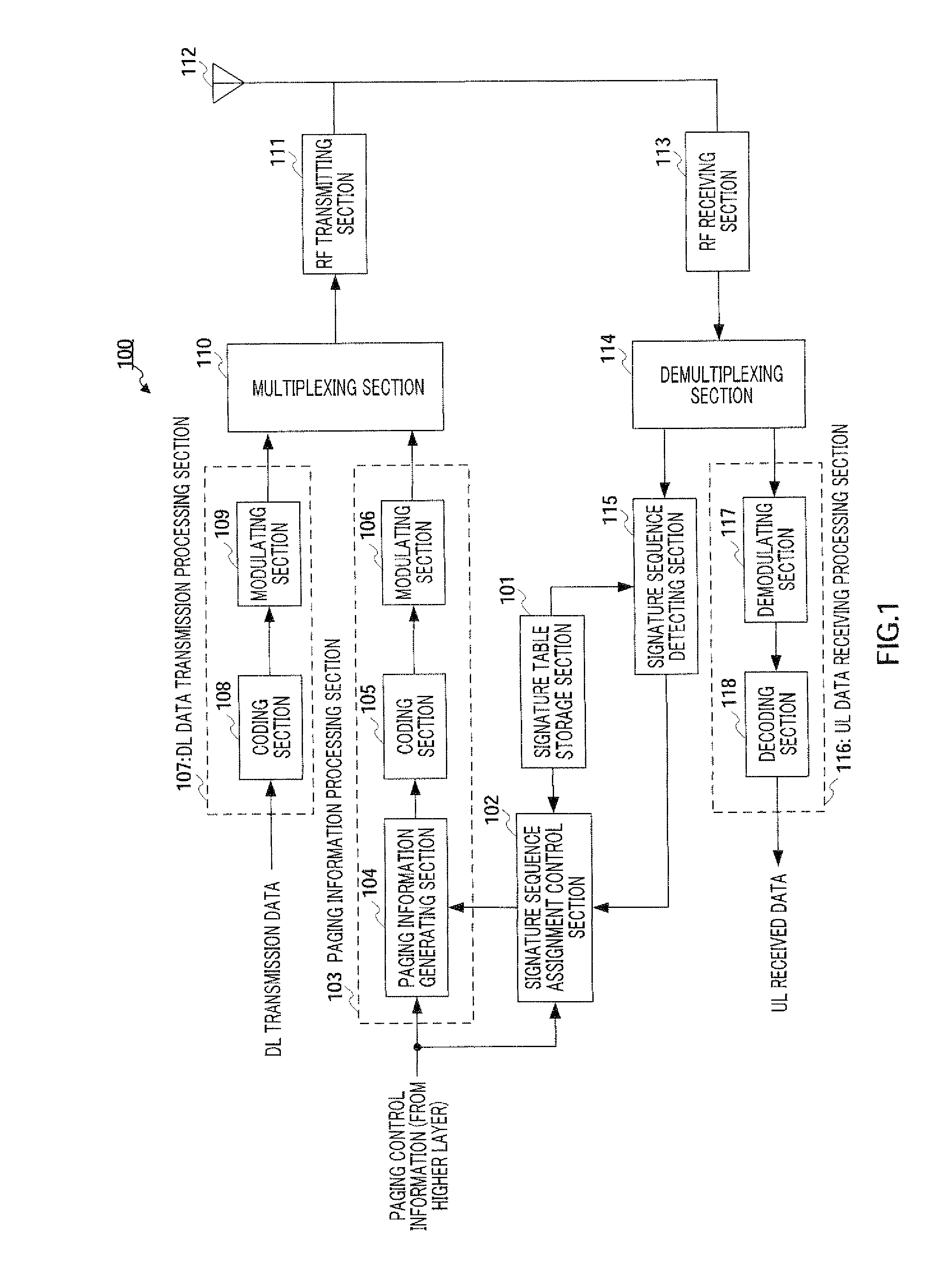
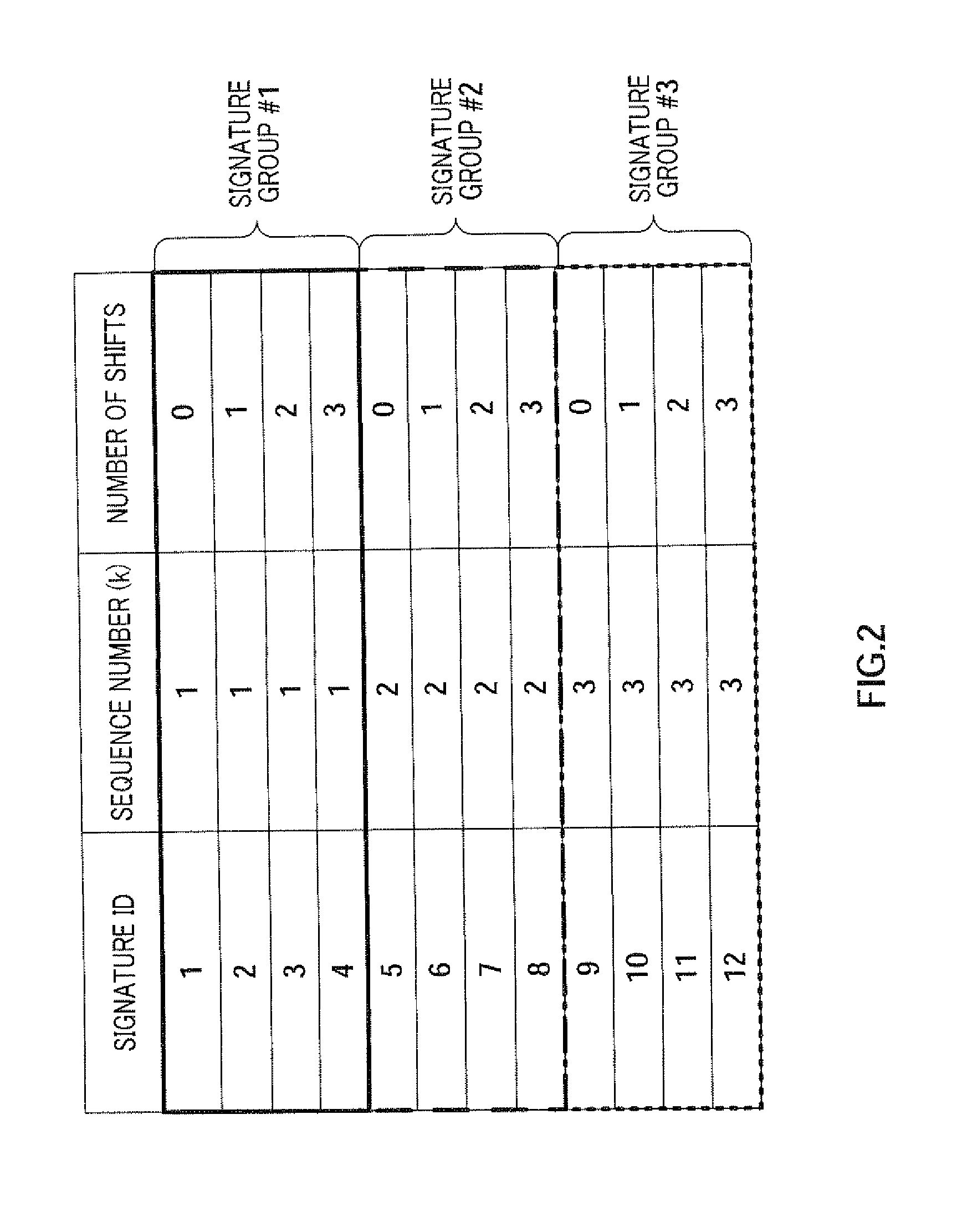
A radio transmitting apparatus and a radio transmitting method wherein the throughput is improved and a fast initial access processing including an RA burst is accomplished. According to these apparatus and method, a signature table storing part (101) has a plurality of signature groups generated from a plurality of different Zadoff-Chu sequences with a set of signatures generated from one Zadoff-Chu sequence being one signature group. A signature sequence assignment control part (102) switches signature groups to be assigned to a UE for each of paging transmissions, thereby assigning a signature sequence, which is to be used for an initial RA, from the same signature group. A paging information generating part (104) causes the ID of the assigned signature sequence to be included into paging information, which is then transmitted to the UE.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Method for generating ACK/NACK (Acknowledge Character/Non-Acknowledgement) signal
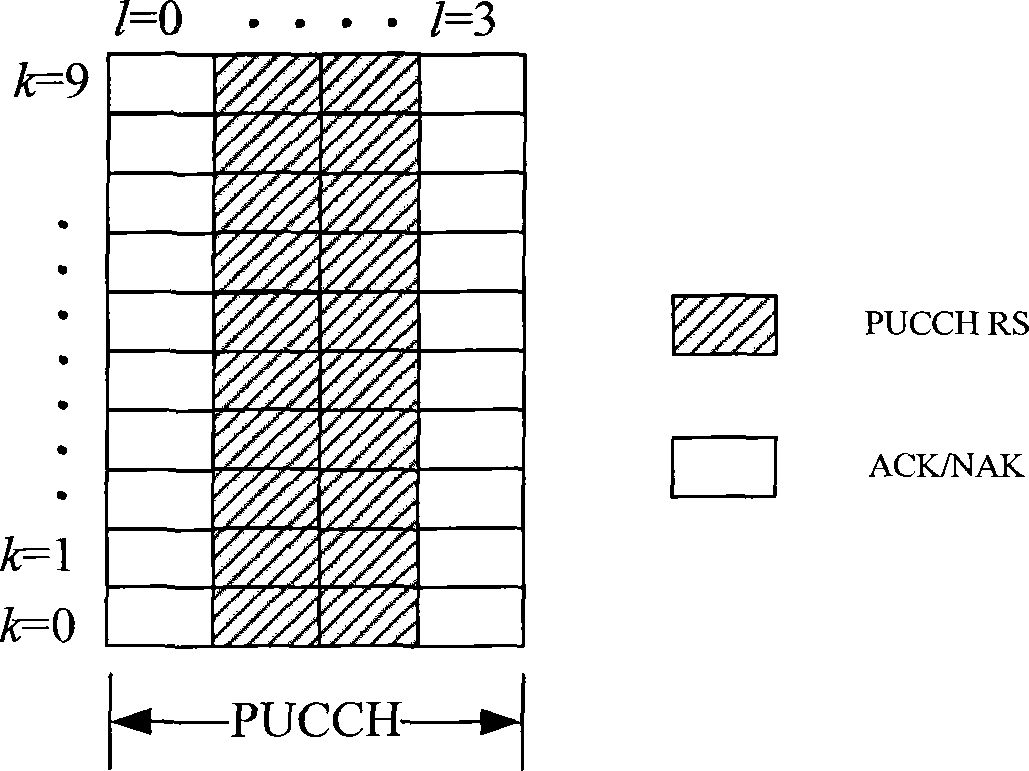
InactiveCN102739597ASimple stepsReduce complexityError prevention/detection by using return channelMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainPower grid
The invention provides a method for generating an ACK / NACK (Acknowledge Character / Non-Acknowledgement) signal. The method comprises the following steps of: mapping ACK / NACK information to be transmitted at present into a symbol corresponding to a constellation point, wherein the symbol obtained after mapping the ACK information is -1 and the symbol obtained after mapping the NACK information is 1; shortening a zadoff-chu sequence into a sequence of which the length is N<RB>SC as a spread spectrum base sequence, and the N<RB>SC is an effective sub-carrier number of a sub-band; for each OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) symbol which is occupied by the ACK / NACK information on a physical uplink channel (PUCCH), determining a circulation displacement value of the spread spectrum base sequence corresponding to the OFDM symbol; carrying out circulation displacement to the spread spectrum base sequence according to the circulation displacement value; multiplying each element in the spread spectrum base sequence after the circulation displacement with the symbol after the mapping; and converting the sequence obtained from the multiplication into a time domain signal. The method is applicable for a power grid system.
Owner:POTEVIO INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Main Synchronization Sequence Design Method for Global Covering Multi-Beam Satellite LTE
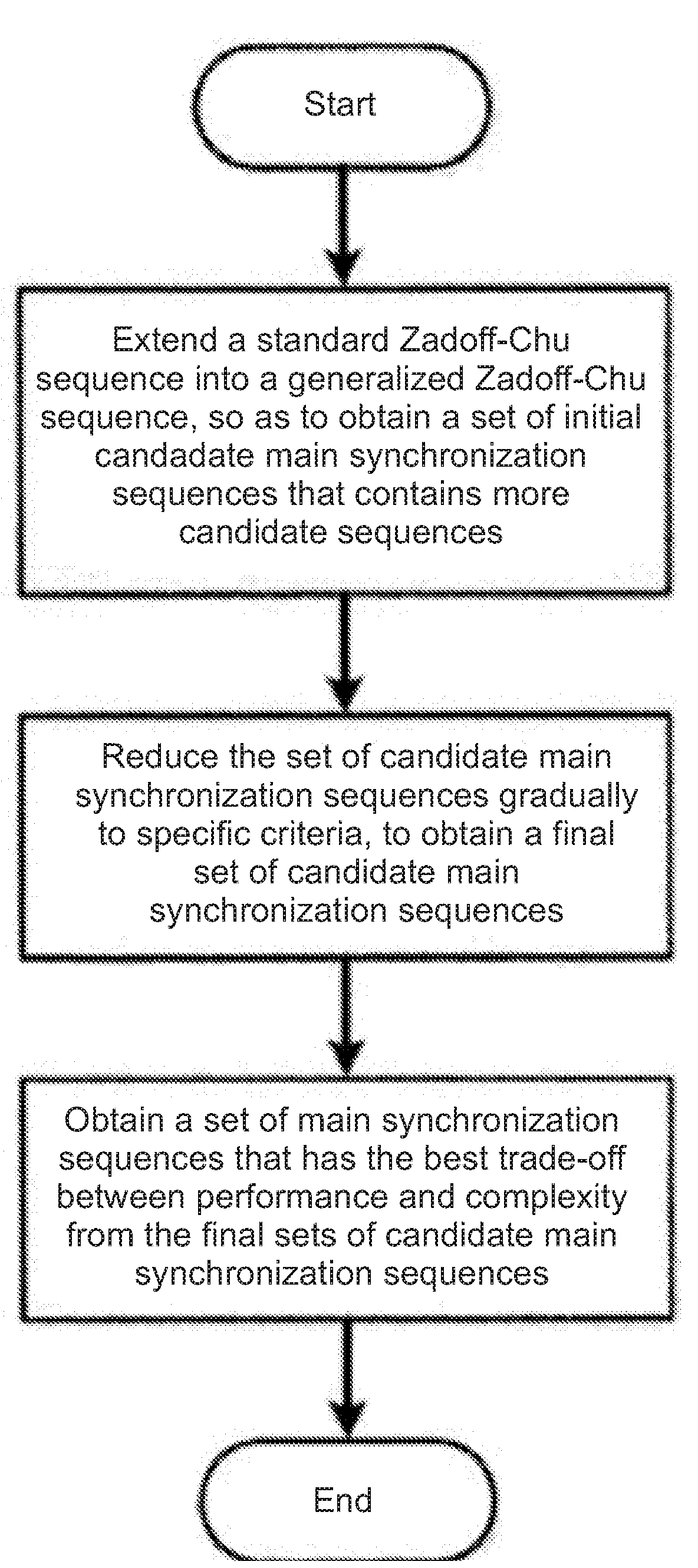
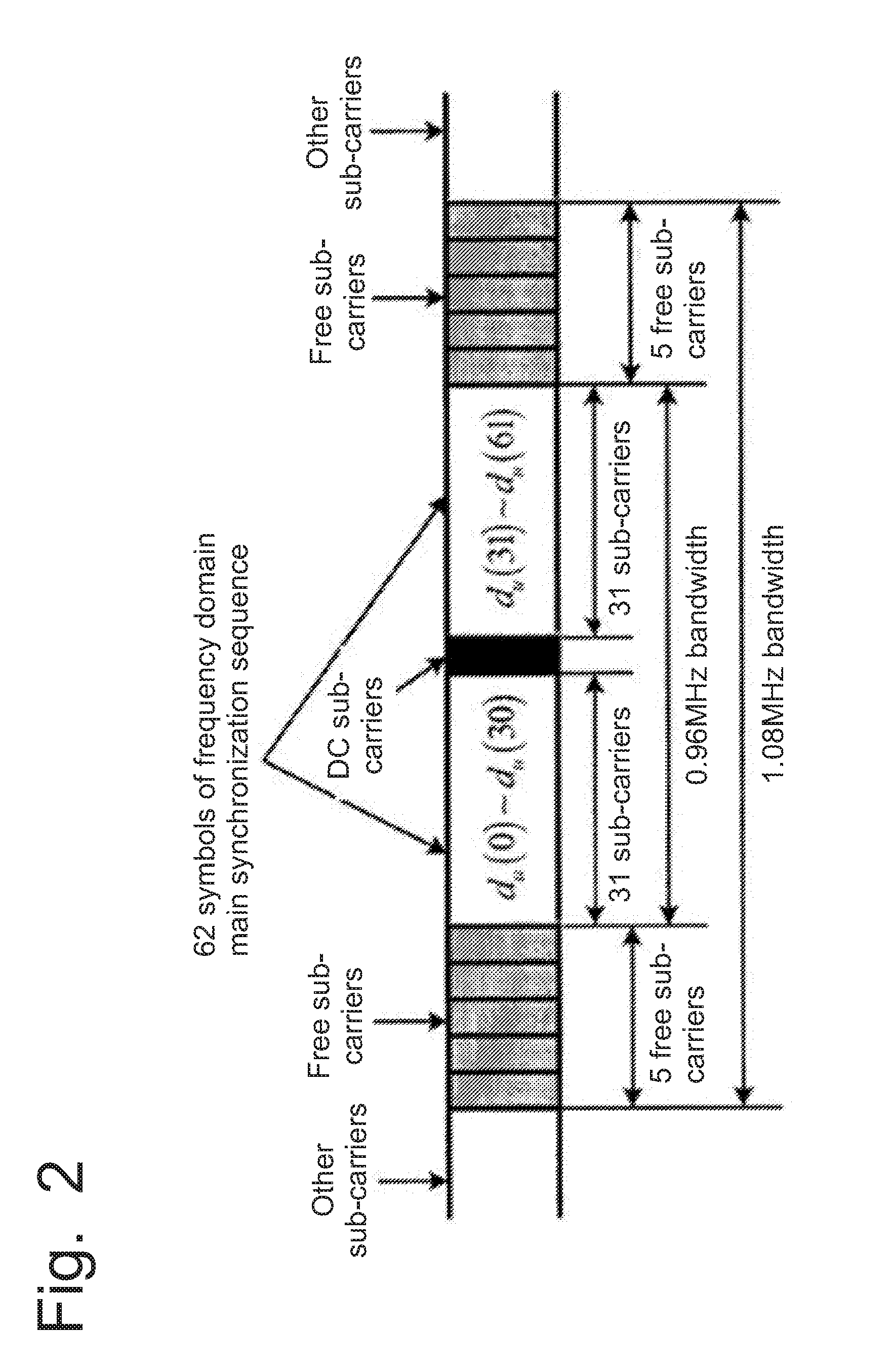
InactiveUS20160112973A1InterferenceExtension of timeSynchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsSequence designComputation complexity
Disclosed is a main synchronization sequence design method for global covering multi-beam satellite LTE, comprising the follow steps: extending a standard Zadoff-Chu sequence to a generalized Zadoff-Chu sequence so as to obtain an initial candidate main synchronization sequence set of more candidate sequences; gradually narrowing down the candidate main synchronization sequence set according to a selection standard of a main synchronization sequence to obtain a final candidate main synchronization sequence set; and obtaining a main synchronization sequence set with optimal eclectic performance and complexity from the final candidate main synchronization sequence set. According to the present invention, a main synchronization sequence with optimal eclectic performance and calculation complexity can be designed for a global covering same-frequency networking multi-beam satellite LTE system.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
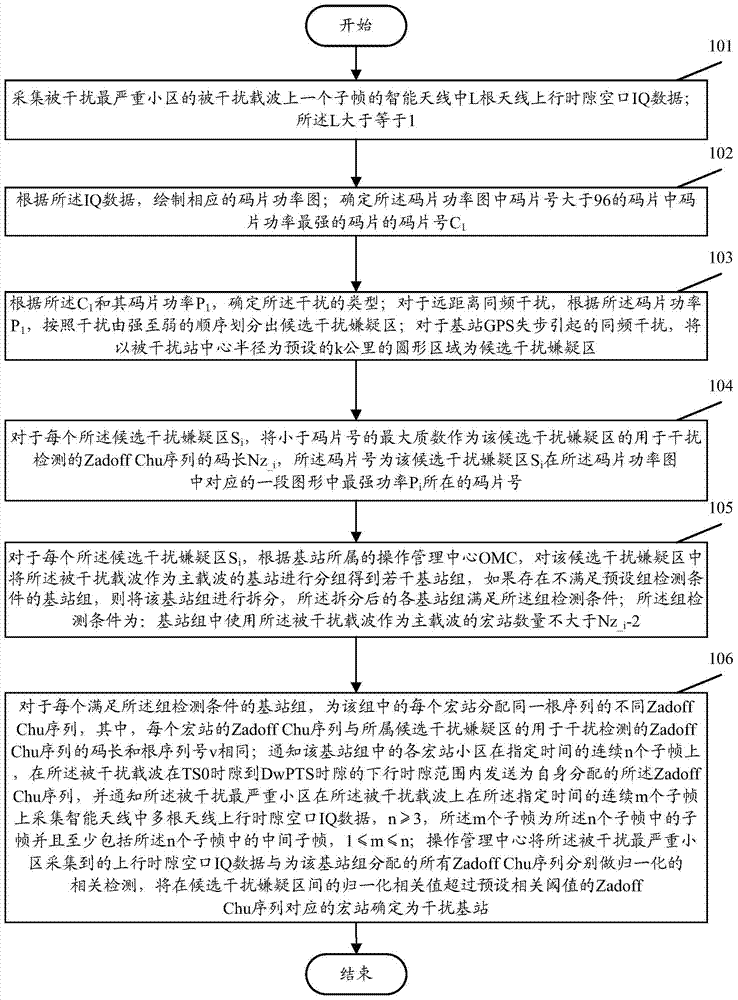
A same-frequency-interference detection method
InactiveCN104519501APrecise positioningTransmission monitoringTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSelf correlationTime-division multiplexing
The present application discloses a same-frequency-interference detection method, wherein, an OMC (Operation Management Center) sends an instruction for coordination and control to each of base stations, so that each of interfering suspected base stations sends a different Zadoff-chu sequence at a certain interfered frequency point at the same time in a downlink time slot from a TS0 time slot to a DwPTS time slot, while an interfered base station receives an interference signal in an uplink time slot; and the OMC executes normalized correlation detection on each of the sent Zadoff-chu sequences in receiving of the signal according to ideal cross-correlation and self-correlation of the Zadoff-chu sequences, finds the Zadoff-chu sequences of which normalized correlation values exceed a threshold, and locates the specific interfering base stations through a corresponding relationship of the Zadoff-chu sequence and the base station. Therefore, the same-frequency-interference detection method can locate the same-frequency-interference of a time division multiplexing system accurately.
Owner:TD TECH COMM TECH LTD
Sequence allocating method, transmitting method and wireless mobile station device
ActiveCN101743709AReduce cross-correlationFrequency-division multiplexMultiplex code allocationMobile stationComputer science
It is an object to provide a sequence allocating method that, while maintaining the number of Zadoff-Chu sequences to compose a sequence group, is configured to make it possible to reduce correlations between different sequential groups. This method comprises the steps of setting a standard sequence with a standard sequence length (Nb) and a standard sequence number (rb) in a step (ST101), setting a threshold value (Xth(m)) in accordance with an RB number (m) in a step (ST103), setting a sequence length (N) corresponding to RB number (m) in a step (ST104), judging whether ]r / N-rb / Nb]<=Xth(m) is satisfied in a step (ST106), including a plurality of Zadoff-Chu sequences with a sequence number (r) and a sequence length (N) in a sequence group (rb) in a step (ST107) if the judgment is positive, and allocating the sequence group (rb) to the same cell in a step (ST112).
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Radio transmitting apparatus and radio transmitting method
InactiveUS20100232284A1Improve throughputFaster initial access processingModulated-carrier systemsAssess restrictionDistribution controlTelecommunications
A radio transmitting apparatus and a radio transmitting method wherein the throughput is improved and a fast initial access processing including an RA burst is accomplished. According to these apparatus and method, a signature table storing part (101) has a plurality of signature groups generated from a plurality of different Zadoff-Chu sequences with a set of signatures generated from one Zadoff-Chu sequence being one signature group. A signature sequence assignment control part (102) switches signature groups to be assigned to a UE for each of paging transmissions, thereby assigning a signature sequence, which is to be used for an initial RA, from the same signature group. A paging information generating part (104) causes the ID of the assigned signature sequence to be included into paging information, which is then transmitted to the UE.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
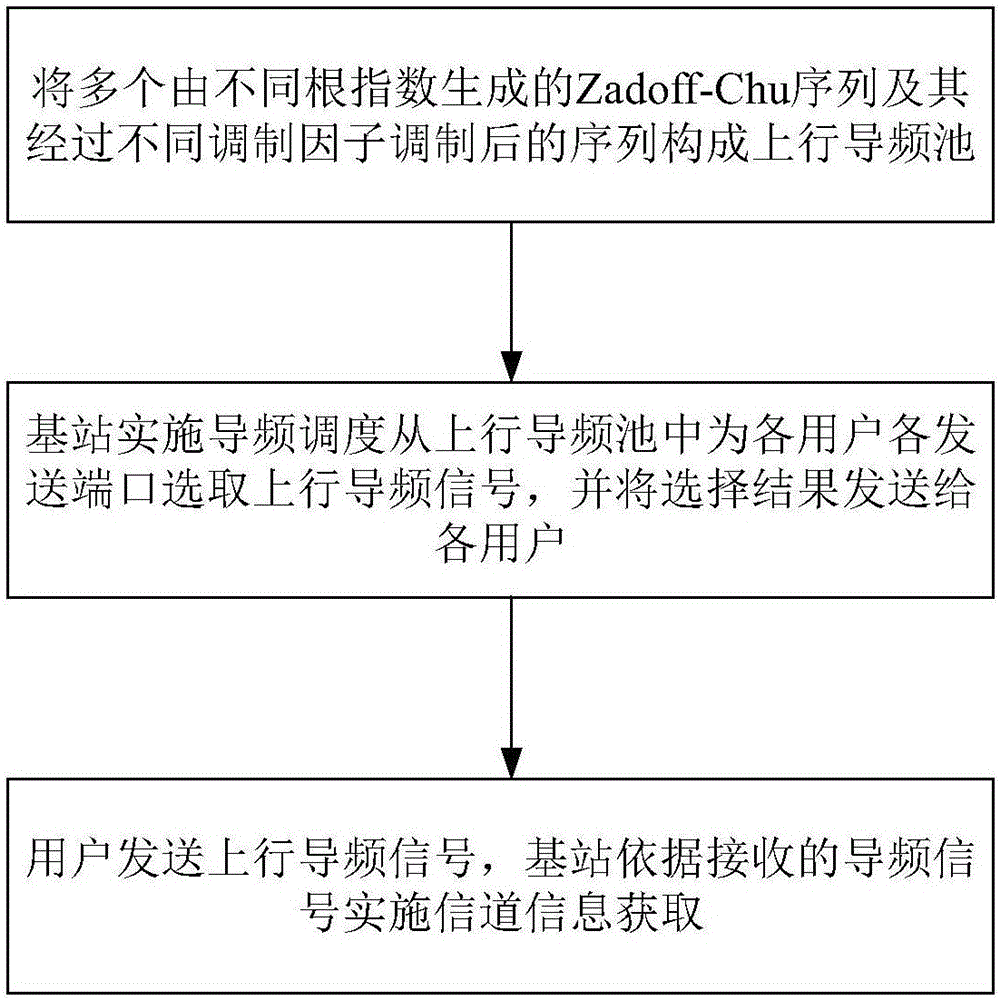
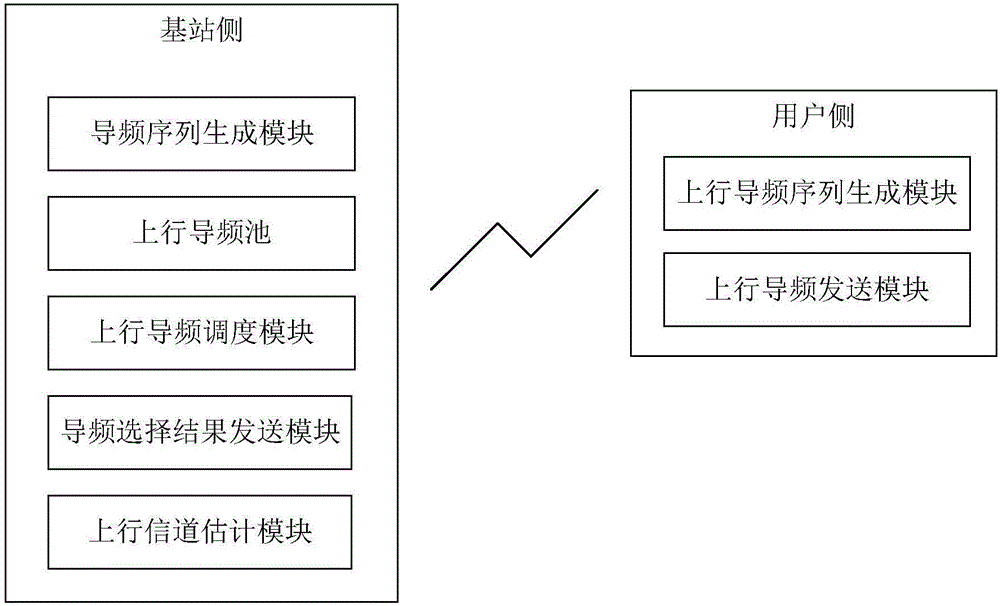
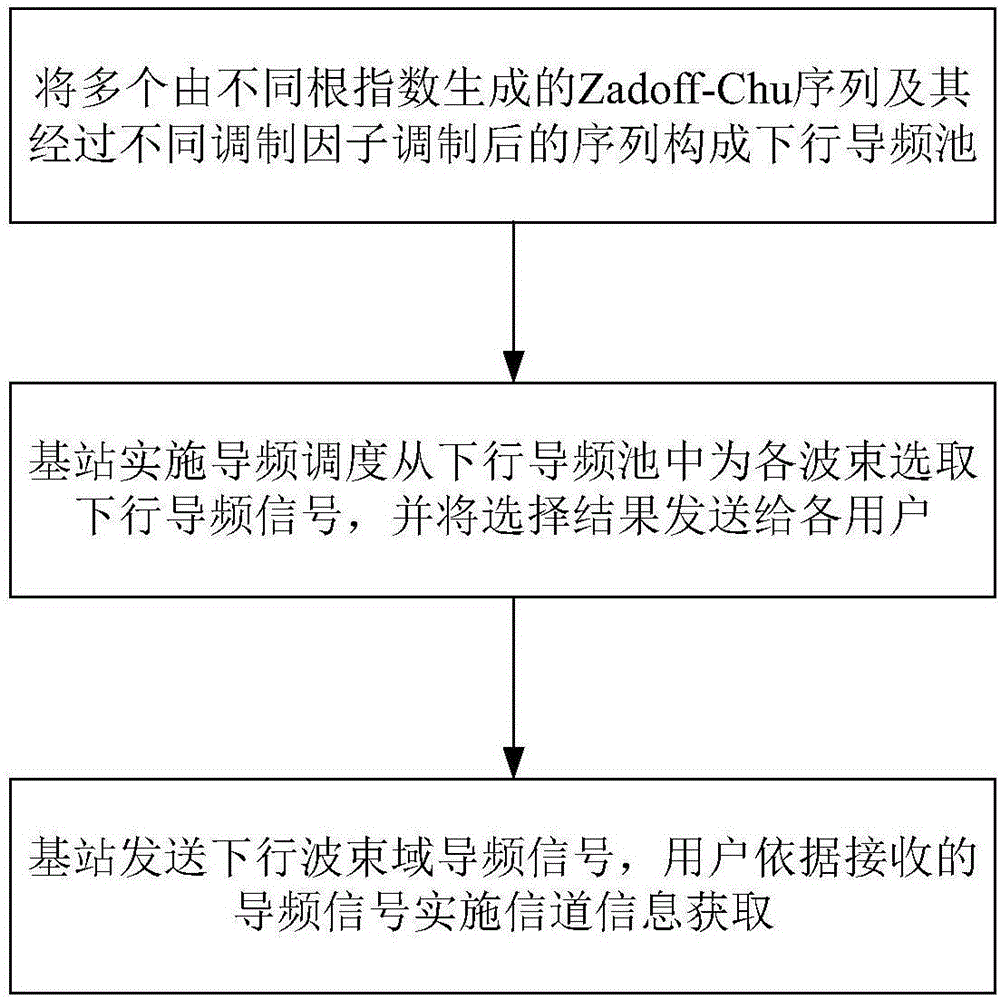
Method and apparatus for obtaining pilot pool and channel information of broadband large-scale MIMO system
ActiveCN106506133AImprove spectral efficiencyReduce pilot overheadRadio transmissionMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumChannel parameter
The invention provides a method and apparatus for obtaining a pilot pool and channel information of a broadband large-scale MIMO system. An uplink pilot pool and a downlink pilot pool are constructed by a Zadoff-Chu sequence and a sequence modulated by the same. A pilot signal sent over each sending port (an antenna or a wave beam) of each uplink user is selected from the uplink pilot pool, a base station side executes uplink pilot resource scheduling according to channel statistical information to determine the pilot signal sent over each sending port of each uplink user, users send uplink pilot signals on the same time-frequency resource at the same time, and the base station side estimates the uplink channel parameters of the users. A downlink pilot signal is sent in a wave beam domain, pilot sequences sent on wave beams are selected in the downlink pilot pool, the base station sends pilot signals on the wave beams at the same time, and the users estimate the channel parameters according to the received pilot signals. In moving processes of the users, pilot scheduling is dynamically executed with the changes of channel long time characteristics. By adoption of the method and apparatus provided by the invention, the pilot cost of the system can be greatly reduced, and the spectral efficiency and the power efficiency of a wireless communication system are improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
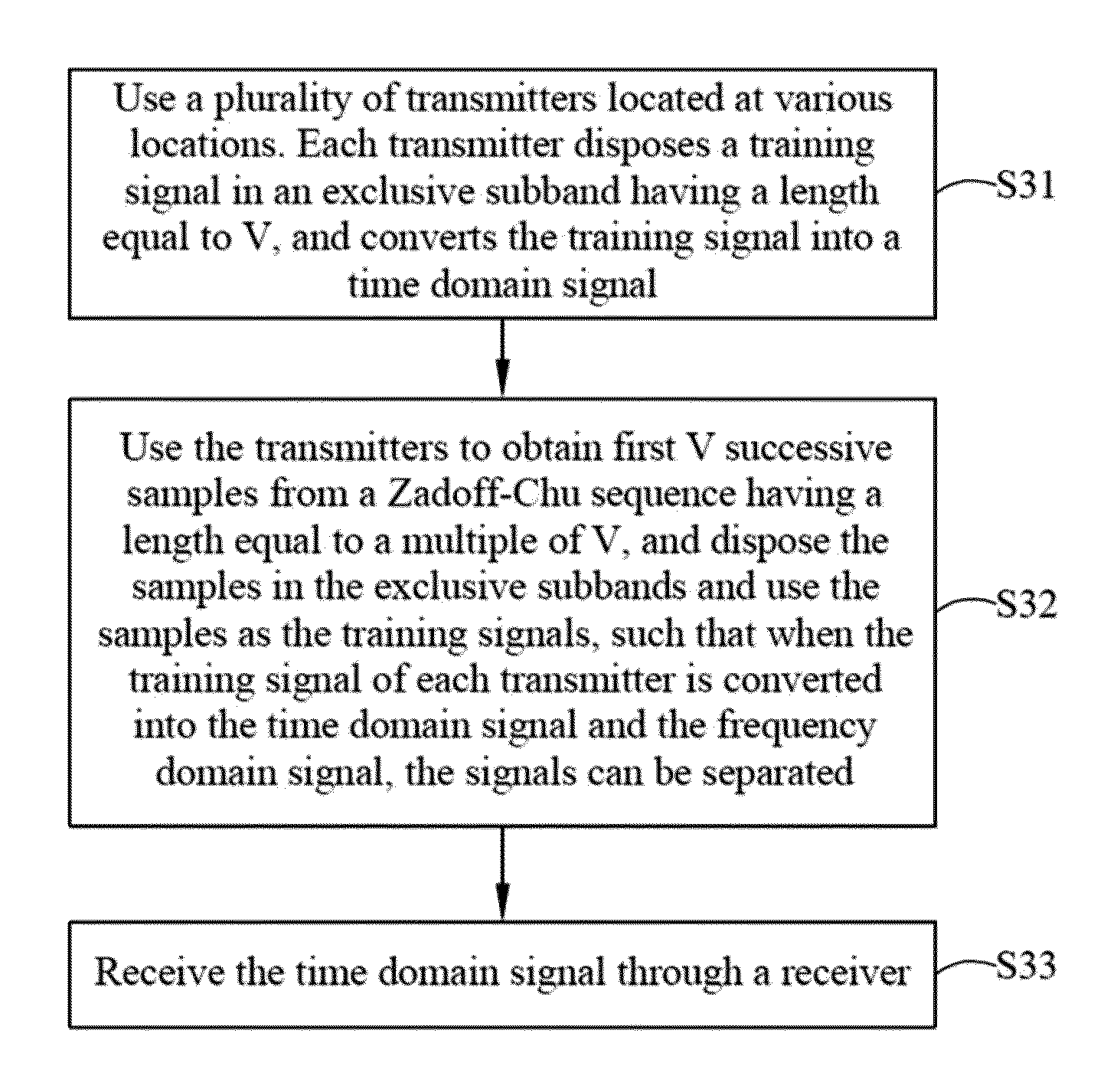
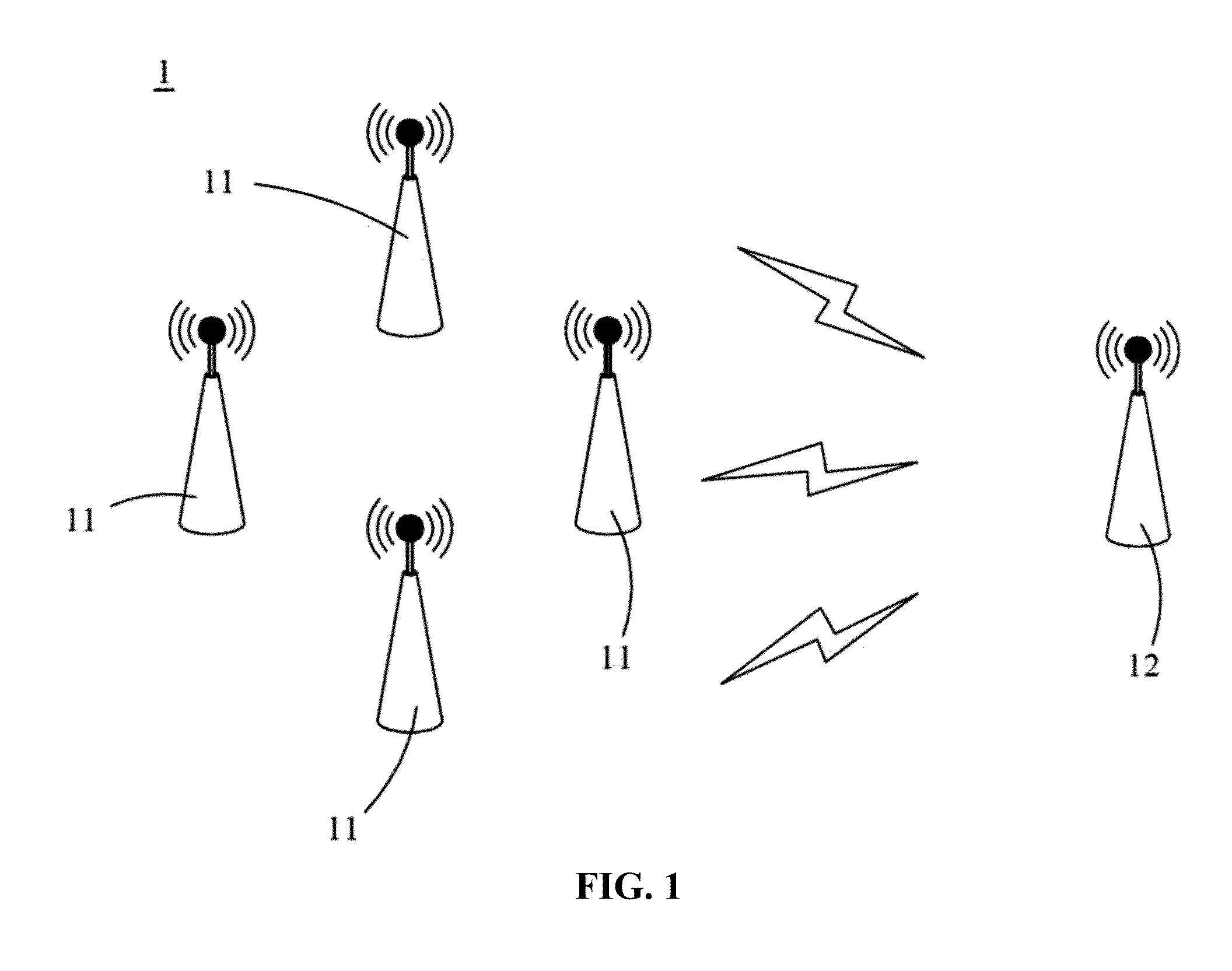
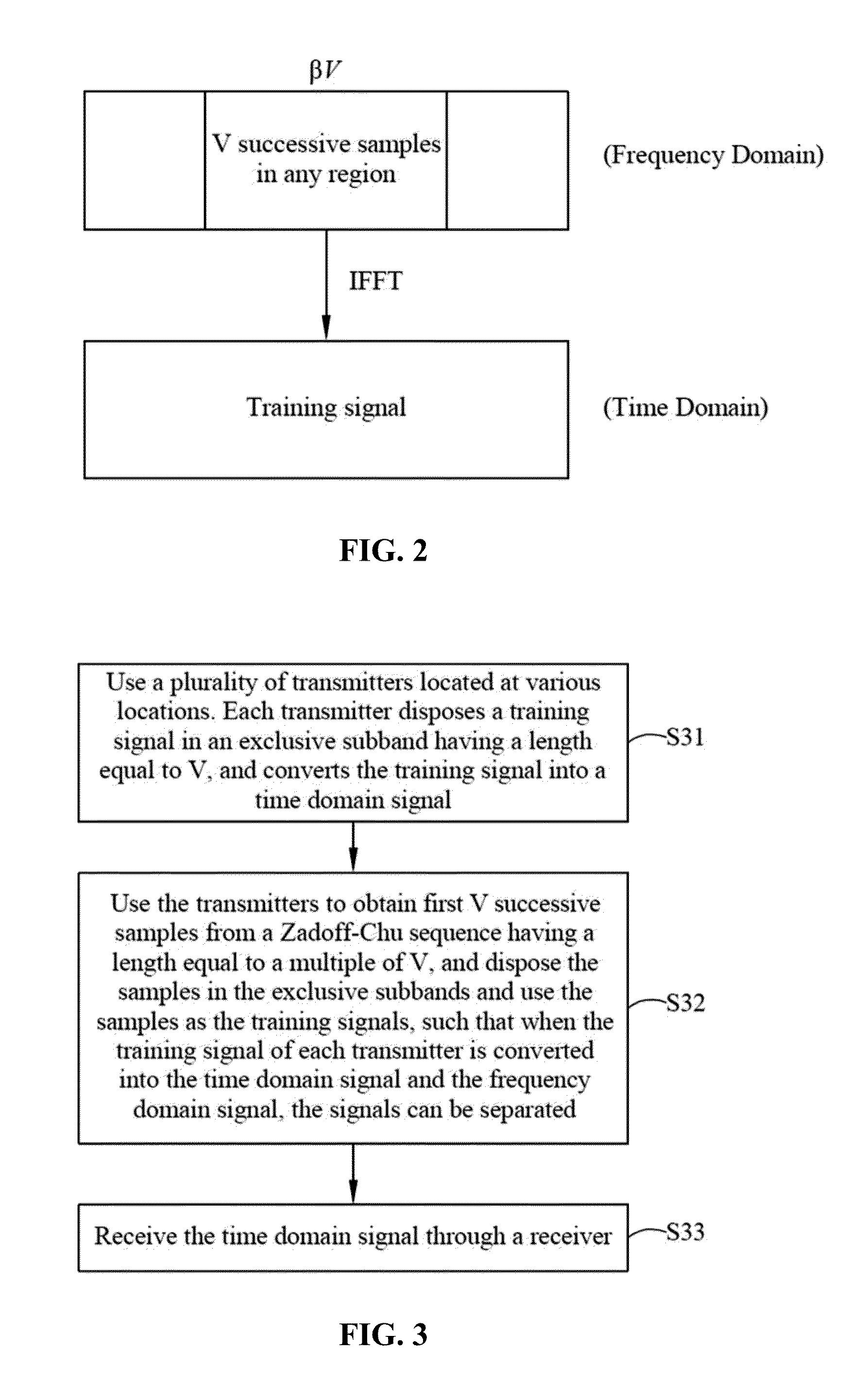
Cooperative MIMO system based on partial zadoff-chu sequence and synchronization method thereof
ActiveUS20130195212A1Reduce system costImprove synchronicitySite diversitySpatial transmit diversityTime domainCooperative MIMO
A cooperative multiple-input multiple-output system based on partial Zadoff-Chu sequences and a synchronization method thereof are disclosed, and the system comprises a plurality of transmitters and a receiver. Each transmitter's training signal is disposed in a subband having a length of V, and the training signal is converted into a time domain signal. The receiver receives the time domain signals of the cooperating transmitters. Each transmitter extracts V successive samples from any region of a Zadoff-Chu sequence having a length equal to a multiple of V and the samples are disposed in an exclusive subband as the training signal. When the training signals of cooperating transmitters are converted into time and frequency domain signals, the training signals of all the transmitters are separated from each other to suppress mutual interference in both time and frequency domains and to improve the performance of synchronization.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
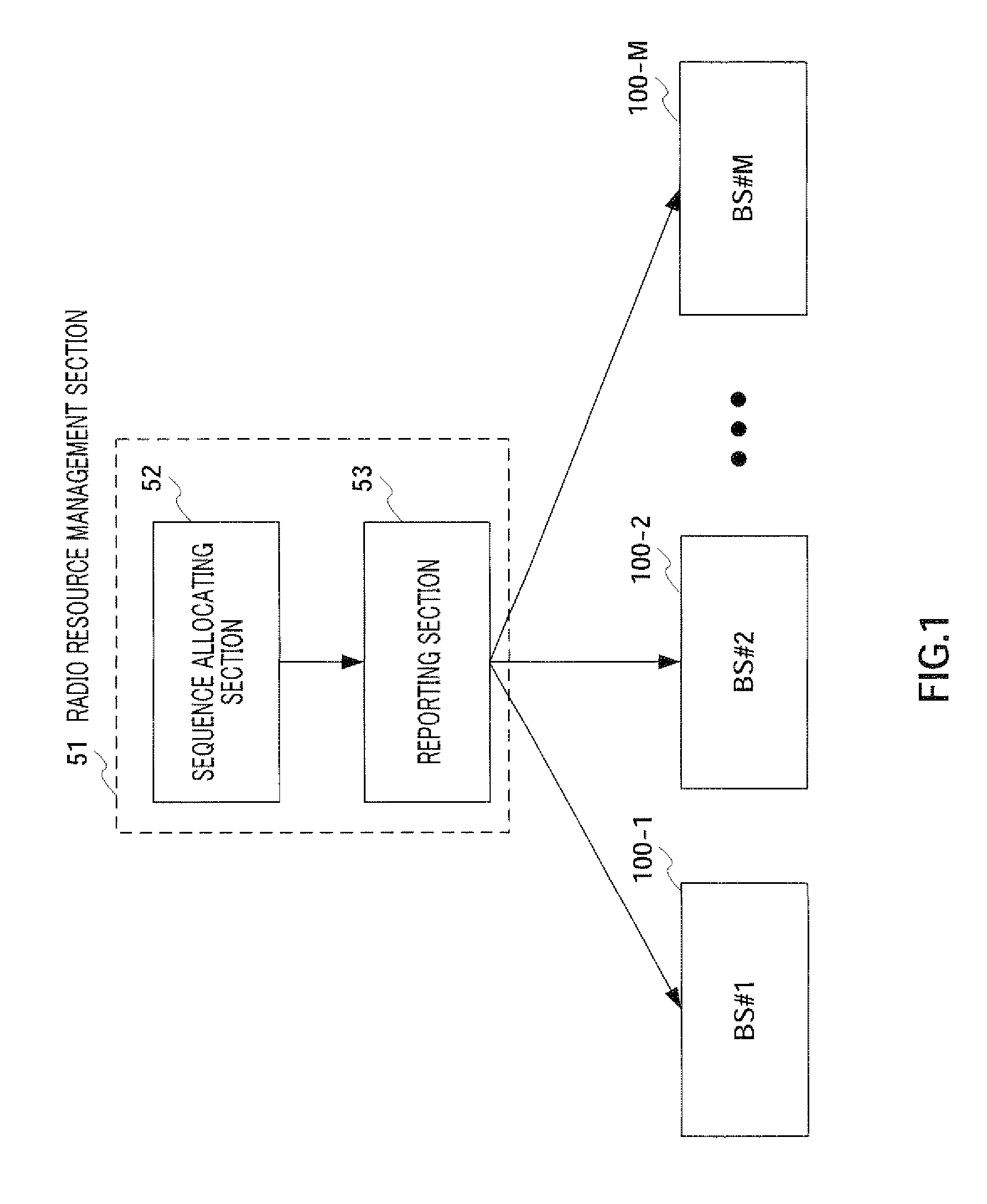
Sequence report method and sequence report device
Disclosed are a sequence report method and a sequence report device for reducing a signaling amount for reporting a Zadoff-Chu sequence or a GCL sequence allocated for a cell. Indexes starting at 1 are correlated to different ZC sequences and are allocated for cells so that the indexes are continuous. When such ZC sequences are reported from BS to UE, a start index indicating the start of the continuous indexes is combined with the number of allocated sequences and they are reported as allocation sequence information by a report channel. The UE and the BS share the correlation between the ZC sequences and the indexes and the UE identifies a usable sequence number according to the correlation and the allocation sequence information reported from the BS.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com