Sequence allocating method, transmitting method and wireless mobile station device
A wireless mobile station and sequence allocation technology, applied in wireless communication, multiplexing code allocation, frequency division multiplexing system, etc., can solve the problem of increased inter-cell interference, degradation of channel estimation accuracy, and degradation of data demodulation performance, etc. problem to achieve the effect of reducing cross-correlation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0059] Figure 8 It is a flowchart showing the procedure of the sequence assignment method in the cellular radio communication system according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0060] First, in step (hereinafter referred to as "ST") 101, the sequence length Nb and the sequence number rb that are the reference of the sequence group to be generated are set. Here, the sequence number rb corresponds to the sequence group number and is smaller than Nb.
[0061] In ST102, the number m of RBs is initialized to 1.
[0062] In ST103, a threshold value Xth(m) corresponding to the number m of RBs is set. In addition, the method of setting the threshold value Xth(m) will be described later.
[0063] In ST104, the ZC sequence length N corresponding to the number m of RBs is set. Assuming that the number m of RBs uniquely corresponds to the sequence length N, for example, N is a prime number that is larger than the size (size) that can be transmitted with the number m of RBs ...
Embodiment approach 2
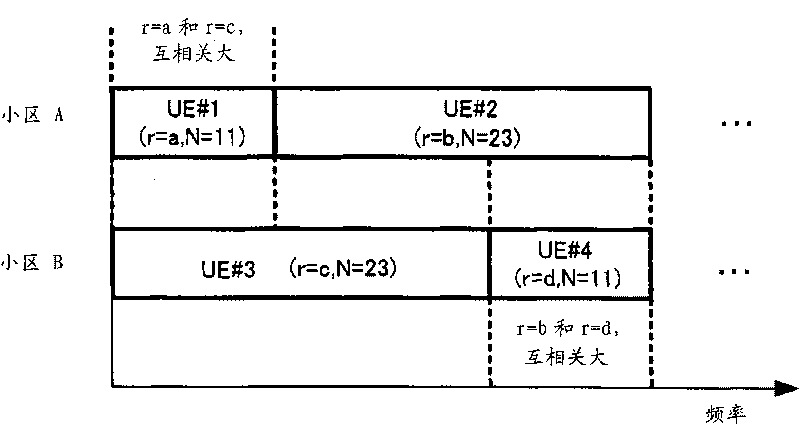
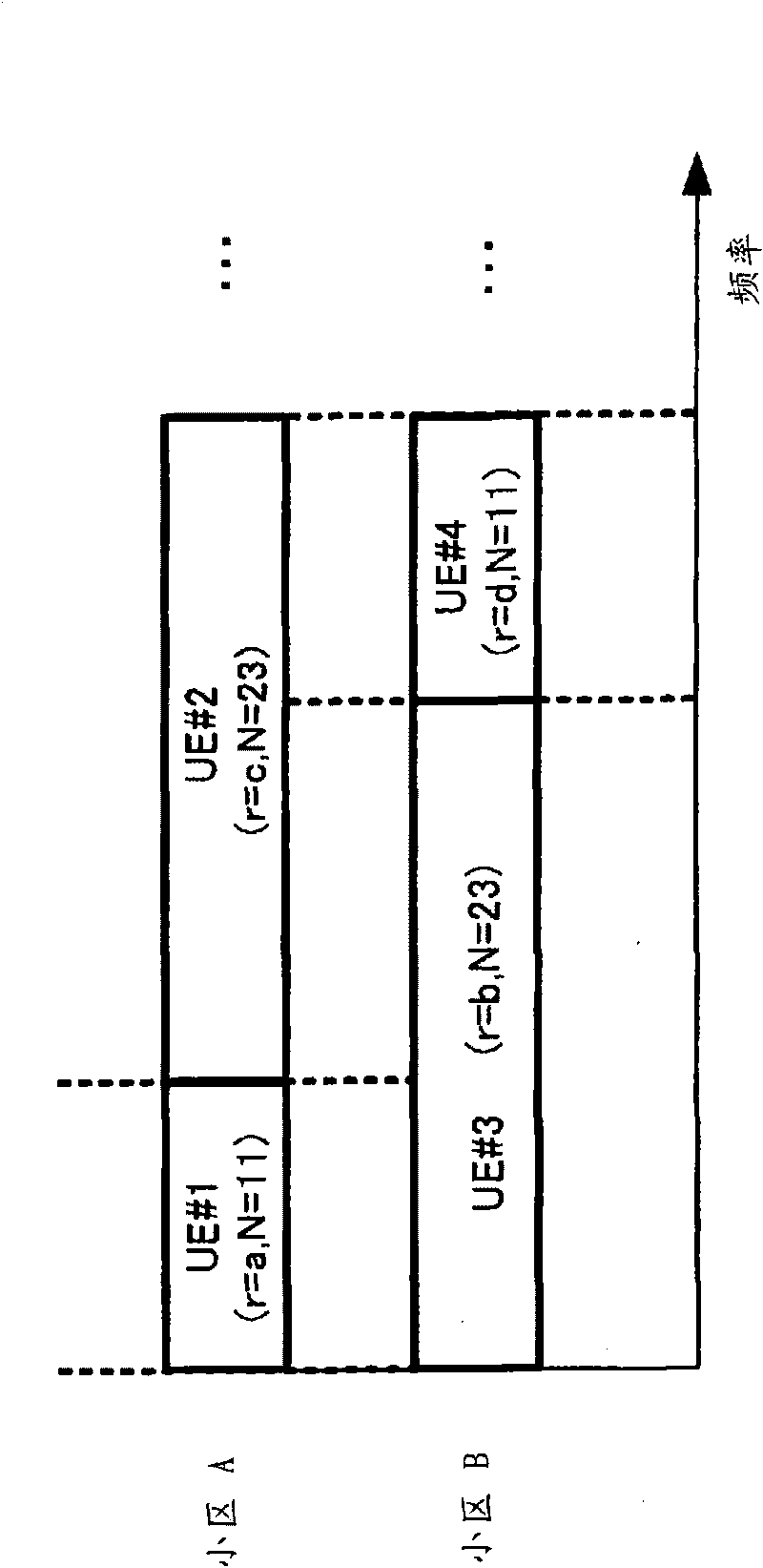
[0134] The sequence assignment method according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention is based on the cross-correlation characteristics of ZC sequences that the present inventors found out through computer simulation.
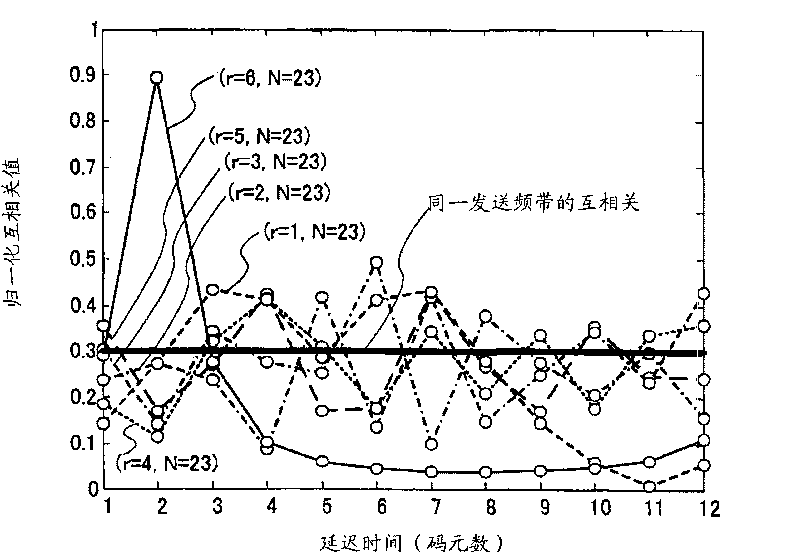
[0135] Figure 16 It is a graph showing the cross-correlation characteristics of the ZC sequence, which the present inventors found out by computer simulation.
[0136] exist Figure 16 In , the horizontal axis represents the r / N difference between ZC sequences with different transmission bandwidths or different sequence lengths, and the vertical axis represents the cross-correlation characteristics between ZC sequences. like Figure 16 As shown, when the r / N difference between ZC sequences with different transmission bandwidths or different sequence lengths is 0.0, the cross-correlation between ZC sequences is the largest, and when the r / N difference is 0.5, the correlation between ZC sequences The cross-correlation forms peaks. That is, the cross-corre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com