Brightness adjustment method and device of display screen and air conditioner
A brightness adjustment and display technology, applied in the field of display screens, can solve the problems of affecting the appearance, the small distance between the display screen and the photosensitive sensor, and interfering with the photosensitive sensor's sensing of ambient light, so as to avoid the effect of halo
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
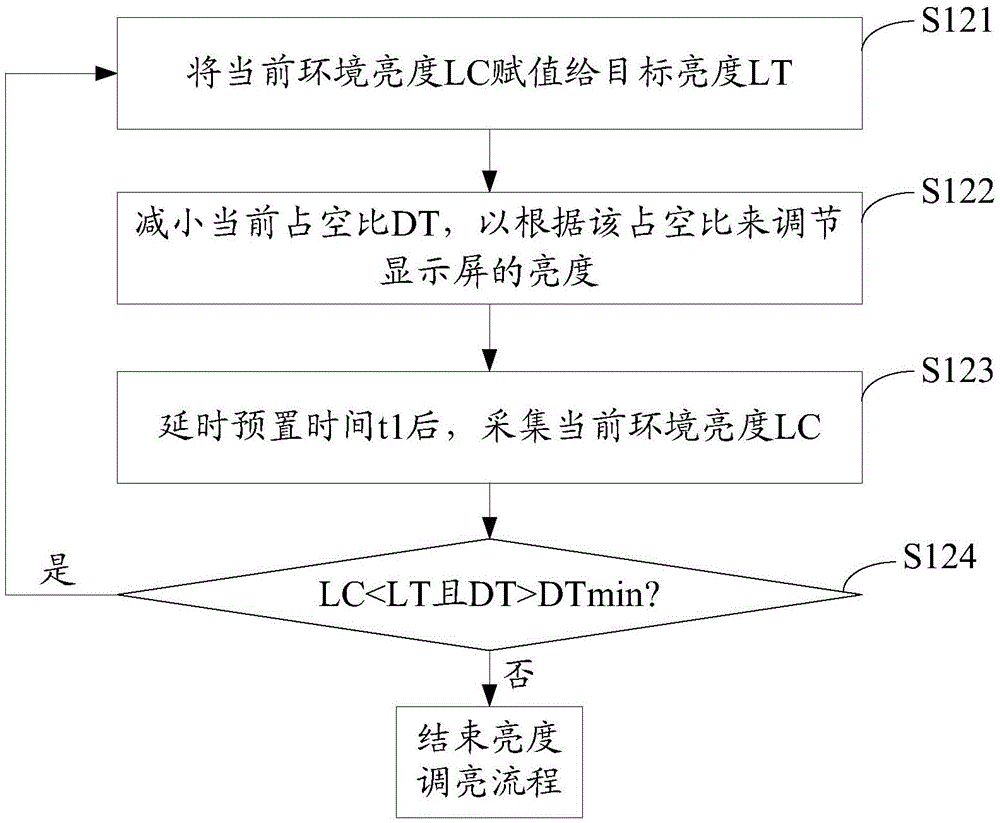
[0072] Example 1: Brightness adjustment during power-on and power-on during the day.
[0073] In this example, t1=50mS is preferred. The AD value of the brightest ambient light is 255, while the AD value of the brightest ambient light that can be detected by the actual user is 200. This value is the maximum brightness that most families can collect. The brightness AD value of the lowest brightness is 0. The maximum duty cycle DTmax=100%, the minimum duty cycle DTmin=10%, that is, the brightness adjustment range of the display screen is 10-100%, the duty cycle when the display screen is darkest is 10%, and the duty cycle when the display screen is brightest is 10%. The empty ratio is 100%. Choose 5 for DF fluctuation range. Take the brightest AD value of 200 at noon during the day, the default duty cycle of power-on is 10%, and the initial target brightness LT=0 to illustrate, the specific execution process is as follows:
[0074] S1, initializing and powering on, assuming t...
example 2
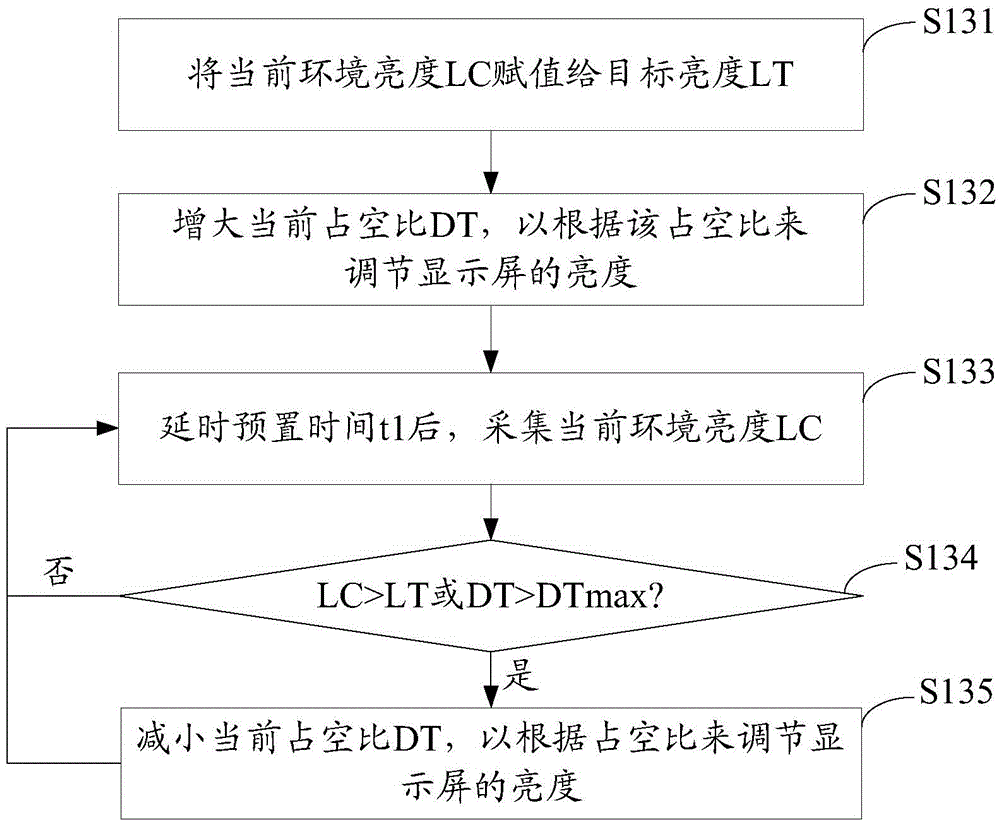
[0082] Example 2: Brightness adjustment for turning on lights at night.
[0083] Other parameters in this example are the same as Example 1. Take the brightest AD value of 109 when the light is turned on at night as an example, and the current duty cycle is 100%. The specific execution process is as follows:
[0084] S3, the target brightness LT=200, the collected current ambient brightness LC=109 after turning on the lights;
[0085] S4, judging whether the current ambient brightness LC is smaller than the target brightness LT or larger than the target brightness LT, and whether the absolute value of the difference between the current ambient brightness LC and the target brightness LT is greater than DF, that is, |LC-LT|>5; because the current ambient brightness LC =109 is less than the target brightness LT=200, and the absolute value of the difference between the current environment brightness LC=109 minus the target brightness LT=200 is greater than the fluctuation range va...
example 3
[0092] Example 3: Brightness adjustment for turning off lights at night.
[0093] Other parameters in this example are the same as Example 1, and the brightest brightness AD value when the light is turned off at night is 14, and the duty cycle is 55%. The specific execution process is as follows:
[0094] Step S5, the target brightness LT=100, and the collected current ambient brightness LC=14 after turning on the lights;
[0095] Step S6, judging whether the current environment brightness LC is smaller than the target brightness LT or greater than the target brightness LT, and whether the absolute value of the difference between the current environment brightness LC and the target brightness LT is greater than DF, that is, |LC-LT|>5; because the current environment brightness LC=14 is less than the target brightness LT=100, and the absolute value of the difference between the current ambient brightness LC=14 minus the target brightness LT=100 is greater than the fluctuation r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com