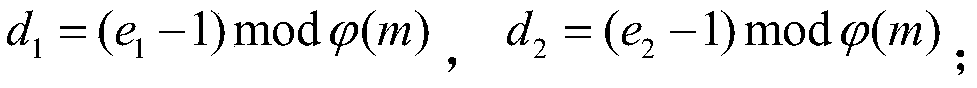A Cluster Key Management Method for Wireless Sensor Networks
A wireless sensor network, key management technology, applied in wireless communication and key distribution, can solve the problems of the number of base stations, storage redundancy, and algorithm can not lose packets, etc., to achieve the effect of solving the problem of signature key update
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
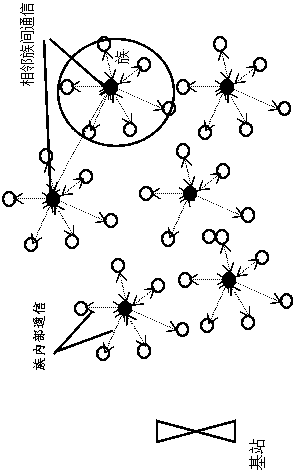
[0042] Embodiment 1, with reference to figure 1 and 2 , a cluster key management method that can be used in wireless sensor networks, this method does not consider the specific division method of the cluster, the node is initialized by the key management center before deployment, including the relevant parameters and algorithms for each sensor node In this invention, the whole wireless sensor network is divided into base station, cluster head and intra-cluster nodes after clustering; the communication and data transmission security between the base station and the cluster head is guaranteed by the composite matrix key , the cluster head and the nodes in the cluster form an internal secure communication area; the cluster head is responsible for the safe data transmission of the nodes in the cluster, when the remaining energy of the cluster head node is lower than the set threshold, the condition of becoming a cluster head is given up and transformed into a normal node , when t...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Embodiment 2, a cluster key management method applicable to wireless sensor networks described in Embodiment 1,
[0044] The specific method is as follows:
[0045] (1) The establishment of the composite secret key matrix between the cluster head and the base station:
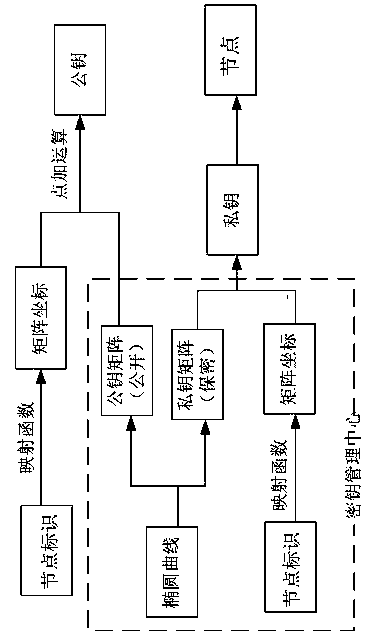
[0046] (1) First, the key management center constructs the initial public / private key moment of the ECC-based CPK authentication system, and determines the elliptic curve, base point G, subgroup S, private key matrix SSK and public key matrix PSK;
[0047] (2) Generation of composite secret key matrix: the identification key is generated through the key matrix through the identity of the entity; the random key is a random sequence defined by the system, which is combined with the identification key to generate a first-order composite secret key, and the random sequence is eliminated The linear relationship between private key variables; the identification key and random key are defined by the key manage...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Embodiment 3, a cluster key management method applicable to wireless sensor networks described in Embodiment 2,
[0060] Its method flow is as follows:
[0061] (1) Initial configuration of the node based on ECC CPK authentication:
[0062] Nodes are initialized by the key management center before deployment, including the setting of relevant parameters and algorithms for each sensor node; specifically include: sensor node ID, node energy threshold, hash function, elliptic curve, base point G, Subgroup S, private key matrix SSK, public key matrix PSK, composite key algorithm and threshold key encryption algorithm, etc. Select an elliptic curve: y 2 =(x 3 +ax+b)modp, G=(x G ,y G ) as a generator, called the base point; E is formed by all the multiple points of the base point G p The subgroup S of (a, b), n is the order of the subgroup S; the elements in the subgroup S generated by G are all the multiple points kG of G, (k=1,2,3,...,n) , namely: S={G,2G,3G,...nG}={...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com