A method for determining the transfer orbit of a lunar probe
A technology for transferring orbits and detectors, applied in the field of spacecraft dynamics research, can solve problems such as incomplete force models, inability to obtain high precision, and inability to obtain GNSS data support, etc., to achieve the effect of improving the progress of orbit calculations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments, and the present invention includes but not limited to the following embodiments.
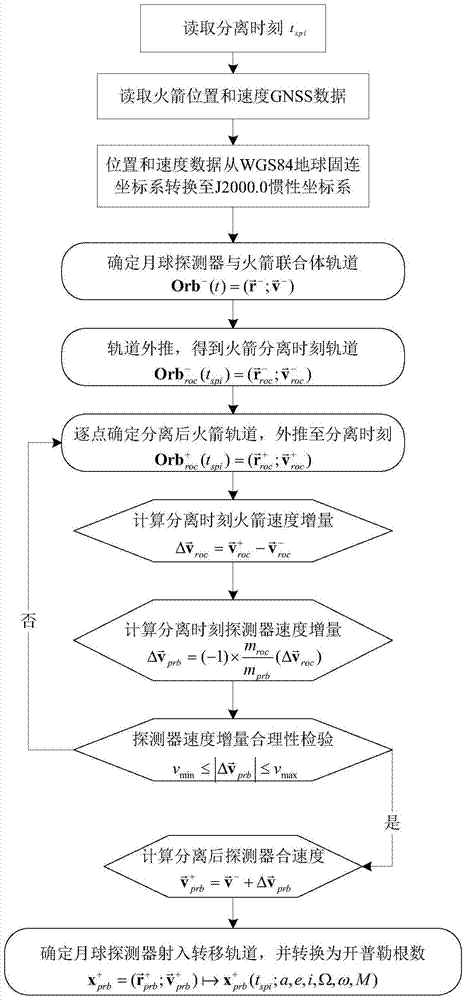
[0026] A method for determining the launch orbit of a lunar probe based on rocket sparse GNSS data, comprising the steps of:
[0027] Step 1: During the launch phase of the lunar probe, process the rocket telemetry data and read the time t when the lunar probe and the rocket separate spi (year-month-day hour:minute:second.millisecond);
[0028] Step 2: Read the GNSS data of the rocket before and after the separation of the lunar probe and the rocket. The data content includes the orbital epoch (year-month-day hour: minute: second. millisecond), and the position in the earth's fixed WGS84 coordinate system and speed The data sampling rate is 1 second, the data time length before separation is 20 seconds, and the data time length after separation is 10 seconds;
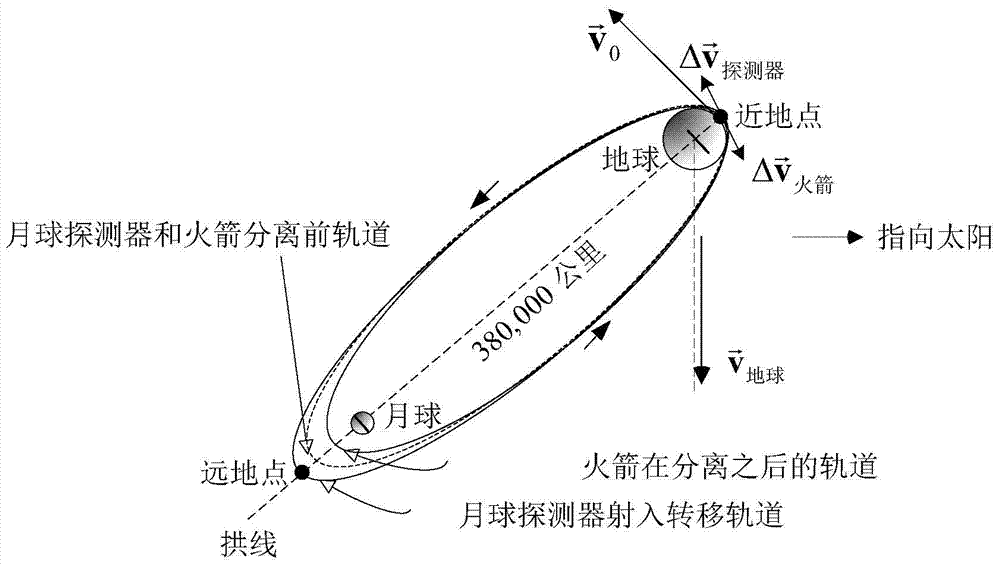
[0029] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com