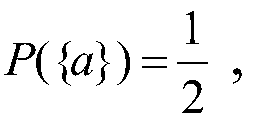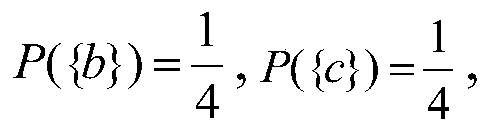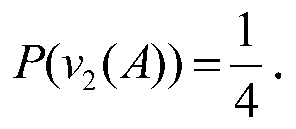Approximate reasoning mode algorithm based on propositional logic probability assignment
A technique of propositional logic and approximate reasoning, applied in the field of computing, which can solve the problem that the connectives of probabilistic logic cannot be explained by the truth function.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0186] The present invention will be further described below:
[0187] The present invention comprises the following steps:
[0188] (1) Probability assignment of propositional logic:
[0189] Let S={q 1 ,q 2 ...} is the atomic formula set, q represents the atomic formula, F(S) is generated by S Type free algebra, the elements in F(S) are called propositional formulas, let (Ω, Λ, P) be the probability space, and the elements in Λ are called events. For α, β∈Λ, α→β=(Ω- α)∪β, but yes Type algebra, and also Boolean algebra, Ω is an inevitable event and is the largest element, φ is an impossible event and is the smallest element;
[0190] Definition 1: ① Suppose (Ω, Λ) is a σ-algebra, the elements in Λ are also called events, and P is the probability on Λ, which is called Type homomorphism v: F(S)→Λ is the (event) assignment of F(S), namely Have
[0191]
[0192] The probability P(v(A)) of the assignment of the formula A is called the true value of the probabili...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com