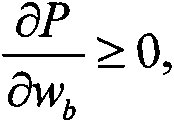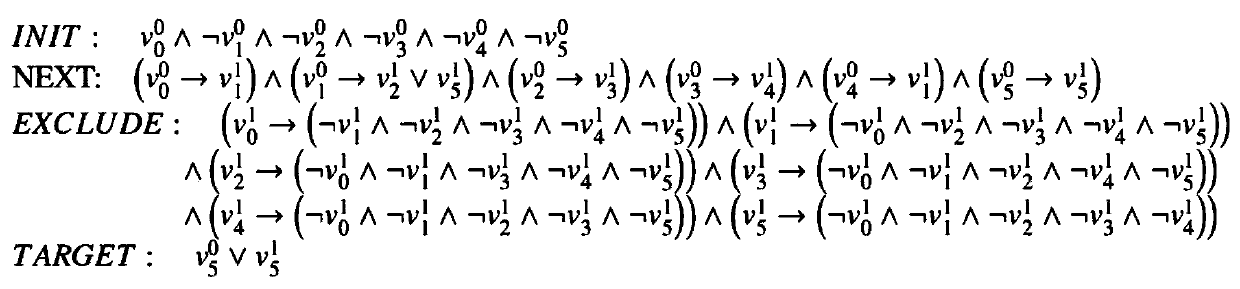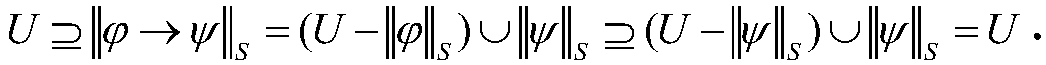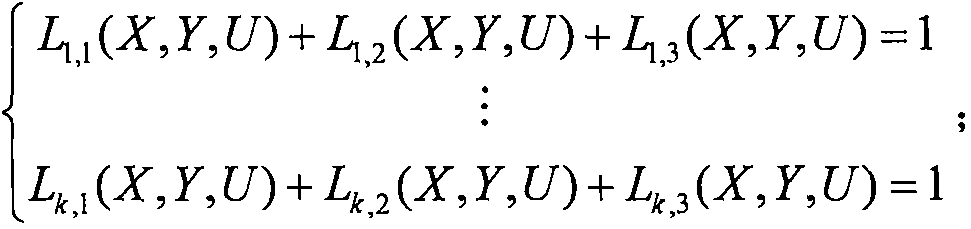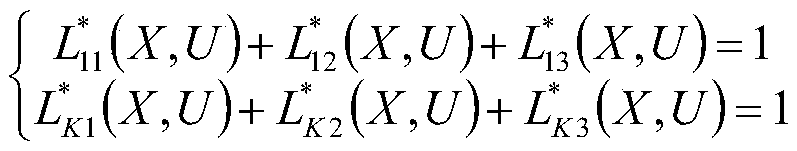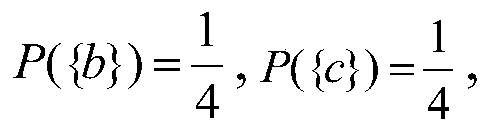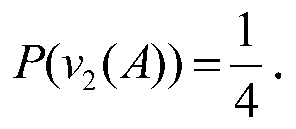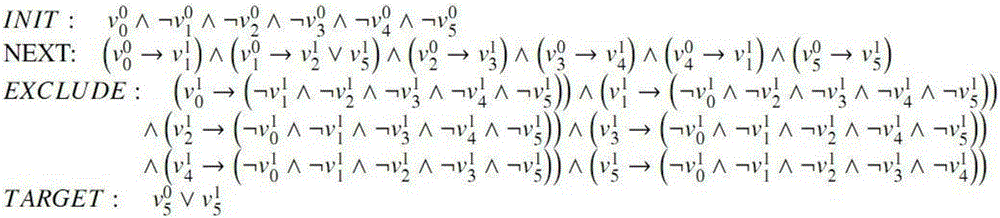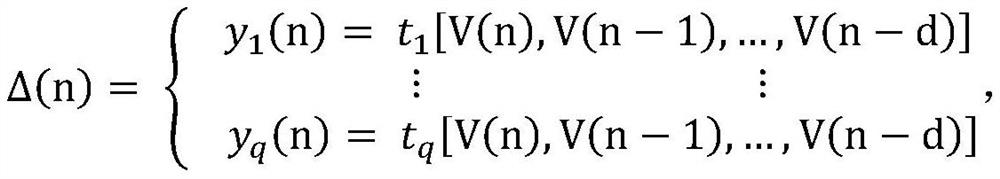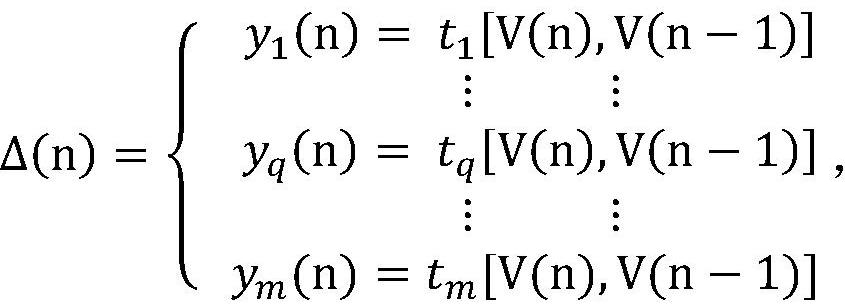Patents
Literature
36 results about "Propositional calculus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Propositional calculus is a branch of logic. It is also called propositional logic, statement logic, sentential calculus, sentential logic, or sometimes zeroth-order logic. It deals with propositions (which can be true or false) and argument flow. Compound propositions are formed by connecting propositions by logical connectives. The propositions without logical connectives are called atomic propositions.
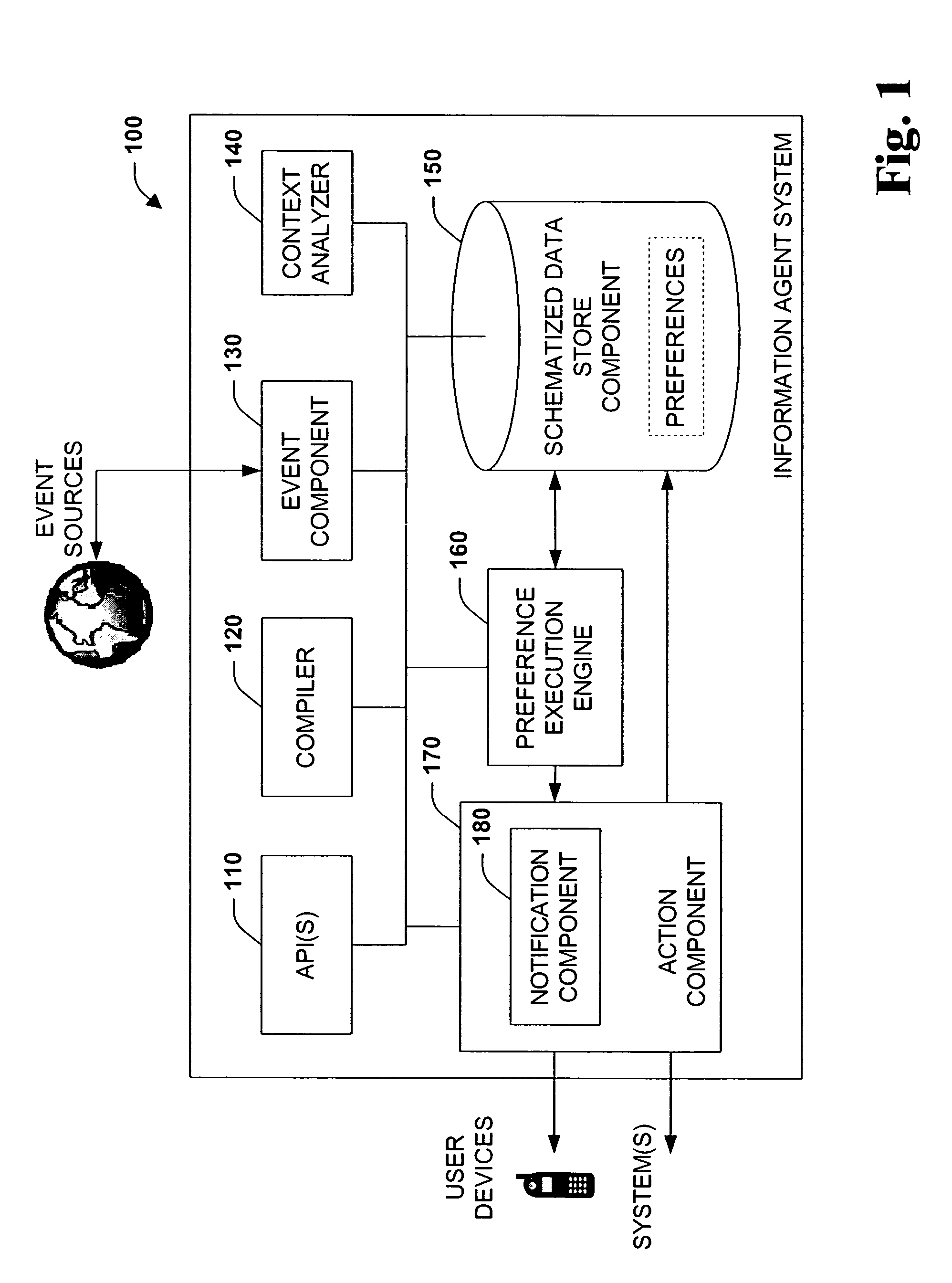
Personalized folders
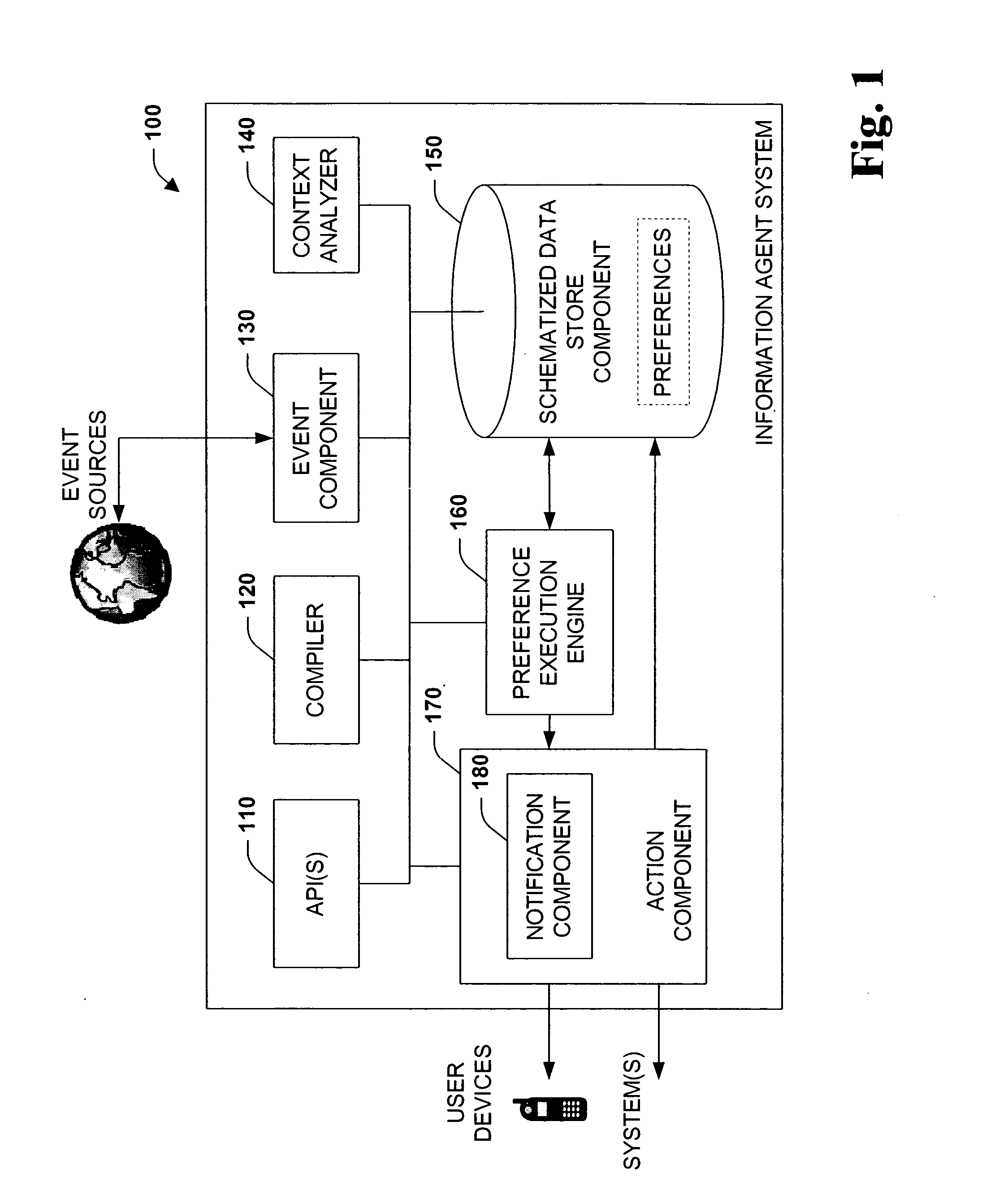
InactiveUS20050091184A1Facilitate information exchangeEasy to shareDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsPersonalizationData sharing
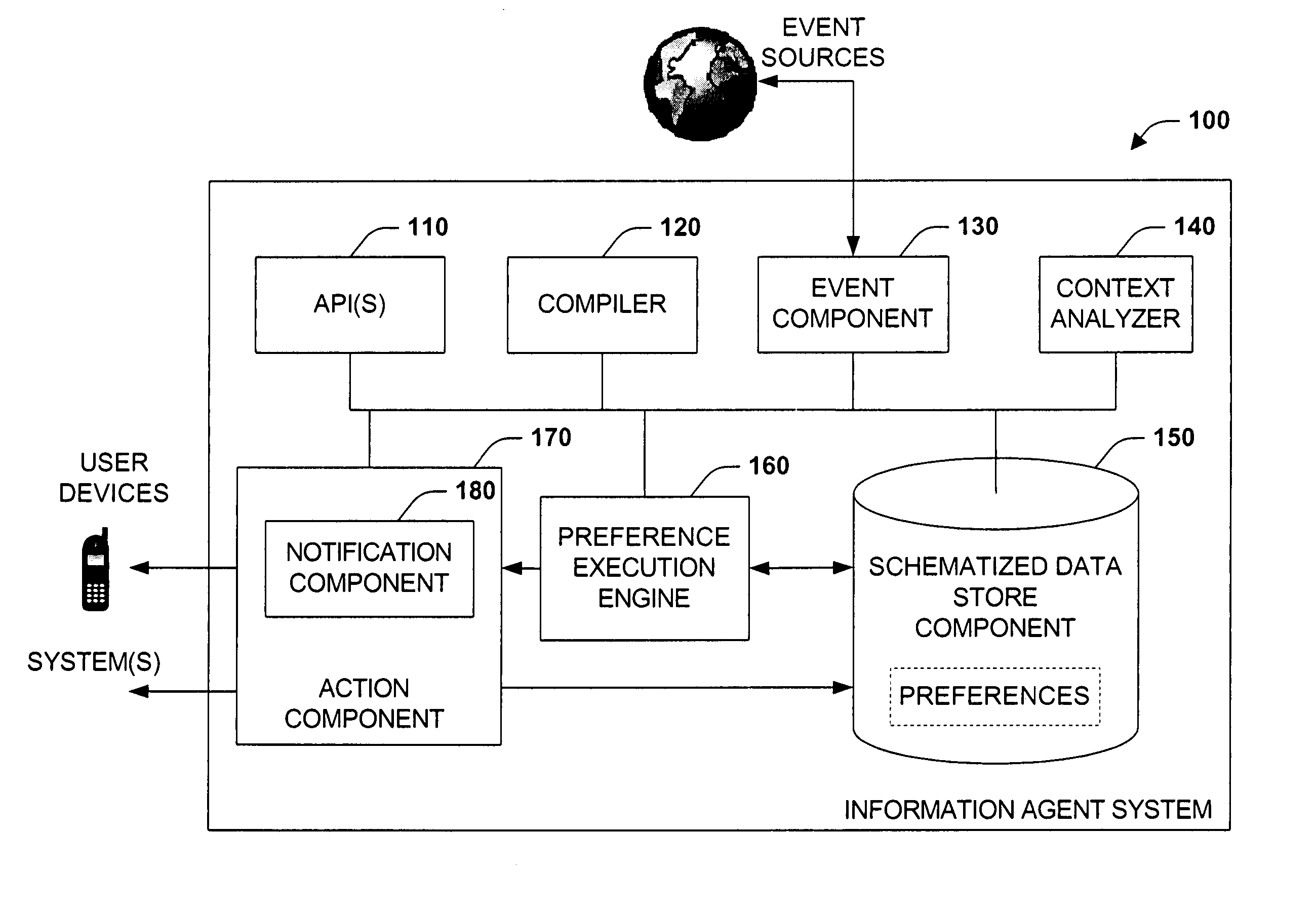
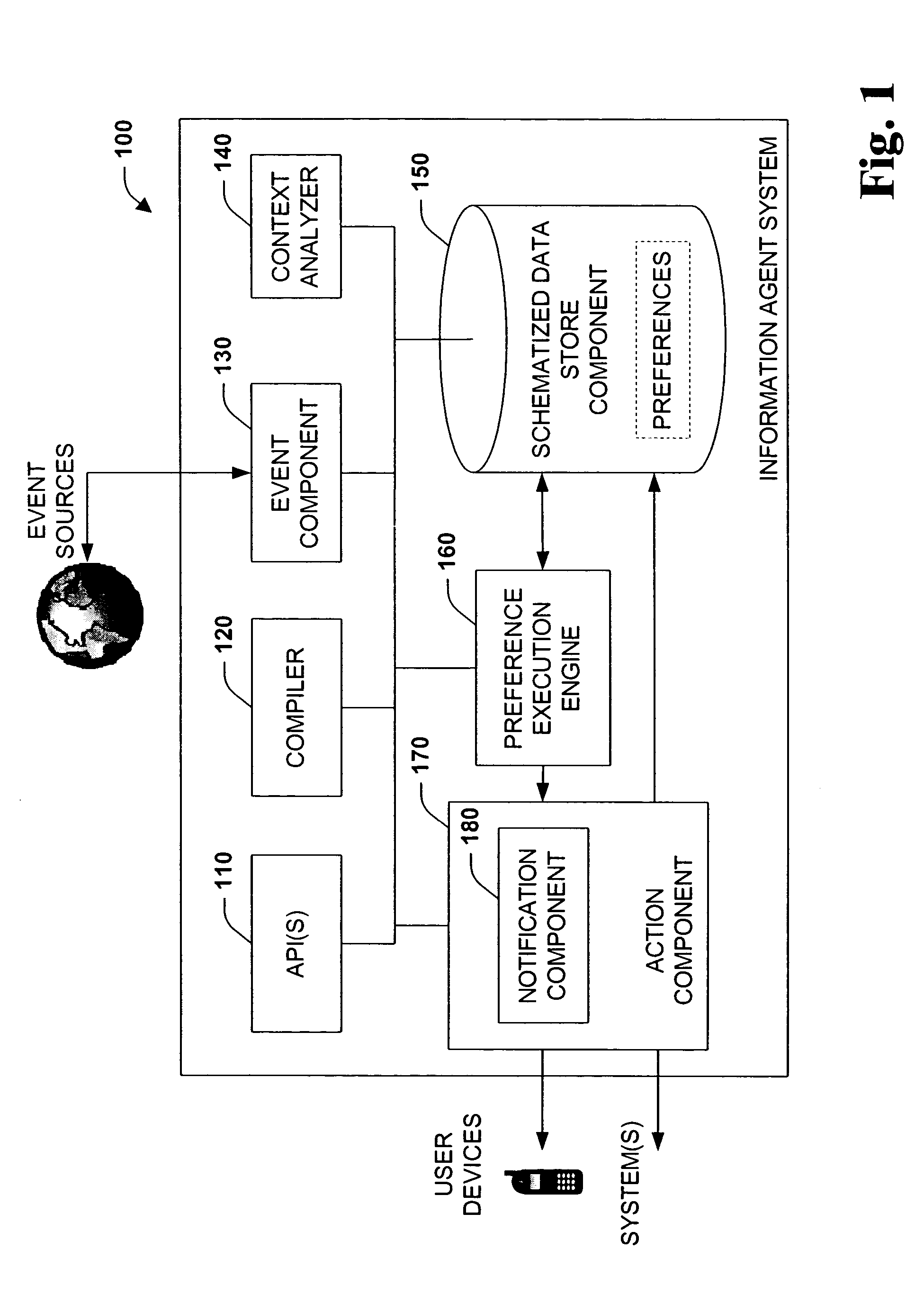
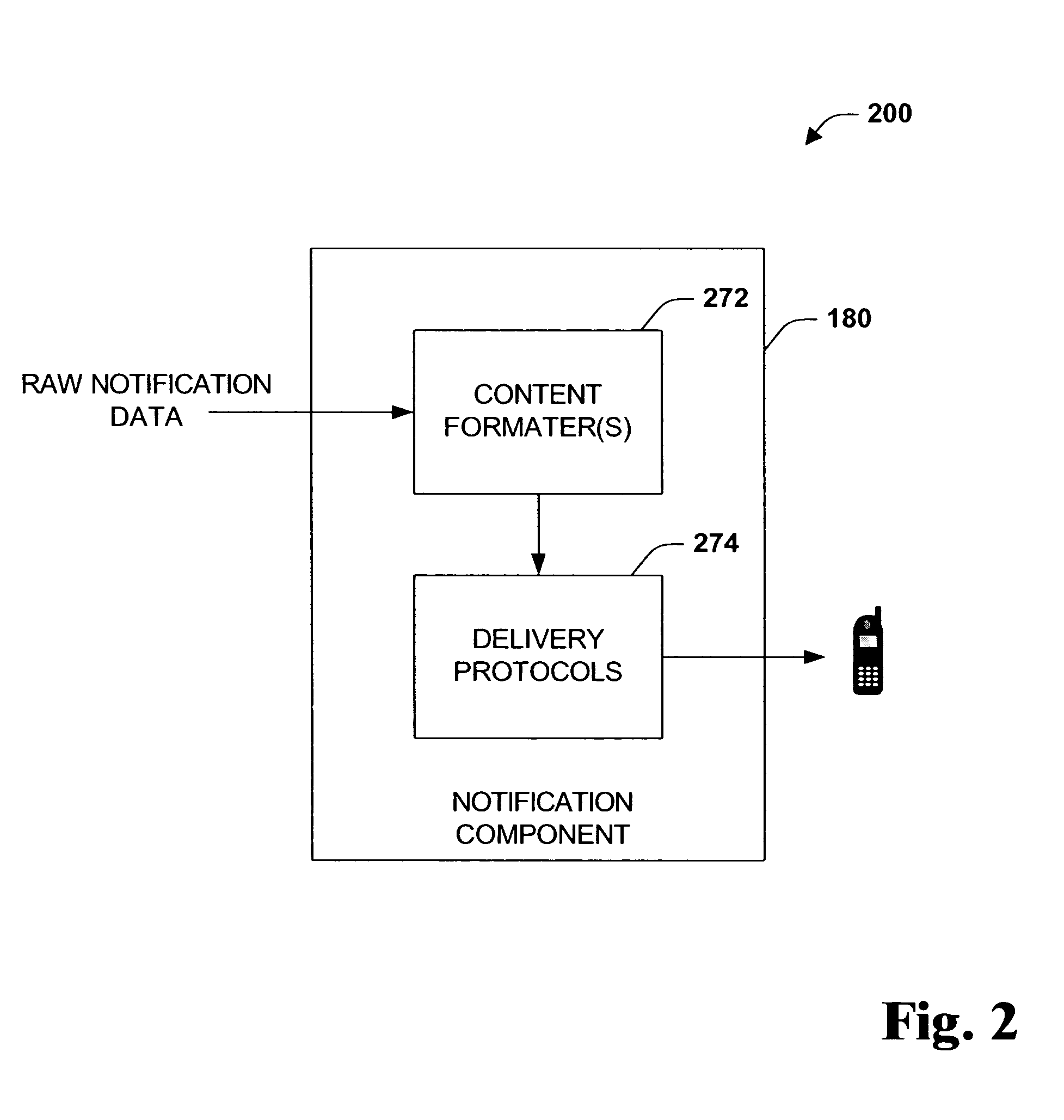
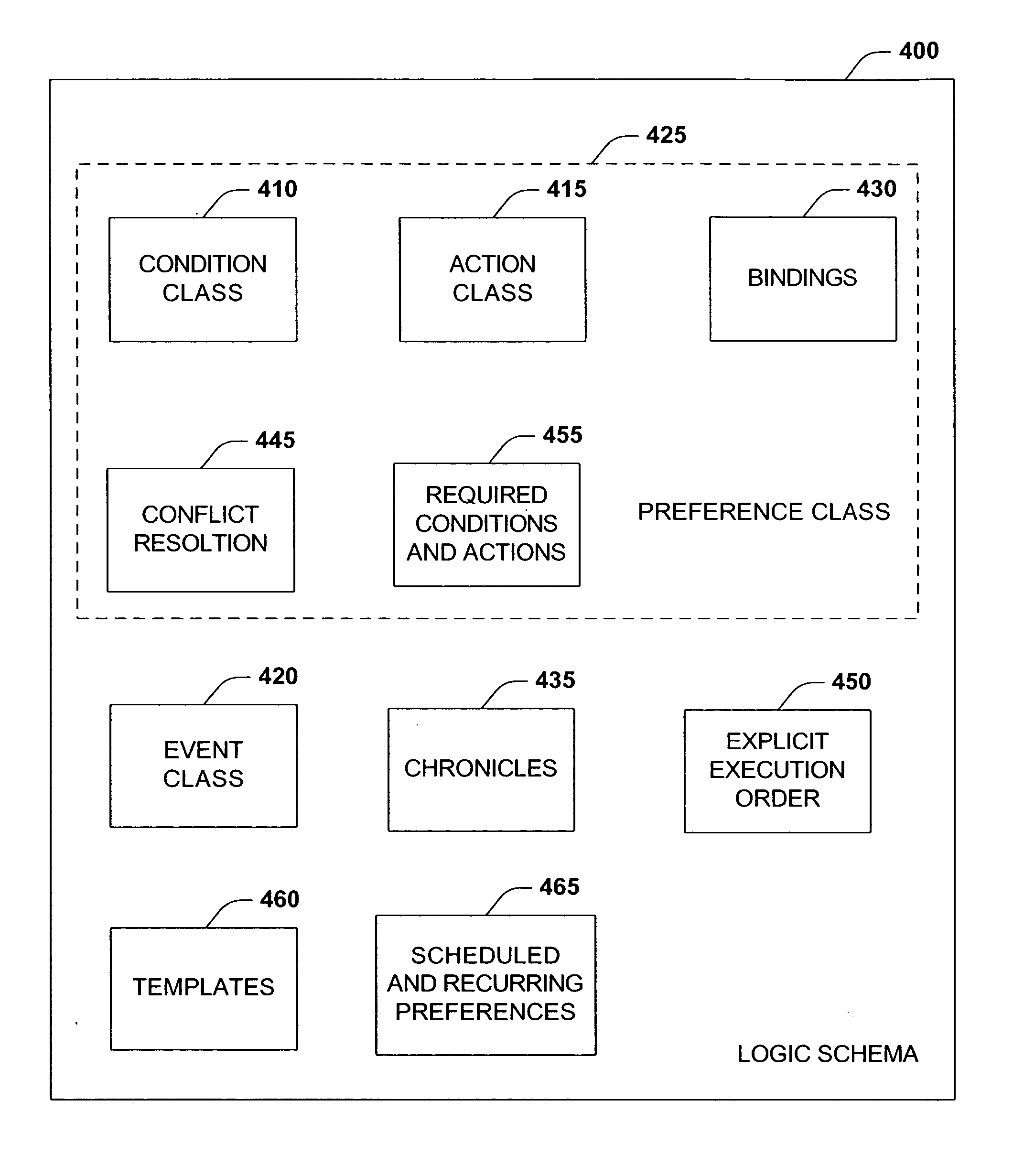
The present systems and methods disclose a system for personalizing computer functionality. End-users are provided with tools to easily write rich and complex preferences, for example, by using a plurality simple IF-THEN propositional logic. The preferences are then transformed into queries and executed efficiently on structured data. Preferences that are satisfied then execute actions such as providing notification or storing data in a particular folder. Furthermore, according to an aspect of the invention, data, logic, events, inter alia, are all schematized, thereby enabling sharing of data between application components and across applications.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
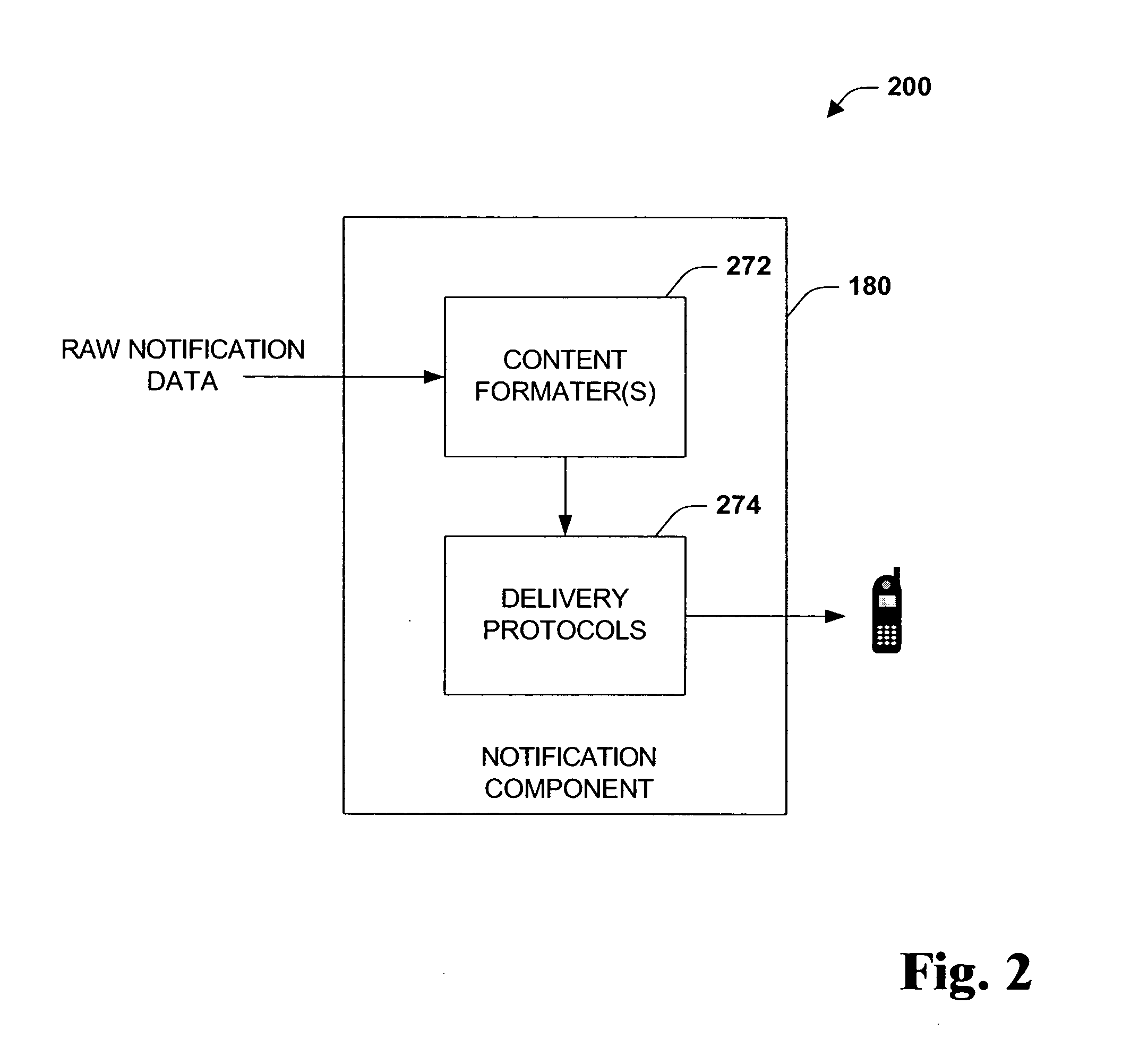
System and method for extending application preferences classes
InactiveUS20050091674A1Easy to understandSmall footprintSoftware maintainance/managementRequirement analysisPersonalizationModelica
The present systems and methods disclose a system for personalizing computer functionality. End-users are provided with tools to easily write rich and complex preferences, for example, by using a plurality simple IF-THEN propositional logic. The preferences are then transformed into queries and executed efficiently on structured data. Preferences that are satisfied then execute actions such as providing notification or storing data in a particular folder. Furthermore, according to an aspect of the invention, data, logic, events, inter alia, are all schematized, thereby enabling sharing of data between application components and across applications.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
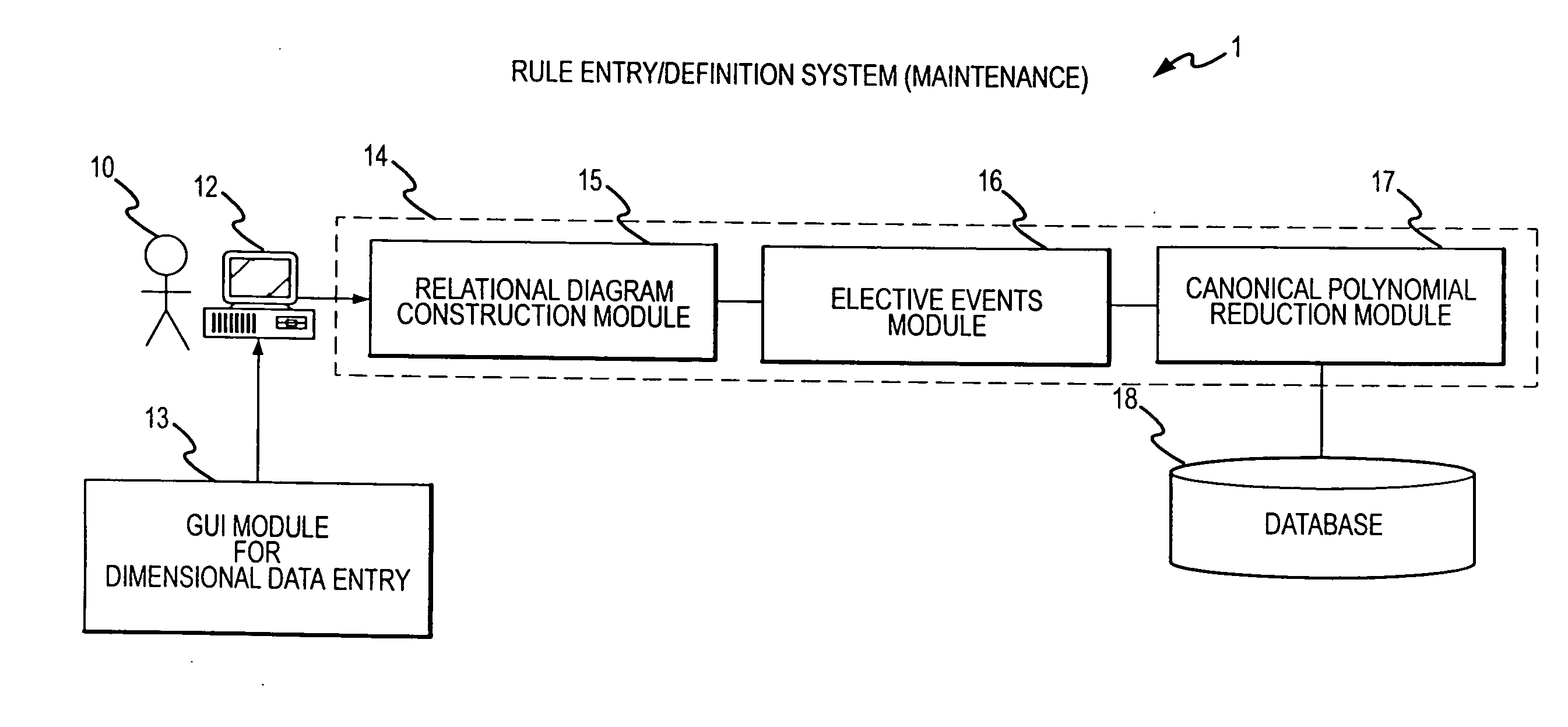
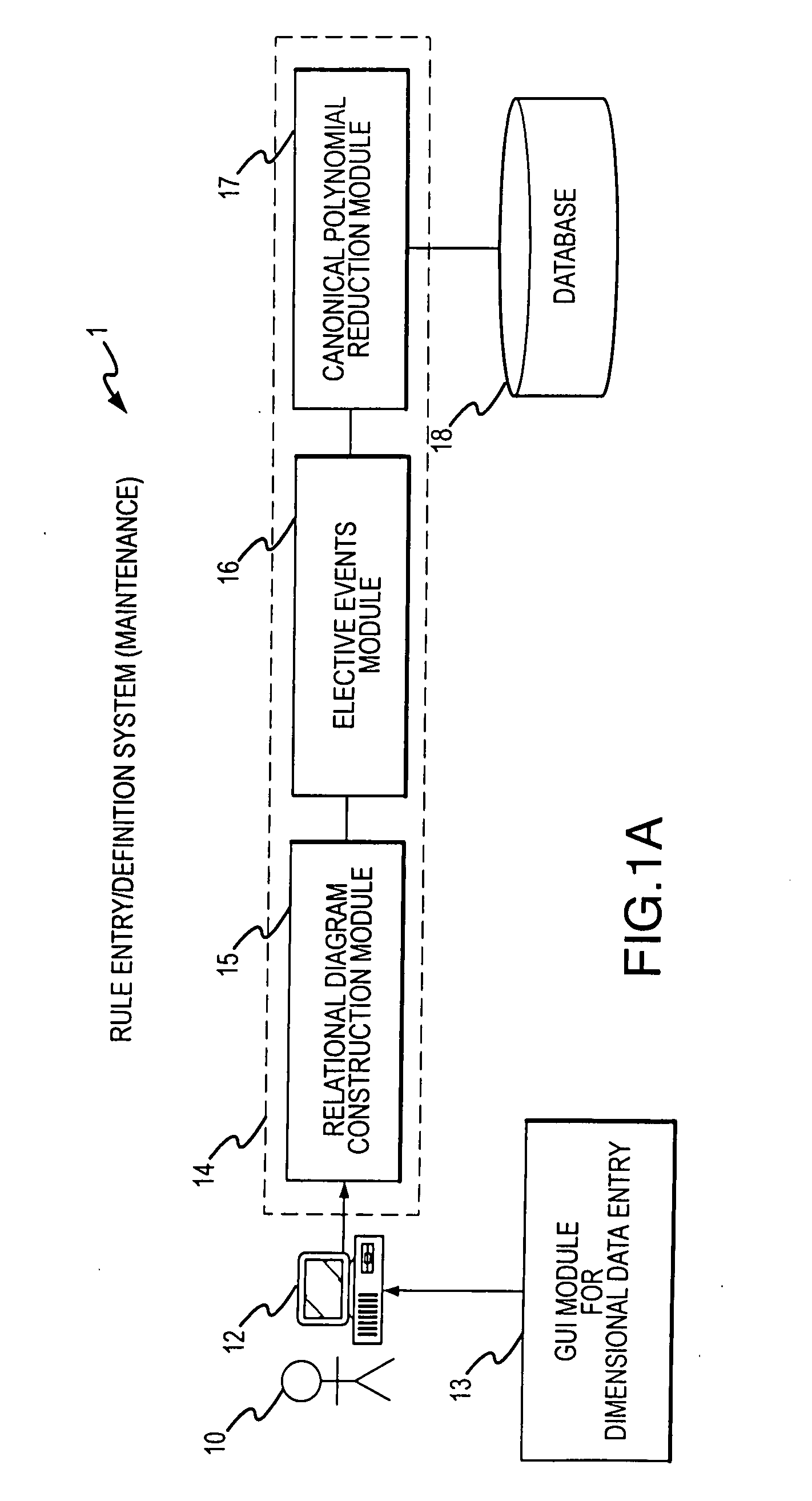
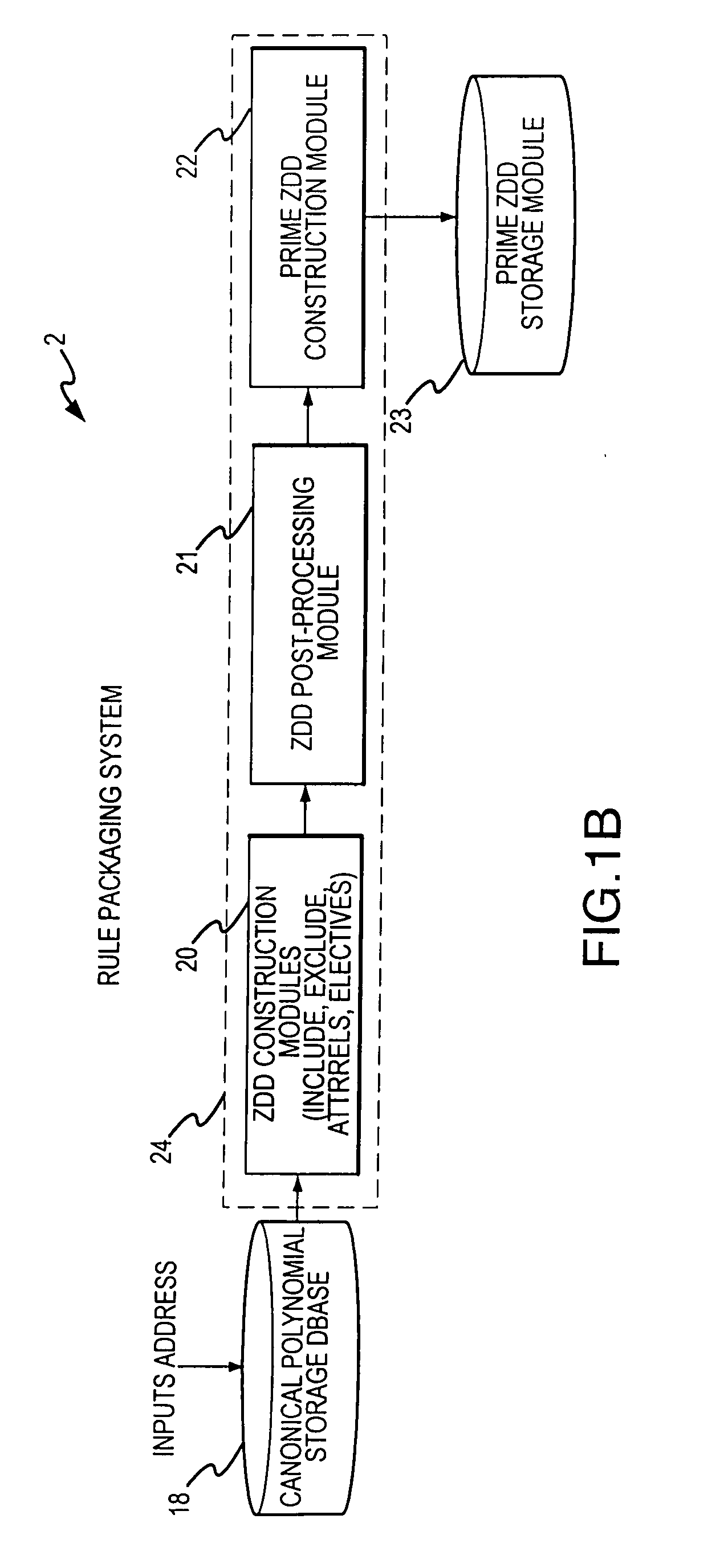
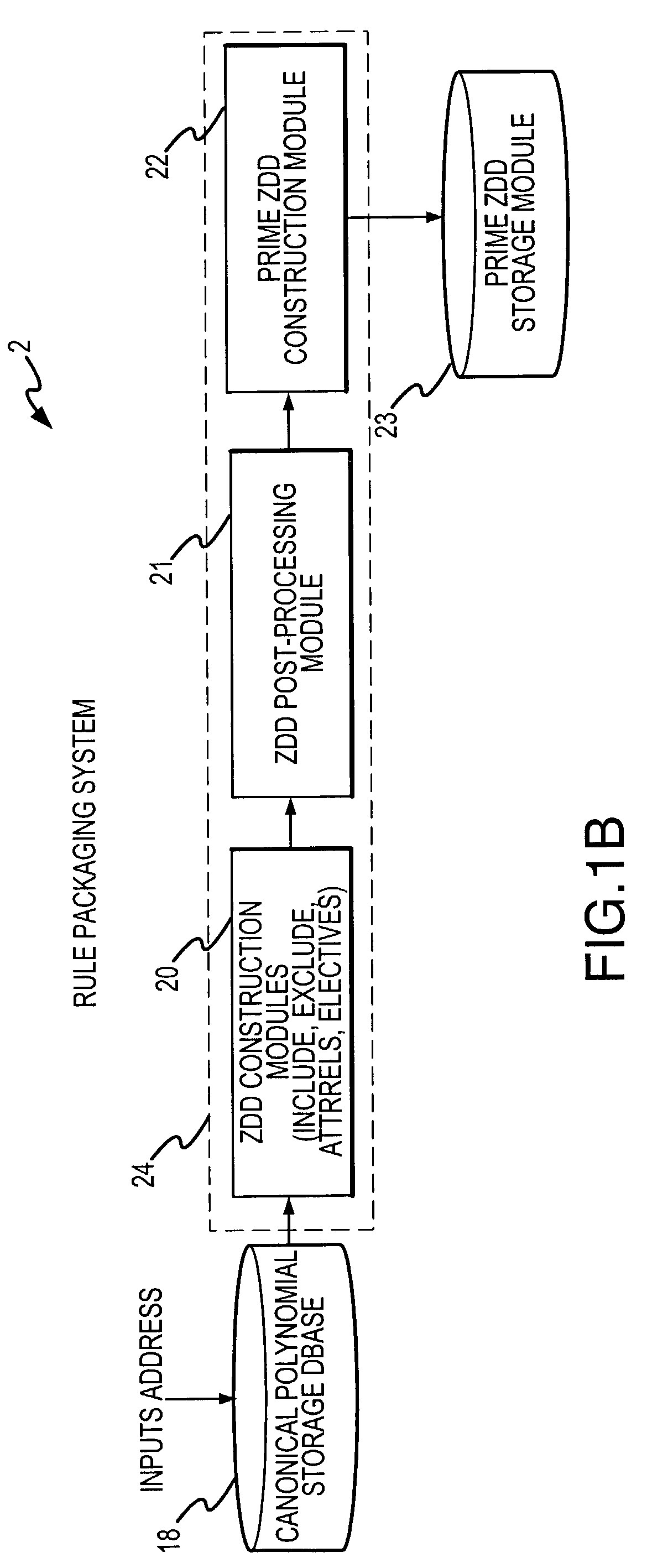
Rule processing system
InactiveUS20070150429A1Exceeding computational capacity of computingDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsPresent dayUser input
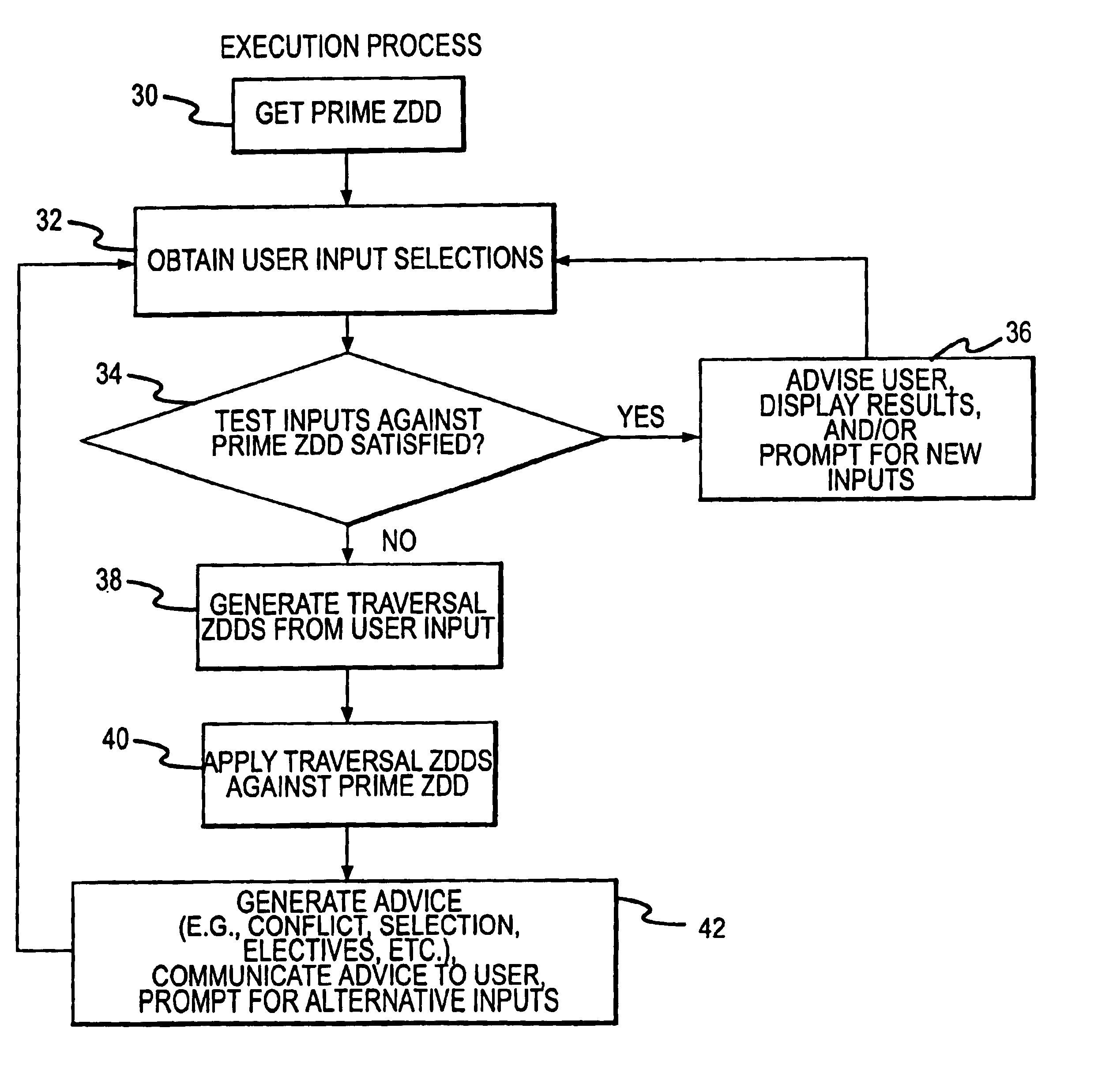
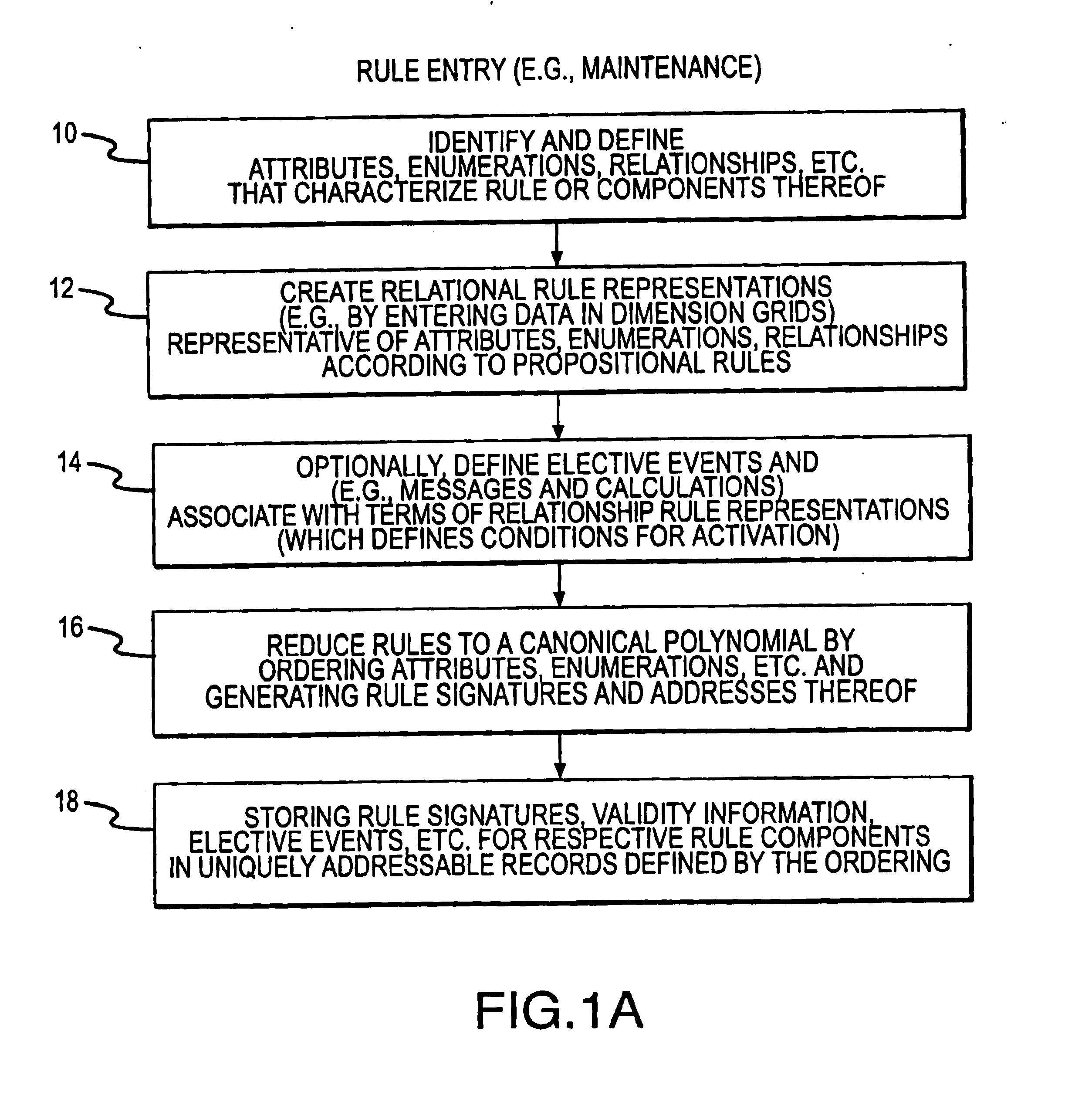
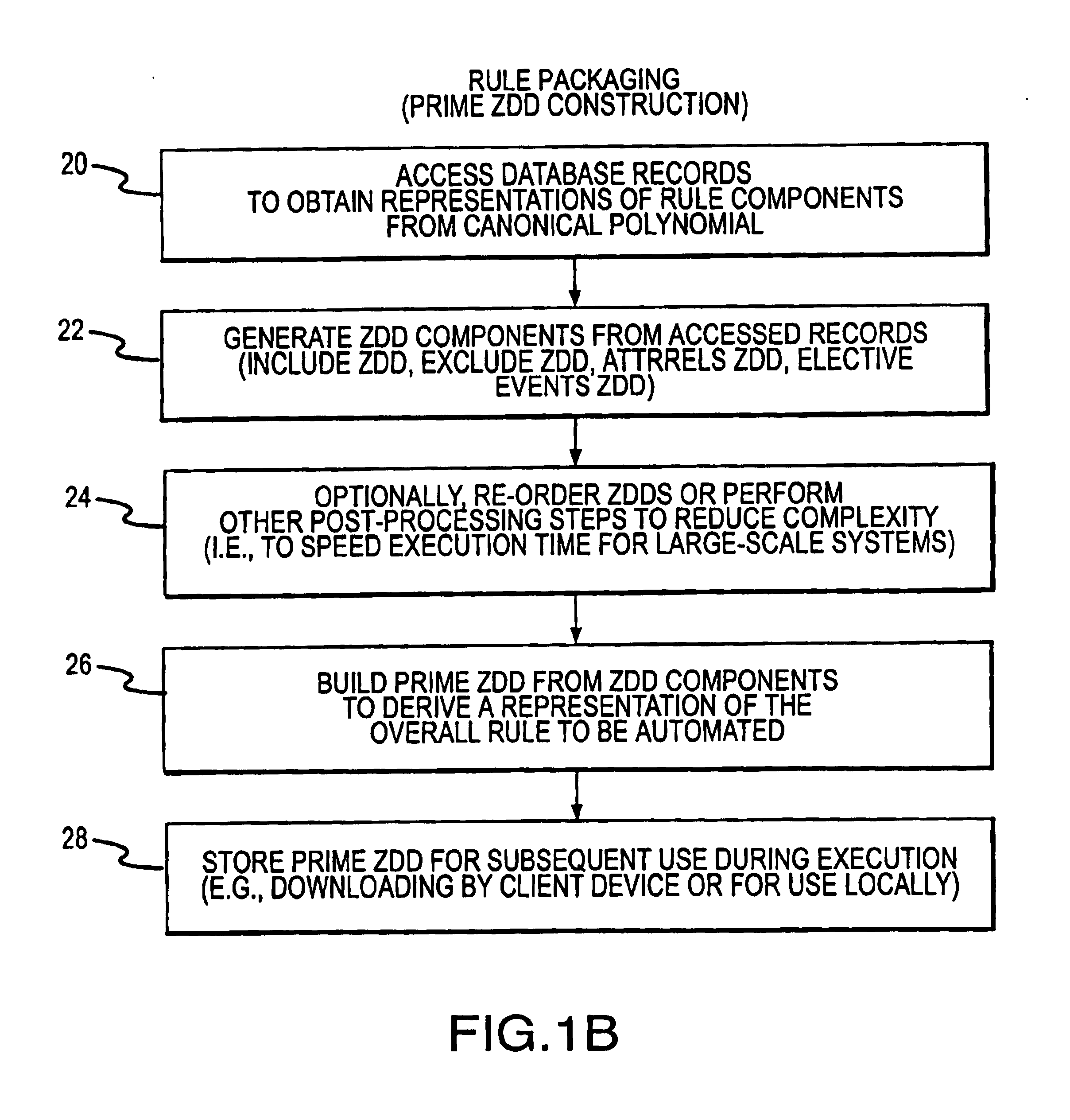
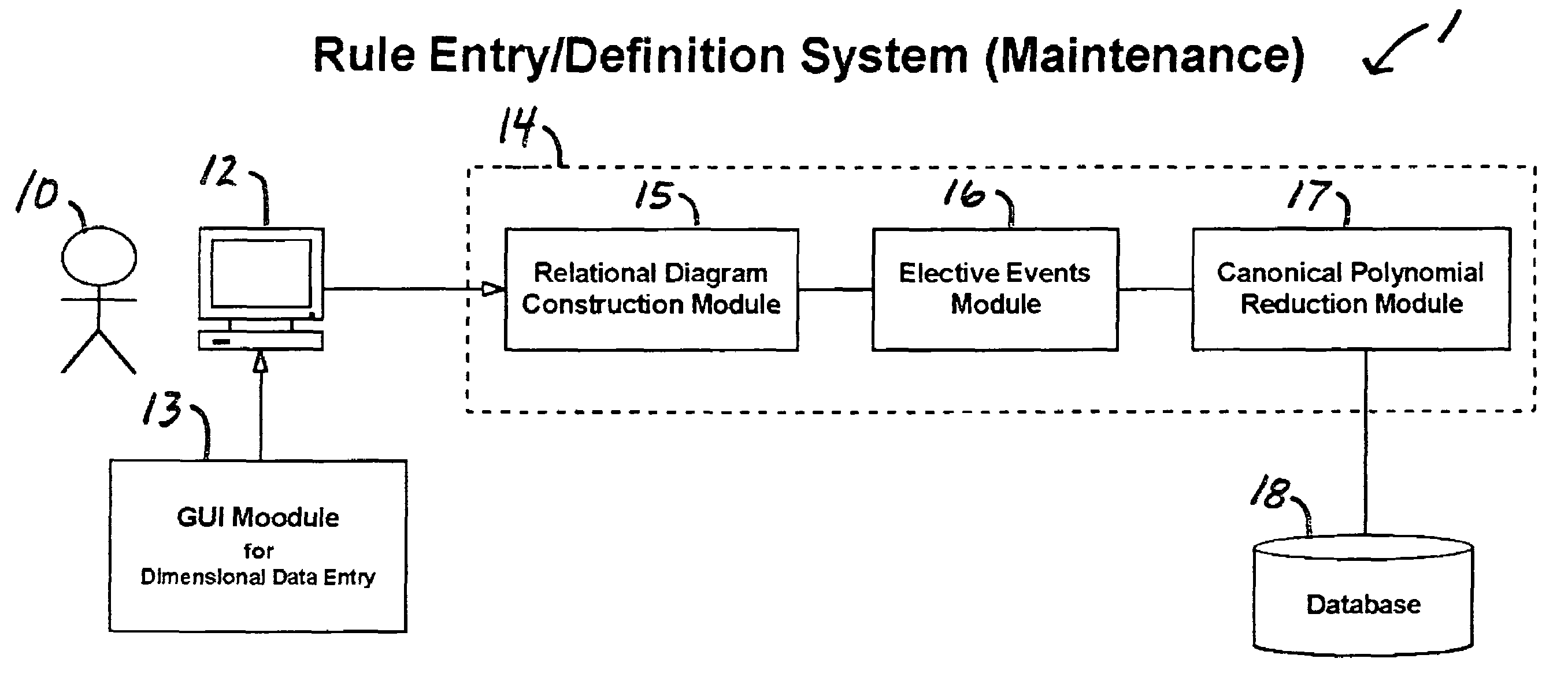
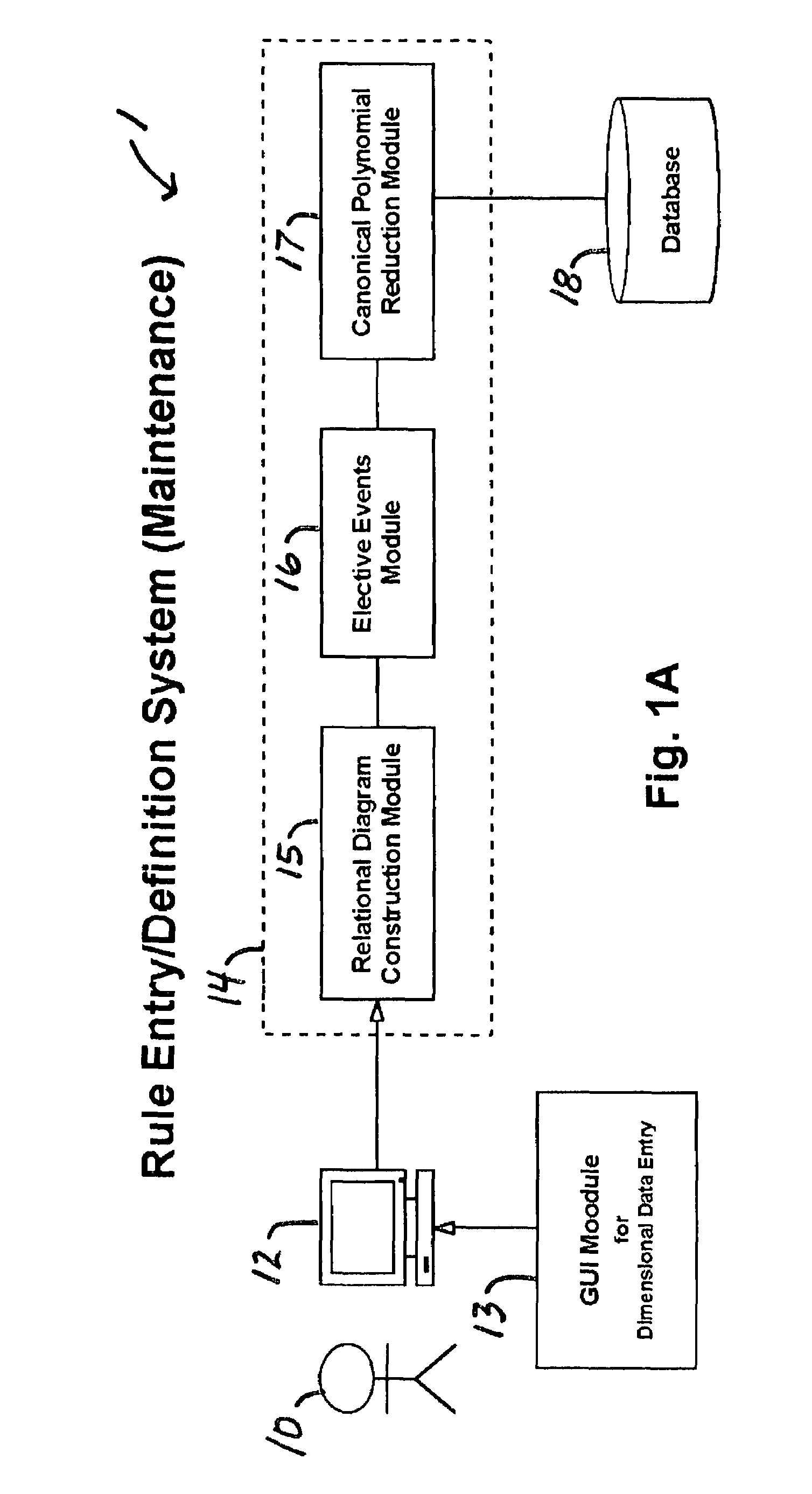
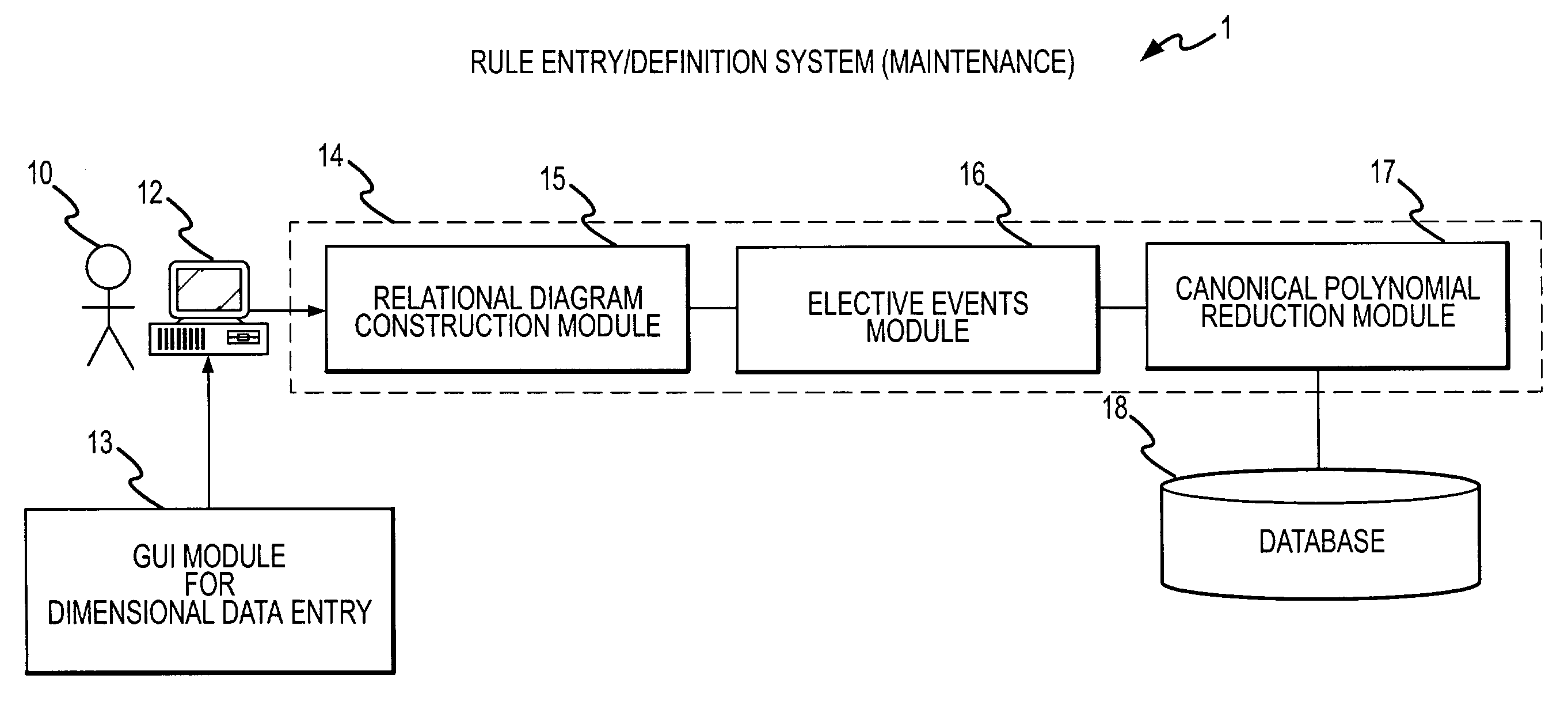
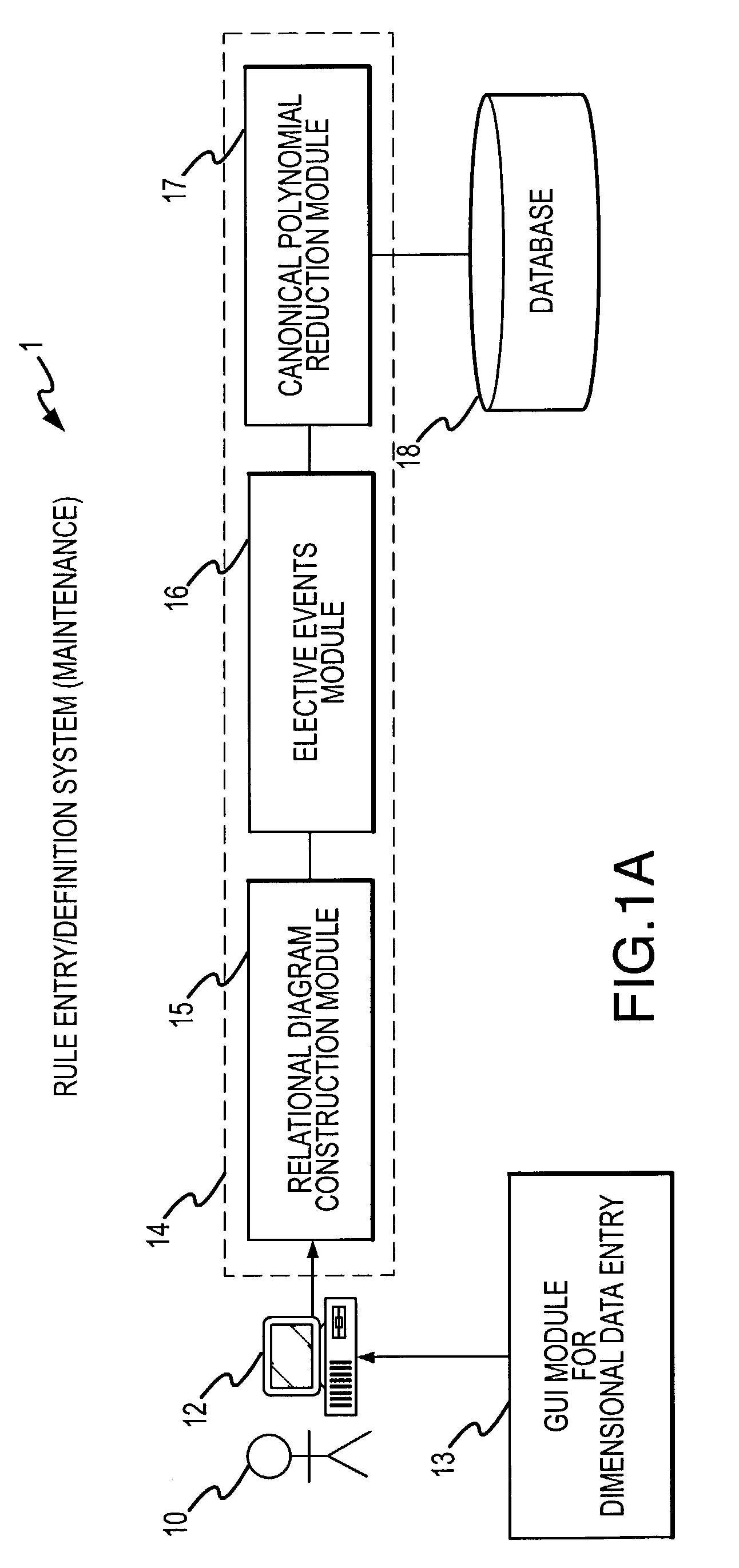
A rule processing apparatus includes modules for defining / entering attributes, enumerations, and / or relationships; packaging the definitions in a reduced canonical form suitable for propositional logic manipulation using zero-suppressed binary decision diagrams (Zdd) to produce a prime Zdd; and / or (iii) executing the rule by applying a series of user inputs to the prime Zdd to determine a result that preferably includes conflict and selection advice to guide the user to satisfaction. Elective events, such as but not limited to the display of messages or the performance of calculations, may optionally be packaged along with the prime rule or components thereof, and presented during execution to help guide the end user to satisfaction or compliancy when choosing among possible selections. The apparatus automates determination of a complex rule having a combinatorial exploded number of rule components, or a combinatorial number of possible outcomes, exceeding computational capacity of present day computing systems.
Owner:MINERAL LASSEN
System and method for preference application installation and execution
InactiveUS7669177B2Improve productivityEasy to understandDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsPersonalizationApplication software
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Rule processing methods for automating a decision and assessing satisfiability of rule-based decision diagrams
InactiveUS6965887B2Exceeding computational capacity of present day computing systemsData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsDecision graphBinary decision diagram
A method of rule processing includes defining / entering attributes, enumerations, and / or relationships; packaging the definitions in a reduced canonical form suitable for propositional logic manipulation using zero-suppressed binary decision diagrams (Zdd) to produce a prime Zdd; and / or (iii) executing the rule by applying a series of user inputs to the prime Zdd to determine a result that preferably includes conflict and selection advice to guide the user to satisfaction. Elective events, such as but not limited to the display of messages or the performance of calculations, may optionally be packaged along with the prime rule or components thereof, and presented during execution to help guide the end user to satisfaction or compliancy when choosing among possible selections. The invention automates determination of a complex rule having a combinatorial exploded number of rule components, or a combinatorial number of possible outcomes, exceeding computational capacity of present day computing systems.
Owner:MINERAL LASSEN
Rule processing system
ActiveUS7188091B2Exceeding computational capacity of computingDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsPresent dayUser input
A rule processing apparatus includes modules for defining / entering attributes, enumerations, and / or relationships; packaging the definitions in a reduced canonical form suitable for propositional logic manipulation using zero-suppressed binary decision diagrams (Zdd) to produce a prime Zdd; and / or (iii) executing the rule by applying a series of user inputs to the prime Zdd to determine a result that preferably includes conflict and selection advice to guide the user to satisfaction. Elective events, such as but not limited to the display of messages or the performance of calculations, may optionally be packaged along with the prime rule or components thereof, and presented during execution to help guide the end user to satisfaction or compliancy when choosing among possible selections. The apparatus automates determination of a complex rule having a combinatorial exploded number of rule components, or a combinatorial number of possible outcomes, exceeding computational capacity of present day computing systems.
Owner:MINERAL LASSEN
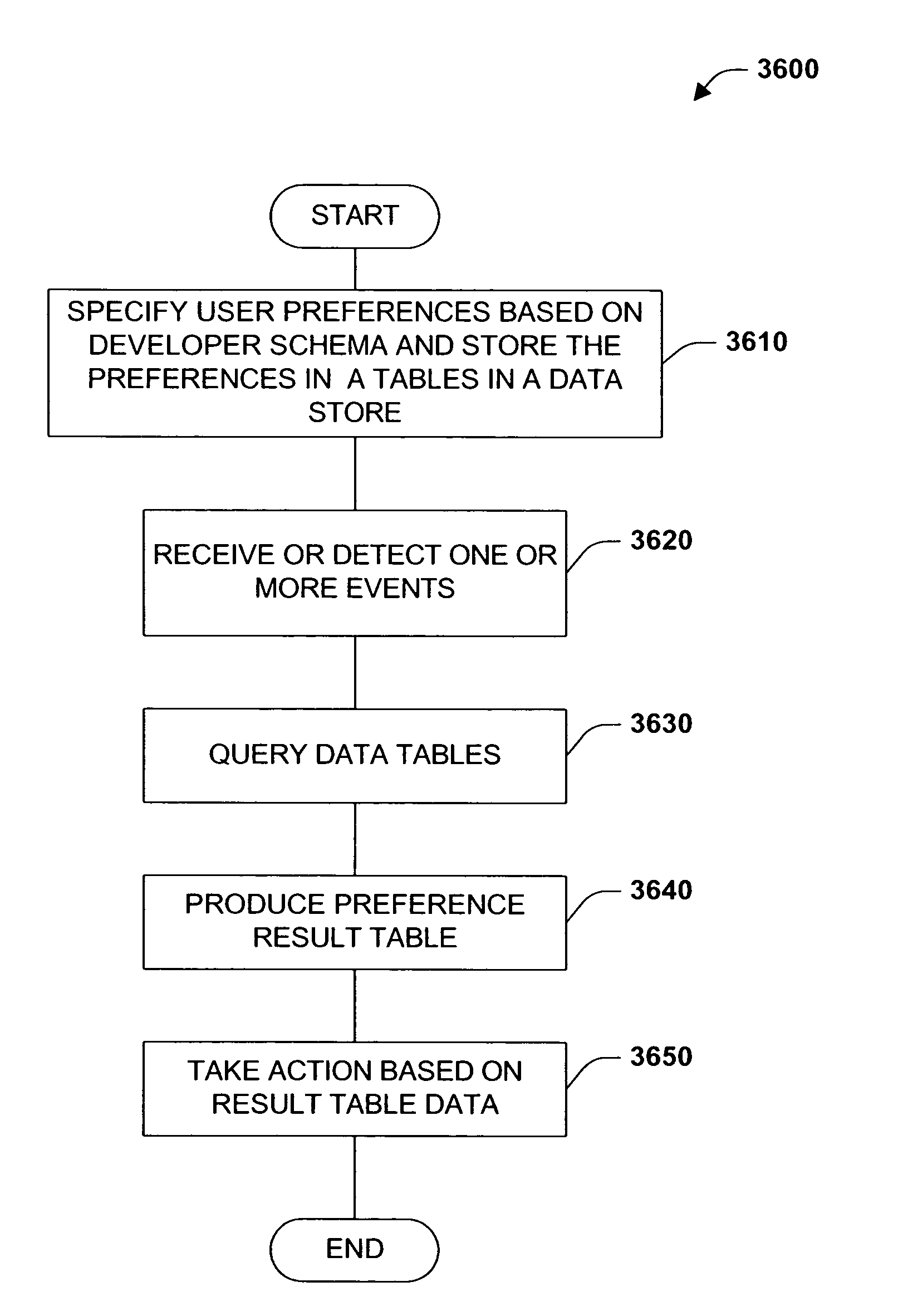
Method and system for capturing business rules for automated decision procession
ActiveUS7587379B2Achieve of complexComplex serviceDigital computer detailsKnowledge representationPresent dayUser input
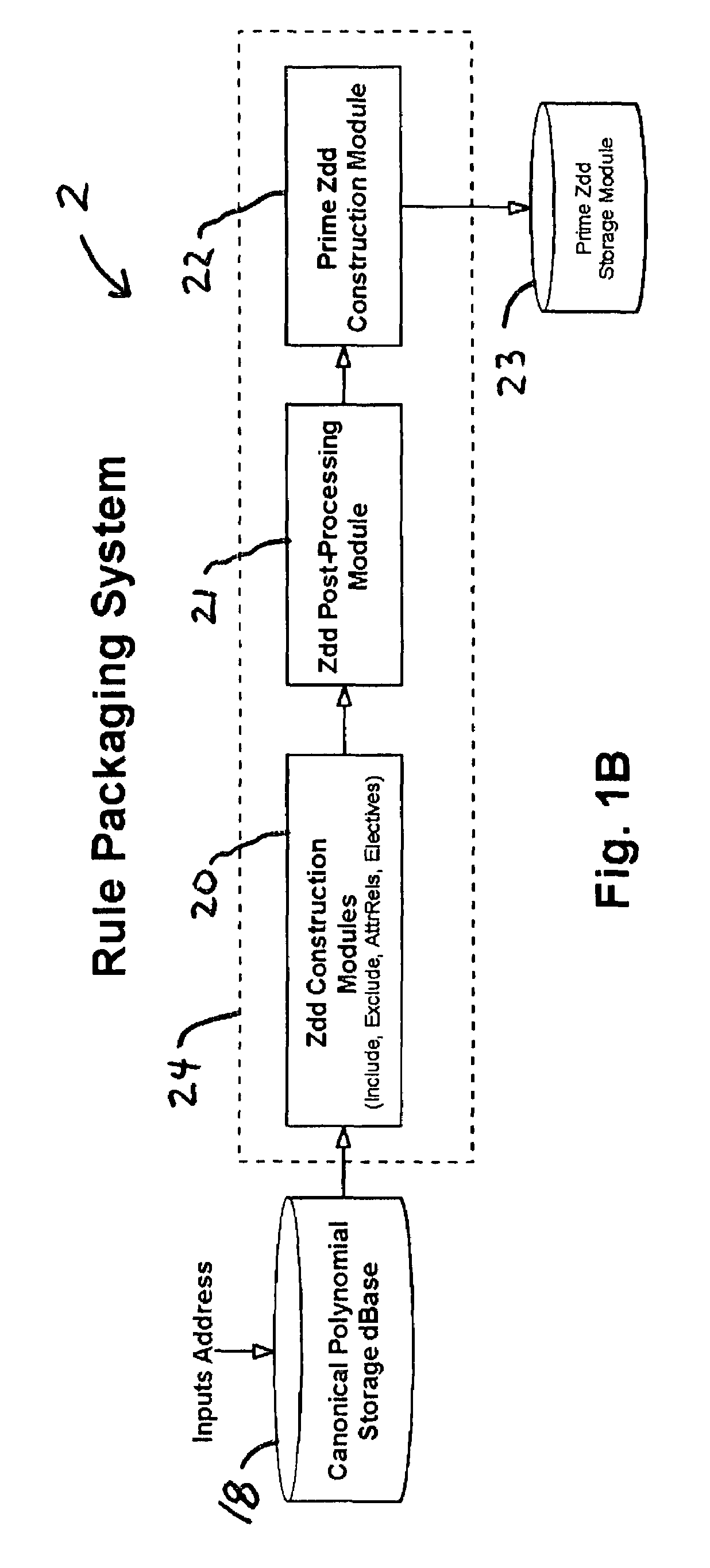
A rule packaging system and method to define and / or package parameters, attributes, enumerations of a prime rule in a reduced canonical form suitable for propositional logic manipulation using, for example, zero-suppressed binary decision diagrams. The reduced form of the prime rule is subsequently used by applying a series of user inputs to determine a result that preferably includes conflict and selection advice to guide the user to satisfaction. Elective events, such as but not limited to the display of messages or the performance of calculations, may optionally be packaged along with the prime rule or components thereof, and presented during execution to help guide an end user to satisfaction or compliancy when choosing among possible configuration parameters. The apparatus automates determination of a complex rule having a combinatorial exploded number of rule components, or a combinatorial number of possible outcomes, exceeding computational capacity of present day computing systems.
Owner:MINERAL LASSEN
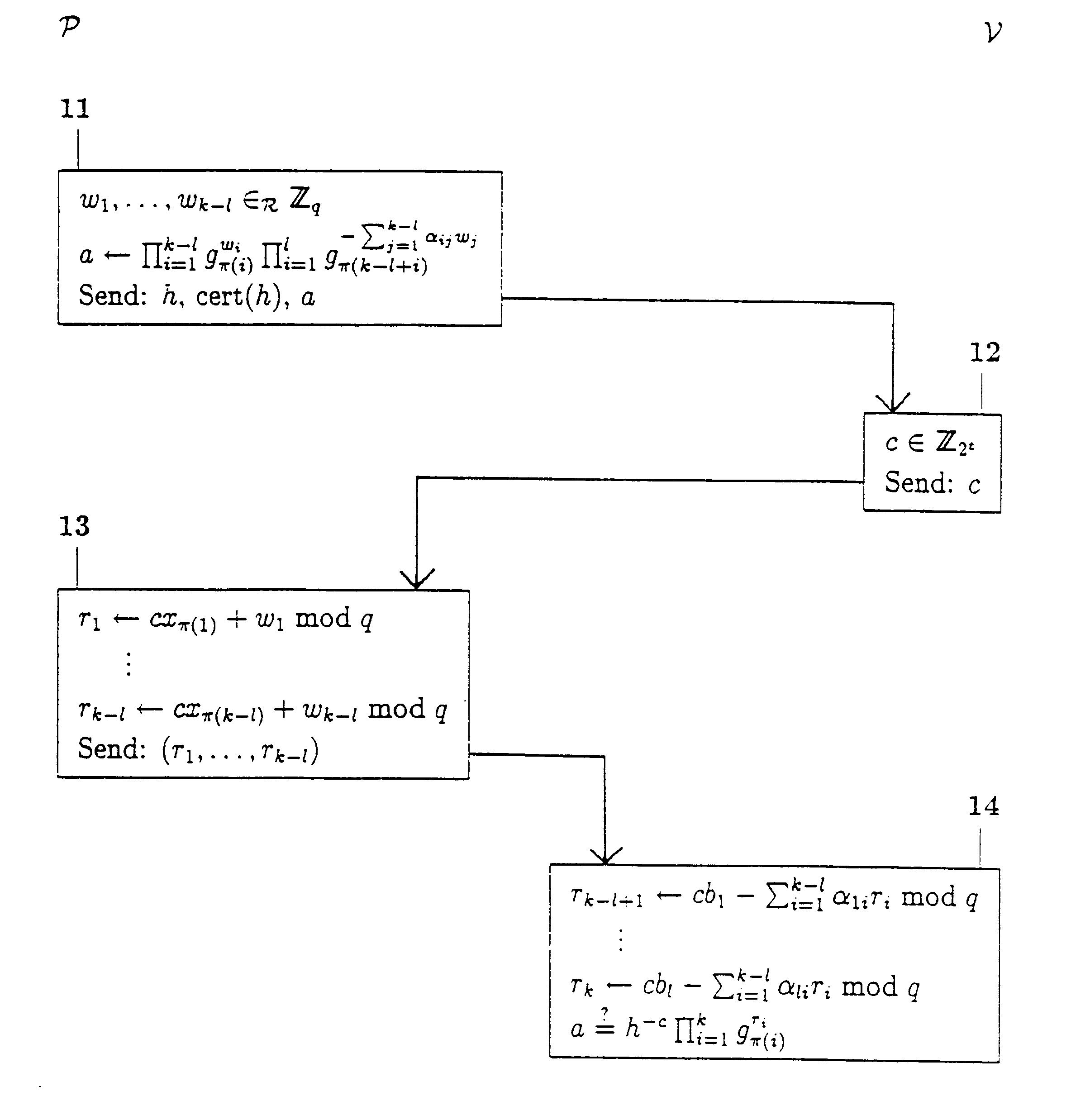
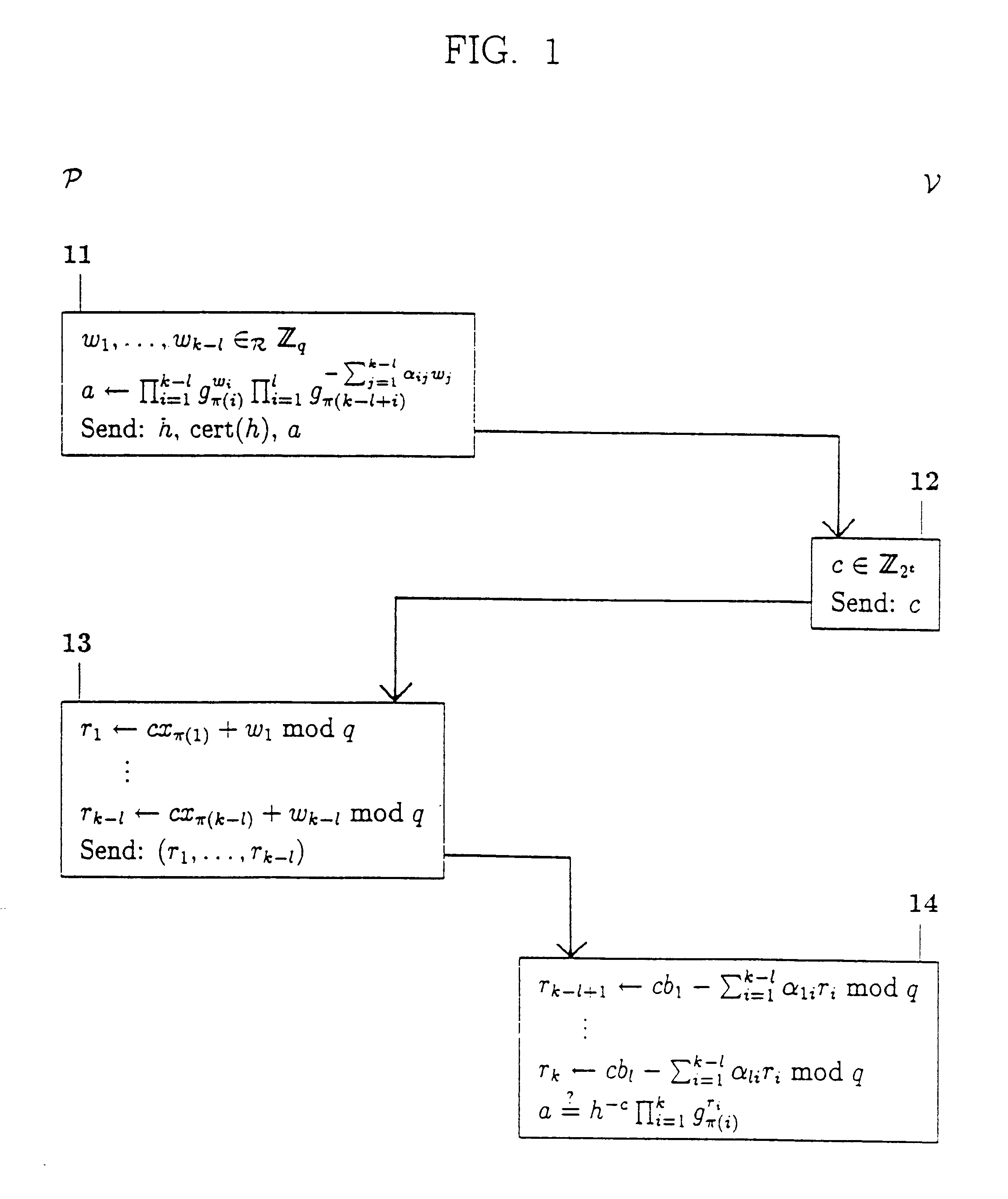
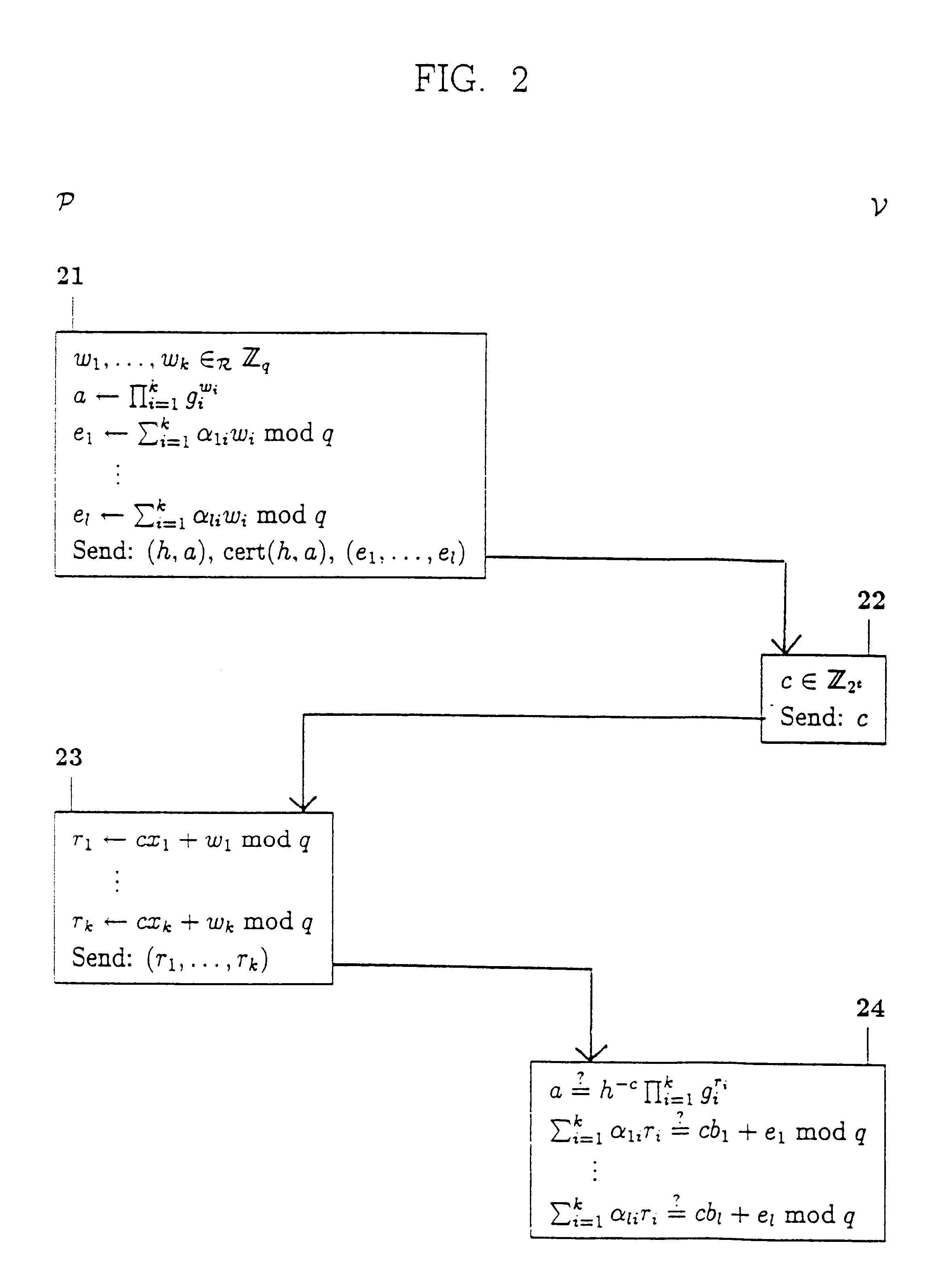
Cryptographic methods for demonstrating satisfiable formulas from propositional logic
InactiveUS6320966B1Improve computing efficiencyRapid assessmentUser identity/authority verificationSecret communicationLinearityComputer science
Owner:ZERO KNOWLEDGE SYST INT INC +1
Web text sentiment analysis method based on propositional logic
InactiveCN103123620AAccurate analysisSmall time complexitySpecial data processing applicationsAnalysis methodContent security
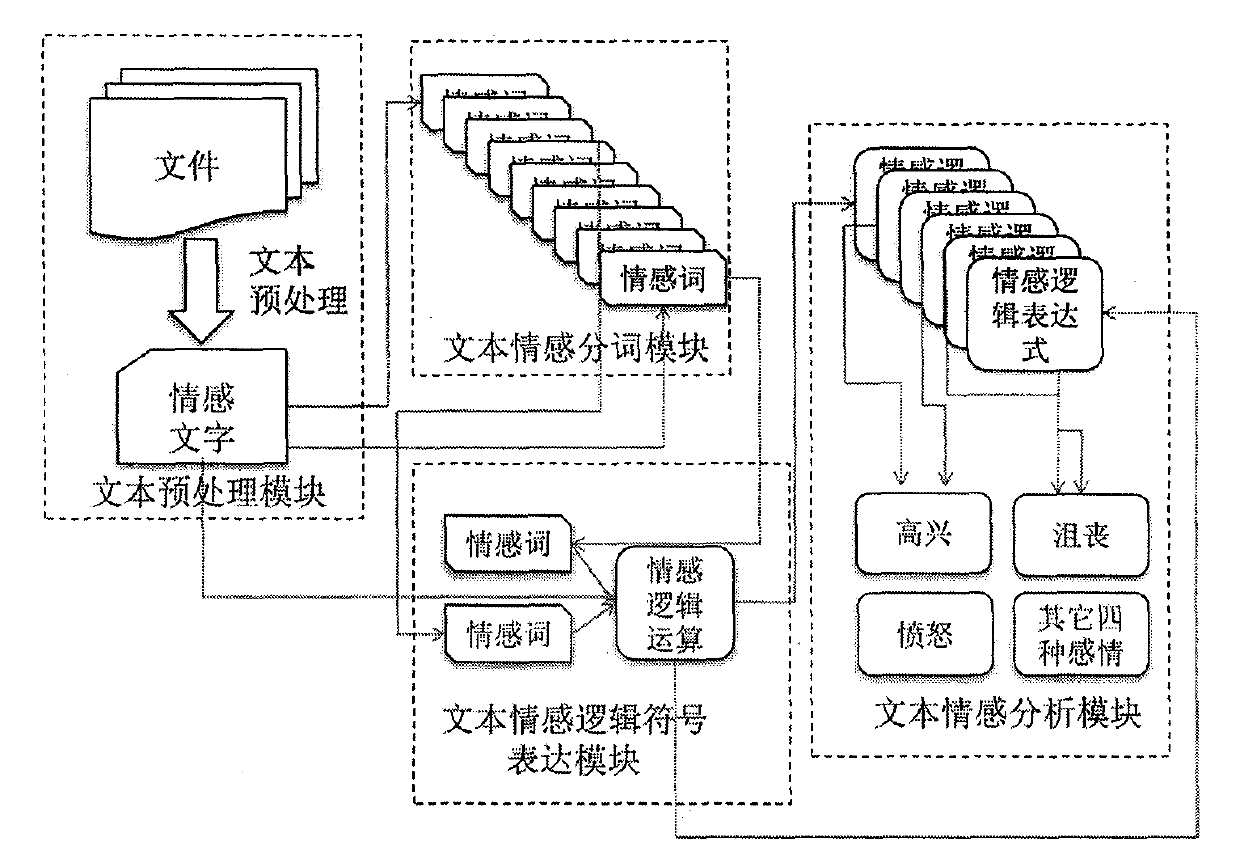
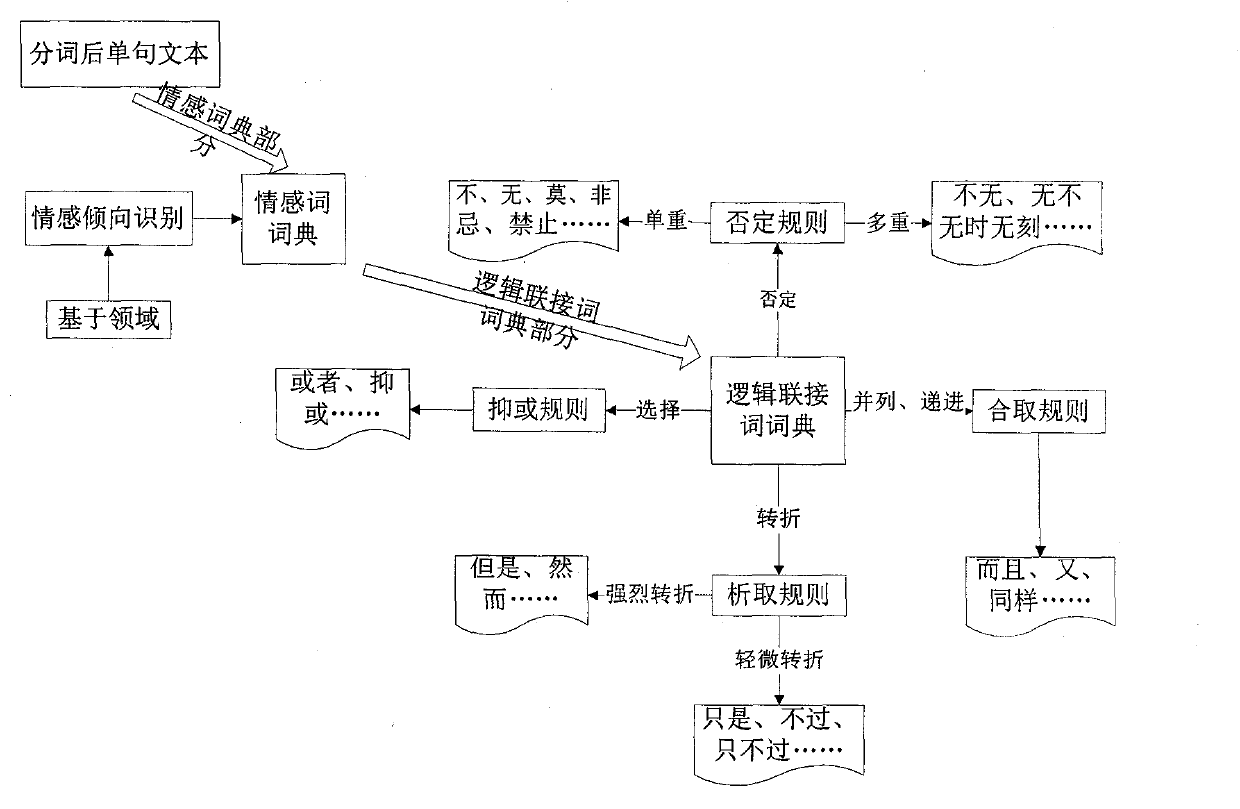
The invention relates to a web text sentiment analysis method based on propositional logic. The web text sentiment analysis method comprises four modules which are respectively text preprocessing, text sentiment word segment, text sentiment logic symbol expression and text sentiment analysis. The web text sentiment analysis method has the functions of conducting standard preprocessing, redundant text information removing such as non-sentiment, logic connecting word extraction, text symbolization, clause sentiment tendency analysis, sentiment quantitative analysis, sentiment tendency calculation, full text sentiment analysis and the like to a web text, extraction and quantitative analysis of sentiment words are achieved, and the web text sentiment analysis method plays an important role in sentiment finding application, public sentiment searching application, content safety application, search engine application and the like.
Owner:中国互联网新闻中心 +1
Propositional-logic-based principle feature analysis method and system in data mining
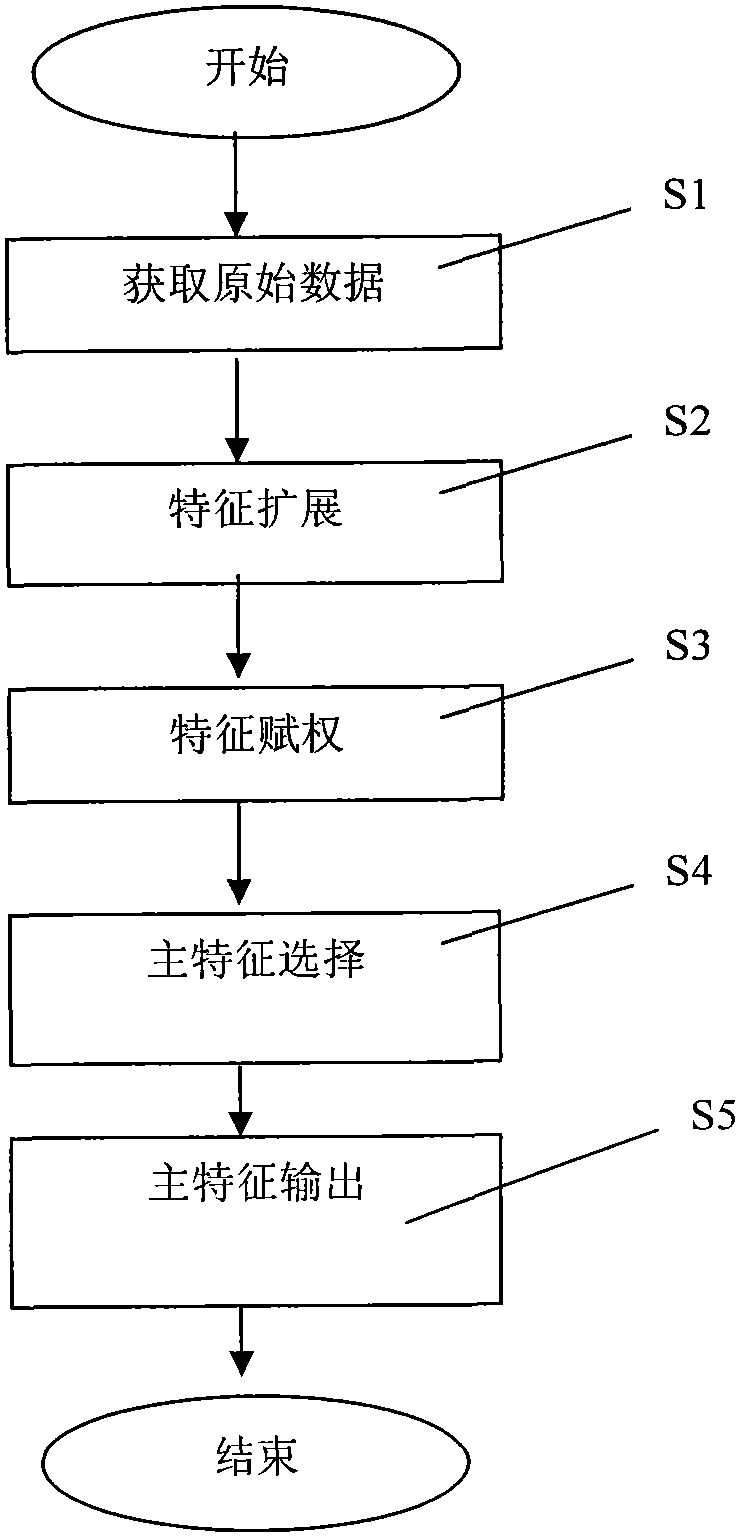
ActiveCN103425716AReduce processing timeEasy to handleSpecial data processing applicationsData dredgingFeature set
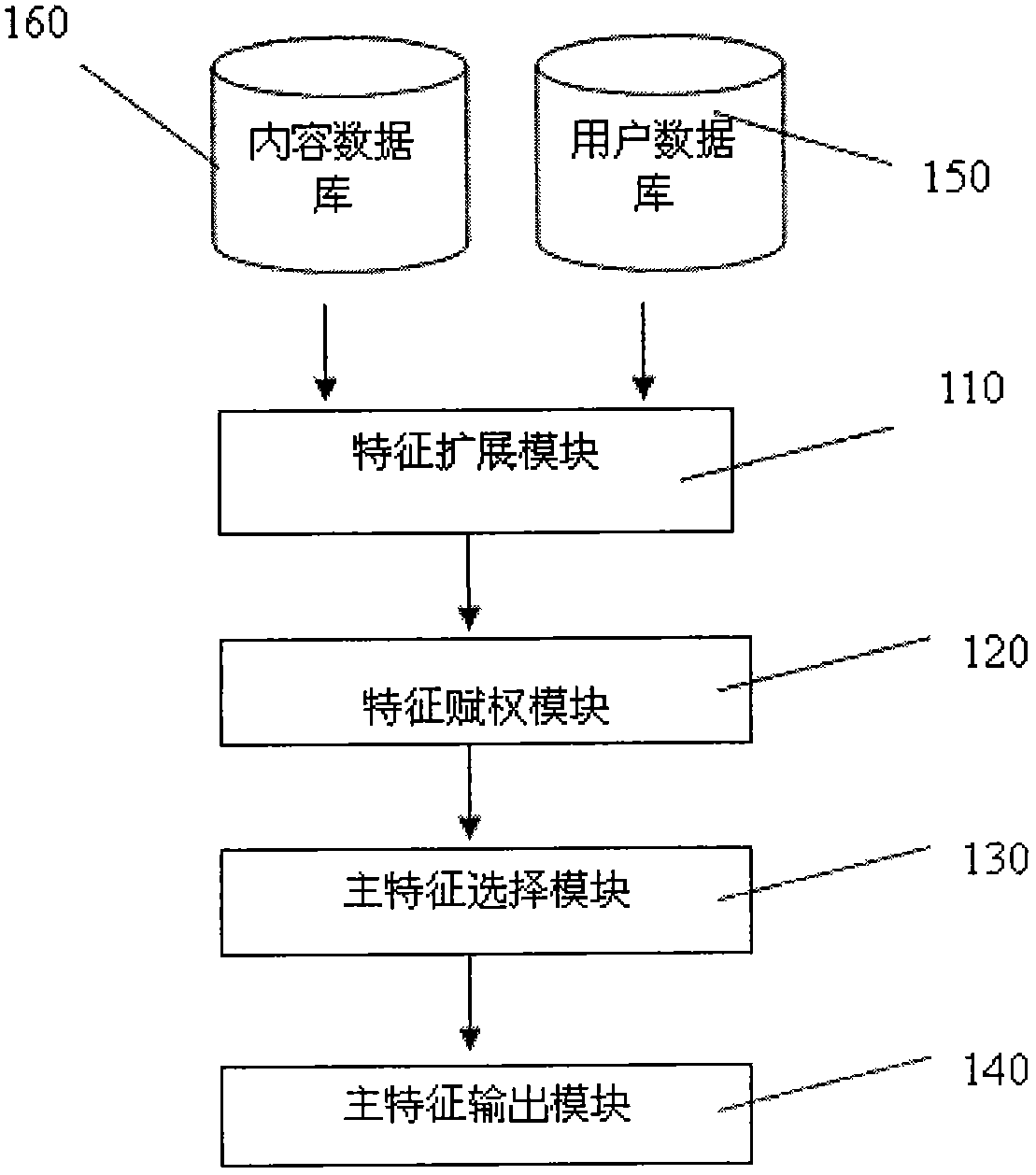
The invention discloses a propositional-logic-based principle feature analysis method and system in data mining. The principle feature analysis method comprises the following steps of feature extension of extendingly describing the feature sets of content data through propositional logic to form a content data extended feature set; feature weight setting of analyzing the use history and the content data of a user through a content-based data mining and collaborative filtering method to set the important weight of the features; principle feature selection of selecting principle features from the extended feature set according to input content sets and the weight of the features and outputting the principle features. Through the calculation of the extension and the weight of features, the propositional-logic-based principle feature analysis method and system in data mining can select out and output the principle features to find the generality of data and expresses the data in extended features with richer meanings to provide effective support for subsequent data mining treatment.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Method for setting up knowledge map and navigating disciplinary knowledge
InactiveCN104463330AFacilitate automatic reasoningKnowledge representationInference methodsBoolean networkData science
A method for setting up a knowledge map comprises the steps that propositions are used as nodes, implication operators used for showing logical relations between the propositions are linked with the nodes, a special Boolean network is formed, and the knowledge map is set up. The logical relations are the relations between logical connectors and Boolean functions, and the implication operators comprise binary implication operators, ternary implication operators and multivariate implication operators. The method extends the working method of a propositional logic, and develops an undirected acyclic graph knowledge expressive method having nothing to do with specific application scenes, and automatic reasoning of knowledge of the mathematics and sciences can be more conveniently achieved.
Owner:刘泊荣
Reachability analysis method of hybrid system
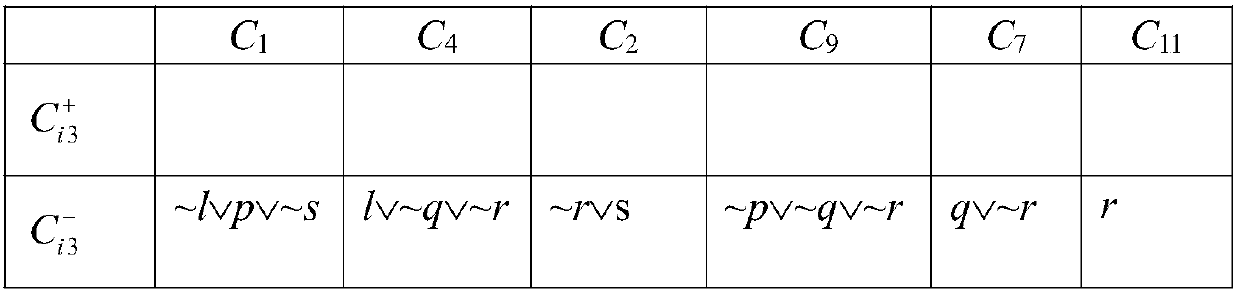
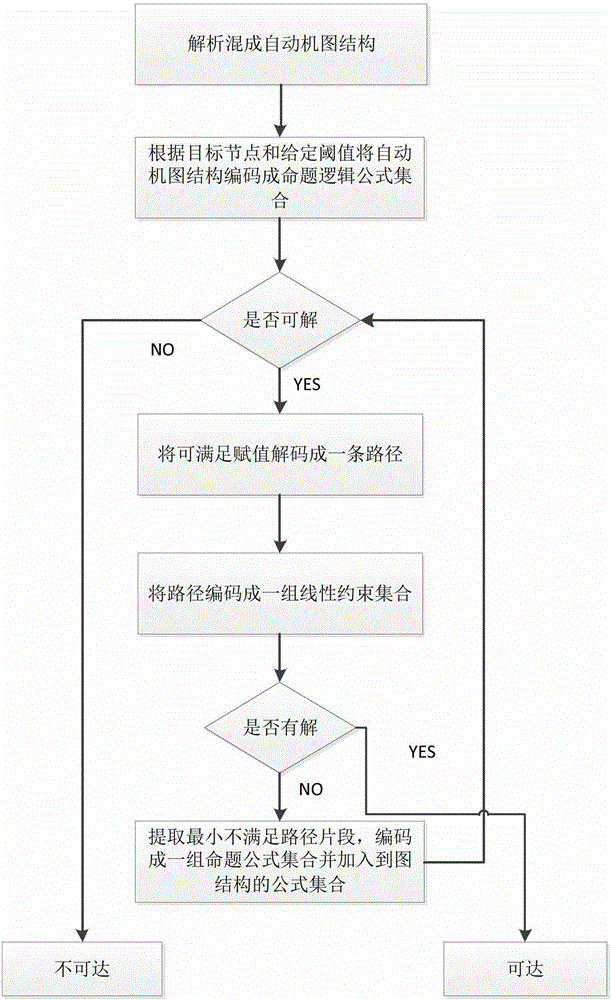
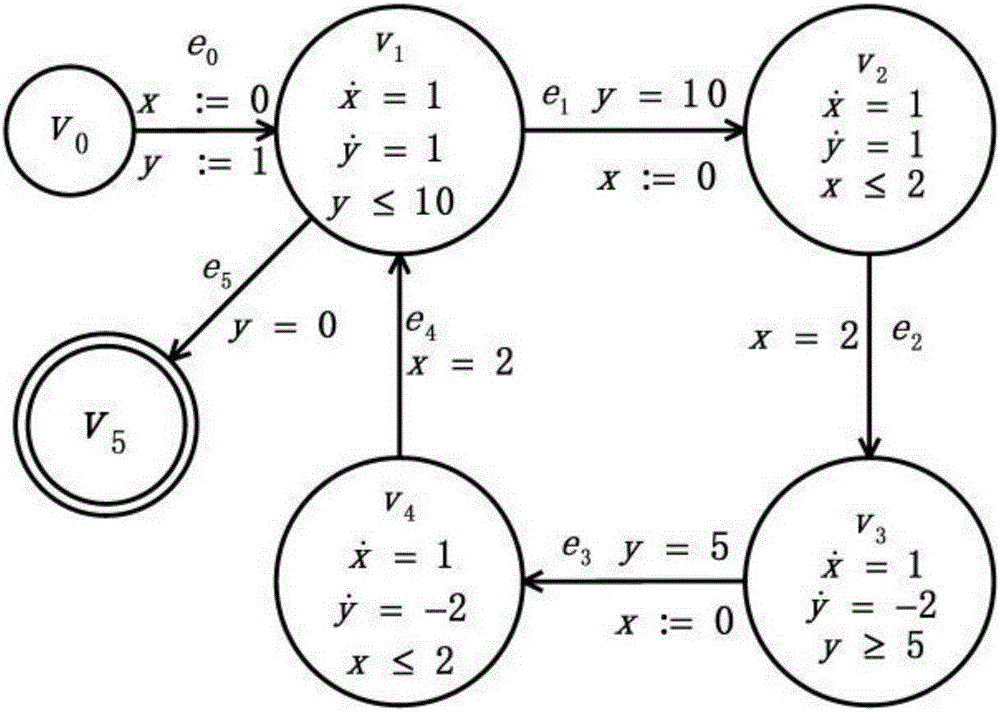
ActiveCN103400025AShorten the timeReduce memory usageSpecial data processing applicationsReachabilityHybrid automaton
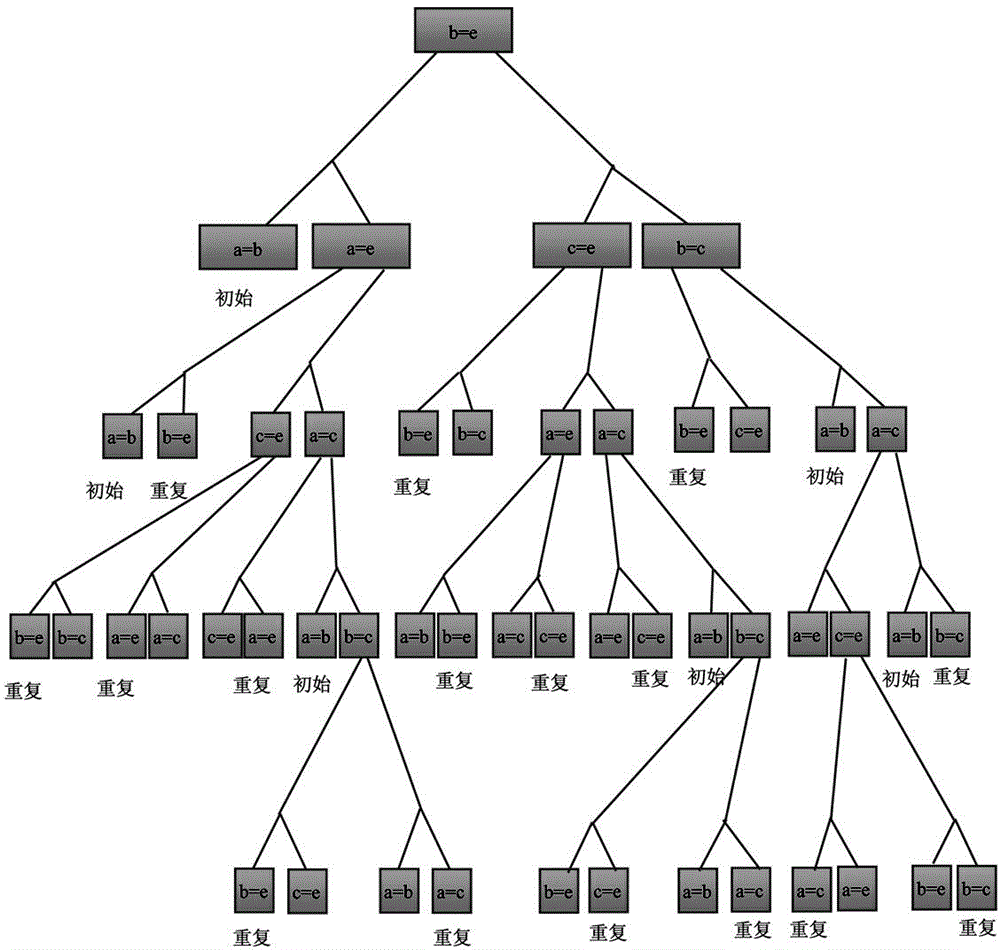
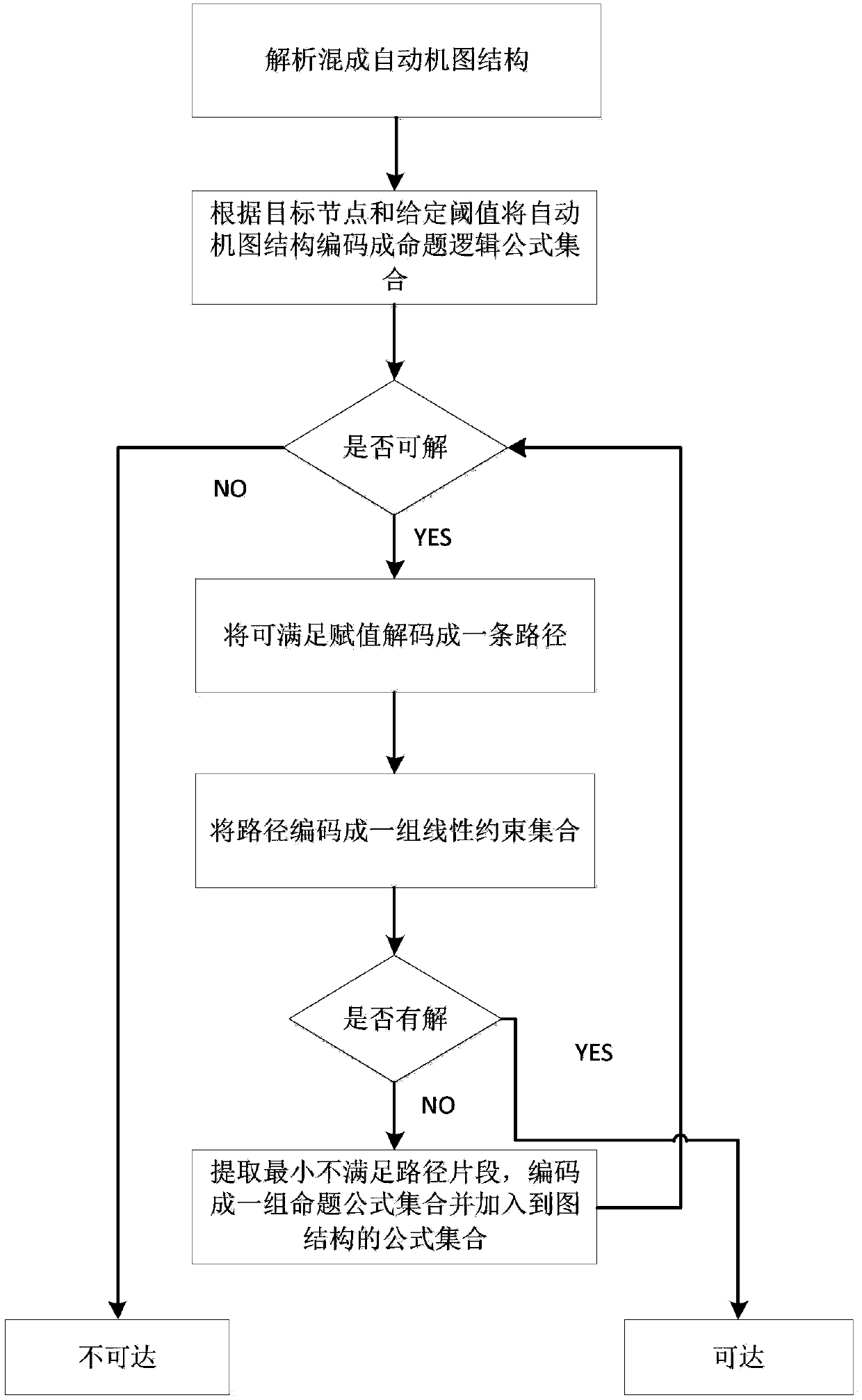
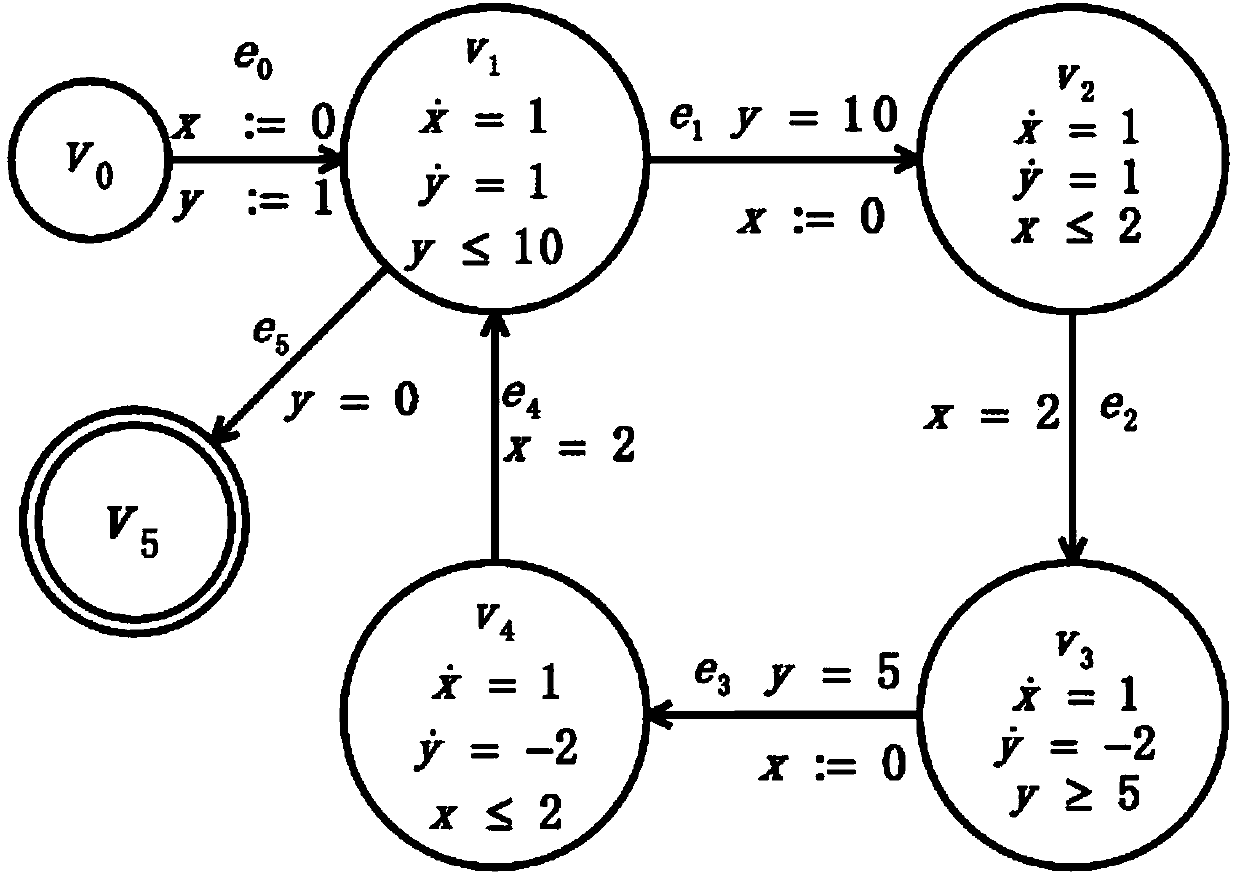
The invention provides a reachability analysis method of a hybrid system. The reachability analysis method comprises the following steps that input files of a hybrid automaton are analyzed, and the bounded figure structure of the automaton is encoded into a propositional logic formula set; an SAT solver is used for solving the formula set, if the formula set can not be solved, an output result is insoluble, and if the output result is soluble, an assignment capable of being met is decoded to be a path on the figure structure of the automaton; a target path is encoded to form linear constraint according to the meaning of the hybrid automaton; the linear constraint is solved, if the linear constraint is soluble, the path is output as a result, and if the linear constraint is insoluble, a next step is turned; an irreducible and insoluble set of the linear constraint is given; an unreachable path is encoded into the propositional logic formula set and then is added into the formula set of the figure structure of the automaton. The reachability analysis method is used so that the candidate path for reaching a target node can be quickly found out, and the time for searching the figure structure of the hybrid automaton can be shortened.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
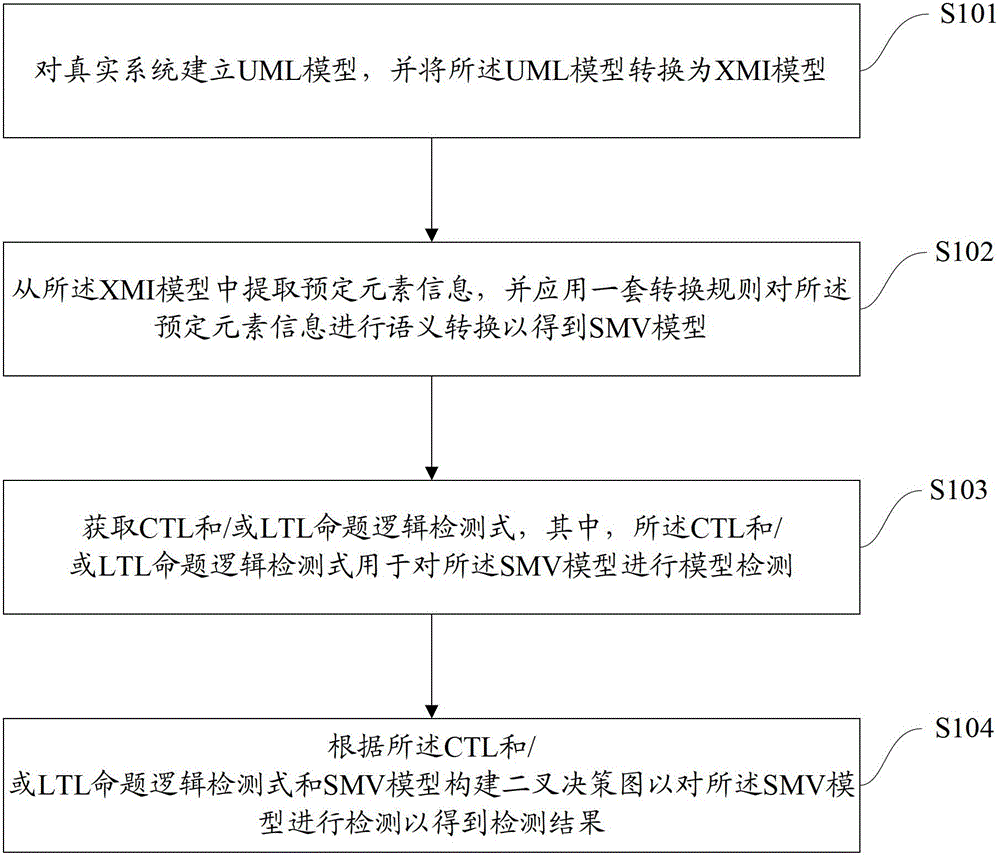
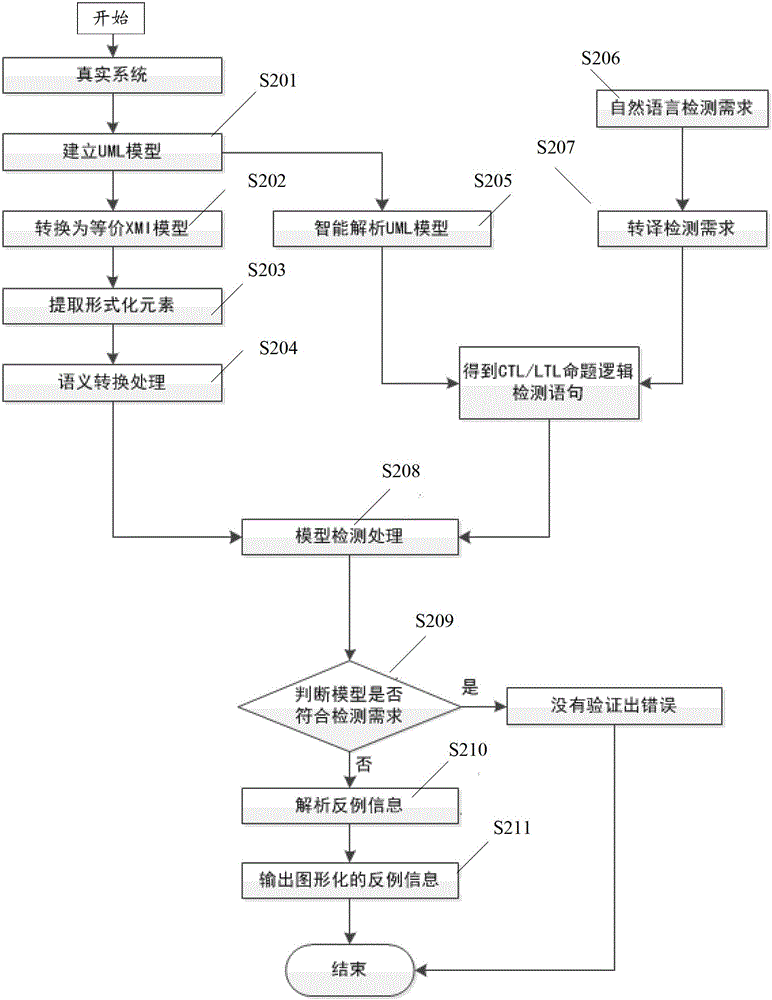
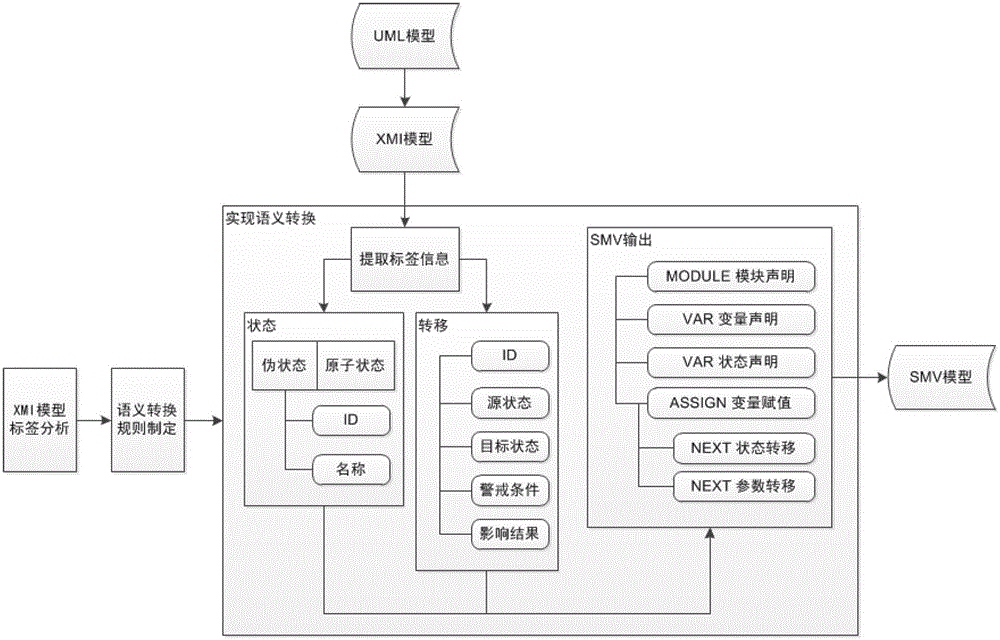
Formalized detection method of intelligent UML (Unified Modeling Language) model and device
ActiveCN102722441AImprove user experienceGood application effectSoftware testing/debuggingSoftware development processBinary decision diagram
The invention provides a formalized detection method of an intelligent UML (Unified Modeling Language) model and a device. The method comprises the steps of: establishing an UML model for a true system and converting the UML model into an XMI (Extensible Markup Language) model; extracting predetermined element information from the XMI model and converting the predetermined element information semantically to obtain an SMV (Symbolic Modeling Verification) model by applying a set of conversion rule; acquiring an CTL (Complementary Transistor Logic) and / or an LTL (Linear Temporal Logic) propositional logic detection formula, wherein the CTL and / or LTL propositional logic detection formula are / is used for detecting the SMV model; and constructing a binary decision diagram according to the CTL and / or LTL propositional logic detection formula and the SMV model to detect the SMV model so as to obtain a detection result. According to the embodiment disclosed by the invention, the formalized detection method has the advantages of high detection accuracy and wide application, and can comprehensively detect the UML model which has higher demand on safety in a software development process.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
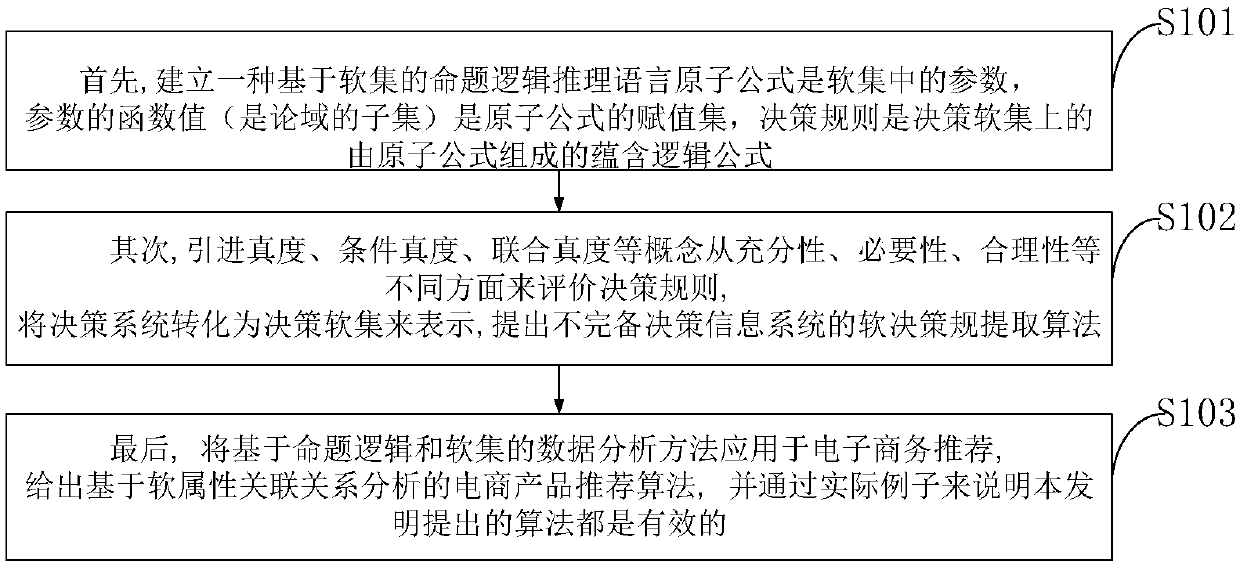
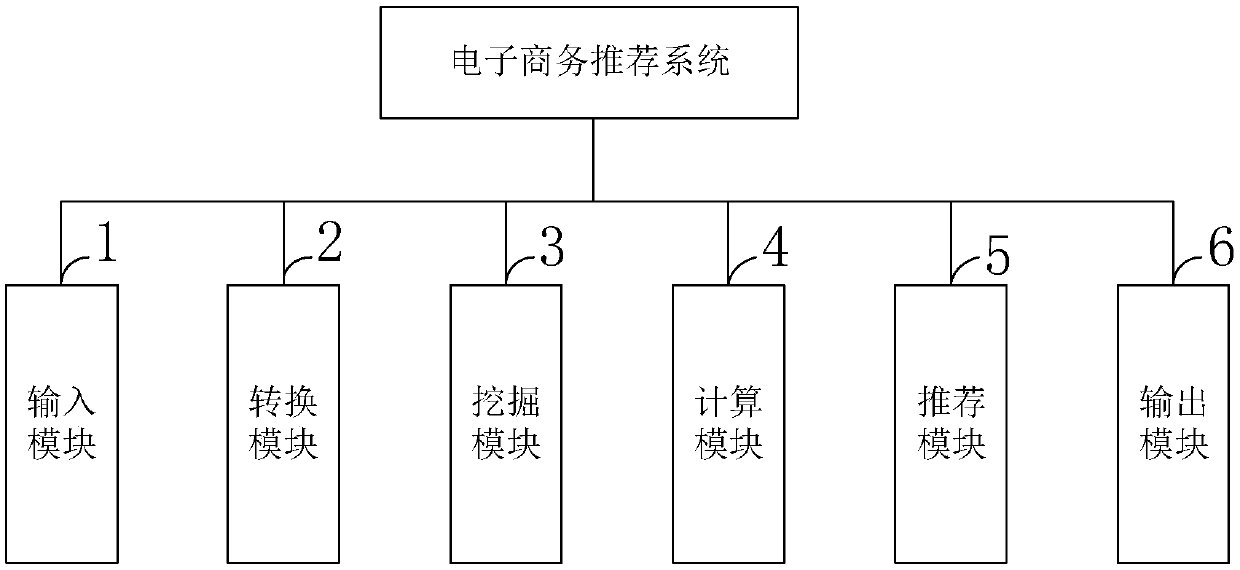
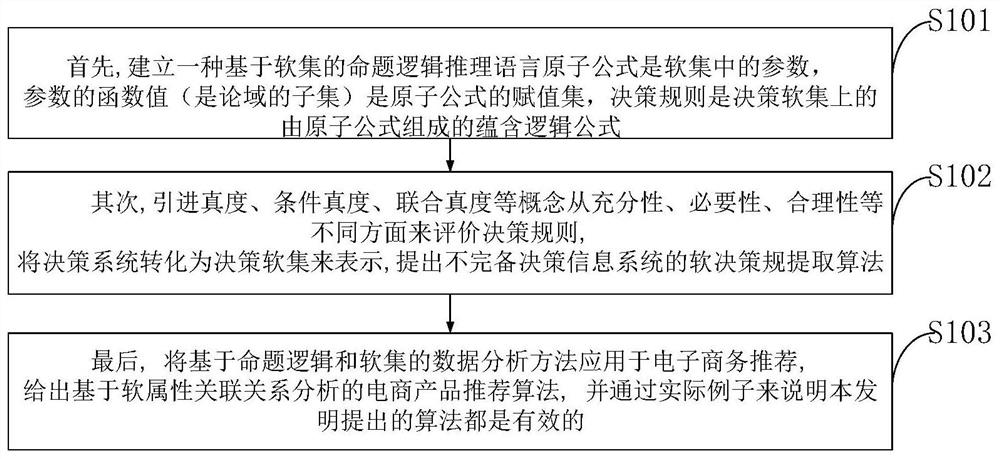
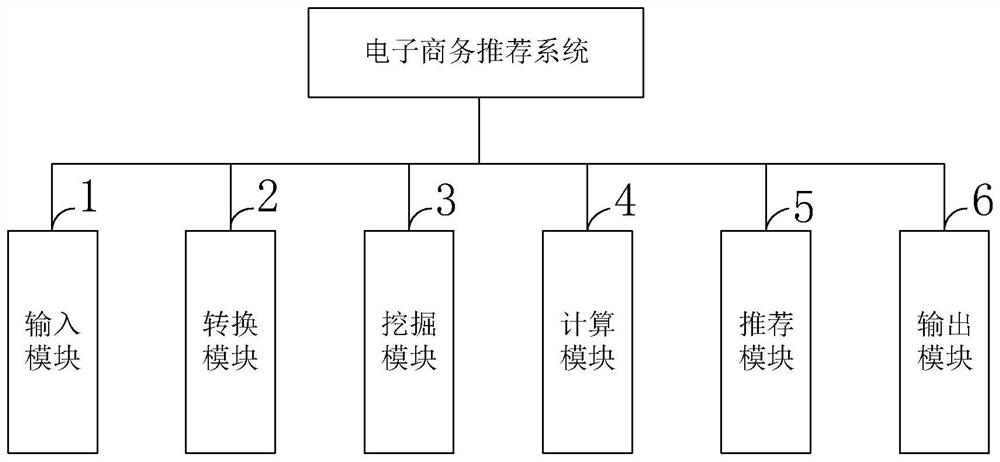
E-commerce recommendation technology and system based on soft-set decision rule analysis
ActiveCN108133407AInnovativeNovel method constructionVisual data miningStructured data browsingValue assignmentHuman language
The invention belongs to the technical field of computers, and discloses an e-commerce recommendation technology and system based on soft-set decision rule analysis. A propositional logical reasoninglanguage based on soft sets is established, and in the reasoning language, an atomic formula is a parameter e in a soft set, a function value F(e) of the parameter e is a value assignment set of the atomic formula e, and a soft decision rule is an implicit logical formula formed by atomic formulas on a decision soft-set; quantitative indexes of soft truth degrees, conditional soft truth degrees, joint soft truth degrees, soft similarity degrees, logical soft degrees and the like are introduced to evaluate soft decision rules from different aspects of adequacy, necessity and rationality; a decision system is transformed into the decision soft set, and a soft-decision-rule extraction method of the incomplete decision system is provided; and a data analysis method based on propositional logicand the soft set is applied to e-commerce recommendation. Through practical examples of the invention, it is illustrated that the methods provided by the invention are all effective; and theoreticalanalysis of the technology has innovativeness, method construction novelty and technical-means practicability.
Owner:XIANGNAN UNIV
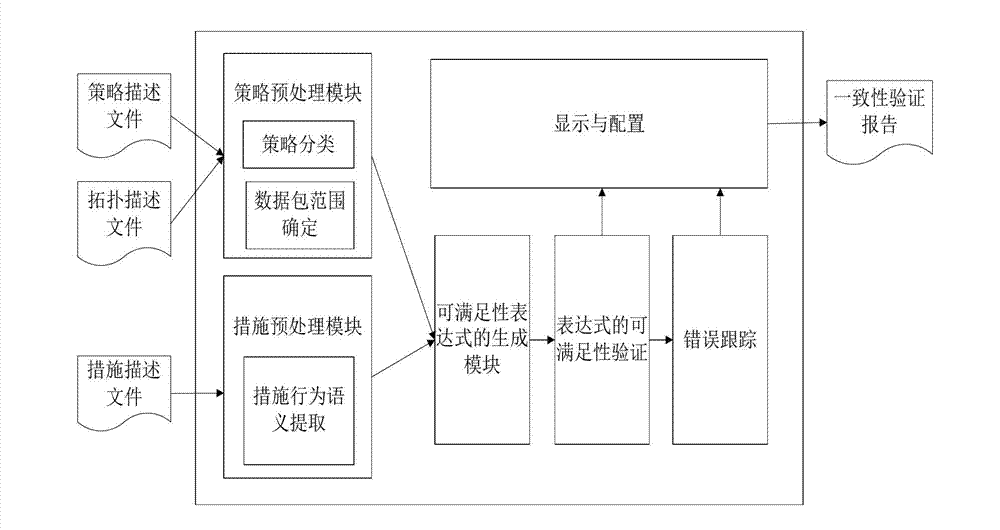
Transition consistency verification method of computer network defending strategy
InactiveCN103116670APrecise positioningNo state explosion problemPlatform integrity maintainanceSpecial data processing applicationsDecision toolProtection domain
Disclosed is a transition consistency verification method of a computer network defending (CND) strategy. The steps are as follows: (1) strategy preprocessing is firstly carried out; the input strategy description files and topology description files are analyzed through a lexical analyzer and a grammar analyzer generated by a lex (lexical analyzer) / yacc (yet another compiler compiler) tool, and a data package range of processing actions of each kind is obtained. A corresponding subject and a corresponding object are elaborated; (2) then measure preprocessing is carried out: the input measure description files are analyzed through the lexical analyzer and the grammar analyzer generated by the lex / yacc tool so as to confirm a protection domain managed by the equipment, irrelevant configuration rules are removed, and the data package range processed by the regulated actions is taken out; (3) data package ranges of actions of various kinds are formed in logical expressions, and the logical expressions correspond to related safety equipment. Solving of a property decision tool Yices can be met by propositional logic, all the data package ranges are browsed, and whether redundancy or deficiency of the measures exists is detected.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Boolean satisfiability judgment method based on linear programming
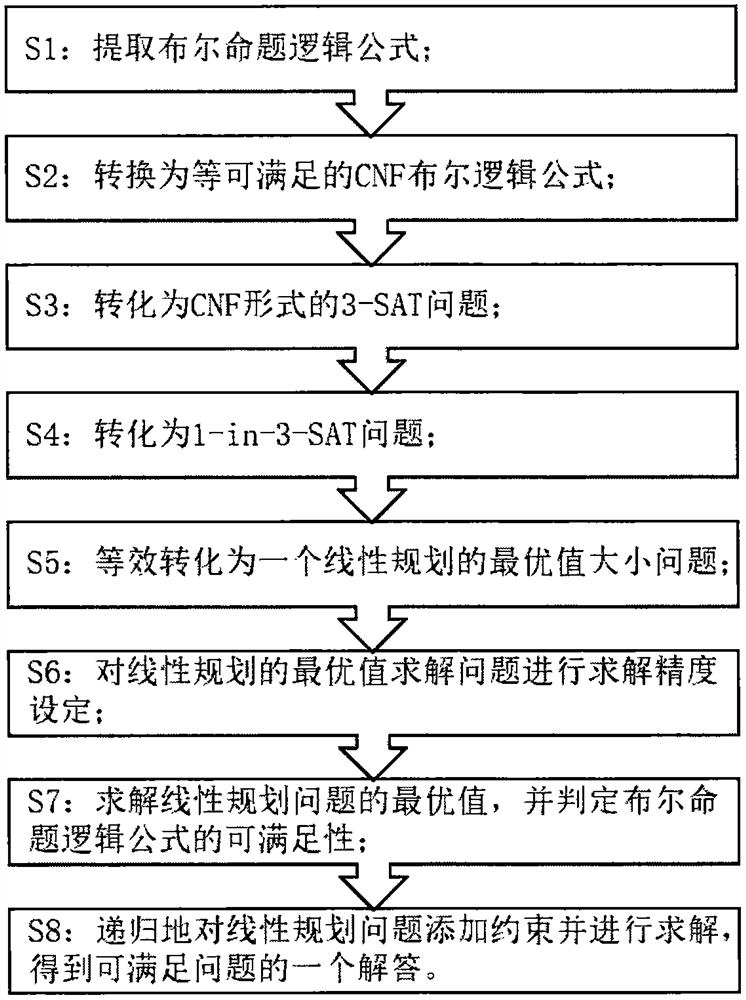
PendingCN114091392AQuick judgmentImprove efficiencyComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsRound complexitySat problem
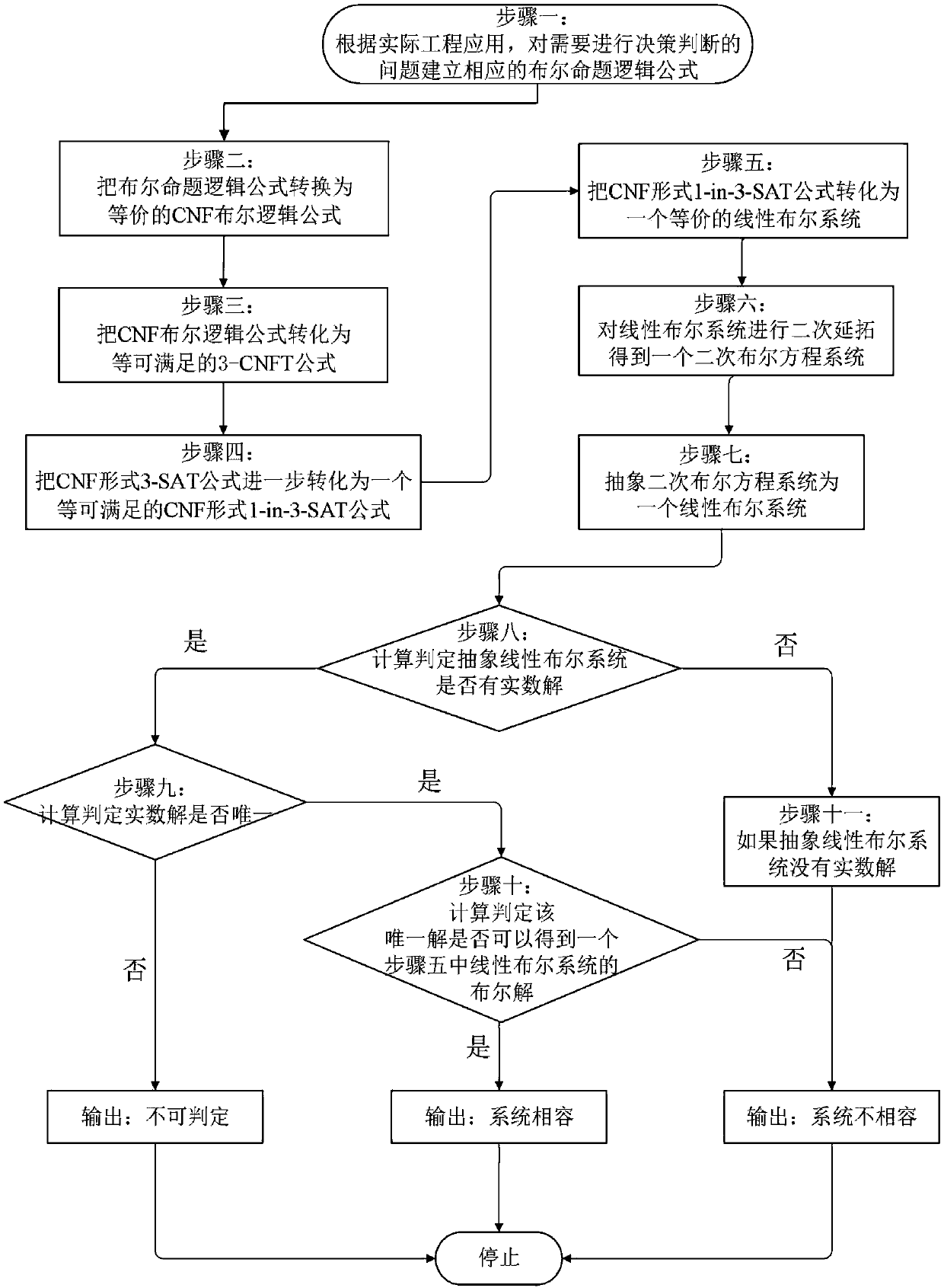
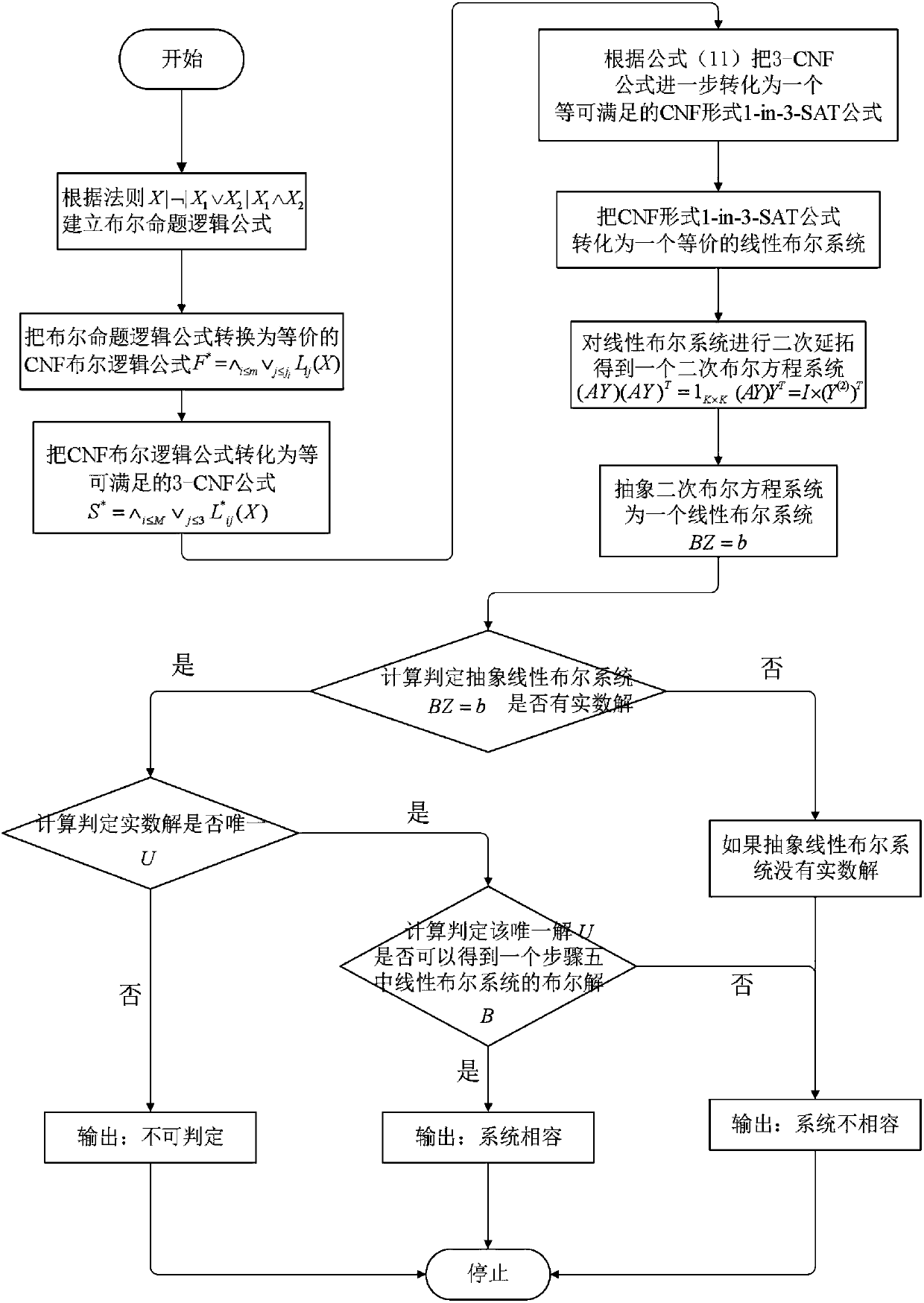
The invention relates to a Boolean satisfiability judgment method based on linear programming, which belongs to the field of logic circuits, and comprises the following steps: S1, extracting a Boolean proposition logic formula; S2, converting into a CNF Boolean logic formula which can be satisfied; S3, converting the problem into a 3-SAT problem in a CNF form; S4, converting the problem into a 1-in-3-SAT problem; S5, equivalently converting into an optimal value problem of linear programming; S6, solving precision setting is carried out on an optimal value solving problem of linear programming; S7, solving the optimal value of the linear programming problem, and judging the satisfiability of the Boolean proposition logic formula according to the optimal value; and S8, for the satisfactory Boolean proposition logic formula, recursively adding constraints to the linear programming problem and solving the linear programming problem to obtain an answer of the satisfactory problem. Rapid judgment under the polynomial time complexity is realized, the judgment efficiency can be improved, and energy is saved.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
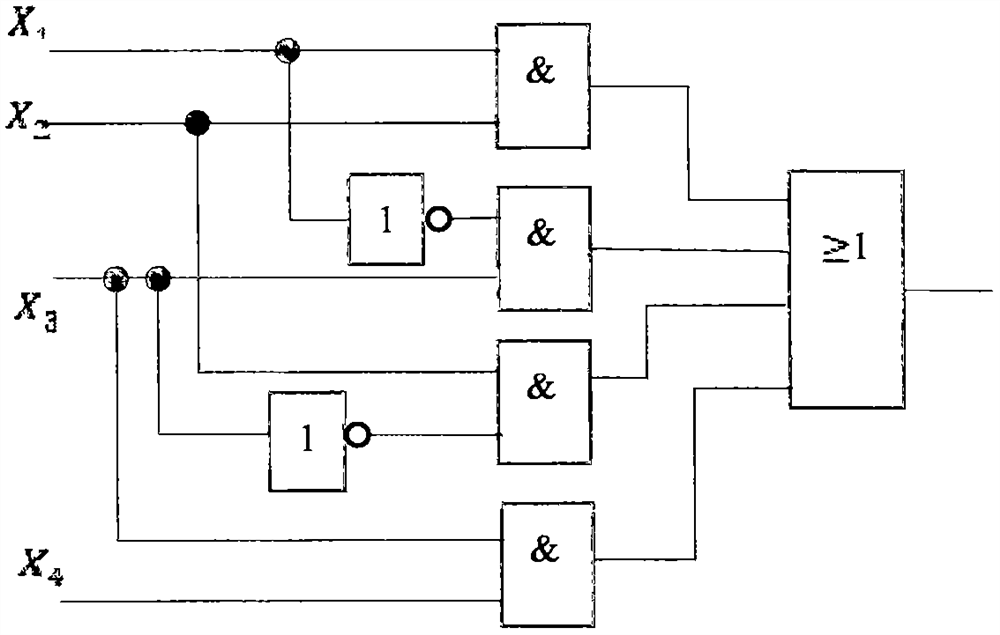
Algebraic-based fast logic decision-making method
InactiveCN107945275AImprove efficiencySave energy3D modellingComputer graphicsElectronic design automation
The invention relates to an algebraic-based fast logic decision-making method, and belongs to the field of computers. According to the method, the inner nature and secondary invariant properties of the boolean value are fully utilized, and an abstract extraction technology is adopted to turn the satisfaction problem of a boolean propositional logic into a problem for solving a linear equation set,so that the non-satisfaction logic decision problem can be rapidly judged under the complex degree of the polynomial time. Meanwhile, the core technical support is provided for fast judging whether the logic decision-making problem can be met. The method can be applied to artificial intelligence, robots, automatic reasoning, logic planning, graph matching, network structure comparison, computer-aided manufacturing, computer graphics, computer system structure design, electronic design automation, database system and the scheduling optimization and the like can be realized, the efficiency canbe improved, and the energy can be saved.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
An Automatic Verification Method for Synchronous Language Programs Based on Satisfiability Solving
ActiveCN112269734BTroubleshoot auto-authentication issuesResolve verificationSoftware testing/debuggingData streamTerm memory
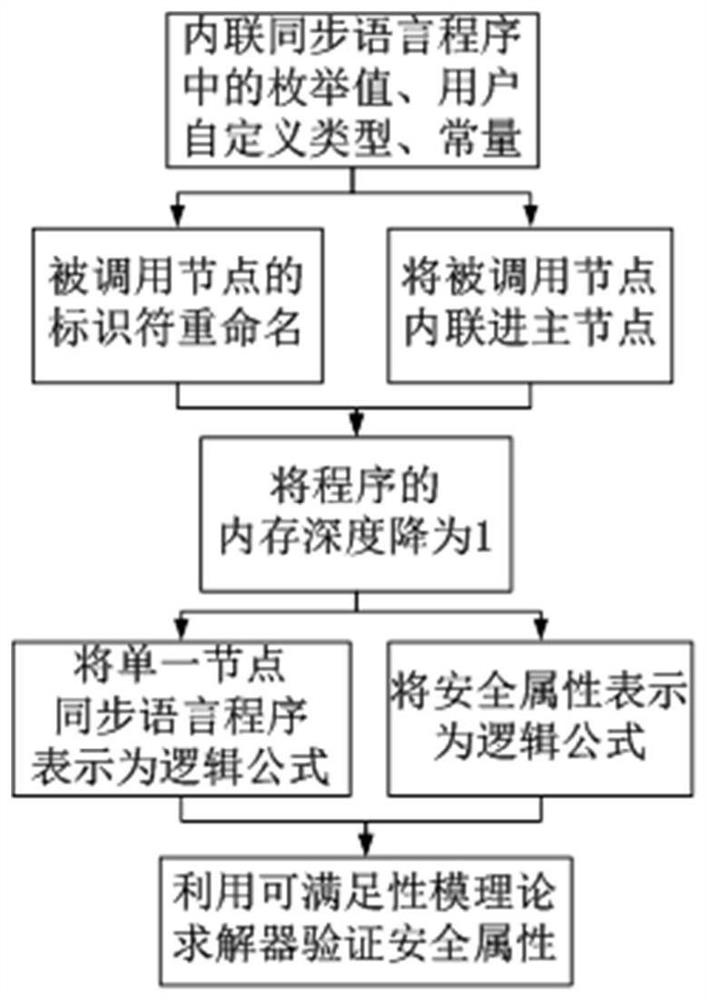
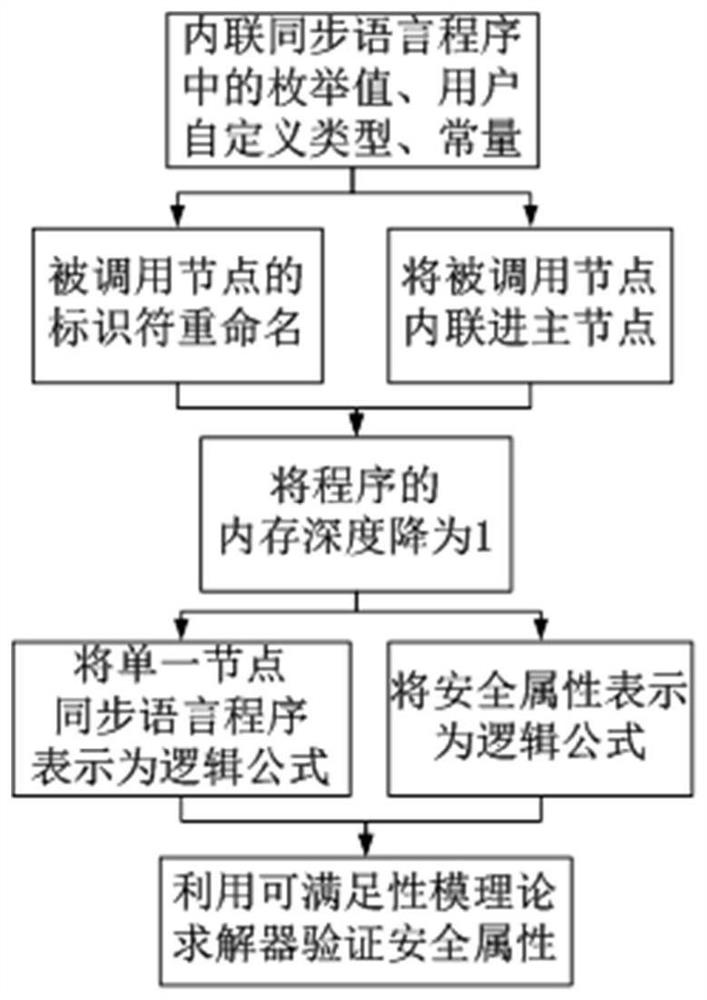
The invention discloses an automatic verification method of a synchronous language program based on satisfiability, which includes inlining the enumerated values, user-defined types and constants in the synchronous language program into the nodes of the synchronous language program, and in the synchronous language program recursively inline all the called nodes in the main node of , and get a synchronous language program containing a single node, and then reduce the memory depth of the program to 1 by introducing a new local data flow, and finally the synchronous language program containing a single node and Its security properties are expressed as propositional logic formulas, and a satisfiability modulo theory solver is used to verify whether a synchronous language program satisfies the security properties to be verified. The invention supports direct verification of large-scale complex synchronous language programs, can improve the verification ability and efficiency, and can ensure the reliability and safety of the programs.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Automatic reasoning method based on maximum contradiction in propositional logic
The invention discloses an automatic reasoning method based on a maximum contradiction in propositional logic. The automatic reasoning method comprises the steps of firstly, generating the maximum contradiction by utilizing k variables appearing in a clause set S; secondly, finding out the contradiction by utilizing the maximum contradiction, and after texts in the contradiction are deleted, extracting all remaining texts to form a contradiction separation formula; and finally, judging attributes of the clause set S by utilizing the contradiction separation formula, thereby finishing the reasoning. The method breaks through the limitation that only two clauses can participate in each deduction of a traditional resolution principle; static, bivariate and resolution deduction is developed into dynamic, multivariate and contradiction separation deduction; and the method has stronger pertinency and higher flexibility, and is stronger in capability of judging logical formula attributes.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Contradiction separating deductive reasoning based on standard continuation triangle in propositional logic
The invention provides contradiction separating deductive reasoning based on a standard continuation triangle in propositional logic. The method sequentially comprises the following steps: constructing a standard continuation triangle-based contradiction; forming a contradiction separating formula; according to the characteristics of the contradiction separating formula and clauses, determining the attribute of a clause set; if the clause set is judged to be unsatisfiable or satisfiable, stopping, otherwise, adding the contradiction separating formula to an original clause set to form a new clause set; then constructing and separating the standard continuation triangle-based contradiction until the condition is satisfied and the conclusion of clause set attributes is obtained. The invention can efficiently construct the contradiction, realizes the improvement and popularization of the static and dual resolution deductive reasoning mechanism into a dynamic and multiple deductive reasoning mechanism based on the separation of the contradiction, and is an essential breakthrough in the field of automatic deductive reasoning.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
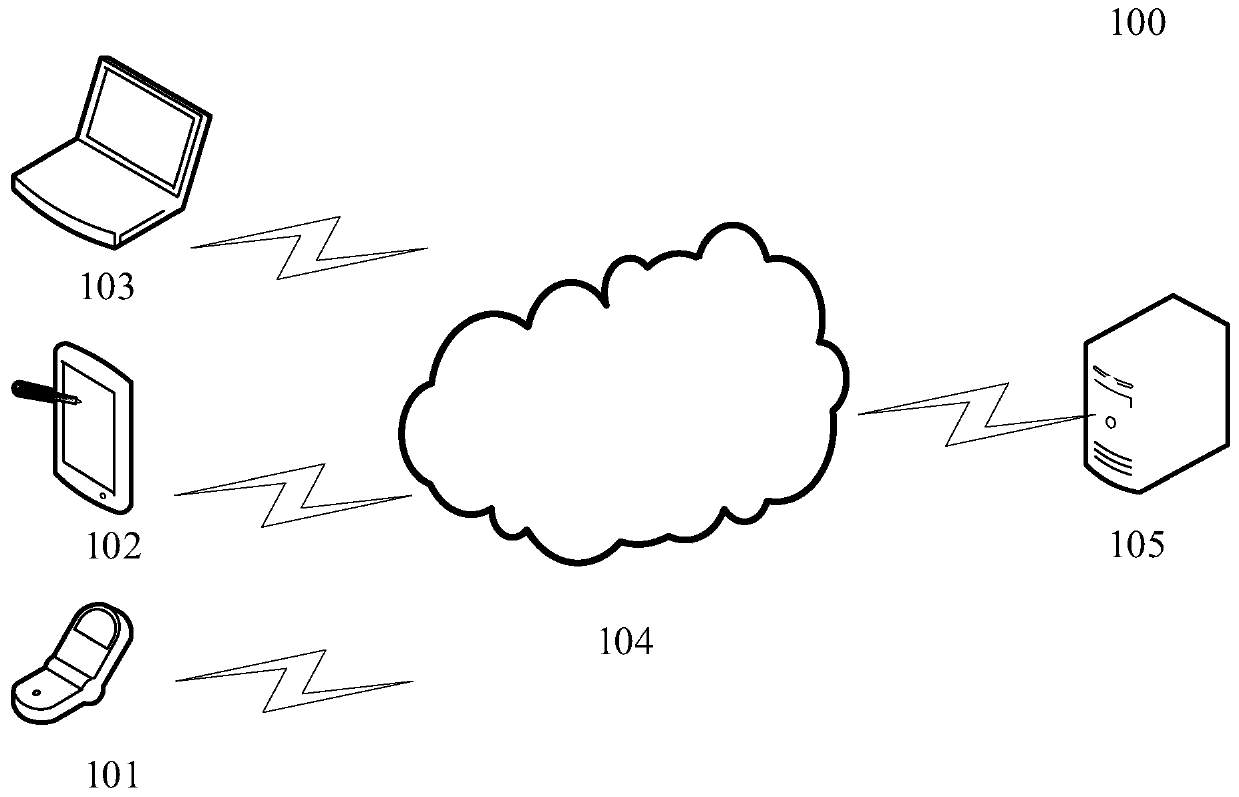
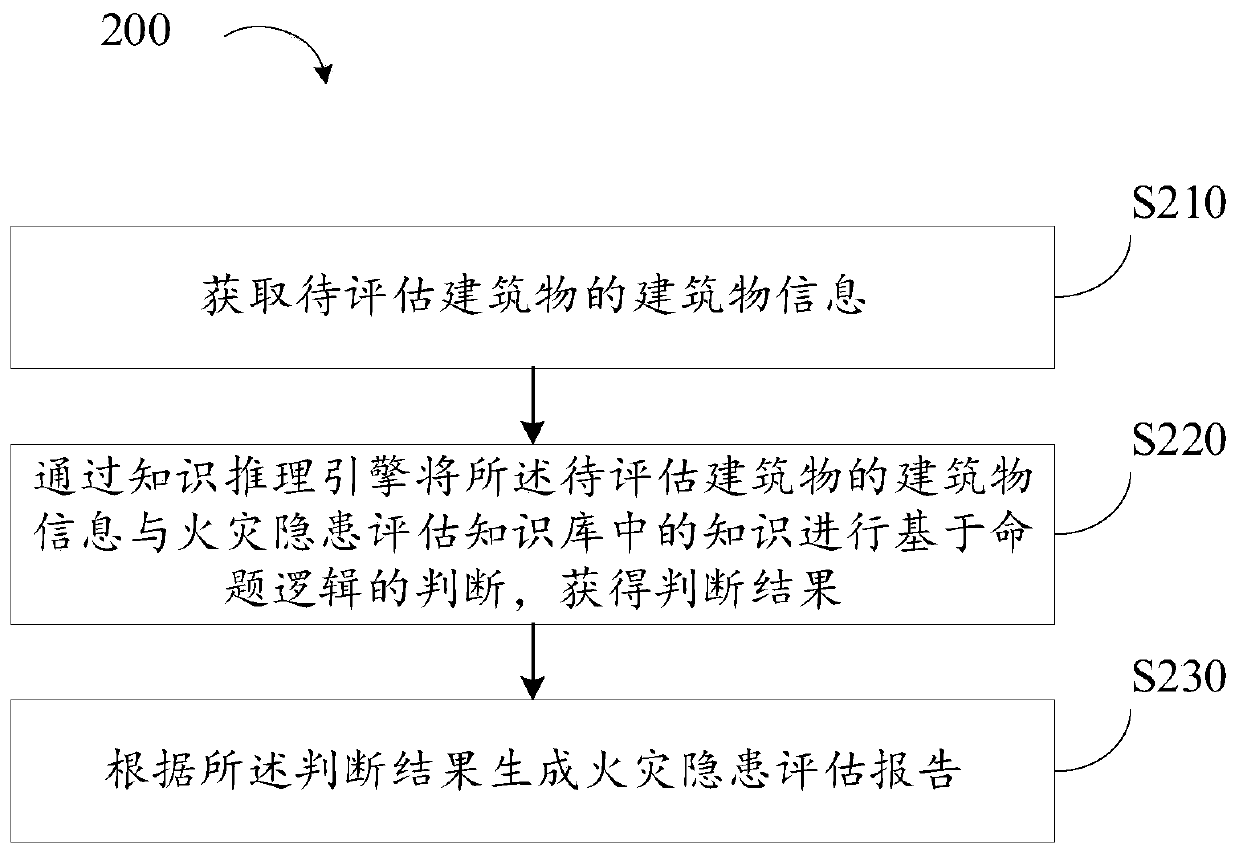
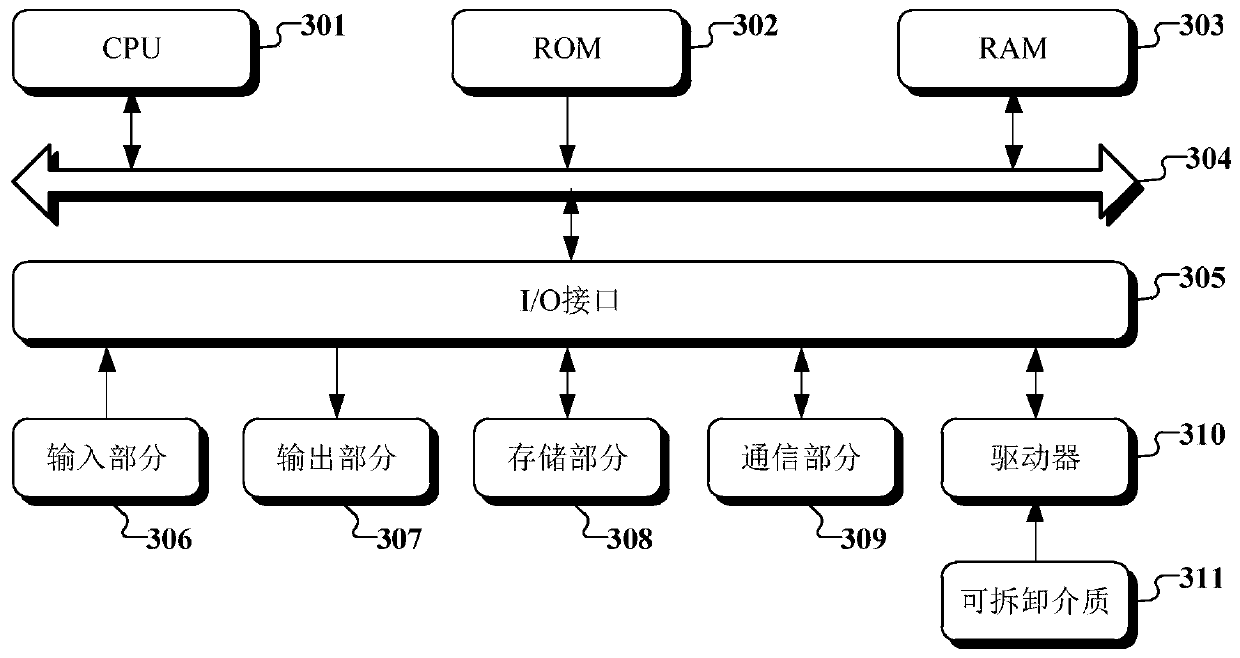
Fire hazard assessment method, device and equipment and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN111242447AEasy to understandAchieve consistencyResourcesFire - disastersReliability engineering
The embodiment of the invention provides a fire hazard assessment method, device and equipment and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining building informationof a to-be-evaluated building; performing propositional logic-based judgment on the building information of the to-be-evaluated building and pre-stored knowledge in a knowledge base through a knowledge reasoning engine to obtain a judgment result; and generating a fire hazard assessment report according to the judgment result. In this way, the fire hazard of the building can be intelligently found, meanwhile, the labor cost is reduced, the consistency of program behaviors and manual expert experience is easily guaranteed, and the maintenance is convenient.
Owner:THINVENT DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
Propositional logic correcting method based on representative model
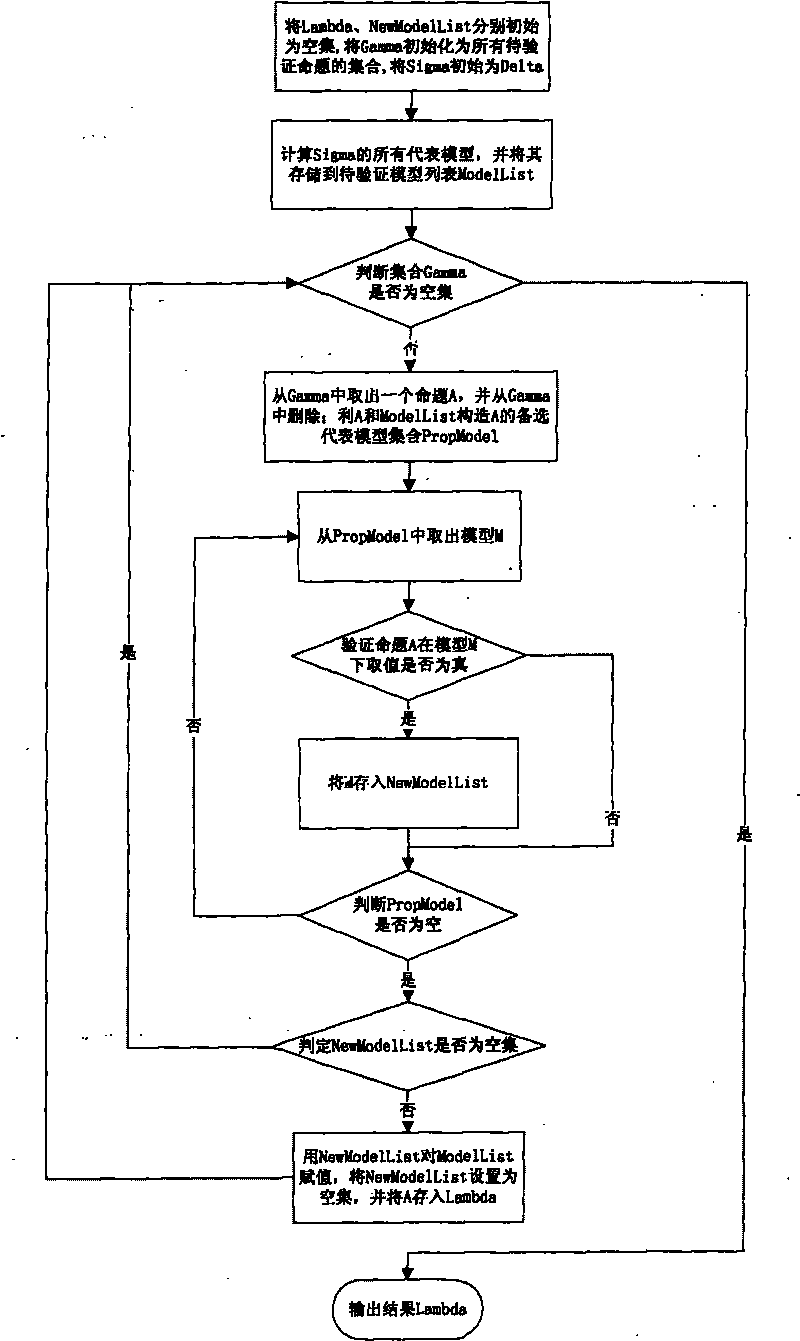
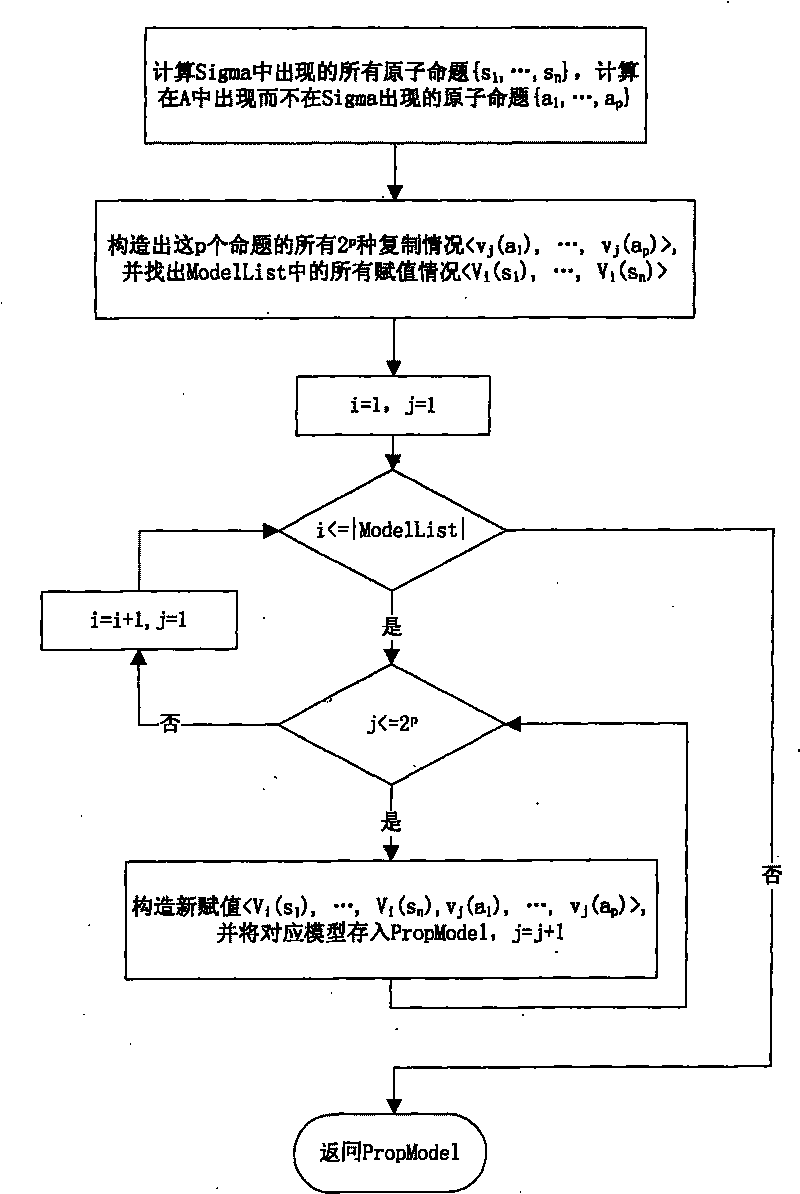
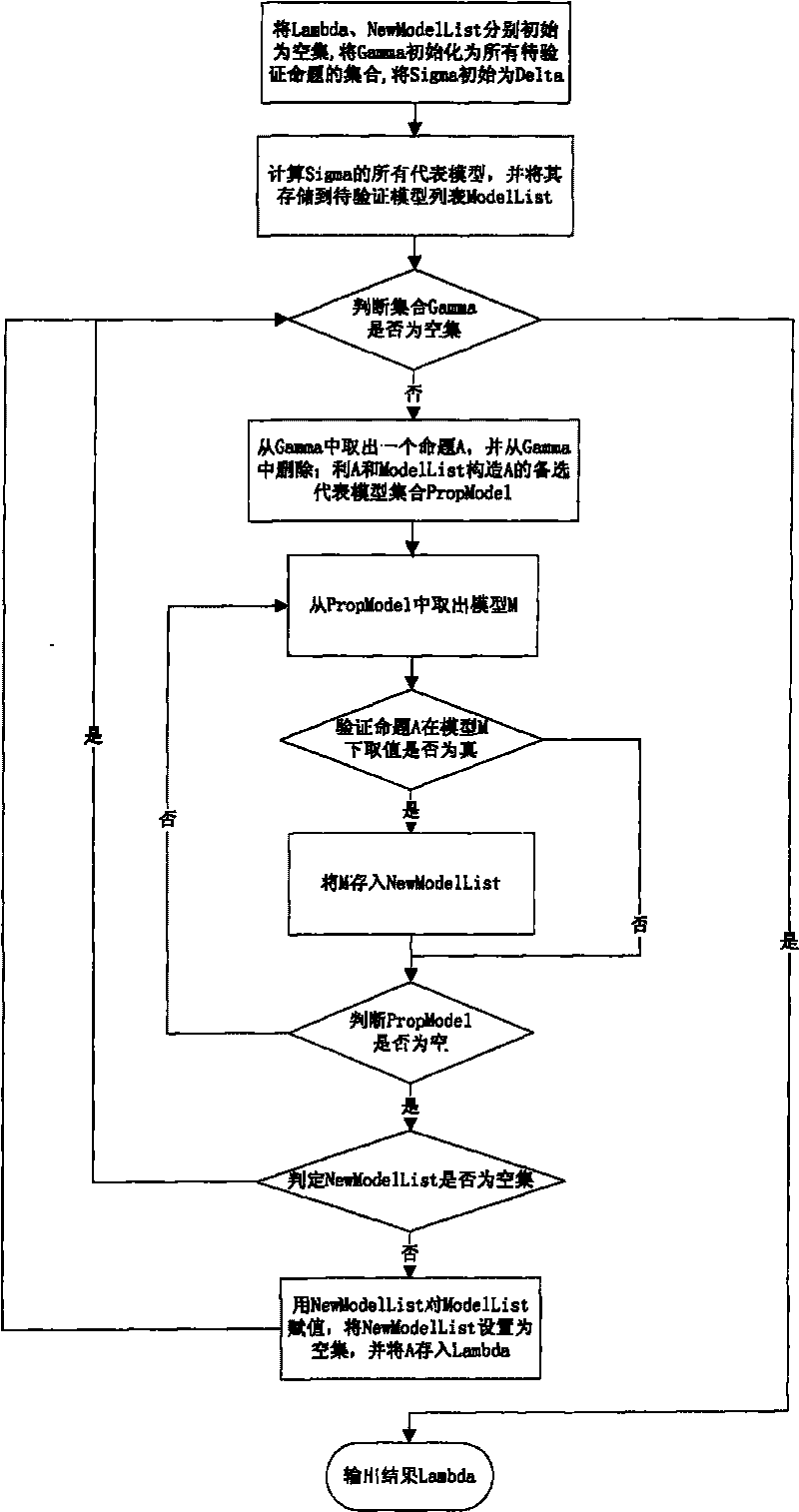
The invention relates to a propositional logic correcting and calculating method based on a representative model, comprising the following steps: (1) initiating a result set Lambda, accepting a set Sigma, a system set Gamma and a new representative model list (New Model List); (2) initiating a representative model list (Model List) by using all representative models of Sigma; (3) if the system set Gamma is an empty set, turning to step (8); (4) taking out and deleting a proposition A from Gamma; (5) constructing an alternative representative model set Prop Model of A by using A, Sigma and Model List; (6) carrying out verification to A by all alternative representative models in Prop Model one by one: if an alternative representative model M leads A to be true, storing M into New Model List; (7) if New Model List is not an empty set, assigning a value to Model List by using New Model List, resetting New Model List to be the empty set, storing A into Lambda and Sigma respectively, and turning to step (3); and if New Model List is an empty set, directly turning to step (3); and (8) outputting the result Lambda. In the method, the representative model is constructed according to every proposition condition in the system set, and a method for only verifying related models is used so as to reduce the checking times of models, thus improving the efficiency of correction and calculation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Approximate reasoning mode algorithm based on propositional logic probability assignment
The invention discloses an approximate reasoning mode algorithm based on a propositional logic probability assignment. Compared to the prior art, by using the method in the invention, an assignment domain of a classic proposition logic is extended to a given probability space from a binary value {0,1}; and a probability assignment of a propositional formula is introduced, wherein the probability assignment is promotion of a classic proposition logic binary value assignment and various kinds of true degree concepts. Through using the probability assignment, a probability truth degree, an unreliable degree, a probability truth degree based on an independent event assignment set and other concepts of the propositional formula is introduced. A property of the probability truth degree is discussed so as to prove that a truth degree set of all the proposition formulas based on the independent event assignment set does not have an isolated point in [0,1]. In proposition logic form deduction, an unreliable degree of an effective inference conclusion does not exceed a product sum of an unreliable degree of each precondition and a necessary degree. Based on the probability assignment, an a.e. conclusion, a conclusion in probability, a truth degree conclusion in probability and other concepts of a proposition formula set are introduced; connection between the concepts is discussed and two different types of approximate reasoning modes are provided.
Owner:XIANGNAN UNIV
Paradox separation type-based reverse parallel deductive reasoning method in propositional logic
The invention discloses a paradox separation type-based reverse parallel deductive reasoning method in propositional logic. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a paradox and forming a paradox separation type for a sub-sentence set S in the naming logic; judging whether the S can be satisfied or not according to the paradox separation type; if the S cannot be satisfied, stopping the operation, and otherwise, constructing a reverse deduction sub-sentence set on the basis of the paradox separation type so as to obtain t new sub-sentence sets, and carrying out deductive reasoning; and if the t new sub-sentence sets are deduced to be empty sub-sentences, considering that the S cannot be satisfied, and otherwise, circulating the above steps, and stopping the operation untila judging conclusion of attribute of the S is obtained or a set condition is satisfied. The method is capable of dynamically decomposing paradox separation types to form dynamic reverse deduction targets so as to effectively guide deductive reasoning of the next step, and carrying out parallel processing on decomposed logic formula set attribute judgement so as to effectively improve the deduction efficiency of a paradox separation-based dynamic automatic deductive reasoning system; and the method can be applied to the field of program verification, automated theorem proving and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
An Accessibility Analysis Method for Hybrid Systems
ActiveCN103400025BShorten the timeReduce memory usageSpecial data processing applicationsNODALReachability
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Reverse parallel deductive inference method based on paradox internal clauses in propositional logic
InactiveCN108875940AImprove deductive reasoning skillsGood orientationInference methodsReasoning systemTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a reverse parallel deductive inference method based on paradox internal clauses in propositional logic. The method comprises the steps that a paradox is constructed for a clause set S in the propositional logic, and a paradox separation formula is formed; whether deductive inference is terminated is judged according to the paradox separation formula, wherein if the paradoxseparation formula is null, the process is stopped, and the conclusion that S cannot be met is obtained; or otherwise, the paradox internal clauses (shown in the description) are extracted, and the obtained t clauses (shown in the description) are used as targets to perform deductive inference on S respectively, wherein if the t clauses can be deduced, the process is stopped, and the conclusion that S cannot be met is obtained; or otherwise, the process is circulated till a determination conclusion of S properties is obtained or set conditions are met, and then the process is stopped. Throughthe method, the paradox internal clauses can be dynamically extracted to form dynamic reverse deductive targets, parallel processing is performed on the properties of a decomposed logic formula set, and the efficiency of a dynamic automatic deductive inference system based on paradox separation is effectively improved; and the method can be applied to the fields of program verification, theorem machine proving, etc.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Formal semantic analysis and inspection method for demand table model
PendingCN114741052AImprove completenessQuality improvementSemantic analysisRequirement analysisSemantics of logicAlgorithm
The invention discloses a formal semantic analysis and inspection method for a demand table model, which comprises the following steps: mapping the demand of airborne safety key software into a mathematical model based on propositional logic and relation theory, carrying out strict mathematical definition on the semantics, and then designing a series of automatic algorithms to verify the multilayer semantic constraint of the demand.
Owner:CHINESE AERONAUTICAL RADIO ELECTRONICS RES INST
Synchronous language program automatic verification method based on satisfiability solution
ActiveCN112269734ATroubleshoot auto-authentication issuesResolve verificationSoftware testing/debuggingData streamTerm memory
The invention discloses a synchronous language program automatic verification method based on satisfiability solution, which comprises the following steps: inlinking enumeration values, user-defined types and constants in the synchronous language program into nodes of the synchronous language program, recursively inlinking all called nodes in a main node of the synchronous language program, obtaining a synchronous language program containing a single node, then reducing the memory depth of the program to 1 by introducing a new local data stream, and finally enabling the synchronous language program containing the single node and the security attribute of the synchronous language program to be expressed as a proposition logic formula, and verifying whether the synchronous language program meets the security attribute to be verified or not by utilizing a satisfiability model theory solver. The invention supports the direct verification of large-scale complex synchronous language programs, can improve the verification capability and efficiency, and guarantees the reliability and safety of the programs.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Paradox separation deductive reasoning method based on extended triangle in propositional logic
PendingCN108875950AHave diversityDynamicInference methodsAutomated theorem provingDeductive reasoning
The invention discloses a paradox separation deductive reasoning method based on an extended triangle in propositional logic. The method comprises the following steps that: for a clause set S in the propositional logic, constructing an extended triangle paradox, forming a paradox separation formula, and judging clause set attributes according to the paradox separation formula; if a judgment resultshows that the clause set can not be satisfied, stopping; otherwise, adding the obtained paradox separation formula into an original clause set to form a new clause set; and then, constructing and separating the extended triangle paradox, and stopping until the judgment conclusion of clause set attributes is obtained or a set condition is met. The invention provides an effective dynamic automaticdeductive reasoning method based on paradox separation, a collaborative logic relationship among a plurality of clauses can be effectively described, and the method can be applied to fields includingprogram verification, automated theorem proving and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
An e-commerce recommendation technology and system based on analysis of soft set decision rules
ActiveCN108133407BInnovativeNovel method constructionVisual data miningStructured data browsingTheoretical computer scienceDecision taking
The invention belongs to the field of computer technology, discloses an e-commerce recommendation technology and system based on the analysis of soft set decision rules, and establishes a propositional logic reasoning language based on soft sets. In the reasoning language, the atomic formula is the parameter e in the soft set , the function value F(e) of the parameter e is the assignment set of the atomic formula e, and the soft decision rule is an implication logic formula composed of atomic formulas on the decision soft set; the introduction of soft truth, conditional soft truth and joint soft truth , soft similarity, logical soft distance and other quantitative indicators to evaluate soft decision rules from different aspects of sufficiency, necessity and rationality; transform the decision system into a decision soft set, and propose a soft decision rule extraction method for incomplete decision systems; Data analysis methods based on propositional logic and soft sets are applied to e-commerce recommendation. The present invention demonstrates that the methods proposed by the present invention are all effective through practical examples; the theoretical analysis of the present invention is innovative, the method structure is novel, and the technical means are practical.
Owner:XIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com