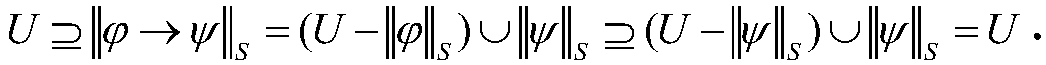E-commerce recommendation technology and system based on soft-set decision rule analysis
An e-commerce and soft decision-making technology, applied in the computer field, can solve problems such as affecting the application of correlation analysis technology, the overall sparse distribution of e-commerce product sales data, and dislike of e-commerce product ratings or verbal evaluations.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 6
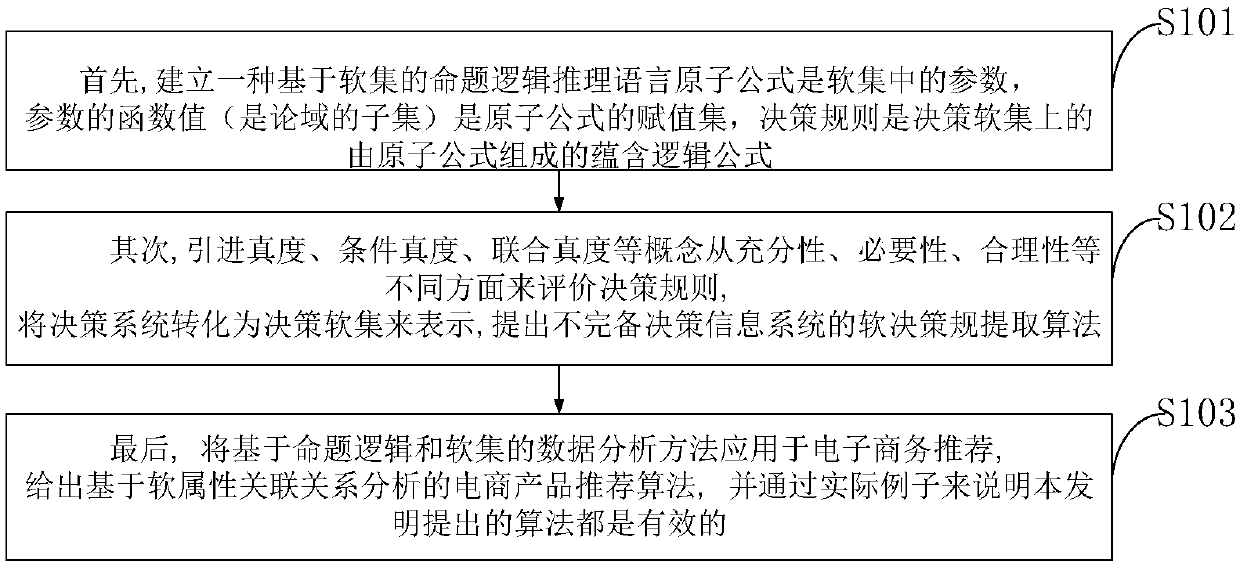
[0126] Example 6. A probabilistic decision soft set (F, C, D) is shown in Table 1 below.
[0127] Table 1 Probabilistic Decision Soft Set (F, C, D)
[0128]
e 1
e 2
e 3
d
u 1
1
0
0
0
u 2
1
0
1
1
u 3
0
0
1
0
u 4
1
1
1
1
[0129] Among them, U={u 1 , u 2 , u 3 , u 4}, the normal probability distribution on U is: P({u 1})=1 / 3,P({u 2})=1 / 3,P({u 3})=1 / 6,P({u 4})=1 / 6, condition parameter set C={e 1 ,e 2}, the meaning of the parameter is e 1 ="headache", e 2 = "muscle pain", e 3 = "fever", the decision parameter set D = {d}, the meaning of the parameter is d = "flu".
[0130] The basic soft truth of each decision rule is: τ(e 1 →d)=2 / 3,τ(e 2 →d)=1,τ(e 3 → d) = 5 / 6.
[0131] The conditional soft truth of each decision rule is: γ(e 1 →d)=3 / 5, γ(e 2 →d)=1,γ(e 3 → d) = 3 / 4.
[0132] The joint soft truth of each decision rule is: ρ(e 1 →d)=5 / 9, ρ(e 2 →d)=1 / 6, ρ(e...
example 7
[0133] Example 7. (1) The three truth values of a decision rule describe the numerical characteristics of the decision rule from three different perspectives. Generally speaking, the soft truth focuses on the validity of the decision rule; the conditional soft truth emphasizes the condition The certainty of the implication relationship between the attribute and the decision attribute; the joint soft truth takes into account both the validity of the decision rule and the support strength of the conditional attribute to the decision rule.
[0134] (2) It can also be seen from Example 6 that although the decision rule e 2 → d has high validity and certainty (strength 1), decision rule e 2 → condition attribute e in d 2 The support strength for the decision rule is very low (strength is 1 / 6). Intuitively, we can understand it as: Since u 2 also satisfy e 1 and e 3 , thus supporting the decision rule e 2 → Evidence u of d 2 May not actually work. In other words, u 2 His "f...
example 8
[0170] Example 8. Analysis of decision rules for some patient decision information systems.
[0171] Table 2 Certain Patient Decision Information Systems
[0172]
[0173]
[0174] For the convenience of description, the above attributes and attribute values are respectively symbolized, where a = "headache", b = "muscle pain", c = "body temperature", d = "flu". a = two attribute values of "headache" Yes and no respectively use a 1 ,a 2 Represent; b = "muscle pain" two attribute values yes, no use b respectively 1 ,b 2 Indicate; the three attribute values of c = "body temperature" are very high, high, and normal, respectively use c 1 ,c 2 ,c 3 Represent; the two attribute values of d=“influenza” are yes and no respectively use d 1 , d 2 .Using the rough set theory to reduce the attributes of the information system, the minimum attribute reduction set is {headache (a), body temperature (c)}. The reduced and symbolized attribute table is converted into a s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com