A Data Reduction Method for Decision Table
A decision table and data technology, applied in the field of data processing, can solve the problems of wasting time and calculation times, and achieve the effect of good repeatability, simple calculation and fast calculation speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0009] The specific implementation manners of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. The following examples are used to illustrate the present invention, but are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
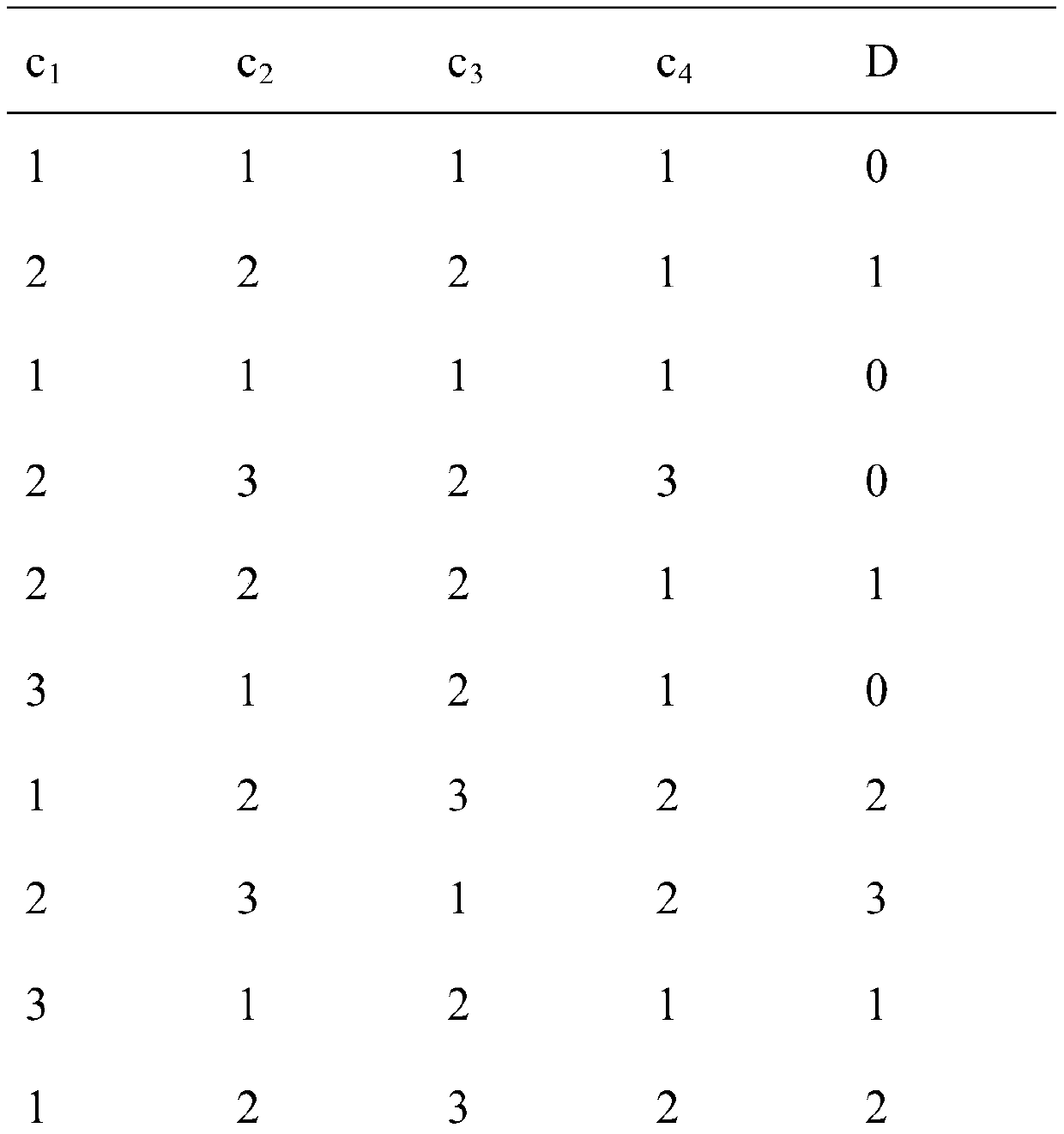
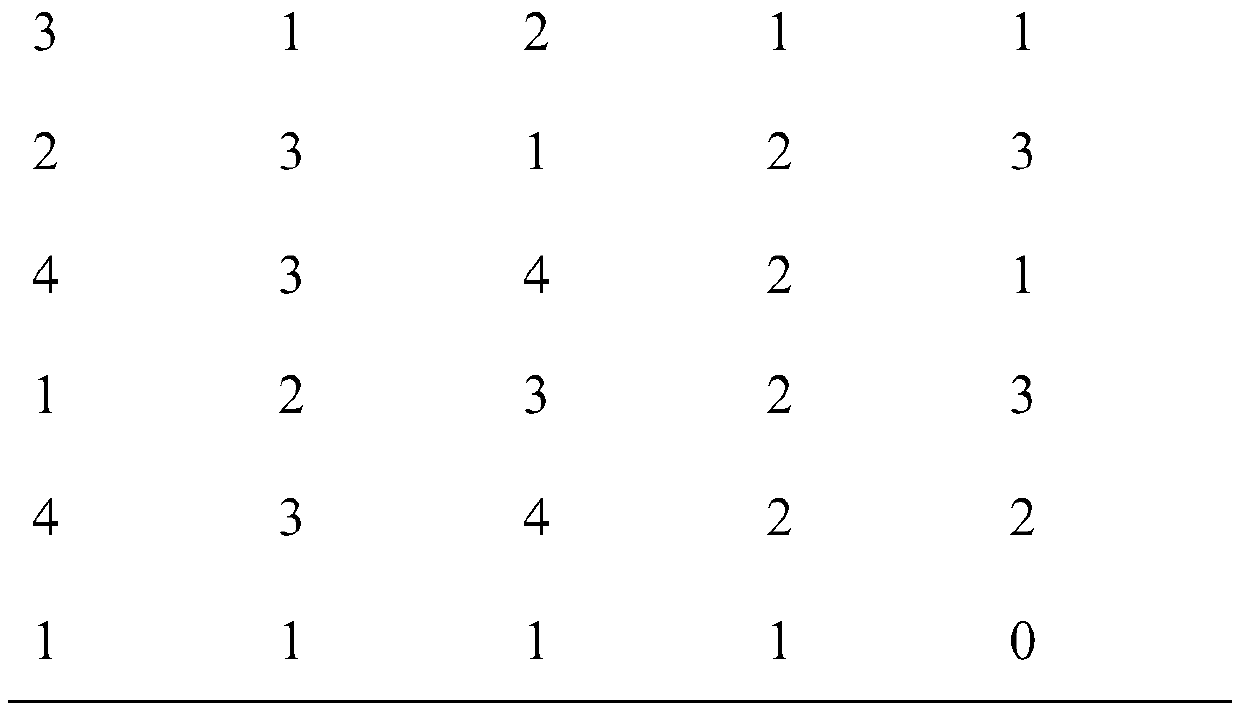
[0010] The present invention mainly deals with decision table data, expressed as S=a |a∈At},{I a |a∈At}>, where U is the set of all samples, At=C∪D, C={c 1 ,c 2 ,...,c n} is called condition attribute set, D={d} is called decision attribute set.
[0011] figure 1 , in a specific embodiment of the present invention, shows the overall flow of a method for reducing decision table data. Generally speaking, it includes: step 1, judge whether the last conditional attribute in the decision table data set is the core attribute of the decision table, if so, add the data of this attribute to the reduction set R, and perform step 2; otherwise, delete the last column of condition...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com