Method and system for dynamic node allocation in data flow architecture
An architecture and dynamic node technology, applied in resource allocation, multi-program device, program synchronization, etc., can solve the problem of slow execution of key nodes, different node fragments with data flow graph congestion, long preprocessing time of static optimization methods, etc. problems, to achieve efficient acceleration and flexible acceleration methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The following will clearly and completely describe the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only some, not all, embodiments of the present invention. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
[0033] The invention discloses a dynamic node allocation method in a data stream architecture, which comprises the following steps:
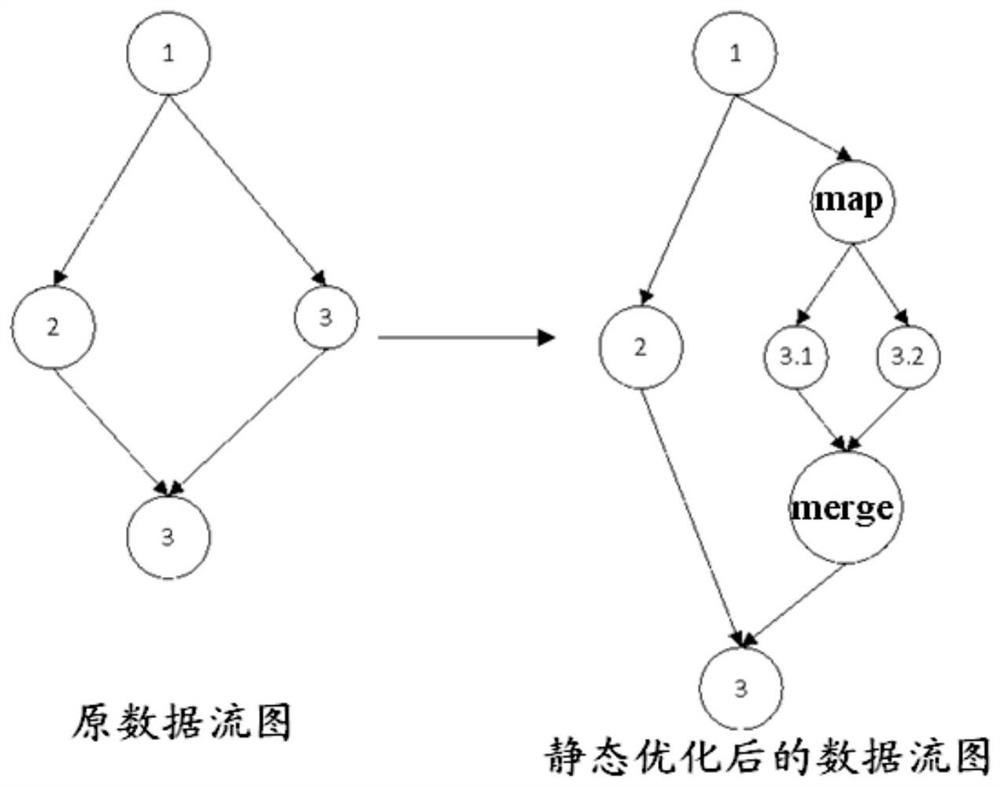
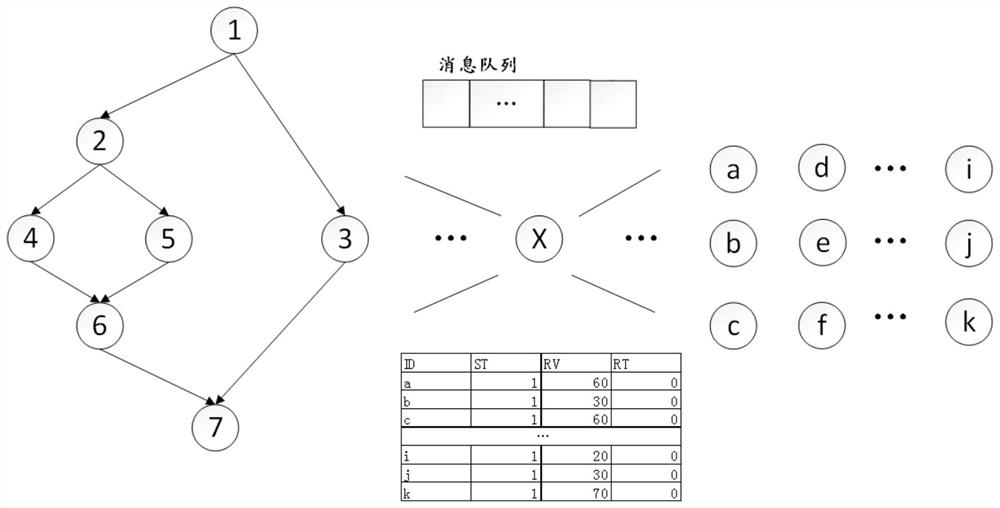
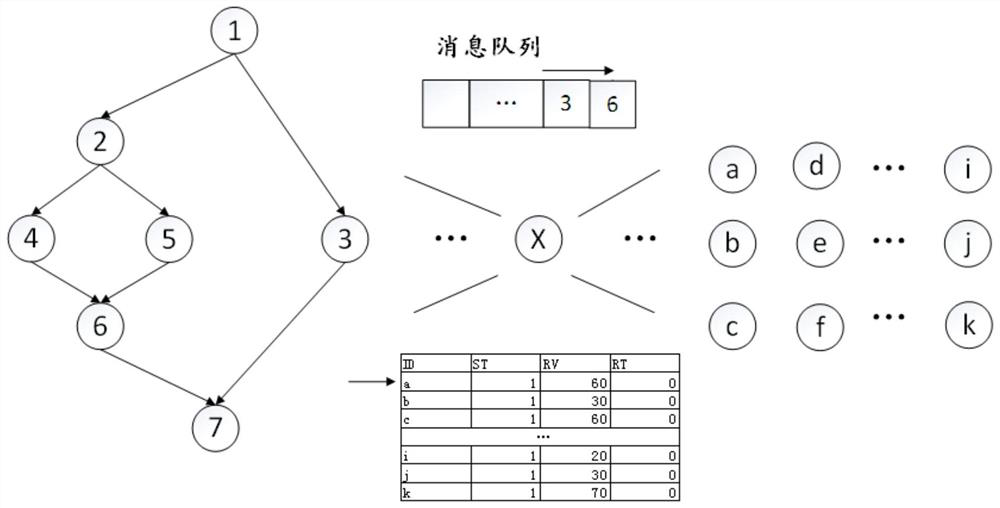
[0034] Map the nodes in the data flow graph to the physical execution unit one by one, where the mapped nodes in this step are called dead nodes, and live nodes include unmapped nodes and not fully utilized nodes, among which, not fully utilized nodes Utilized nodes refer to the fact that the computing resources of the physical ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com