Calculation method for transient stability evaluation index of system after multi-loop DC commutation failure
A calculation method and evaluation index technology, applied in power transmission AC networks, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in quantitative calculation, inability to provide quantitative evaluation indicators, poor adaptability to high-power tie lines, etc., and achieve deceleration. area reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
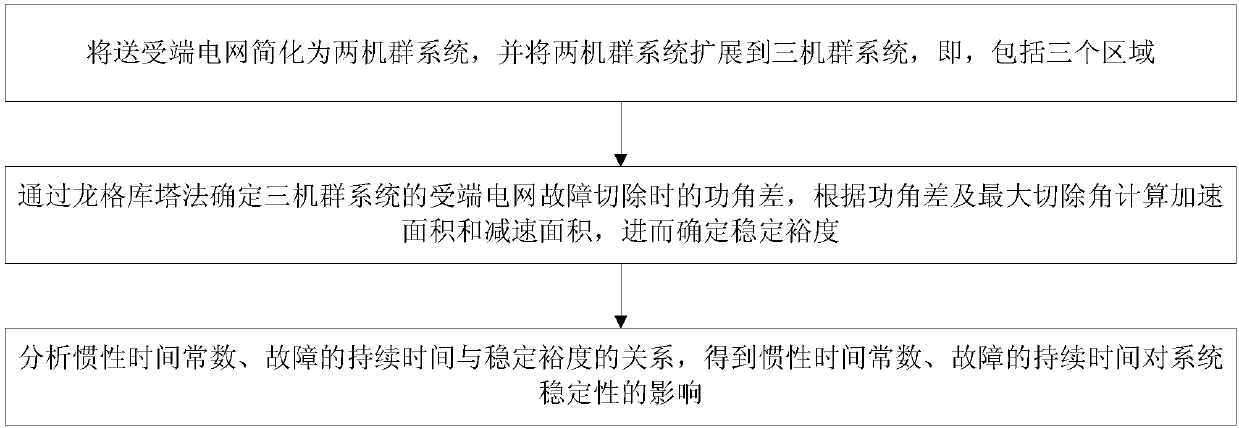
[0041] A calculation method for the transient stability evaluation index of the system after multiple DC commutation failures, see figure 1 , the calculation method includes the following steps:
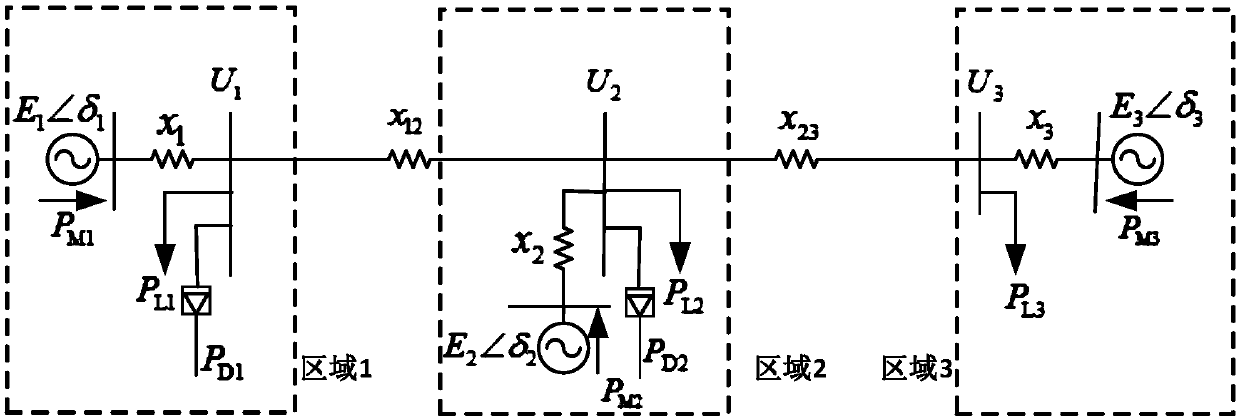
[0042] 101: Simplify the sending and receiving end power grid into a two-machine cluster system, and extend the two-machine cluster system to a three-machine cluster system, that is, including three regions;
[0043] 102: Use the Runge-Kutta method to determine the power angle difference of the receiving end power grid fault removal of the three-unit system, calculate the acceleration area and deceleration area according to the power angle difference and the maximum removal angle, and then determine the stability margin;
[0044] 103: Analyze the relationship between inertial time constant, fault duration and stability margin, and obtain the influence of inertial time constant and fault duration on system stability.
[0045] Wherein, in step 101, the power grid at the sending and re...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Combined with the specific calculation formula, Figure 1-Figure 6 1. Examples further introduce the scheme in Example 1, see the following description for details:
[0060] 201: Simplify the power grid at the sending and receiving end to a two-cluster system, and expand the two-cluster system to a three-cluster system;
[0061] Wherein, the step 201 is specifically:
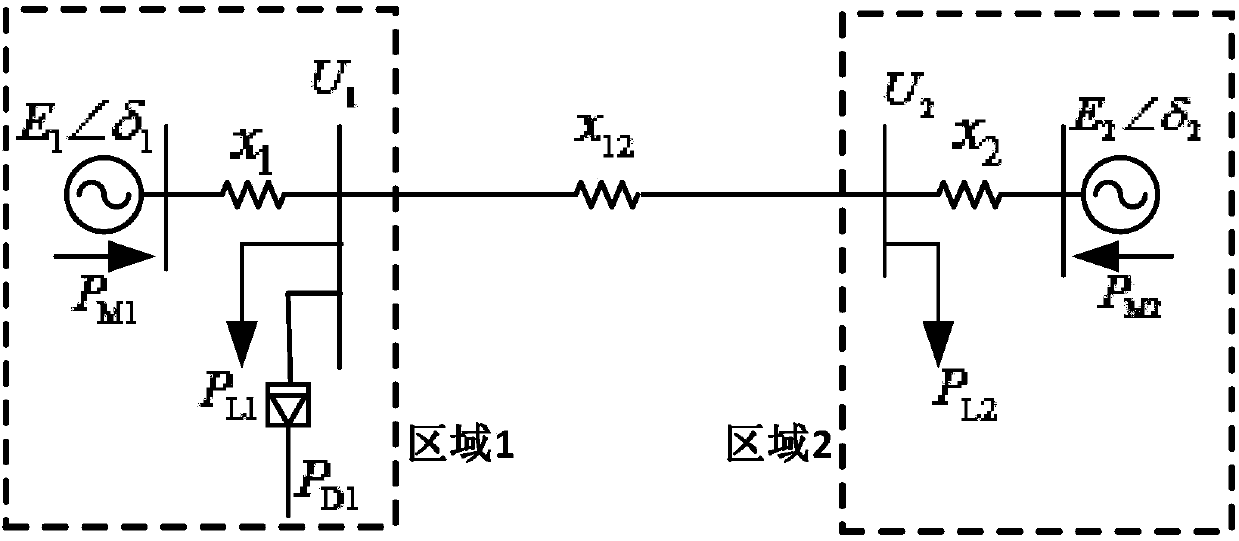
[0062] 1) Simplify the sending and receiving end power grid into a second-order model of the two-machine cluster system, and obtain the motion equation of the relative speed of the rotor;
[0063] In the actual power system, in order to facilitate the analysis of the physical nature of the stability problem, the power grid at the sending and receiving end is simplified as figure 1 Two-fleet system shown.
[0064] figure 2 Among them, areas 1 and 2 are equivalent sending-end systems and receiving-end systems, E 1 ,E 2 is the equivalent generator internal potential of the sending-end and receiving-en...
Embodiment 3
[0132] Below in conjunction with specific experimental data, table 1-table 4, carry out feasibility verification to the scheme in embodiment 1 and 2, see the following description for details:
[0133] 1. Analyze the transient stability of the two-machine system
[0134] Using the PSD-BPA developed by China Electric Power Research Institute as the simulation program (this simulation program is well known to those skilled in the art, and the embodiment of the present invention will not repeat this), a three-phase short-circuit fault occurs in the receiving end system, causing DC P D1 When commutation failure occurs, the stability of the power system has two states: system stability and system instability. System stability refers to the maximum relative power angle difference Δδ of all generators after the fault max max ≥360°, analyze the influence of moment of inertia and fault duration on system stability.
[0135] (1) Influence of unit inertia time constant on transient stab...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com