Low-energy orbit capture method for multi-body system taking into account initial and terminal constraints
An energy capture, multi-system technology, applied in the aerospace field, which can solve the problems of reducing the incremental demand for capture speed, unsuitable mission orbits, and difficult practical applications.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
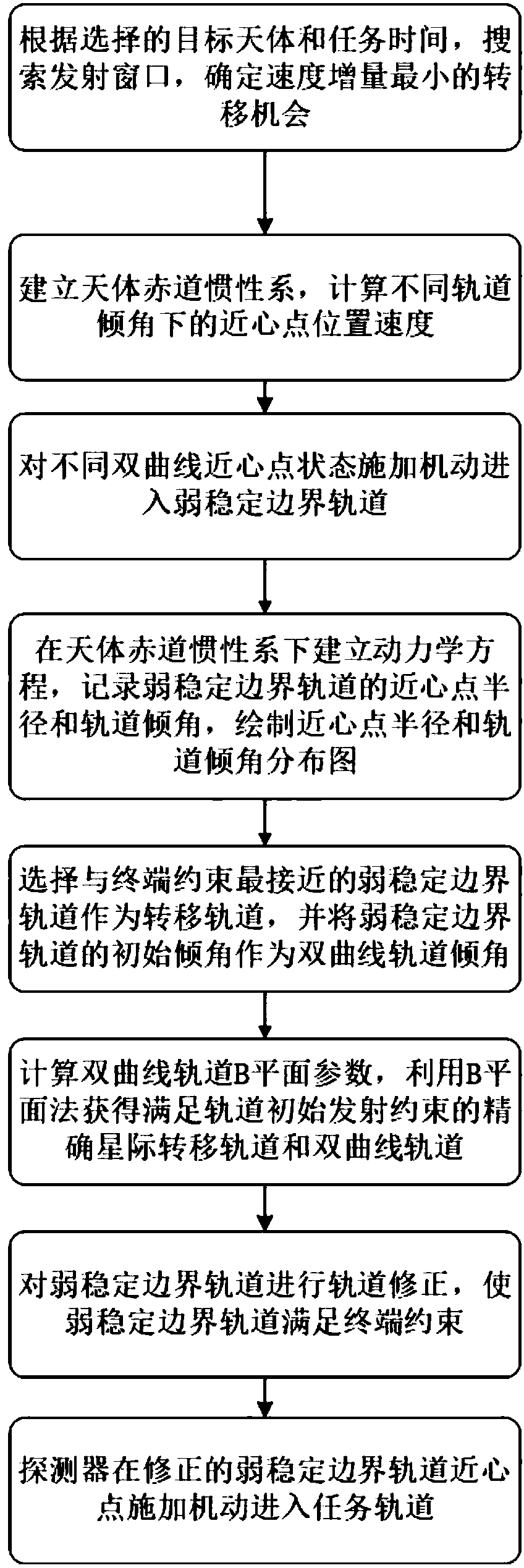
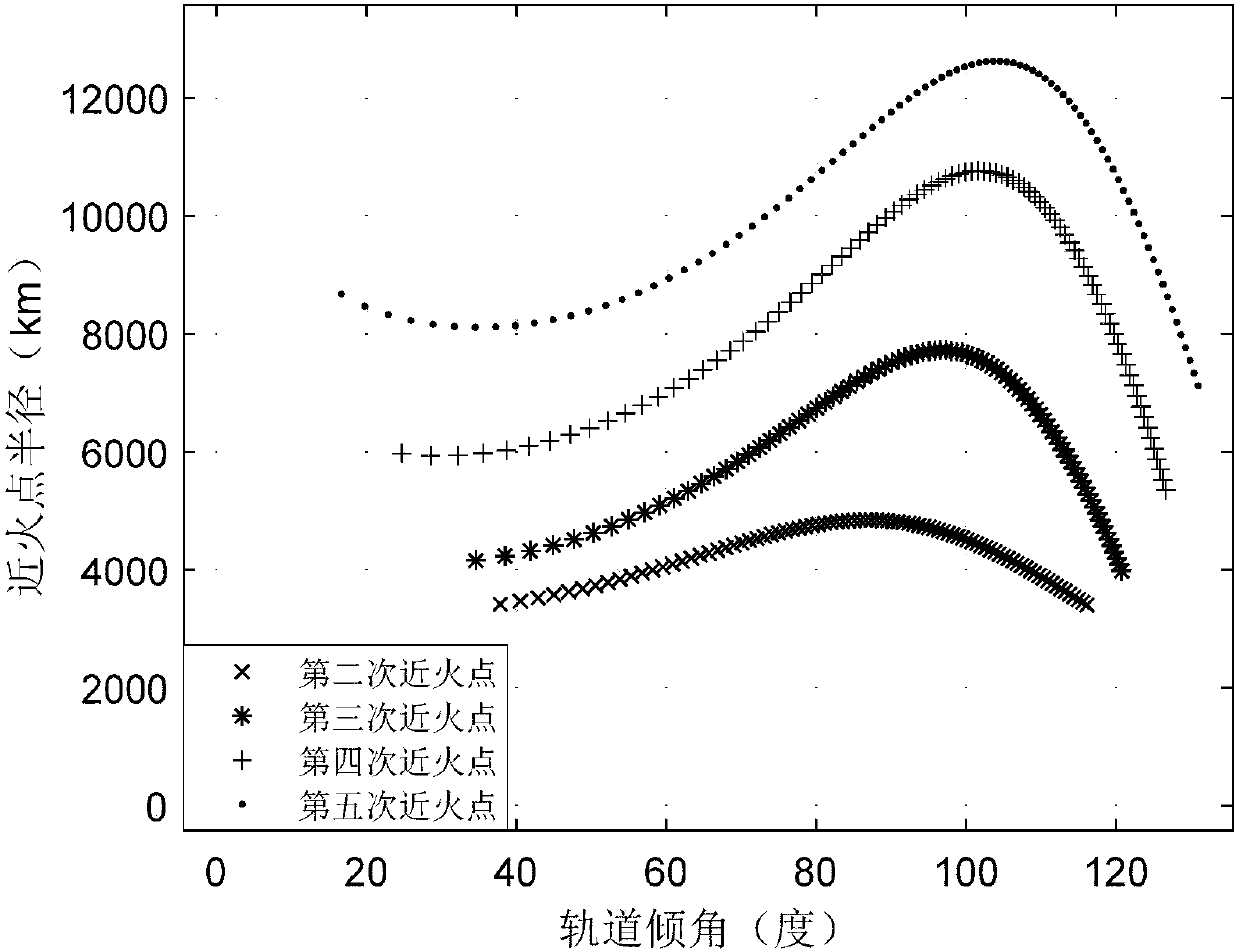
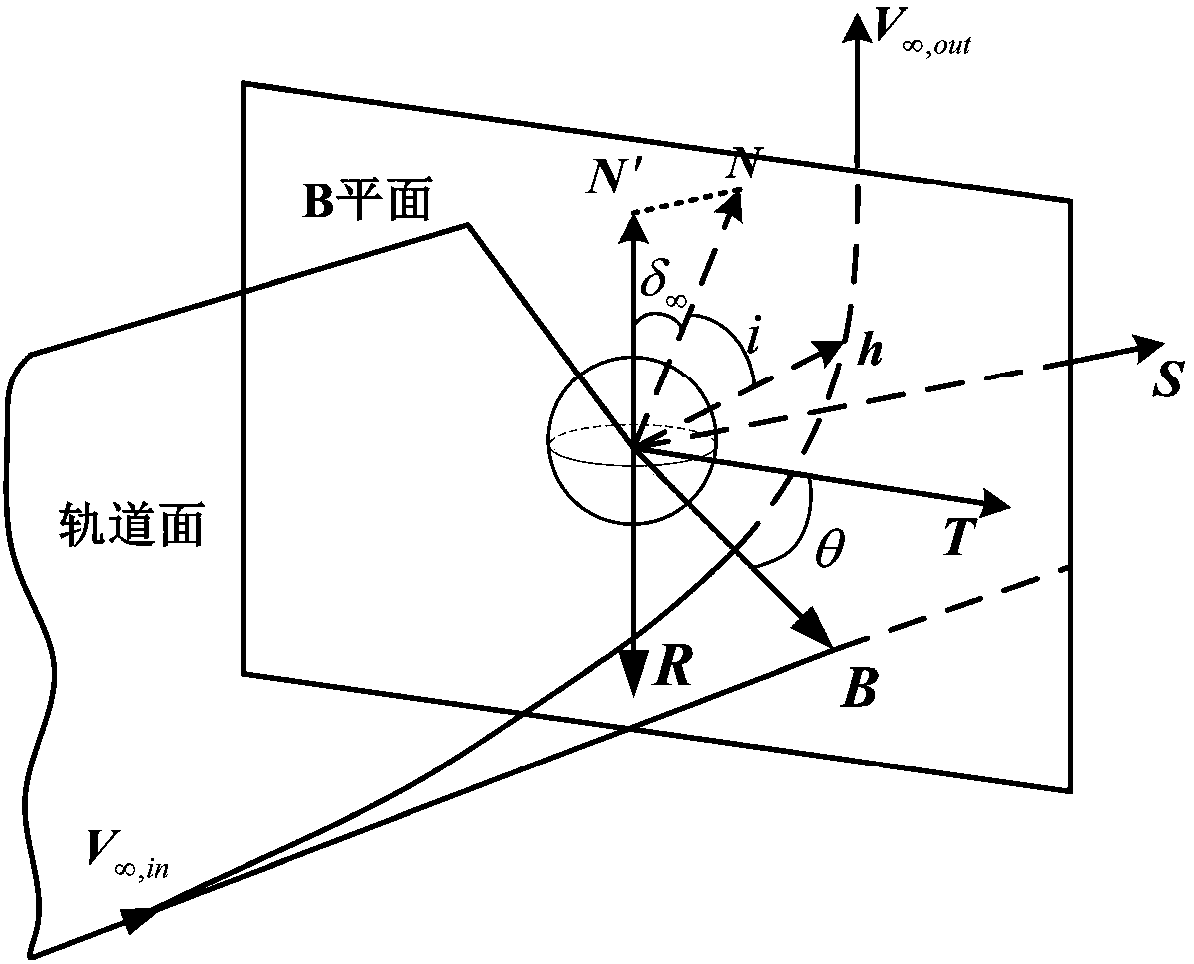
[0069] Such as figure 1 As shown, taking Mars orbit capture as an example, a two-pulse planet capture orbit method based on a weakly stable boundary disclosed in this embodiment, the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0070] Step 1: According to the selected target celestial body and mission time, search for the interstellar transfer launch window under the heliocentric ecliptic system, and determine the transfer opportunity with the smallest velocity increment Δv.
[0071] According to the detection target selection and mission time constraints, the two-pulse transfer opportunity from the earth to the target celestial body with the optimal speed increment is designed, and the departure time of the probe from the earth is T 0 , the corresponding starting state R under the heliocentric zodiac system 0 ,V 0 It can be determined by the ephemeris, the transfer time of the probe from the earth to the target celestial body is T, so the time when the probe reaches the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com